Opposites Attract Lesson Plan
advertisement

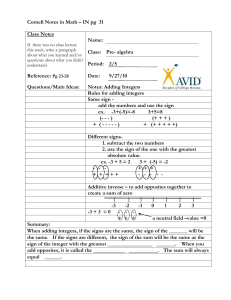
SUSME Study Lesson Title: Opposites Attract Authors: Melissa O’Neal, Lolete Wilson, Karita Sullen, Carla Jackson, Moriel Purnell, Tina Pettway, Pamela Fisher, Cassandra Chandler Grade/Subject: 8th/ Pre-Algebra Date: July 24, 2009 I. Need for this Lesson Students will acquire an understanding of combining values that are greater than or less than zero. Real life situations such as temperature, sports including golf and football, and distance in elevation require knowledge of integers. II. Unit Information A. Name of the unit: Real Numbers B. Goal(s) of the unit: Students will solve problems involving adding, subtracting, multiplying and dividing integers. C. Relationship of the Unit to the Curriculum Prerequisite Knowledge Previously Learned Concepts Adding, Subtracting, Multiplying and Dividing Whole Numbers Finding Patterns Evaluating Algebraic Expressions Concepts for this Unit Comparing and ordering integers Finding the absolute value of an expression Finding the average of a set of data Applying the rules for adding, subtracting, multiplying and dividing integers Graphing on a coordinate plane Related Concepts to be Learned in Future Units and Courses Real Numbers/Algebra 1: Apply the rules for adding, subtracting, multiplying, and dividing integers to solve equations. Graphing/Algebra 1: Concepts will be used to graph linear equations, systems of linear equations and linear inequalities on a coordinate plane. D. Possible Student Misconceptions Gaps with adding integers: What sign should my answer have? If adding means to combine, why should I subtract or take away when adding integers? E. Instructional Plan for the Unit: Concept/Topic Integers and Absolute Value Adding Integers Multiplying and Dividing Integers Subtracting Integers * Indicates the lesson developed in this lesson plan # of Lessons (1) (2)* (1) (1) III. Instructional Plan for this Study Lesson A. Title of the study lesson: Opposites Attract B. Standards Addressed (national, state): NCTM Principles and Standards Numbers and Operations Understand numbers, ways of representing numbers, relationships among numbers, and number systems Understand the meaning of operations and how they relate to each other Compute fluently and make reasonable estimates Alabama Course of Study Demonstrate computational fluency with addition, subtraction, and multiplication of integers. C. Lesson Overview: The lesson will focus on one method adding integers and creating zero pairs. D. Performance Objective(s): Students will use color counters to explore the laws of integers. E. Assessment Timeline Diagnostic - Before student work begins Formative - During lesson Summative - After lesson is completed Pre-Test Observation Test Whole-class discussion Questioning Project Journal Entry Portfolio F. Materials/Resources Integer Flash Cards Handout Two Color Counters Pencil Color Pencil Overhead Counters Group Instructional Overhead Projector or Elmo Paper Plastic Bags or Cup Basic Tile Mat Magnets Poster Paper/Board G. Teaching/Learning Process of the Study Lesson Step and time allocation (min) Engage (10 min) Explain (10 min) Teaching/Learning Activities Students will create a number line using flash cards that are assigned various colors on the back. Colors are called out randomly and students will place their numbers in order from least to greatest. Teacher will give examples of opposite situations: up & down; black & white; in & out; Predict the opposite of positive values are ______ Values. Handouts, equipment, supplies. Points to remember. Integer Flash Cards (Use Magnets and Bold, Bright Colors on Flashcards) Evaluate: Objective(s) addressed & how assessed. Compare and order integers. Students will be assessed through observation and whole class discussion. Students with exceptionalities will be given first opportunity to use cards on whiteboard. Overhead Add integers. Overhead Counters Basic Mat Teacher will demonstrate how to use color counters along with illustrations using + and - signs to model and explain zero Model 3 problems pairs; that combine integers with the Students will write the mathematical same signs. equivalent of the teachers' model atop the Basic Tile Mat. Model 3 problems that combine integers with Teacher will display the Key Question: different signs. each group is expected to discover: How can we predict the solution without using drawings or other handson materials? Students will be assessed through observation and group discussion. Desk 1 - Materials Handler/Manager Picks up and Returns Materials for the group Desk 2 - Illustrator/Materials Manipulator Draws diagrams, pictures, and manipulates materials for the group Desk 3 - Group Writer/Author Writes answers and responses to questions for the group Explore (20 min) Desk 4 - Time Keeper Allows no more than 2 to 4 minutes per questions and keeps members on task for the group Group 1: Students will model given problems using positive and negative illustrations. Students will create zero pairs and tell how many zero pairs exist within each problem. Group 2: Students will model given problems using yellow and red counters that represent positive and negative values, respectfully. Students will solve each problem by creating and removing zero pairs. The remaining values are the solution to the problem. Group 3: Students will toss coloredcounters to create problems and solve the problems by creating zero pairs. Students will provide and explanation in writing for each toss. All students will be given an anchor activity to complete after their group assignment. Two Color Students will be Counters assessed through observation and group Plastic discussion. Bag Students' group activity sheet Group Instruction will be scored al Handout based upon student participation, Anchor fulfillment of Activity duties Handout (individual and group), and supplying the correct solutions to each exercises. Evaluation Student representative from each group (15 min) will read and model their groups specific activity. Closest to Zero Game Two counter colors Each pair of students will compare scores to determine the overall winner. Students will be paired to toss 10 counters five times. Students will find the sum of the counters each round. At the end of five rounds, the person with a sum closest to zero wins. General Rule: Students will recite rules for adding integers with like signs: If the signs are the same add the numbers and keep the sign. Students will recite rules for adding integers with different signs: If the signs are NOT the same subtract the numbers and take the sign of the integers farthest from zero. IV. Attachments (worksheets, labs, project guides, tests, rubrics, etc.) Adding integers Group3.doc ; Adding integers Group2.doc; Adding integers Group1.doc Anchor Activity Handout