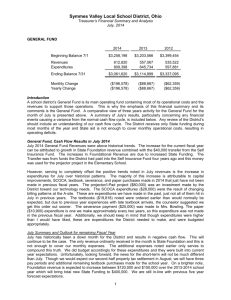
Red Book - School District of Osceola County
advertisement

The School District of Osceola County, Florida Financial and Program Cost Accounting and Reporting for Florida Schools Effective 2001 Includes DOE updates 06/10/09 (in Italic) SDOC modifications 11/04/10 (in Arial Front) TABLE OF CONTENTS Chapter One.......................................................................................................................................... 2 Introduction .............................................................................................................................. 2 Chapter Two ......................................................................................................................................... 6 Balance Sheet Accounts ........................................................................................................... 6 Chapter Three ..................................................................................................................................... 28 Revenue Accounts .................................................................................................................. 28 Chapter Four ....................................................................................................................................... 41 Expenditure Accounts ............................................................................................................ 41 Chapter Five ....................................................................................................................................... 65 Program Cost Accounting and Reporting .............................................................................. 65 Chapter Six ......................................................................................................................................... 76 Internal Service Funds ............................................................................................................ 76 Chapter Seven .................................................................................................................................... 78 School Internal Funds ............................................................................................................. 78 Chapter Eight ...................................................................................................................................... 94 Fiduciary Funds ...................................................................................................................... 94 Appendix A ........................................................................................................................................ 95 Supplies and Equipment ......................................................................................................... 95 Appendix B ........................................................................................................................................ 96 Optional Object Codes ........................................................................................................... 96 Appendix C ........................................................................................................................................ 97 Alphabetical List of Supplies, Equipment, AV ...................................................................... 97 Index ................................................................................................................................................. 125 1 Chapter One Introduction The primary purpose of this manual is to provide Florida school districts with a uniform chart of accounts for budgeting and financial reporting. Topics including governmental accounting standards, program cost accounting and reporting, and school internal funds are also addressed. This document is incorporated by reference in Rule 6A-1.001, Florida Administrative Code, pursuant to the requirements of Sections 237.01 and 237.02, F.S The chart of accounts included herein is adapted from the United States Department of Education publication, Financial Accounting for Local and State School Systems, which establishes a comprehensive and uniform structure for reporting education fiscal data. The Florida chart of accounts was modified following the initial publication of the Federal manual in 1957 and the major revision of 1973. Subsequent Federal revisions in 1980 and 1990 have also been addressed to ensure compatibility in national statistical reports. OVERVIEW This section presents a brief overview of the accounting structure including fund, revenue, and expenditure classifications. Fund. A fund is defined as a fiscal and accounting entity with a self-balancing set of accounts recording cash and other financial resources, together with all related liabilities and residual equities or balances, and changes therein, which are segregated for the purpose of carrying on specific activities or attaining certain objectives in accordance with special regulations, restrictions, or limitations. (NCGA Statement 1, paragraph 2) The basic fund structure for Florida school districts follows generally accepted accounting principles for governments. Governmental Funds General Fund Special Revenue Funds Debt Service Funds Capital Projects Funds Special Revenue Funds Permanent Funds Proprietary Funds Enterprise Funds Internal Service Funds Fiduciary Funds Pension Funds Investment Trust Funds Private-purpose Trust Funds Agency Funds Revenues are categorized by fund, source, and appropriation. Since revenues are usually determined by law, revenue accounts are structured by source (Federal, State, and Local) and specific appropriation. 2 1 Introduction Expenditures are categorized using the following elements. Fund Function Object Facility (School) Program Fiscal Year Grant Project Function refers to the objective or purpose of an expenditure. Functions are the activities performed to accomplish the objectives of the organization. The activities of school districts are classified into four major functional categories as follows: Instruction. The activities dealing directly with the teaching of pupils or the interaction between teacher and pupils. Instruction is further classified as Basic (K-12), Exceptional, VocationalTechnical, and Adult General. Another subfunction, "Other Instruction", is provided for programs such as recreation and enrichment and prekindergarten instruction. Instructional Support Services. This includes administrative, technical, and logistical support to facilitate and enhance instruction. Support Services include Pupil Personnel Services, Instructional Media, Instruction and Curriculum Development Services, and Instructional Staff Training Services. General Support Services. Those activities associated with establishing policy, operating schools and the school system, and providing the necessary facilities and services for the staff and pupils. This includes salaries and expenses for the Board, General Administration, School Administration, Facilities Acquisition and Construction, Fiscal Services, Food Services, Central Services, Pupil Transportation Services, Operation of Plant, and Maintenance of Plant. Community Services. Community Services consist of those activities that are not directly related to providing education for pupils in a school system. These include noninstructional services provided by the school system for the community. Object means the goods purchased or the service obtained. There are eight major object categories provided in this manual: Salaries Employee Benefits Purchased Services Energy Services Materials and Supplies Capital Outlay Other Expenses Transfers Facility. The school or office location that is the center for accumulation of costs. Program. Activities, operations, or organizational units designated to accomplish an objective or purpose. Educational programs are established by law for Florida school districts and are the basis for the program cost accounting and reporting system (see Chapter 5). 3 1 Introduction Fiscal Year. Denotes the twelve month period to which the annual budget applies. This designation is useful in analyzing costs of programs that extend over more than one fiscal year. Grant. Code numbers assigned by DOE for reporting state and federal grants. Project. This classification is used to identify expenditures related to a specific activity such as a construction project or a project funded through grants. For reporting purposes, grant and project numbers are five character codes, that are designated by DOE. Districts may elect to crosswalk from a local coding structure to the state-designated grant and project numbers. ACCOUNTING STANDARDS Generally accepted accounting principles for governmental entities are established by the Governmental Accounting Standards Board and provide the foundation for financial accounting and reporting for school districts. Basis of accounting refers to when revenues, expenditures, expenses, and transfers--and the related assets and liabilities--are recognized in the accounts and reported in the financial statements. Generally accepted accounting principles require the use of the modified accrual basis of accounting for governmental funds. This means that revenues are recognized when they become both measurable and available to finance expenditures of the fiscal period. Expenditures are generally recognized when the related fund liability is incurred, if measurable. Proprietary and fiduciary funds utilize the “full accrual” basis of accounting. That is, revenues and expenses are recognized when they occur regardless of the timing of the related cash flows. Florida school districts operate the following types of budgetary funds: general, special revenue, capital project, and debt service. As indicated above, the modified accrual basis should be used in accounting and reporting for these funds. Districts maintaining propriety and fiduciary funds should apply the accrual basis of accounting. Most grants accounted for in the special revenue funds require the expenditure of funds as the primary determinant of eligibility for funding. Therefore, the date of expenditure also becomes the point of revenue recognition for the grant. An encumbrance system which charges each purchase order, contract, or salary commitment to an appropriation should be used as part of a budgetary accounting system. These transactions cease to be encumbrances when paid, canceled, or when the actual liability is recorded. GOVERNMENTAL ACCOUNTING STANDARDS BOARD STATEMENT 34 In June, 1999, the Governmental Accounting Standards Board (GASB) issued Statement 34, Basic Financial Statements--and Management’s Discussion and Analysis--for State and Local Governments which requires all governments, including special-purpose governments such as school districts, to implement a new financial reporting model. The model includes management’s discussion and analysis (MD&A), basic financial statements, notes to the financial statements, and certain other required supplementary information (RSI) other than MD&A. 4 1 Introduction The MD&A is a component of RSI that precedes the financial statements. The basic financial statements include 1) government-wide financial statements, 2) fund financial statements, and 3) notes to the financial statements. The government-wide financial statements report information for the government as a whole, except for its fiduciary funds. These statements reflect the economic resources measurement focus and the full accrual basis of accounting. The fund financial statements for governmental, proprietary, and fiduciary funds follow the government-wide financial statements. The governmental and enterprise fund statements reflect major funds and combined non-major funds rather than a fund-type presentation. The fiduciary and proprietary funds continue to utilize the economic resources measurement focus and accrual basis of accounting while the governmental fund financial statements are presented using the current financial resources measurement focus and the modified accrual basis of accounting. A reconciliation is required to explain the differences between the change in fund balances reported in the fund financial statements and the change in net assets reported in the government-wide financial statements. Reconciling items arise from differences in the measurement focuses and bases of accounting between the statements, and certain required eliminations. The notes to the financial statements are an integral part of the basic financial statements and additional disclosures are required for the new reporting model. RSI is supplementary financial information that is required to be presented with the basic financial statements. Required budgetary comparisons include the original and final budgets for the general fund and each major special revenue fund that has a legally adopted annual budget. One of the primary differences between the government-wide statements and the fund financial statements is the measurement focus and basis of accounting. The government-wide statements reflect the economic resources measurement focus and the full accrual basis of accounting while the fund financial statements for governmental funds continue to reflect the current financial resources measurement focus and the modified accrual basis of accounting. The following chapters of this manual have been modified to address the requirements of GASB Statement 34 as it relates to the chart of accounts, student internal funds, internal service funds, and fiduciary funds. Additional guidance in the implementation of Statement 34 is available through the Department’s publication, Financial Reporting Model Implementation Guide for Florida School Districts. 5 1 Introduction Chapter Two Balance Sheet Accounts This chapter provides balance sheet account numbers and related definitions. 1000 ASSETS AND OTHER DEBITS 100000 Assets are probable future economic benefits obtained or controlled by an entity as a result of past transactions or events. Other debits are budgetary accounts that normally have debit balances. 1100 Current Assets. 110000 Current assets include cash or other assets that are expected to be converted to cash within the operating cycle. 1110 Cash. Currency, coin, checks, money orders, and banker's drafts on hand or on deposit with an official or agent designated as custodian of cash and bank deposits. 1111 Cash on Demand Deposit. 111100 Deposits with fiscal agents, such as commercial banks, for the payment of normal operating expenditures and subject to withdrawal by board warrant. 111101 111104 111105 111106 111107 111108 111109 111110 111111 111112 111113 111114 111115 111116 111180 111181 111182 111183 111184 District Master-Bank America Health/Life Local-Bank America Health/Life EMI-Bank America Federal Funds-Bank America Food Service-Bank America Health/Life Ins-Cigna Pre-K Collection Fund Extended Day Financial Aid Trust Health/Life Ins-Fla Hospital Acclaris Flexible Savings Acct Conexis Flex Benefits Admin Cigna Flexible Savings Account TSA Consulting Account Four Corners, Inc General Acct Four Corners, Debt Serv Subact Four Corners, Admin Fee Four Corners Incent Fee Four Corners Maintenance Subact 1112 Petty Cash. 111200 Cash on hand maintained for the purpose of paying small obligations when the issuance of a formal voucher and check is not cost-effective. Also, funds established for the purpose of 6 2 Balance Sheet Accounts making change or immediate payments of relatively small amounts. 1113 Cash Change Funds. 111300 Cash on hand maintained for the purpose of providing cash register change. 111301 Extended Day 1114 Cash with Fiscal/Service Agents. 111400 Deposits with fiscal agents, such as commercial banks, for the payment of matured bonds and interest. Also, deposits with self-insurance plan agents. 1114C1 111401 111402 111403 111404 111405 111406 111407 111408 111409 111410 111412 111413 111414 111415 111416 111417 111418 111419 Lasalle Bank Escrow Acct Lease Payment Account Reserve Account Cost of Issuance Acquisition Account United Financial (HW) UMB Bank Escrow Account Cash with Fiscal Agent Escrow Account L08 FREFBD Interest Account FREFBD Cap Interest Acct Escrow Account L12 Escrow Lasalle L13 Assessment Account Impact Fee Account BEFBD 2004B Interest Account BEFBD 2004B Acquisition Acct BEFBD 2004B Reserve Bellalago Sinking Fund 1115 Cash - Interest Earning Deposits. 111500 Deposits which generate interest income usually stipulating the duration of deposit and rate of interest. 111501 1117 1120 112000 Savings 72 Bonds-Nations Cash on Hand. Currency, coins, and checks received but not yet deposited. Taxes Receivable . The uncollected portion of taxes that a governmental unit has levied and billed. 1121 Taxes Receivable . 112100 Taxes which were levied for the current operating year but are uncollected. This account should be closed at June 30 and 7 2 Balance Sheet Accounts amounts held by the Tax Collector on behalf of the School Board should be recorded in account 1220, Due From Other Agencies. 112200 Cash with Fiscal Agent 1130 113000 Accounts Receivable . Amounts due on open account from private persons, firms, or corporations for goods and services furnished by the school district. 113001 113002 113003 113004-12 113013 113014 113015 113016 113017 113018-22 113023 113024-36 113037 113038-54 113055 113056-99 113100 113101-08 113109 113110-16 113117 113118-21 113122 113123 113124-34 113135 113136-39 113140 113141-42 113143 113144-45 113146 113147 113148 113149-54 113155 113156-73 113175 113176 113177-88 Cent FL Educ Fed Cr Union Salary Overpayments – Other FICA Repay Vehicle/Flex Salary Overpayments NSF Checks Salary Overpayments Nest Entertainment Salary Overpayments IKON Salary Overpayments Child Support Salary Overpayments ACH Error Salary Overpayments Four Corners Charter Accts Salary Overpayments Portable Equipment Salary Overpayments DOE OSFA/Peterson Salary Overpayments OSI Collections Salary Overpayments FICA Taxes Due/Dearing Child Support Salary Overpayments Taxes Receivables Flex Sav Acct Salary Overpayments Garnishment Salary Overpayments Teamsters Union Salary Overpayments OCTA Salary Overpayments VOID CU Ded Salary Overpayments Amer Express Fin Adv Salary Overpayments Flora Ridge Elem FSBIT Salary Overpayments 8 2 Balance Sheet Accounts 113189 ACH Return 113190-204 Salary Overpayments 113853 New Dimensions Charter Sch 113863 Four Corners Charter Sch 113866 City of Kissimmee Chtr Sch 113891 From Internal Accounts 1140 114000 Due From Other Funds. Amounts due for goods or services provided by a particular fund to another fund or for interfund loans. 114B10 114B30 114F10 114F41 1140C1 1140C2 1140F3 1140R1 Bellalago Bellalago Cap Proj Four Corners General Four Corners Co BEFBD General Fund BDFBD Debt Service FCCS Capital Fund FREFBD General 1141 Due From Budgetary Funds. 114100 Amounts due from one fund to another. Separate accounts should be maintained for each interfund loan. 1142 Due From Internal Funds. 114200 Amounts due for advances to internal accounts. Separate accounts should be maintained for each advance. 1142A1 1142A3 114222 114252 114259 11429A 11429C 11429K 11429Q 11429S 11429Y 11429Z 114296 114297 114298 1143A1 1143A2 1143A4 11431A 11431B 114311 11434A 2007 Sales Tax Bonds 2007 COPS Debt Serv 72 Bonds Debt Service DS 2002 GO Bonds 92 Bonds Debt Service Classrooms First 03 99 COP Debt Service 2000 COP 2002 COPS Debt Serv Sales Tax Bonds DS 2004 COPS DS 2005 COPS DS 95 COPS Debt Service Debt Serv Cap Leases Bellalago EFBD DS 2007 Sales Tax Bonds CSR Penalties 2008 Impact Fees COBI Bonds 2005 COBI Bonds 2006 COBI Bonds PECO Gen Rev 2000 9 2 Balance Sheet Accounts 11434B 11434C 11434D 11434E 11434F 11434G 114340 114341 114342 114348 114349 114360 11437B 11437C 11437D 11437E 11437F 11437G 114370 114371 114372 114373 114377 114378 114379 11439A 11439B 11439C 11439D 11439E 11439F 11439G 11439H 11439I 11439J 11439K 11439L 11439M 11439N 11439P 11439Q 11439R 11439S 11439T 11439U 11439V 11439W 11439X 11439Y 11439Z PECO Schl Tr FD 2000 PECO 2005 PECO 2006 PECO 2007 PECO 2008 PECO 2009 PECO 2000 PECO 2001 PECO 2002 PECO 1998 PECO 1999 CO & DS CO Tax 2004 CO Tax 2005 CO Tax 2006 CO Tax 2007 CO Tax 2008 CO Tax 2009 CO Tax 2000 CO Tax 2001 CO Tax 2002 CO Tax 2003 CO Tax 1997 CO Tax 1998 CO Tax 1999 Classrooms First Impact Fees 99 COP 99 COP Reserve 94 COP Reserve 95 SIT Funds Settlement Impact Fees 2000 Effort Index Grant Sales Tax COP 2000 Impact Fees 2001 Class Size Reduction Charter Schools CO Impact Fees 2002 COP 2002 High Growth Grant Sales Tax Proceeds Impact Fees 2003 Impact Fees 2004 Escrowed Impact Fees Impact Fees 2005 COPS 2004 COPS 2004 Impact Fees 2006 10 2 Balance Sheet Accounts 114390 114391 114393 114398 114410 114420 114421 114422 114423 114490 114491 114492 114493 114710 114711 114713 114731 1148B1 1148B3 1148R3 114891 1150 115000 Inventory. Materials and supplies on hand for future use in operations. Subaccounts may be used to identify different types of inventory such as Materials, Purchased Food, and Commodities. 115110 115120 115121 115122 115130 115131 115140 115150 115160 115170 1160 116000 LCIF Impact Fees 2007 Impact Fees 1998 Disney Celebration Food Service Special Revenue Pell Grants Other Federal Extended Day Extended Day Extended Day Pre-K Extended Day ECTAC Insurance Trust H&L Int Service Fund Flex Spending Acct East Coast Consortium Ballealgo Charter ACA BCA Capital Fund Flora Ridge EFBD Cap Internal Accounts Maintenance F/S Supplies Commodities Purchased Food Warehouse Warehouse Equipment Gas Diesel Tires & Tubes Transportation Parts Investments. Securities and real estate held for the production of income in the form of interest, dividends, rentals, or lease payments. This account does not include assets used in school district operations. Separate accounts for each category of investments may be maintained. 1161 Investments - U. S. Government Securities. 116100 Securities of the U. S. Government acquired by the district school board as authorized by statute and held for the production of income in the form of interest. 1161P1 PFM P1 72 Bonds DS 11 2 Balance Sheet Accounts 1161P2 1161P3 116101 116102 116103 Bonds Res 2001 Bonds Project Fund 2001 First American MMF/Wachovia Transamerica Rabobank 1162 Investments - Section 237.161 Loans. 116200 Amounts invested from proceeds of loans made pursuant to Section 237.161, F.S. 1163 Investments - SBE/COBI Bonds. 116300 State Board of Education Bonds issued on behalf of school districts under Section 18, Article XII of the State Constitution. 1164 Investments - State Board of Administration. 116400 Amounts placed with the State Board of Administration for investment. 1164BT 11640B 116401 116402 116403 116404 116407 116408 11647B SBA Fund B Trust Agent SBA-Acct XXXX11B SBA Lease Payment Account SBA Reserve Account SBA Cost of Issuance SBA Acquisition Account SBA-Acct XXXX13 SBE Bonds SBA-Acct XXXX13B 1169 Other Governmental Securities. 116900 Securities of other governmental agencies authorized by Florida Statutes and not identified above. 1170 117000 Interest Receivable on Investments. The amount of interest receivable on investments, excluding purchased interest. 1170P1 Accr Int – 72 Bonds DS 1170P2 Accr Int – 2001 Bonds Res Inv 1180 118000 Due from Reinsurer. Amounts to be recovered from reinsurance policies. 119404 Intercompany Four Corners Inc 119863 Intercompany Four Corners Elem 119891 Intercompany Four Corners Middle 1200 12000 Other Current Assets. All other assets, current in nature, that are not specifically provided for in other sections. 12 2 Balance Sheet Accounts 1210 Deposits Receivable . 121000 Funds deposited by the school district as a prerequisite to receiving services and/or goods. 1220 Due From Other Agencies. 122000 Amounts due from other governmental units for revenues from Federal, Federal through State, State or other sources. 122010 M Bronson 122030 IRS 122200 Due from Bureau of Uncl Prop 122853 122863 122866 122881 122891 122900 122911 122916 122917 122932 New Dimensions HS Four Corners Elem Kissimmee Charter El PM Wells Charter Four Corners Middle UCP Child Dev Center Harmony Neigh School Canoe Creek Charter Foundation Middle Bellalago Charter 1230 123000 Prepaid Expenses. Payment of items which will benefit future accounting periods. 124000 Issuance Costs 1300 Capital Assets. 130000 Fixed Assets Land, land improvements, buildings, machinery, furniture, equipment, and all other tangible and intangible assets that are used in operations and have useful lives that extend beyond a single accounting period. If acquired through donation, the capital asset should be recorded using the fair value at the time of acquisition. 1310 131000 Land. The acquisition cost of land owned by a school system. If land is purchased, this account includes the purchase price and other costs incurred to prepare the land for use such as legal fees, filling and excavation costs, and other improvements. 131001 Right of Way 131002 Excav, Fill, Grading, Util 1315 Land Improvements – Nondepreciable . 131500 The cost of permanent improvements to land that are not subject to depreciation. 131501 Landscaping 13 2 Balance Sheet Accounts 1320 132000 Improvements Other Than Buildings. The cost of permanent improvements, other than buildings, which add value to land. Examples include fences, retaining walls, sidewalks, sewage treatment systems, original or expanded paving projects, fixed playground apparatus, flagpoles, gateways, underground storage tanks, etc., which are not part of the building service systems and similar improvements. 132001 132002 132003 132004 132005 132006 132007 132010 Sidewalks (Concrete) Parking Lots, Driveways Retaining Walls Sewage Treatment Plants Fence Underground Storage Tanks Fixed Playground Equipment Investment in EFBD 1329 Accumulated Depreciation – 132900 Improvements Other Than Buildings. The accumulation of systematic and rational allocations of the cost of improvements other than buildings over the useful lives of the assets. 1330 133000 Buildings and Fixed Equipment. The cost of permanent structures used to house persons and property owned by a school system. If buildings are purchased or constructed, this account includes the acquisition or construction costs of permanent buildings and fixtures attached to and forming a permanent part of such building. 133001 133002 133003 133004 133005 133006 133007 133008 133009 Permanent Structures Relocatables Modular/Fixed Furniture Sprinkler System Electrical System Water System Heating, Cooling, Air Circ System Roof Electronics 1339 Accumulated Depreciation -Buildings and Fixed Equipment. 133900 The accumulation of systematic and rational allocations of the cost of buildings and fixed equipment over the useful lives of the assets. 1340 134000 Furniture, Fixtures, and Equipment. The cost of furniture, fixtures, and equipment owned by a school system. This account includes teaching, laboratory, research, diagnostic and testing, and administrative equipment used y or for students. 14 2 Balance Sheet Accounts 134001 Fund 100 134003 Fund 300 134004 Fund 400 1349 Accumulated Depreciation - Furniture, Fixtures, and 134900 Equipment. The accumulation of systematic and rational allocations of the cost of furniture, fixtures and equipment over the useful lives of the assets. 1350 135000 Motor Vehicles. The cost of all transportation equipment including vehicles used for pupil transportation and service vehicles (trucks, vans, scooters, motorcycles, passenger cars, or other motorized units). 1359 Accumulated Depreciation - Motor Vehicles. 135900 The accumulation of systematic and rational allocations of the cost of vehicles over the useful lives of the assets. 1360 136000 Construction in Progress. The actual cost incurred to date for construction work undertaken but not yet completed. This account reflects the total construction costs recorded as expenditures in the capital projects funds. 1370 137000 Property under Capital Lease. The net present value of lease payments capitalized as assets. When title to the property passes, the value is transferred to the appropriate capital asset account. 1379 Accumulated Depreciation – Property under Capital Lease. 137900 The accumulation of systematic and rational allocations of the cost of property under capital lease over the useful lives of the assets. 1380 138000 Audio Visual Materials and Computer Software. The cost of audio visual materials and computer software which meet the criteria for capitalization. 1381 Audio Visual Materials. 138100 The cost of audio visual materials owned by a school district. 1382 Computer Software. 138200 The cost of computer software purchased by a school district. Specifically this refers to the set of programs and associated documentation used to control the operation of a computer. The two primary types of software are (1) systems software which include operating systems, programming languages, and utility programs; and (2) application programs that are designed to perform tasks such as data base management, spreadsheet functions, instruction, and word processing. Generally, when software is acquired with computer hardware for a single 15 2 Balance Sheet Accounts purchase price and the relative value of the software is material to the total cost, it is necessary to allocate the acquisition cost to both the software and hardware in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles for lump-sum or basket purchases. However, systems software acquired in conjunction with computer hardware may be recorded as part of the equipment purchase (no allocation of cost to the software) when the software will not be removed, transferred, or in any way separated from the original hardware. In the event that software which was originally recorded as equipment is subsequently removed, transferred, or detached from the original hardware, it would be necessary to retroactively allocate a portion of the original cost, if material, to the software for proper recording of the removal or transfer. 1388 Accumulated Depreciation - Audio Visual Materials. 138800 The accumulation of systematic and rational allocations of the cost of audio visual materials over the estimated useful lives of the assets. 1389 Accumulated Amortization - Computer Software. 138900 The accumulation of systematic and rational allocations of the cost of computer software over the estimated useful lives of the assets. 139000 Investment in EFBD 139100 Inv in Educ Fac Benefit Dist 139900 Accumulated Deprn 1400 Other Debits. 140000 Due to the elimination of the general long-term debt account group by GASB Statement 34, Accounts 1410 through 1450, used for Amounts Available/To Be Provided for Debt Service, are no longer necessary and therefore, have been deleted. 1410 141000 Other Post-Employment Benefits Asset. Amt Avail for Debt Serv Princ To account for funded other post-employment benefits (OPEB) assets set aside in advance to pay for future benefits, resulting in a net obligation asset for government-wide and proprietary fund financial statement presentation (Added 2007-08) 141061 141062 141063 141064 141065 141069 142000 SBE/COBI,PECO Spec Act Bonds Go Refund 2002 Sales Tax 2001 District Bonds COP Amt to Be Prov for Debt Serv 16 2 Balance Sheet Accounts 142061 142062 142063 142064 142065 142066 142080 143000 SBE/COBI, PECO Spec Act Bond Sec 237 Loans GO Refund 2002 District Bonds Sales Tax 2001 Arbitrage Rebate Amt to Be Prov for Comp Absenc 143066 Comp Absences 144000 Amt Prov for Cap Leases & COP 144067 To Be Prov – Capital Leases 144069 To be Prov – COP 145000 Amt Provided for Future Claims 1500 Budgetary Debits. 150000 A group of general ledger accounts that normally have debit balances and are used to achieve budgetary integration within the accounting system. 1510 151000 Estimated Revenues. The amount of revenues estimated to be realized during a budget period, whether collected in the same or subsequent periods. 1520 152000 Encumbrances. Commitments in the form of purchase orders or contracts which are chargeable to an appropriation and which represent a reserve of the budgetary fund balance. Once a purchase order or contract is fulfilled, the encumbrance is removed from the accounting records. 152010 Asset Trade 153000 Expenditures 153001 Expenditure Offset 2000 LIABILITIES, OTHER CREDITS, AND FUND BALANCES/NET ASSETS 200000 Liabilities represent probable future sacrifices of economic benefits arising from present obligations to transfer assets or provide services as a result of past transactions. Other Credits are budgetary accounts that normally have credit balances. 2100 Current Liabilities. Current liabilities represent obligations expected to be paid from current financial resources usually within the operating cycle or one year. 17 2 Balance Sheet Accounts 2110 Salaries, Benefits and Payroll Taxes Payable . Amounts due to employees or others for salaries, benefits, and payroll taxes. 2120 212000 Accounts Payable. Liabilities representing amounts due on open account to private persons or organizations for goods and services received by a school system. (Does not include amounts due to other funds or other governments.) 212001 212002-03 212003 212004 212010 212011 212012-15 212016 212017 212018 212019-26 212070 212071 Child Support Payable Garnishment Garnishment ACH Ret/Feliciano Unclaimed Checks Unclaimed Teac Lead Chks Garnishment Delta Care Vision FICA Adj Garnishment CIGNA Health Claims CIGNA FSA Claims 212810 School Operating 212811 Contra 212820 Debt Service 212821 Contra 212830 Facility & Maintenance 212831 Contra 212840 Admin Fee Base 212841 Contra 212850 Admin Fee Inc 212851 Contra 212860 Admin Fee Condtnal 212861 Contra 2130 Judgments Payable Amounts owed as a result of court decisions, including condemnation awards for private property taken for public use. 2140 214000 Construction Contracts Payable. Amounts due by a school system on contracts for construction of buildings or other structures, and other improvements. 2150 Construction Contracts Payable - Retained Percentage. 18 2 Balance Sheet Accounts 215000 Amounts due on construction contracts representing a percentage of the total contract price that is not paid pending final inspection, the lapse of a specified time, or both. 2160 216000 Due to Other Funds. Amounts owed for goods and services rendered by a particular fund to another fund within the school district or interfund loans due within one year. 216B10 216B30 216F41 2160C1 2160C3 2160R3 2162A1 2162A3 Bellalago Oper Acct Bellalago Cap Proj Fund Four Corners Spec Rev Bellalago EGBD General BEFBD Capital Fund FREFBD Capital 2007 Sales Tax Bond 2007 COPS 2161 Due To Budgetary Funds. Amounts owed by a particular fund to another fund within the school district (excluding amounts due to school internal funds). 2162 Due to Internal Funds. Amounts owed by a particular fund to school internal funds within the district. Separate accounts should be maintained for each liability. 216232 216252 21629A 21629C 21629K 21629Q 21629S 21629Y 216296 216297 216298 2163A1 2163A3 2163A4 216340 216341 216342 216348 216349 21630 21637B 21637C 21637D 21637E Section 237 Loan 2002 GO Bonds Classrooms First COP Debt Service 99 COP 2000 COP Debt Service 2002 Sales Tax Bond COPS 2004 COP 95 Cap Lease Dept Serv Bellalago EFBD Sales Tax Bond Procceds 2007 COP COPS 2007 Impact Fees 2008 PECO 2000 PECO 2001 PECO 2002 PECO 98 PECO 99 CO & DS CO Tax 2004 CO Tax 2005 CO Tax 2006 CO Tax 2007 19 2 Balance Sheet Accounts 21637F CO Tax 2008 216370 CO Tax 2000 216371 CO Tax 2001 216372 CO Tax 2002 216373 CO Tax 2003 216377 Capital Projects 97 216378 CO Tax 98 216379 Co Tax 99 21639A Classrooms First 21639B Impact Fees 99 21639C COP 99 21639D COP Reserve 94 21639E COP Reserve 95 21639F SIT Fund 21639G PHS Settlement 21639H Impact Fees 2000 21639I Effort Index Fund 21639J Sales Tax 21639K COP 2000 21639L Impact Fees 2001 21639M Class Size Reduction 21639P Impact Fees 2002 21639Q COP 2002 21639R High Growth Grant 21639S Sales Tax Proceeds 21639T Impact Fees 2003 21639U Impact Fees 2004 21639V Escrowed Impact Fees 21639W Impact Fees 2005 21639X COP 2004 21639Y COPS 2004 21639Z Impact Fees 2006 216390 LCIF 216391 Impact Fees 2007 216393 Impact Fees 98 216410 Food Service 216420 Special Revenue 216422 Federal-Other 216423 Extended Day 216491 Extended Day 216492 Pre-K Extended Day 216493 ECTAC 216710 Insurance Trust 216711 H&L Int Service Fund 216712 AL/GL Internal Svc Fund 216713 Flex Spending Acct 216731 East Coast Consortium 2168B1 Bellalago Oper Acct 20 2 Balance Sheet Accounts 2168B3 Ballalago Sch Capt Funds 2168R3 Flora Ridge EGBD 2170 217000 Payroll Deductions and Withholdings. Amounts deducted from employees’ salaries for withholding taxes and other purposes. A separate liability account may be used for each type of deduction. 217030 Other Payroll Deductions 217031 FICA & Withheld Tax Payable 217032 TSA Funds Returned 217033 TSA Funds Payable 2180 218000 Matured Bonds Payable. Unpaid bonds that have reached or passed their maturity date. Account 1114, Cash with Fiscal Agent, should be used to record amounts remitted to the paying agent for payment of this liability. 218020 Returned from PA 2190 219000 Matured Interest Payable. Unpaid interest on bonds that have reached or passed their maturity date. Account 1114, Cash with Fiscal Agent, should be used to record amounts remitted to the paying agent for payment of this liability. 219020 Returned from PA 2200 Other Current Liabilities. 220000 All other current liabilities that are not provided for specifically in preceding subsections. 2210 221000 Accrued Interest Payable. Interest costs related to the current and/or prior periods, but not due until a later date. Also, amounts received at the time of a bond sale for interest accrued from the date of issuance to the date of sale. 2220 222000 Deposits Payable. Liability for deposits received as a prerequisite to providing services and/or goods. 2230 223000 Due to Other Agencies. Amounts owed by the reporting school district to other governmental units. Separate accounts may be maintained for each liability. 223010 223011 223020 223021 IRS Retirement Payable Retirement Payable Retirement Suspense 21 2 Balance Sheet Accounts 223030 223040 223050 223853 223863 223866 223881 223891 223900 223911 223916 223917 Cert Fee EFBD Flora Ridge New Dimensions High Sch Four Corners Elementary Kissimmee Charter Elem PM Wells Charter Sch Four Corners Middle UCP Child Dev Center Harmony Neigh School Canoe Creek Charter Foundation Middle 2240 224000 Due to Fiscal Agent Amounts due to fiscal agents, such as commercial banks, for servicing the district’s matured debt. 2250 225000 Section 237.151 Notes Payable Amounts due on current loans authorized by Section 237.151, F.S. 2260 226000 Sales Tax Payable Sales taxes collected by the district which must be remitted to the state. 2270 227000 Estimated Liability for Self-Insurance Program 2271 Estimated Unpaid Claims- Self-Insurance Program. 227100 Amount needed to provide for the estimated ultimate cost of settling claims for events that have occurred on or before the balance sheet date, including reported claims and claims incurred but not reported. 2272 Estimated Liability for Claim Adjustment Expenses. 227200 Amount needed to provide for the estimated ultimate cost required to investigate and settle claims relating to insured events that have occurred on or before the balance sheet date, whether or not reported to the district. 2280 228000 Estimated Liability for Arbitrage Rebate. Districts with a calculated arbitrage rebate liability should abate the amount of the "rebate set aside" against the interest revenue account within the fund which has generated interest earnings which are subject to rebate. This amount should be recorded as a liability of the fund earning the interest. 2290 Internal Accounts Payable. Amounts held on behalf of others in the internal accounts agency fund. 2300 Long-Term Liabilities. 230000 Long-term liabilities are debts which a school district plans to hold more than one year. 22 2 Balance Sheet Accounts 2310 231000 Notes Payable. An unconditional written promise signed by the maker to pay a certain sum of money on demand or at a fixed or determinable future time, either to the bearer or to the person designated therein. 231063 Sec 237 Loans 2312 Section 237.161/237.162 Notes Payable. 231200 Obligations authorized under the provisions of Sections 237.161 and 237.162, F.S. This includes installment loan contracts approved under this statutory authority. 2313 Bond Anticipation Notes. 231300 Short-term notes sold in anticipation of a bond issue which are full faith and credit obligations of the school district and are to be retired from the proceeds of the bonds to be sold. 2315 Obligations Under Capital Leases. 231500 The present value of future payments on capitalized lease agreements. 231567 Obligations Under Cap Leases 231600 Installment Purchases Payable 2320 232000 Bonds Payable. The face value of obligations representing a written promise, generally under seal, to pay a specified sum of money at a designated maturity date with a fixed rate of interest payable periodically. 232001 232061 232062 232065 232070 232090 Sales Tax Rev 2001 SBE/COBI,PECO Spec Act Bonds District Bonds Def Amt on Refunding Bonds Unamortized 2321 State Board of Education/Capital Outlay Bond Indebtedness 232100 (COBI) Bonds Payable. Principal balance due on bonds issued by the SBE on behalf of the school district under Section 18, Article XII, of the State Constitution. Such bonds have been designated SBE or Capital Outlay Bonded Indebtedness (COBI). 2322 District Bonds Payable . 232200 Principal balance due on bonds issued by the school district as authorized by the voters of the district. 232201 GO Refunding 2002 23 2 Balance Sheet Accounts 2323 Special Act Bonds Payable. 232300 Balance due on the principal amount of bonds or revenue certificates issued by the school district pursuant to authority granted by special acts of the Legislature. 2324 Motor Vehicle License Revenue Bonds Payable. 232400 Balance due on principal amount of bonds or revenue certificates of the school district as authorized by the legislature. 2330 233000 Liability for Compensated Absences. Amounts owed to employees for unpaid vacation and sick leave liabilities based on the right to receive compensation for future absences attributable to services already rendered. 233066 Liab for Compensated Absence 2340 234000 Certificates of Participation Payable. Obligations resulting from the issuance of certificates of participation, a financing instrument which provides the issuer with cash to finance construction or capital acquisitions. 234069 Cert of Participation Payable 234090 COP Unamortized Discount 2350 235000 Estimated Liability for Long-Term Claims. Amounts due for long-term claims which are not otherwise classified, including estimates of insurance claims and judgments. 2360 236000 Other Post-Employment Benefits Liability. To account for the actuarial calculations for OPEB benefits net of funded amounts, resulting in a net obligation liability for governmentwide and proprietary fund financial statement presentation. (Added 2007-08) 2370 237000 Estimated PECO Advance Payable. Obligation for the repayment of PECO funds received pursuant to Section 235.435(2), F.S. 2380 238000 Other Long Term Liabilities. 238100 Edu Fac Benefit Dist Agree Pay 2400 240000 Other Credits. All other liabilities not provided for in preceding subsections. 2410 241000 Deferred Revenues. Liabilities resulting from the receipt of unearned revenue. 24 2 Balance Sheet Accounts 2411 Deferred Revenue-Public Education Capital Outlay (PECO). 241100 The annual allocation of PECO funds for which encumbrance authorizations have not been issued. 2412 Deferred Revenue-Cash Advance From Grants. 241200 Unearned revenues represented by cash advanced for grants, etc. 2413 Deferred Revenue - Other. 241300 241301 Prepaid Meals 2414 Deferred Revenue - Classrooms First Program. 241400 Unearned revenues represented by cash advanced for the Classrooms First Program. 2500 250000 Budgetary Credits. A group of general ledger accounts that normally have credit balances and are used to achieve budgetary integration within the accounting system. 2510 251000 Appropriations. Authority granted by the school board to make expenditures and to incur obligations in the name of the school district for specified purposes and amounts during the fiscal year. 251001 Budget Amendment Offset 252000 2700 270000 Revenues Fund Equity. The excess of fund assets over fund liabilities. In governmental funds, this difference represents fund balance. In proprietary and fiduciary funds, the difference represents net assets. 2705 Reserved for Endowments. The segregated portion of fund balance indicating that permanent trust fund balance amounts are legally restricted for endowment purposes. 2710 271000 Reserved for State Required Carryover Programs. The segregated portion of fund balance representing the unexpended balances of categorical program funds and earmarked funds carried forward to the subsequent fiscal year pursuant to Rule 6A-1.0141, FAC. 2720 272000 Reserved for Encumbrances. An account representing a portion of a fund balance segregated for outstanding encumbrances. 272010 Asset Trade 25 2 Balance Sheet Accounts 2730 273000 Reserved for Inventory. Segregation of a portion of fund balance for the amount of ending inventory. 2740 Reserved for Ending Cash Balance. An account used to restrict a portion of fund balance for the amount of cash which is to be carried over for the payment in the subsequent period of expenditures related to the current period. 2750 275000 Reserved for Debt Service. 2751 Bond Reserve. 275100 An account used to restrict a portion of the fund balance in a debt service fund which is required to be established by bond resolution. 2752 Other Amounts Reserved for Debt Service. 275200 Segregation of a portion of the fund balance in a debt service fund required by legal restrictions. 275201 Adjustment to Beginning Fund Bal 175240 Sinking Fund 2760 276000 Unreserved Fund Balance. The portion of fund balance representing expendable available financial resources. 2762 Designated for Insurance Loss Recoveries. 276200 Designated amounts of insurance proceeds which will be used to replace the loss. 2763 Designated for (Special Purpose). 276300 276301 Debt Service 276302 Arbitrage Rebate 276310 F/B-Inventory Rep 276320 Debt Service- Oper 276321 Cap 276330 F/B Facil & Maint – Oper 276350 Admin Fee-Incentive 276360 Admin Fee-Condition 2764 Designated for Special School Maintenance, Section 236.25(2), F.S. 2769 Undesignated. 276900 276901 Adjustment to Beginning Fund Bal 26 2 Balance Sheet Accounts 276902 Budget Amendment Offset 276921 Charter Capital 2770 277000 Net Assets, Invested in Capital Assets, Net of Related Debt. Contributed Capital The component of the difference between assets and liabilities of proprietary funds that consists of capital assets less accumulated depreciation and the outstanding balance of debt that is directly attributable to the acquisition, construction, or improvement of those assets. 2780 278000 Net Assets, Restricted. Retained Earnings The component of the difference between assets and liabilities of proprietary funds that consists of assets with constraints placed on their use by external parties or through constitutional provisions or enabling legislation. 2785 Net Assets, Held in Trust. The difference between assets and liabilities of fiduciary funds. 2790 279000 Net Assets, Unrestricted. The difference between assets and liabilities of proprietary funds that is not reported as net assets, invested in capital assets, net of related debt or restricted net assets. 279001 Beg Net Assets-Audit Adj 2800 Beginning Fund Balance. A measure of available expendable financial resources in a governmental fund at the beginning of the accounting period. 2880 Beginning Net Assets. The assets of a proprietary or fiduciary fund less the liabilities, as of the beginning of the accounting period. 2891 Adjustments to Fund Balances. Prior year adjustments and/or other increases/decreases in governmental fund balances that are not reflected in the current year activity. 2896 Adjustments to Net Assets. Prior year adjustments and/or other increases/decreases in proprietary or fiduciary fund equity that are not reflected in the current year activity. 27 2 Balance Sheet Accounts Chapter Three Revenue Accounts This chapter provides revenue account numbers and related definitions. 3100 Federal Direct. Revenue received by the district directly from the federal government without the state as a distributing agency. 3120 Federal Impact Funds. Funds provided to the district as non-earmarked funds to be used for the support of the total school program when increased enrollment is attributable to federally connected activities. 3121 3200 Federal Impact, Current Operations. These are non-earmarked funds, accounted for through the district school fund, to be used for the support of the total school program. A district may qualify for revenue from this source during any school year, when minimum conditions are met. In order to be eligible, not less than three percent (3%) of the total average daily attendance (K-12) must result from pupils who have a parent employed on an eligible federally owned property within the state of Florida. The parent may be a member of the Armed Forces stationed on such property as a private individual, a civil service employee, or an employee of a contractor working on this property. Application forms and instructions are available from the Department of Education. 3170 Workforce Investment Act. Amounts received directly to assist in providing jobtraining and employment opportunities for the economically disadvantaged unemployed, and to assure that training and other services lead to maximum employment opportunities. 3180 Community Action Programs. Funds provided by the federal government for community action programs to help urban and rural communities mobilize their resources to combat poverty. 3190 Other Federal Direct. Other amounts received directly from the federal government. 3191 R.O.T.C. Amounts received to assist districts in establishing Reserve Officers Training Corps programs. 3199 Miscellaneous Federal Direct. Other sources of direct federal funding not previously classified. Federal Through State. Federal funding distributed through the state to the district. 3201 Vocational Education Acts. Formula grant funds provided to assist in conducting and strengthening vocational education programs. 3202 Medicaid. Funds received as reimbursement through the federal Medicaid program. 3210 State Fiscal Stimulation Funds – K12. Funds received for K-12 through ARRA Stabilization Funds. (Effective 7/1/09 for use in Fund 431) 28 3 Revenue Accounts 3211 State Fiscal Stabilization Funds – Workforce. Funds received for Workforce Education through ARRA Stabilization Funds. (Effective 7/1/09 for use in Fund 431) 3212 State Fiscal Stabilization Funds – Voluntary Prekindergarten Program. Funds received for VPK through ARRA Stabilization Funds. (Effective 7/1/09 for use in Fund 431) 3220 Workforce Investment Act. Amounts received to assist in providing occupational training for the unemployed that cannot obtain appropriate full-time employment without training. 3226 Eisenhower Math and Science. Funds received to improve the skills of teachers and the quality of instruction in mathematics and science in elementary and secondary schools. 3227 Drug Free Schools. Funds received for drug and alcohol abuse education and prevention programs. 3230 Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA). Amounts received from grants for handicapped students, including preschool children ages 3-5. 3240 Elementary and Secondary Education Act, Title I. Amounts received from grants to assist in the education of disadvantaged and handicapped students. 3251 Adult General Education. Funds provided to encourage and expand basic educational programs for adults. 3253 Vocational Rehabilitation. Funds provided for vocational rehabilitation training. 3255 National Forest Funds. Revenue received by a district from the sale of timber and forest products from a national forest within the boundaries of the county. 3260 National School Lunch Act. Funds, grants-in-aid, and other assistance for providing an adequate supply of foods and facilities for the establishment, maintenance, operation, and expansion of nonprofit school lunch programs. 3261 School Lunch Reimbursement. Federal reimbursement distributed by the state for lunches served through this program. 3262 School Breakfast Reimbursement. Federal reimbursement distributed by the state for breakfasts served through this program. 3263 After School Snack Reimbursement. Federal reimbursement distributed by the state for snacks served through this program. 3264 Child Care Food Program. Reimbursements for food served in daycare centers, including food and milk reimbursements. 3265 U.S.D.A. Donated Commodities. This account reflects the fair market value of foods donated by USDA. 29 3 Revenue Accounts 3266 Cash in Lieu of Donated Foods. Amounts received in cash through the donated food program. 3267 Summer Food Service Program. Reimbursement for feeding programs, usually conducted during the summer, that are not part of the regular school lunch reimbursement program. 3268 Nutrition Education and Training Program. Funding for training of children, teachers and school food service personnel on nutrition and health. 3269 Other Food Services. Other food service revenue not previously classified. 3270 Elementary and Secondary Education Act (ESEA), Title VI. 3280 Federal Through Local. Revenues from the federal government distributed through an intermediate agency. 3290 Other Federal Through State. Other federal funds received from the state. Accounts 3291-3293 are provided for federal funds administered through the state for programs for Cuban, Haitian, Indo-Chinese, or other refugee students. 3291 Cuban and Haitian Refugee Program. 3292 Transition Program For Refugee Children. (Deleted 2006-07) 3293 Emergency Immigrant Education Program. 0294 FEMA 3299 3300 Miscellaneous Federal Through State. Other sources of federal through state revenues not previously classified. . (Account Number Correction) Revenue from State Sources. 3310 Florida Education Finance Program (FEFP). Revenue received for current operations under this program. 3315 Workforce Development. Amounts received from state funded program for adult education. 3316 Workforce Development Capitalization Incentive Grant. Grant funds provided by the state to defray costs associated with the start up or expansion of workforce development programs. 3317 Workforce Education Performance Incentives. To account for workforce education performance incentives identified in the General Appropriations Act. (Added 2007-08) 3318 Adults With Disabilities. Amounts received from the state to fund programs for adults with disabilities. 30 3 Revenue Accounts 3320 3330 State Auto License, CO&DS. Since January 1, 1953, all state appropriations for Capital Outlay and Debt Service have been secured through the first receipts from the sale of state automobile license tags. The amount is computed pursuant to Section 236.602, F.S. These funds are earmarked for approved capital outlay and debt service by the Constitution and State Board of Education rules. Separate depository accounts are required for these funds. 3321 CO&DS Distributed. Funds remitted by the state to the district that are available for approved projects. 3322 CO&DS Withheld for SBE/COBI Bonds. Section 18, Article XII of the Constitution, authorizes the State Board of Education to sell bonds and revenue certificates for and on behalf of district school boards. These bonds, when issued, must be retired from a portion of the Capital Outlay and Debt Service funds available to participating districts. The state acts as fiscal and paying agent for the districts and computes the annual requirement for reserves, principal, interest, and other debt service items. The debt service requirement is deducted from the district's CO&DS funding and the amounts needed for reporting these items are provided by the Department of Education. 3323 CO&DS Withheld for Administrative Expense. The state acts as paying agent for SBE bonds and plan review. The Constitution, implemented by State Board rules, authorizes a minor charge for these services. This is a book entry provided by the state. 3324 Cost of Issuing SBE/COBI Bonds. An additional charge made of districts participating in the SBE bond sale during the current fiscal year. This is a book entry provided by the state. 3325 Interest on Undistributed CO&DS. Interest earnings on CO&DS funds held in trust for distribution to districts in the subsequent fiscal year. 3326 SBE/COBI Bond Interest. Interest earnings from required reserve maintained during the first three years of each SBE bond issue as provided by the resolution authorizing sale of SBE bonds. The reserve is invested by the state and each district is credited with the pro rata share of interest earnings. The amount of the revenue will be provided by the Department of Education. Categorical State Sources. 3334 Florida Teacher’s Lead Program. Funds received for disbursement in the form of stipends to classroom teachers for materials and supplies to be used by students assigned to the teachers. 3335 Diagnostic and Learning Resources Centers. Funds for use in promotion of an exceptional child program usually restricted by an approved plan or budget. 31 3 Revenue Accounts 3340 3336 Instructional Materials. Funding allocation for instructional materials. Does not include receipts from collections for lost or damaged textbooks or sale of textbooks. 3337 School Breakfast Supplement. Revenue received for the elementary student breakfast supplement pursuant to Section 228.195, F.S. 3338 School Lunch Supplement. State reimbursement to the districts for required matching of Federal funds. Other State Revenue. 3341 Racing Commission Funds. Revenue provided to districts pursuant to law from racetrack receipts. Funds may be restricted by terms of this act. (Racetrack funds provided by the Board of County Commissioners as a grant, rather than from a legal requirement, should be recorded in account 3440, Gifts, Grants, and Bequests.) 3342 State Forest Funds. Amounts received by those districts in which a state forest is located. 3343 State License Tax. Receipts provided from mobile home licenses in accordance with Section 320.081, F.S. 3344 District Discretionary Lottery Funds. Funding allocated from the Educational Enhancement Trust Fund pursuant to appropriation by the Legislature. 3350- Other Categorical Sources. 3370 3354 Transportation. Funding provided by the state for student transportation per Section 236.083, F. S. 3355 Class Size Reduction Operating Funds. Revenue received in accordance with Section 1011.685, F.S., to be used to reduce class size in any lawful manner if the district has not met the constitutional maximums or the reduction of two students per year. To be used for any lawful operating expenditure, if the district has met the constitutional maximums or the reduction of two students per year, with priority given to increasing salaries of classroom teachers and implementing the salary career ladder. 3361 School Recognition Funds. Funding for the School Recognition Program awarded to schools that sustain high performance or demonstrate substantial improvement in student performance. 3362 Teacher Recruitment and Retention. Revenue received for the recruitment and retention of full-time instructional personnel. (Deleted 2006-07) 3363 Excellent Teaching Program. Revenue received in the amount of the employer’s share of Social Security and Medicare taxes for those teachers who qualify for 32 3 Revenue Accounts national board certification and receive bonuses in accordance with Section 236.08106, F.S. 0370 Other Categorical Sources 3371 Voluntary Prekindergarten Program. Revenue received for Voluntary Prekindergarten Program as provided in Chapter 2004-484, Laws of Florida. 3372 Preschool Projects. Programs and initiatives designed to provide funding and services in local communities to children, birth to five years of age, and their families. Includes Prekindergarten Early Intervention, Florida First Start, Collaborative Partnership Incentives, Migrant Pre-School, and Regional Assistance. 3373 Reading Programs. Revenue received for intensive reading programs targeted at improving the reading proficiency of students. 0374 Supplemental Academic Instruction 3390 3375 Public School Technology. Revenue received to enhance the use of technology in the instruction of students. (Deleted 2006-07) 3376 Teacher Training. Revenue received for teacher training including the funds required for inservice personnel training as prescribed in Section 236.081(3), F.S. (Deleted 2006-07) 3378 Full Service Schools. Funding received for the continuation and expansion of the Full Service Schools project. Miscellaneous State Revenue. Other amounts received from the state. 3391 Public Education Capital Outlay (PECO). Capital outlay funds derived from the Gross Receipts Tax and distributed pursuant to Section 235.435, F.S. Funds are distributed based upon cash flow needs for projects rather than in a lump sum or annual disbursement. Allocations are initially recorded as deferred revenue with revenue recognition on issuance of an encumbrance authorization. 3392 Classrooms First Program. Funding provided for the Classrooms First Program pursuant to Section 235.187, F.S., for the construction, renovation, remodeling, repair, or maintenance of education facilities; or debt service on Classrooms First bonds. Allocations are initially recorded as deferred revenue with revenue recognized on issuance of an encumbrance authorization. 3393 School Infrastructure Thrift (SIT) Program. Revenue awarded through the SIT program pursuant to Section 235.2155, F. S. 3394 Effort Index Grants. Revenues received through Effort Index Grants for educational facilities construction projects pursuant to Section 235.186, F. S. . 33 3 Revenue Accounts 3395 Smart Schools Small County Assistance Program. Funding provided to small counties for the construction, expansion, repair, and renovation of school facilities. The program is a supplement to the Special Facilities Construction Account. 3396 Class Size Reduction/Capital Outlay. Capital outlay funds received for the construction of classroom facilities to serve public school students in kindergarten through grade 3. 3397 Charter School Capital Outlay Funding. Capital outlay funds provided to charter schools pursuant to Section 228.0561, F.S. (Deleted 2007-08) 3399 Other Miscellaneous State Revenue. Other sources of state funding not previously classified. 3400 Revenue From Local Sources. 3410 Taxes. Taxes levied by a school system on the assessed valuation of real and personal property located within the district. The budgeted tax revenues must represent at least 95 percent of the yield from the proposed millage (millage x assessed valuation x 95%). 3411 District School Taxes. Tax revenues generated from the operating tax millage. 3412 District I. & S. Debt Services Taxes. Amounts from special tax millages levied for the purpose of retiring indebtedness pursuant to SBE Rule 6A-1.037 and authorizing statutes. 3413 District Local Capital Improvement Tax. Revenues generated from a tax levy authorized by Section 236.25(2), F.S. for the District Capital Improvement Fund. With school board approval, up to two mills may be levied without voter approval, however, district school boards may include a special tax levy on the ballot submitted to the electorate at the district biennial election. 3418 Local Sales Tax. Funds received from a capital outlay sales surtax levied under the authority of a school district or through an interlocal agreement in which the surtax was levied under the county’s authority as provided by Section 212.055, F.S. 3421 Tax Redemptions. Revenue received during the fiscal year from the clerk of the circuit court for tax redemptions and from the sale of lands acquired for delinquent taxes. 3422 Payment in Lieu of Taxes. Amounts received from a local housing authority or similar agency in lieu of the payment of taxes. 3423 Excess Fees. All excess fees received from the tax collector. 3424 Tuition. Amounts received for the education of nonresidents as prescribed by Section 228.121, F.S. 34 3 Revenue Accounts 3425 3430 Rent. Amounts received from the rental of property owned by the district and currently used for school purposes or rent from property other than school facilities. Interest, Including Profit on Investment. Interest earnings from amounts held in daily balances, savings accounts, time deposits, or investments. Also, profit on the sale of investments. (Interest or profit should be recorded in the fund that produced the earnings unless specified otherwise by bond resolution or legal documents.) 3431 Interest on Investments. Interest earnings on investments in United States Treasury bills, notes, bonds, savings accounts, time certificates of deposit, mortgages, or other interest-bearing obligations. 3432 Gain on Sale of Investments. Gains realized from the sale of investments, i.e., the excess of sales proceeds over cost or other basis at the date of sale. 3433 Net Increase (Decrease) in the Fair Market Value of Investments. Account established to recognize the change in fair value of investments in accordance with Governmental Accounting Standards Board (GASB) Statement 31. 3440 Gifts, Grants, and Bequests. Amounts received from a philanthropic foundation, private individual or organization, or county commission for which no repayment or special service to contributor is expected. 3450 Food Service. Revenue received from sale of meals and other related food service activities, including receipts from other agencies or projects for meals provided under contract to various groups or agencies. The following accounts are provided to further classify the various types of receipts such as breakfast, lunch, milk, etc., as required by approved forms. 3460 3451 Student Lunches. 3452 Student Breakfasts. 3453 Adult Breakfasts/Lunches. 3454 Student and Adult a la Carte. 3455 Student Snacks. 3456 Other Food Sales. Student Fees. Student fees which are authorized by statute and established by the school board. 3461 Adult General Education Course Fees. Fees charged to adult students for enrollment in adult general education courses as authorized by Section 239.117, F.S., and annual appropriations provisions. 35 3 Revenue Accounts 3470 3480 3462 Postsecondary Vocational Course Fees. Fees charged to adult students enrolled in adult vocational courses as authorized by appropriations provison and Section 239.117, F.S. 3463 Continuing Workforce Education Course Fees. Fees charged pursuant to Section 239.117, F.S. 3464 Capital Improvement Fees. Capital improvement fees charged to students enrolled in postsecondary adult vocational or adult general courses pursuant to Section 239.117, F.S. 3465 Postsecondary Lab Fees. Lab fees charged to students enrolled in postsecondary adult vocational or adult general courses pursuant to Section 239.117, F.S. 3466 Lifelong Learning Fees. Fees for adult noncredit courses defined by Section 239.105, F.S. and charged pursuant to appropriations provision. (Account Number Correction) 3467 General Education Development (GED) Testing Fees. Testing fees charged to candidates who take the General Education Development (GED) test battery or individual exams including retesting, as authorized in Section 1004.93(4)(a), F.S., and as provided in Rule 6A-6.021, F.A.C. 3468 Financial Aid Fees. Fees charged to adult students enrolled in adult vocational and adult general education courses authorized by Section 239.117, F.S. and appropriations provision. 3469 Other Student Fees. Other student fees authorized by statute and not specified above. Other Fees. Other fees authorized by statute and established by the school board. 3471 Preschool Program Fees. Fees charged for preschool programs pursuant to Section 228.061(1), F.S. 3472 Prekindergarten Early Intervention Fees. Fees charged for prekindergarten early intervention programs pursuant to Section 228.061(2), F.S. 3473 School-Age Child Care Fees. Fees charged for school-age child care programs pursuant to Section 228.061(3), F.S. 3479 Other Schools, Courses, and Classes Fees. Other student fees authorized by 228.061(4), F.S. Operating Revenues. Proprietary fund revenues directly related to the fund's primary activities. These revenues consist primarily of user charges for goods and services. 3481 Charges for Services. Operating revenues generated by a proprietary fund from rendering services to customers. 36 3 Revenue Accounts 3482 3484 3489 3490 Charges for Sales. Operating revenues generated by a proprietary fund from the sale of goods to customers. Premium Revenue. Operating revenues generated by a proprietary fund from insurance premiums. Other Operating Revenue. Other operating revenues generated by a proprietary fund not previously classified. Miscellaneous Local Sources. Other amounts received from local sources. 3491 Bus Fees. Fees received for the use of school buses (except for school activities) including payments from other districts. 3492 Transportation Services Rendered for School Activities. Amounts received from school internal accounts in payment of transportation costs for school related activities such as football games, band, or field trips. 3493 Sale of Junk. Amounts received from the sale of items classified as junk for salvage or recycle purposes. 3494 Receipt of Federal Indirect Cost Rate. Amounts received from federal contracted programs for indirect expenses when an indirect cost rate has been approved by the Department of Education. 3495 Other Miscellaneous Local Sources. Other miscellaneous revenues not previously classified. 3496 Impact Fees. Revenue received from intergovernmental agencies derived from fees assessed for development of real property. 3497 Refunds of Prior Year's Expenditures. 3498 Collections for Lost, Damaged, and Sold Textbooks. Amounts received locally for lost and damaged textbooks and sales of textbooks. 3499 Receipts of Food Service Indirect Costs. Collections from the Food Service Fund for indirect costs. 3600- Other Financing Sources. Increases in current financial resources other than revenues. 3700 3600 Transfers. Nonreciprocal interfund activity represented by disbursement of cash or goods from one fund within the district to another fund without an equivalent return and without a requirement for repayment. 3610 Transfers from General Fund. Amounts received from the general fund with no return or requirement for repayment. 3620 Transfers from Debt Service Funds. Amounts received from debt service funds with no return or requirement for repayment. 37 3 Revenue Accounts 3700 3630 Transfers from Capital Projects Funds. Amounts received from capital projects funds with no return or requirement for repayment. 3640 Transfers from Special Revenue Funds. Amounts received from special revenue funds with no return or requirement for repayment. 3650 Interfund. Amounts received from one fund by another fund within the same fund type with no return or requirement for repayment. 3660 Transfers from Permanent Funds. Amounts received from permanent funds with no return or requirement for repayment. 3670 Transfers from Internal Service Funds. Amounts received from internal service funds with no return or requirement for repayment. 3680 Transfers from Trust Funds. Amounts received from trust funds with no return or requirement for repayment. 3690 Transfers from Enterprise Funds. Amounts received from enterprise funds with no return or requirement for repayment. Long-term Debt Proceeds and Sales of Capital Assets. Increases in current financial resources resulting from the receipt of long-term debt proceeds and sales of capital assets. 3710 Sale of Bonds. Proceeds from the sale of bonds. The par value or discounted amount realized from the sale should be credited to this account in the Capital Projects Fund. Any premium or accrued interest is used to reduce the interest payable on the issue and should be credited to Accrued Interest Payable in the debt service fund until the first interest payment date following the date of sale. 3711 SBE/COBI Bonds. Proceeds from sale of State Board of Education Bonds. Section 18, Article XII, of the State Constitution authorizes district school boards to request the State Board of Education to issue bonds for and on behalf of the local school boards. These bonds do not have to be approved in an election or referendum. The Department of Education acts as agent for the district school board in preparing the resolutions for validation proceedings, requesting bids, printing and delivering the bonds sold, computing the required reserve and the annual amount for the payment of principal, interest and bank charges. 3712 District No. 1 Bonds. Proceeds of District No. 1 bonds as authorized by Florida Statutes. This type of indebtedness is usually retired by a special tax levy on the non-exempt assessed value of the real and personal property within the district that issued the bonds. 3713 Race Track Revenue Bonds. Proceeds of bonds pursuant to special act of the Legislature pledging race track revenue accruing to the district. 3714 Motor Vehicle License Revenue Bonds. Proceeds of bonds pledging motor vehicle license revenue distributed to the districts by the state. 38 3 Revenue Accounts 3715 Proceeds of Refunding Bonds. 3716 Sales Surtax Bonds. Proceeds from bonds issued for capital facilities acquisition and construction. The debt is secured by the pledge of sales tax revenue authorized by Section 212.055, F.S. 0717 Proceeds of CL 1st Loan 3720 Loans. Proceeds of loans not repaid during the fiscal year in which obtained. 3721 Section 237.161/237.162 Loans. Proceeds of loans authorized under Section 237.161 or 237.162, F.S., which permits the school board to borrow money for specific purposes when approved, including installment purchases under Section 237.161, F.S. 3722 Bond Anticipation Loans. Proceeds of notes issued in anticipation of bond sale. These notes must be retired from the proceeds of the bond sale. 3724 Capital Lease Agreements. Source of funds for recording assets acquired under capital lease. Lease must be conditioned on the right of the board to terminate the lease at the end of each fiscal year (AGO 063-53). 0725 Proceeds of Lease Purchases 3730 3740 Sales of Capital Assets. Proceeds from sales of capital assets of a school district. 3731 Sale of Land. Proceeds from sales of real property (unimproved). 3732 Sale of Buildings. Proceeds from sales of land and buildings. 3733 Sale of Equipment. Proceeds from sales of equipment. Loss Recoveries. Amounts received from insurance or other sources as result of the loss of school district property from fire, theft or other causes. 3741 Insurance Loss Recovery. 3742 Other Loss Recovery. 3750 Proceeds of Certificates of Participation. Proceeds from the issuance of certificates of participation for the purpose of capital acquisition or construction. 3760 Proceeds of Forward Supply Contract. Amounts received at the time of bond refunding representing proceeds from a forward supply contract which provides payment to the bond issuer for future interest to be earned on sinking fund investments that are made between the date of maturity and the date of scheduled interest or principal payments. 3770 Proceeds from Special Facilities Construction Advance. Funds received from the Special Facilities Construction Account as authorized by Section 235.435(2), F.S 39 3 Revenue Accounts 3780 Gain on Disposition of Assets. The excess of the financial inflows over the carrying value of the disposed assets. 3790 Premium on Long-term Debt. The amount of premium paid in connection with the issuance of long-term debt. 3791 3792 3793 Premium on Sales of Bonds. Premium on Refunding Bonds. Premium on Certificates of Participation 40 3 Revenue Accounts Chapter Four Expenditure Accounts This chapter presents fund and expenditure account numbers and the related definitions. NOTE: Function and object code field sizes are four and three characters, respectively. The state does not currently require direct coding of the third and fourth characters of function codes or the third character of the object code, but may specify such coding in the future. FUNDS A fund is a fiscal and accounting entity with a self-balancing set of accounts recording cash and other financial resources, together with all related liabilities and residual equities or balances, and changes therein, which are segregated for the purpose of carrying on specific activities or attaining certain objectives in accordance with special regulations, restrictions, or limitations. Code 00X Description Permanent Funds. Funds established to account for resources that are legally restricted to the extent that only earnings, and not principal, may be used for purposes that support the government’s programs. B1X B3X F1X OCX OC1 OC2 OC3 OC5 OFX OF1 OF2 OF3 ORX OR1 OR2 OR3 OR5 100 Bellalago General Bellalago Capital Four Corners Bellalago EFBD Bellalago EFBD General Bellalago EFBD Debt Service Bellalago EFBD Capital Bellalago EFBD-Fixed Assets Four Corners, Inc. Four Corners Charter School Four Corners Charter School Four Corners Charter School Flora Ridge EFBD Flora Ridge EFBD Flora Ridge EFBD Flora Ridge EFBD Flora Ridge EFBD-Fixed Assets General Fund. The fund used to account for all financial resources except those required to be accounted for in another fund. 1XX 10X General Fund General 41 4 Expenditure Accounts 2XX Debt Service Funds. Funds established to account for the accumulation of resources for, and the payment of, general long-term debt principal and interest. Debt service funds are as follows: 2AX 2A1 2A3 21X Sales Tax Bonds Sales Tax Bonds 2007 COPS 2007 SBE/COBI Bonds 210 SBE/COBI Bonds. State Board of Education/Capital Outlay Bond Indebtedness (COBI) Bonds issued by the SBE on behalf of the school district under Section 18, Article XII of the State Constitution. Special Act Bonds. Bonds or revenue certificates issued by the school district pursuant to authority granted by special acts of the Legislature. 220 222 230 Section 237.161/237.162 F.S. Loans. Loans negotiated under authority of the cited statutory provisions. 232 Sec 237 Loan 1999 Celebration 240 Motor Vehicle Revenue Bonds. Bonds issued under this expired authority. 25X District Bonds 250 District Bonds. Bonds issued by the district as authorized by vote of the people of the district. 252 3XX 72 Bonds GO Bonds 2002 29A 29C 29K 29Q 29S 29X 29Y 29Z Classrooms First 2003 COPS 1999 COPS 2000 COPS 2002 Sales Tax Bonds 2001 Other Debt Service COPS 2004 COPS 2005 290 Other Debt Service 294 297 298 COPS 1994 Capital Leases Bellalago EFBD Capital Projects Funds. Funds established to account for financial resources to be used for the acquisition or construction of major capital facilities. Capital projects funds are as follows: 3AX 3A1 Sales Tax Bonds Sales Tax Bond Proceeds 42 4 Expenditure Accounts 3A2 3A3 3A4 3A5 Class Size Reduction Penalties COPS 2007 Impact Fees 2008 Impact Fees 2009 31A 31B 31C 31X COBI Bonds 2005 COBI Bonds 2006A COBI Bonds 2007 COBI Bonds 310 COBI Bonds. Capital projects financed by COBI bond issues. 311 COBI Bonds 33X SEC 1011.14/1011.15 FS Loans 320 330 Special Act Bonds. Capital projects financed by Special Act bonds. Section 237.161/237.162 Loans. Capital projects financed by the cited statutory provisions for loans. 34D 34E 34F 34G 34X PECO 2006 PECO 2007 PECO 2008 PECO 2009 PECO 340 PECO. Capital projects financed through the Public Education Capital Outlay program. 342 343 PECO 2002 PECO 93 350 District Bonds. Capital projects financed through district bonds. 36X CO & DS 360 CO & DS. Capital projects financed through the district's allocation of the state Capital Outlay and Debt Service program. 37A 37B 37C 37D 37E 37F 37G CO Tax 2003 CO Tax 2004 CO Tax 2005 CO Tax 2006 CO Tax 2007 CO Tax 2008 CO Tax 2009 37X Capital Improvement 370 Capital Improvement - Section 236.25(2). Capital projects financed through tax levied pursuant to the cited statutes. 43 4 Expenditure Accounts 372 373 380 Voted Capital Improvement Fund. Capital projects financed by millage levied pursuant to vote of the people of the district. 39A 39B 39I 39J 39L 39M 39Q 39R 39S 39T 39U 39V 39W 30X 39Y 39Z Classrooms First Impact Fees 99 Effort Index Grant Sales Tax Flow Through Impact Fees 2001 Class Size Reduction COPS 2002 High Growth Grant Sales Tax Bond Proceeds Impact Fees 2003 Impact Fees 2004 Escrowed Impact Fees Impact Fees 2005 Other Capital Projects COPS 2004 Impact Fees 2006 390 Other Capital Projects. 391 398 399 4XX CO Tax 2002 CO Tax 2003 Impact Fees 2007 Disney/Celebration Amercian Recovery and Reinvestment Act (ARRA) Economic Stimulus Capital Projects. Capital projects funded by ARRA related to construction, renovation, and remodeling. (Added 2008-09) Special Revenue Funds. Funds used to account for the proceeds of specific revenue sources (other than trusts for individuals, private organizations, or other governments or for major capital projects) that are legally restricted to expenditure for specified purposes. Use of Special Revenue Funds is required only when legally mandated. In Florida school districts, Special Revenue Funds should include federal categorical aid and a Food Services Fund. 41X Food Service 410 Food Services. 42X Other Federal 420 Other Special Revenue. 421 Pell Grants 422 Other-Not Cash Advance 44 4 Expenditure Accounts 430 American Recovery & Reinvestment Act (ARRA) Economic Stimulus Funds. Federal funds to be disbursed through the state over a two year period for the stabilization of local school district funding. (Added 2008-09) 431 State Fiscal Stabilization Funds 432 Targeted ARRA Stimulus Funds 433 Other ARRA Stimulus Grants 49X Other Special Revenue 490-499 Miscellaneous Special Revenue. 491 Extended Day 492 Pre-K Extended Day 493 East Coast Tech Assist Center 5XX 500 GASB 34 7XX 700 Internal Service Funds. Funds established to account for any activity that provides goods or services to other funds, departments, or agencies of the primary government and its component units, or to other governments, on a cost-reimbursement basis, when the reporting government is the predominant participant in the activity. 71X Internal Service 711-715 Self Insurance. 711 Health & Life Int Serv Fund 712 Auto Liab/Gen Liab Int Serv 713 Flexible Savings Account 731 791 8XX Consortium Programs (except self insurance). Other Internal Service. Fiduciary Funds. Funds used to report resources held by a governmental unit in a trustee or agency capacity for others and therefore, cannot be used to support the government’s own programs. 8BX 8B1 8B3 8B5 8CX 8C3 8RX 8R3 Bellalago Charter Academy Bellalago Charter Academy Gen Bellalago Charter Academy Cap Bellalago Chtr Acdmy-Fixed Assets Bellalago EFBD Capital-Agency Bellalago EFBD Capital-Agency Flora Ridge EFBD Capital Flora Ridge EFBD Capital 840-849 Investment Trust Funds. 45 4 Expenditure Accounts 850-859 870-879 890-899 891 9XX Private-purpose Trust Funds. Pension Trust Funds. Agency Funds. School Internal Funds. Enterprise Funds. Funds established to account for any activity for which a fee is charged to external users for goods and services. The use of an enterprise fund is required if (1) the activity is financed with debt that is secured solely by a pledge of the net revenues from fees and charges of the activity, (2) laws or regulations require that the activity’s costs of providing services, including capital costs, be recovered with fees and charges, rather than with taxes or similar revenues, and (3) the pricing policies of the activity establish fees and charges designed to recover its costs, including capital costs. All public entity risk pools (Self Insurance Consortiums) are required to be accounted for as enterprise funds. 911-915 Self Insurance Consortium. 921-922 Other Enterprise Programs. OBJECT CODES The object classification indicates the type of goods or services obtained as a result of a specific expenditure. Seven major object categories are identified and described in this handbook: (1) Salaries, (2) Employee Benefits, (3) Purchased Services, (4) Energy Services, (5) Materials and Supplies, (6) Capital Outlay, (7) Other Expenses, and (8) Transfers. These broad categories are further subdivided to capture more detailed expenditure information. These sub-object codes use two of the three characters in the three character field; the third character is reserved for future state specification. Although specified herein, the second character in the salaries object codes is not required, but is available for district consideration. The optional third characters of the 100, 200 and 600 object codes are provided in Appendix B. Code Description 100 Salaries. 1000 Amounts paid to employees of the school system who are considered to be in positions of a permanent nature, including personnel under written contract substituting for those in permanent positions. See account 750, Other Personal Services, for temporary services. This includes gross salary for personal services rendered while on the payroll of the district school board. Salaries shall be classified as follows: 1010 1020 1030 1040 1050 1060 Additional Time Extra Pay Field Trip Terminal Annual Leave Sick Leave Buy Back 1H Overtime 110 Administrator. Persons with administrative duties who have authority for management policies in district and/or school operations. Included here are the superintendent; deputy, associate, assistant and area superintendents; executive and general directors; assistant directors; supervisors; coordinators; administrators on special assignment; 46 4 Expenditure Accounts principals; assistant principals; curriculum coordinators, deans and persons who carry out the job responsibilities indicated above with an alternate job title. 120 Classroom Teacher. Staff members assigned the professional activity of instructing students in courses. 130 Other Certified. Included here are all other members of the instructional staff (teachers) as defined in Section 228.041 except classroom teachers and their substitutes. Examples include primary specialists, guidance counselors, psychologists, occupational/placement specialists, and media specialists. Salaries of personnel serving in positions which are part-time classroom teaching and part-time primary specialist (or other role) shall be apportioned to the two objects. 140 Substitute Teacher. Persons who substitute for classroom teachers either on a full-time or part-time basis. 150 Aide. Persons who are aides under the supervision of a classroom teacher, library aides, and other school-level aides and paraprofessionals. 160 Other Support Personnel. Included here are all school board employees not listed in another category. Examples include clerical/secretarial staff, technicians, transportation workers, custodians, cafeteria workers, accountants, architects, computer programmers, nurses, skilled craftsmen, engineers, mechanics, and unskilled laborers. 170 Board Members and Attorneys. Persons who serve as school board members and those who are attorneys for the school board. 1990 Salaries Reimbursed 1991 Labor Reimburse Warranty 200 Employee Benefits. 2000 Amounts paid by the school system on behalf of employees. These amounts are not included in gross salary. Such payments are fringe benefits and, while not paid directly to employees, are part of the cost of employing staff. Benefits are to be identified with the function in which the salaries were recorded. In the special case of Worker's Compensation a functional proration based on an approximate premium cost is required. 210 Retirement. 2100 A plan whereby a fund of money, built up through contributions from participants and the employer, is used to make regular payments to those who retire from service in the school system by reason of age, disability or length of service. 2190 Retirement Reimbursed 220 Social Security. 2200 Contributions of the employer's share of social security for district personnel. 2290 Social Security Reimburse 230 Group Insurance. 47 4 Expenditure Accounts 2300 Expenditures to provide group insurance coverage for school personnel, such as life, health, and accident. 240 Worker's Compensation. 2400 Expenditures to provide workers compensation coverage. 250 Unemployment Compensation. 2500 Expenditures for the district's share of unemployment compensation claims arising from former employees. If claims of any year are material, the cost should be distributed to functions on the basis of salaries paid in the current year. If the claims are immaterial, the costs may be charged to Function 7100. 290 Other Employee Benefits. 2900 Expenditures for various non-salary benefits for employees not provided in any other account classification. 2990 Benefits Reimbursed 300 Purchased Services. 3000 Amounts paid for personal services rendered by personnel who are not on the payroll of the district school board, and other services which the Board may purchase. While a product may or may not result from the transaction, the primary reason for the purchase is the service provided. 310 Professional and Technical Services. 3100 Services which by their nature can be performed only by persons with specialized skills and knowledge which are acquired through intensive academic preparation. Included are the services of architects, engineers, auditors, dentists, medical doctors, lawyers, consultants, accountants, etc. 3101 3105 3106 3107 Legal Fees Finger Printing Drug Testing Physicals 311 Subawards Under Subagreements – First $25,000. 3110 For subagreements reported under Professional and Technical Services, record the first $25,000 of each subaward. 312 Subawards Under Subagreements – In Excess of $25,000. 3120 For subagreements reported under Professional and Technical Services, record all subawards in excess of $25,000, regardless of the period covered by the grant or subcontract. 320 Insurance and Bond Premiums. 3200 Expenditures for all types of insurance coverage (other than group insurance (230)) such as property, liability, fidelity, and bond premiums. 3201 Insurance and Bond Prem-FD 712 330 Travel. 48 4 Expenditure Accounts 3300 Costs for transportation, meals, hotel, registration fees, and other expenses associated with traveling on business for the district school board. Payments for per diem in lieu of reimbursement for subsistence (room and board) also are charged here. 3300 3301 3302 3310 3311 3312 3320 3330 3331 3332 3340 3341 3342 3350 3360 3380 3390 In County Out of District Out of State Administrator in County Administrator/Out of County Administrator/Out of State Taxable Meals Board Dev in County Board Dev Out of County Board Dev Out of State Superintendent Dev in County Superintendent Dev Out of County Superintendent Dev Out of State Transportation Grants Non-Employee Field Trips – FL HS AC Field Trips - Instruction 350 Repairs and Maintenance. 3500 Expenditures for repairs and maintenance services not provided directly by district personnel. This includes contracts and agreements covering the upkeep of grounds, buildings and equipment. Costs for new construction, renovations and remodeling are capital expenditures and therefore are not included. NOTE: Equipment repair services which are direct costs of specific programs within the FEFP shall be charged to the function of Instruction. Equipment repair services rendered for the functions of Transportation and Food Services are to be charged to those functions. Routine maintenance of audio visual equipment should be charged to function 6200. All other equipment repairs may be charged to 8100. 360 Rentals. 3600 Expenditures for leasing or renting land, buildings, films, and equipment for both temporary and long-range use of the district school board. Include fees charged for annual maintenance of software and broadcast rights fees. Payments on capital leases are not recorded in this account, but are recorded to recognize principal and interest components of each payment. 3610 Rental Reimbursement 370 Communications. 3700 Expenditures to provide telephone service, telegraph service, and postage for the district school system. Telephone service should be charged to function 7900. Other communication costs should be identified with the appropriate function. 3710 Postage 49 4 Expenditure Accounts 380 Public Utility Services Other than Energy Services. 3800 Expenditures for services usually provided by public utilities except energy services (see Object 400). Examples include water, sewage, and garbage collection. 3810 Garbage & Trash/Other 3850 Water and Sewer 3851 Storm Water Utility Fee 390 Other Purchased Services. 3900 Expenditures for all other purchased services not included above such as printing, binding, reproduction, pest control, and other nonprofessional purchased services. 391 Subawards Under Subagreements – First $25,000. 3910 For subagreements reported under Other Purchased Services, record the first $25,000 of each subaward. 392 Subawards Under Subagreements – In Excess of $25,000. 3920 For subagreements reported under Other Purchased Services, record all subawards in excess of $25,000, regardless of the period covered by the grant or subcontract. 400 Energy Services. 4000 Expenditures for the various types of energy used by the district are to be classified as follows: 410 Natural Gas 4100 420 Bottled Gas 4200 430 Electricity 4300 440 Heating Oil 4400 450 Gasoline 4500 4590 Gasoline Reimbursed 460 Diesel Fuel 4600 4690 Diesel Fuel Reimbursed 490 Other Energy Services 4900 4990 Energy Services Reimbursement 50 4 Expenditure Accounts 500 Materials and Supplies. Amounts paid for items of an expendable nature that are consumed, worn out, or deteriorated in use, or items that lose their identity through fabrication or incorporation into different or more complex units or substances. 510 Supplies. 5100 Expenditures for consumable supplies for the operation of a school system, including freight and cartage. Examples include expenditures for instructional, custodial, maintenance supplies, etc. 5110 Supplies 520 Textbooks. 5200 State Adopt. Expenditures for textbooks furnished free by districts, including freight. This category also includes the costs of workbooks, textbook binding or repair, and text related materials. 5250 Local Funds 5290 State Flexibility 530 Periodicals. 5300 Expenditures for periodicals and newspapers ordered for the media center (function 6200). Periodicals for other functions should be charged to supplies (510). A periodical is any publication appearing at regular intervals of less than a year and continuing for an indefinite period. 540 Oil and Grease. 5400 Expenditures for oil and grease for all types of motor vehicles. 5490 Oil & Grease Reimbursed 550 Repair Parts. 5500 Expenditures for repair parts, antifreeze, and supplies used in district-owned vehicles, pupil transportation or otherwise, with the exception of gas, oil, grease, gear lubricants, tires, and tubes. 560 Tires and Tubes. 5600 Expenditures for tires and tube replacement, including recapping. If done in a districtoperated garage, labor costs would be recorded under salaries. 570 Food. 5700 Expenditures for food purchased for use in the food service program. Food or food products used in instructional programs should be charged to materials and supplies, object code 510. 580 Commodities. Market value of USDA donated commodities. 5800 USDA Donated Food 590 Other Materials and Supplies. 5900 Expenditures for all other supplies and materials not included above. 51 4 Expenditure Accounts 5910 5930 5950 5970 5980 5990 Gifts & Awards Budget Reserves Maintenance Allocation Warranty Reimbursement Field Trip Reimbursement Supplies Reimbursed 600 Capital Outlay. 6000 Expenditures for the acquisition of fixed assets or additions of fixed assets. These are expenditures for land or existing buildings, improvements of grounds, construction of buildings, additions to buildings, remodeling of buildings, initial equipment, and additional equipment. 610 Library Books. 6100 Expenditures for regular or incidental purchases of school library books available for general use by students, including any reference books, even though such reference books may be used solely in the classroom. Also recorded here are costs of freight for school library books. 620 Audio-Visual Materials (Non-Consumable). 6200 Expenditures for non-consumable materials such as film, filmstrips, recordings, exhibits, charts, maps and globes, regardless of cost, are charged to this account. 621 Capitalized AV Materials 6210 622 Noncapitalized AV Materials. 6220 6230 St Inst Materials-A/V No P/R 6240 St Inst Materials Flex-A/V No P/R 630 Buildings and Fixed Equipment. 6300 All expenditures to acquire existing buildings or to construct new buildings and additions. Construction costs of buildings and additions consist of all expenditures for general construction, advertisements for contracts; payments on contracts for construction; installation of plumbing, heating, lighting, ventilating and electrical systems; built-in lockers; elevators, architectural and engineering services; travel expenses incurred in connection with construction; paint and other interior and exterior decorating; and any other costs connected with planning and construction of buildings or additions to buildings. 6310 6311 6312 6320 6350 6360 6370 6380 6390 Construction Contractor Direct Purchase Labor Architect/Engineer Services Inspection Services Surveys & Tests Other Buildings Costs Contingencies 52 4 Expenditure Accounts 640 Furniture, Fixtures and Equipment. 6400 Expenditures for initial or additional items of equipment such as furniture, furnishings, machinery, and portable bleachers that are not integral parts of the building or building service systems. 641 642 643 644 Capitalized Furniture, Fixtures and Equipment. Noncapitalized Furniture, Fixtures and Equipment. Capitalized Computer Hardware. A computer is a digital, electronic device capable of reading, processing and executing software designed for administrative and instructional uses. The term computer includes not only the main processing unit, but also expansion cards, upgrade devices and peripherals, such as: operating system software (ROM based), installable memory, processor upgrades, video boards, sound cards, network connectivity boards or cards, other expansion and upgrade devices, monitors, printers, scanners, internal and external hard disk drives, floppy disk drives, CD-ROM drives, plotters, modems, computer projection devices, adaptive hardware and other peripherals that attach to the main unit. Noncapitalized Computer Hardware. 6470 Equipment Reimburse 6490 Set-up Labor Costs 650 Motor Vehicles. Expenditures for all types of motor vehicles. Buses are motor vehicles regularly used for the transportation of pupils of the public schools to and from school or to and from school activities, excepting motor vehicles of the type commonly called pleasure cars and carrying eight pupils or less. 651 6510 652 6520 Buses Buses – Prop Record Other Motor Vehicles Motor Vehicle Other Than Buses 660 Land. 6600 Expenditures for the purchase of any land by the school district. 670 Improvements Other Than Buildings. 6700 Construction costs of permanent improvements and additions, other than buildings and additions, consisting of all expenditures for general construction, advertisements for contracts, payments, or construction. Examples of such improvements are fill dirt, sod, shrubs, fences, retaining walls, sidewalks, sewage treatment systems, original or expanded paving projects, the initial purchase of fixed playground apparatus, flagpoles, gateways, underground storage tanks, etc., which are not parts of building service systems, and similar improvements. If the improvements are purchased or constructed, this account contains the purchase or contract price and related costs. If improvements are obtained by gifts, it records the fair market value at time of acquisition. Include under this classification permanent bleachers requiring footings or foundations, natatoriums and swimming pools, and the necessary filtering and plumbing equipment. 671 Capitalized Improvements Other Than Buildings. 53 4 Expenditure Accounts 6710 Fixed assets recorded in Capital Asset Account Number 1320 (Improvements Other Than Buildings). Examples include sidewalks, parking lots, driveways, retaining walls, sewage treatment plants, fences, underground storage tanks, and fixed playground equipment. 6712 Direct Purchase 672 Noncapitalized Improvements Other Than Buildings. Fixed assets recorded in Capital Asset Account Number 1315 (Land Improvements – Nondepreciable). Examples include excavation, fill, grading, utility installation, and landscaping demolition. 680 Remodeling and Renovations. 6800 Expenditures for major permanent structural alterations and the initial installation of heating and ventilating systems, electrical systems, plumbing systems, fire protection systems, and other service systems in existing buildings are renovations which should be capitalized. Installation of replacement systems should be capitalized and the replaced systems removed from the accounting records. Remodeling projects should be capitalized. Remodeling or improvement of buildings usually takes place within the existing floor area, while a building addition extends the floor area. See Section 235.011(16) and (17), F.S. Repairs to buildings and service systems are classified as maintenance of plant. 6801 Renovations/Direct Purchase 6802 Direct Purchase 681 Capitalized Remodeling and Renovations. 6810 Fixed assets recorded in Capital Asset Account Number 1330 (Buildings and Fixed Equipment). Examples include permanent structures, relocatables, modular/fixed furniture, sprinkler systems, electrical systems, water systems, heating/cooling/air circulation, and roofing. 6811 Remodeling Capitalized 6812 Direct Purchase Capitalized 682 Noncapitalized Remodeling and Renovations. Remodeling and renovation purchases that will not be capitalized. 690 Computer Software. 6900 The set of programs and associated documentation used to control the operation of a computer. The two primary types of software are (1) systems software which include operating systems, programming languages, and utility programs; and (2) application programs that are designed to perform tasks such as data base management, spreadsheet functions, instruction, and word processing. Generally, when software is acquired with computer hardware for a single purchase price and the relative value of the software is material to the total cost, it is necessary to allocate the acquisition cost to both the software and hardware in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles for lump-sum or basket purchases. However, systems software acquired in conjunction with computer hardware may be recorded as part of the equipment purchase (no allocation of cost to the software) when the software will not be removed, transferred, or 54 4 Expenditure Accounts in any way separated from the original hardware. In the event that software which was originally recorded as equipment is subsequently removed, transferred, or detached from the original hardware, it would be necessary to retroactively allocate a portion of the original cost, if material, to the software for proper recording of the removal or transfer. 691 Capitalized Software 6910 6913 Capitalized Software Flex P/R 692 Noncapitalized Software 6920 6923 Noncapitalized Software – Flex 700 Other Expenses. 7000 Amounts paid for goods and services not otherwise classified above. This includes expenditures for the retirement of debt, the payment of interest on debt, judgments against the school system, and the payment of dues and fees. 710 Redemption of Principal. 7100 Expenditures from current funds to retire serial bonds or Section 237.161 loans. 7101 Pmt to Rfdg Bond Escrow Agent 720 Interest. 7200 Expenditures from current funds for interest on serial bonds, Section 237.161 or Section 237.151 loans. 7201 Prompt Payment Act Interest 7202 Other Interest Penalties 730 Dues and Fees. 7300 Expenditures for dues and fees include dues in professional organizations as determined by school board policy and procedures. Also included are tuition fees for employee training activities when paid separately from travel. Fees paid relative to the issuance or service of debt and commissions for collection of taxes are also recorded here. 7301 Costs of Issuance 740 Judgments/Settlement of Litigation Against School System. 7400 Expenditures from current funds for all judgments (except as indicated) against the school system that are not covered by insurance. Judgments against the school system resulting from failure to pay bills or debt service are recorded under the appropriate expenditure accounts as though the bills or debt service had been paid when due. Also record settlements of litigation in this account. 750 Other Personal Services. 7500 Compensation paid to persons (including substitute teachers not under written contract) on temporary appointment. See temporary position definition in rules of the Division of Retirement. These services may be in lieu of those rendered by an absent regular employee or for the creation of temporary additional capacity as authorized by the board. 55 4 Expenditure Accounts The annual budget should anticipate the payment of such compensation prior to payment of same. Payments made from these funds are not subject to retirement deductions; however, Federal income tax is to be withheld in accordance with the withholding tables. Other personal services may be budgeted in any area of responsibility. 7510 7530 7580 7590 Salary Replacement Other Pers Serv –Field Trip Other Pers Serv Coach Supply Other Pers Serv Reimburse 760 Payments to Refunded Bond Escrow Agent. 7600 Payments escrowed pursuant to refunding contract. 770 Claims Expense. 7700 Expenditures by Internal Service Fund to settle claims of participating funds or agencies. 780 Depreciation Expense. 7800 The portion of the cost of a fixed asset which is charged to expense during a particular period. See Balance Sheet accounts 1339, 1349, and 1359. 790 Miscellaneous Expense. 7900 Expenditures for other expenses which cannot be assigned to one of the above categories are to be charged to this account. Included here is the expenditure for Federal Indirect Cost and for Food Service Indirect Cost. 810 Loss on Disposition of Assets. The excess of the carrying value of the disposed assets over the financial inflows generated from the disposition. 890 Discount on Long-term Debt. The amount of discount required in connection with the issuance of long-term debt. 891 Discount on Sale of Bonds. 8910 892 Discount on Refunding Bonds. 893 Discount on Certificates of Participation. 900 Transfers. 9000 Nonreciprocal interfund activity represented by disbursement of cash or goods from one fund within the district to another fund without an equivalent return and without a requirement for repayment. 910 Transfers to the General Fund. 9100 Amounts disbursed to the general fund with no return or requirement for repayment. 920 Transfers to Debt Service Funds. 9200 Amounts disbursed to debt service funds with no return or requirement for repayment. 930 Transfers to Capital Projects Funds. 56 4 Expenditure Accounts 9300 Amounts disbursed to capital projects funds with no return or requirement for repayment. 940 Transfers to Special Revenue Funds. 9400 Amounts disbursed to special revenue funds with no return or requirement for repayment. 950 Interfund Transfers. 9500 Amounts disbursed to a fund within the same fund type with no return or requirement for repayment. 960 Transfers to Permanent Funds. Amounts disbursed to permanent funds with no return or requirement for repayment. 970 Transfers to Internal Service Funds. 9700 Amounts disbursed to internal service funds with no return or requirement for repayment. 980 Transfers to Trust Funds. Amounts disbursed to trust funds with no return or requirement for repayment. 9890 Transfers from Internal Funds 990 Transfers to Enterprise Funds. Amounts disbursed to enterprise funds with no return or requirement for repayment. FUNCTION Function classifications indicate the overall purpose or objective of an expenditure. Functions are grouprelated activities aimed at accomplishing a major service or regulatory responsibility. The activities of a local school system are classified into five broad areas: Instruction, Instructional Support, General Support, Community Services, and Non-program Charges (Debt Service and Transfers). The four character field required for function codes does not currently specify the third and fourth characters. The subfunctions presently identified for 6100 and 7700 are recommended but not required. The following expenditures should be classified by function as indicated below: Employee Benefits Function Employee Health, Life and Accident Identify or allocate to employee function on basis that reflects cost incidence. Identify or allocate to employee function on basis that reflects cost incidence. Identify or allocate to employee function (see p. 4-4) on basis that reflects cost incidence. Identify or allocate to employee function (see p. 4-4) on basis that reflects cost incidence. If immaterial, may be charged to Function 7100. Cafeteria Benefits Workers Compensation Unemployment Compensation Insurance 57 4 Expenditure Accounts Property Boiler Casualty (General Liability & Automobile) Casualty-Pupil Transportation Fidelity Bonds Code 5000 6000 Function 7900 Function 7900 Function 7900 Function 7800 Function 7100 Description Instruction. Instruction includes the activities dealing directly with the teaching of pupils, or the interaction between teacher and pupils. Teaching may be provided for pupils in a school classroom, in another location such as in a home or hospital, and other learning situations such as those involving co-curricular activities. It may also be provided through some other approved medium such as television, radio, telephone, and correspondence. Included here are the activities of aides or assistants of any type which assist in the instructional process. Pupil transportation costs are not to be charged to Instruction. 5100 Basic (FEFP K-12). The Basic Program is that part of the school board's Full-Time Equivalent (FTE) eligible instructional program which is not identified as Special Programs for Exceptional Students, Vocational-Technical or Adult General Education. Programs for Students at Risk are included in the function. 5200 Exceptional. Programs for exceptional student education are determined by law. Criteria for each program is specified by State Board of Education Rule. 5300 Vocational-Technical. Vocational-Technical programs are established by law with program criteria established through State Board of Education Rule. All vocational courses are categorized into programs established by the Legislature. 5400 Adult General. All Adult General course offerings which are funded under Work force Development. 5500 Prekindergarten. Prekindergarten program expenditures, including voluntary prekindergarten. Childcare programs, if fee supported, should be coded to function 9100. Project or cost center accounting may be needed for such programs in order to capture support costs. 5900 Other Instruction. Instruction not qualifying for FEFP funding; such as instruction provided in recreation and leisure courses, Lifelong Learning. (Account Number Change) Instructional Support Services. Provides administrative, technical (such as guidance and health), and logistical support to facilitate and enhance instruction. Instructional Support Services exist as adjuncts for the fulfillment of the behavioral objectives of the instruction functions, rather 58 4 Expenditure Accounts than as entities within themselves. Although some supplies and operational costs are generated in instructional support, the major concern will be in the area of personnel. 6100 6200 Pupil Personnel Services. Those activities which are designed to assess and improve the well-being of pupils and to supplement the teaching process. These activities are classifiable under the following subfunctions: 6110 Attendance and Social Work. Pertains to promoting and improving school attendance of pupils. It includes early identification of patterns of nonattendance, promoting positive pupil and parent attitudes toward attendance, analysis of causes of nonattendance, and enforcement of compulsory attendance. 6120 Guidance Services. Pertains to helping pupils assess and understand their abilities, aptitudes, interests, environmental factors, and educational needs; assisting pupils in increasing their understanding of educational and career opportunities; and aiding pupils in making optimum use of educational and career opportunities through the formulation of realistic goals. It includes counseling pupils and parents, evaluating the abilities of pupils, assisting pupils in making their own educational and career plans and choices, assisting pupils in personal and social adjustments, and working with other staff members in planning and conducting guidance services. 6130 Health Services. Pertains to physical and mental health services which are not direct instruction. It includes activities involved with providing the pupil with appropriate medical, dental, psychiatric, and nurse services. 6140 Psychological Services. This area includes the professional services of a psychologist for pupil test analysis and for mental diagnosis. Pertains to supplementing the school system reservoir of information identifying the individuality of each pupil, his capacities, achievements, interests, potentialities, and needs; studying individual pupils who are experiencing acute problems of educational development in order to furnish diagnostic information; and suggesting programs concerning the psychological aspects of these problems. 6150 Parental Involvement. This function primarily relates to federal projects that require parent participation as a requirement of the grant. 6190 Other Pupil Personnel Services. Pupil personnel services not classified elsewhere in 6100 subfunctions. This would include positions such as diagnostic and child find specialists. In making the program cost report, these specialists are to be identified to appropriate FEFP programs through use of school/program tables. Instructional Media Services. Consists of those activities concerned with the use of all teaching and learning resources, including hardware and content materials. Educational Media are defined as any devices, content materials, methods, or experiences used for teaching and learning purposes. These include printed and non-printed sensory materials. Included are school media centers (school libraries) and central media center operations. Routine repair and maintenance of audio visual equipment should be coded to this function. 59 4 Expenditure Accounts 7000 6300 Instruction and Curriculum Development Services. Activities designed to aid teachers in developing the curriculum, preparing and utilizing special curriculum materials, and understanding and appreciating the various techniques which stimulate and motivate pupils. Included in this function are the following instructional support specialists: primary, technology, learning resource, and behavioral. In making the program cost report, these specialists are to be identified to appropriate FEFP programs through use of school/program tables. 6400 Instructional Staff Training Services. Activities designed to contribute to the professional or occupational growth and competence of members of the instructional staff (defined in Rule 6A-1.051, FAC) during the time of their service to the school board or school. Among these activities are workshops, demonstrations, school visits, courses for college credits, sabbatical leaves, and travel leaves. All Inservice Training costs are to be recorded in this function and Function 7730 (Non-Instructional). Substitute teachers hired to cover classes of teachers participating in training is a cost of inservice training. 6500 Instructional-Related Technology. Technology activities and services for the purpose of supporting instruction. These activities include expenditures for internal technology support as well as support provided by external vendors using operating funds. These activities include costs associated with the administration and supervision of technology personnel, systems planning and analysis, systems application development, systems operation, network support services, hardware maintenance and support services, and technology-related costs that relate to the support of instructional activities. Specifically, costs associated with the operation and support of computer learning labs, media center computer labs, instructional technology centers, instructional networks, and similar operations should be captured in this code. General Support Services. Consist of those activities concerned with establishing policy, operating schools and the school system, and providing the essential facilities and services for the staff and pupils. 7100 Board. Consists of the activities of the elected or appointed body which has been created according to state law and vested with responsibilities for educational activities in a given administrative unit. Also included here are expenses of Board Attorney and other legal services, independent auditors, internal auditors that report directly to the Board, negotiators, lobbyists, etc. 7200 General Administration (Superintendent's Office). Consists of those activities performed by the superintendent and assistant superintendents in general direction and management of all affairs of the school system. This includes all personnel and materials in the office of the superintendent. Activities of the offices of the deputy superintendent and associate or assistant superintendents should be charged here unless the activities can be placed properly into another function. When two or more functions are directed by the same individual, the services of that individual's office are charged to the office of the superintendent or prorated between the functions. 7300 School Administration (Office of the Principal). Consists of those activities concerned with directing and managing the operation of a particular school. It includes the activities performed by the principal, assistant principal, and other assistants in general 60 4 Expenditure Accounts supervision of all operations of the school, evaluations of staff members of the school, assignment of duties to staff members, supervision and maintenance of the records of the school, and coordination of school instructional activities with instructional activities of the school system. Includes clerical staff for these activities. 7400 Facilities Acquisition and Construction. Consists of those activities concerned with the acquisition of land and buildings, remodeling buildings, construction of buildings and additions, initial installation or extension of service systems and other built-in equipment, and improvements to sites. 7410 Facilities Acquisition and Construction – Current Expenditures 7420 Facilities Acquisition and Construction – Capital Outlay 7500 Fiscal Services. Consists of those activities concerned with fiscal operation of the school system. This function includes budgeting, receiving and disbursing cash, financial accounting, payroll, inventory control, and internal auditing. 7600 Food Services Function. Consists of those activities concerned with providing food to pupils and staff in a school or school system. This function includes the preparation and serving of regular and incidental meals, lunches or snacks in connection with school activities and the delivery of food. Food purchased and served outside the district's defined Food Services program are to be charged as a purchased service of the applicable function. 7700 Central Services Function. Activities, other than general administration, which support each of the other instructional and supporting services programs. These activities are defined in the following sub-functions: 7710 Planning, Research, Development, and Evaluation Services Function. Activities, on a systemwide basis, associated with conducting and managing programs of planning, research, development, and evaluation. 7720 Information Services. Activities concerned with writing, editing, and other preparation necessary to disseminate educational and administrative information to pupils, staff, managers, or to the general public through direct mailing, the various news media, or personal contact. 7730 Staff Services. Activities concerned with maintaining an efficient staff for the school district including such activities as recruiting and placement, staff transfers, health services, and staff accounting. Inservice training of noninstructional personnel is to be recorded as a cost of this function. 7740 Statistical Services. Activities concerned with manipulating, relating, and describing statistical information. 7750 Data Processing Services. Activities concerned with preparing data for storage, storing data, and retrieving data for reproduction as information for management and reporting. 61 4 Expenditure Accounts 7760 Internal Services. Activities concerned with buying, storing, and distributing supplies, furniture, and equipment; activities concerned with duplicating and printing for the school board; and mail room and courier services. 7790 Other Central Services. 7800 Pupil Transportation Services. Consists of those activities which have as their purpose the conveyance of pupils to and from school activities, either between home and school, school and school or on trips for curricular or co-curricular activities. Expenditures for the administration of pupil transportation services are recorded under these accounts, together with other pupil transportation expenses. 7900 Operation of Plant. Consists of activities concerned with keeping the physical plant open and ready for use. Major components of this function are utilities, including telephone service, custodial costs, and insurance costs associated with school buildings. Includes cleaning, disinfecting, heating, moving furniture, caring for grounds, school crossing guards, security and other such activities that are performed on a daily, weekly, monthly or seasonal basis. Operation of plant does not encompass repairs and replacements of facilities and equipment. Custodians may do "light" maintenance tasks, but should be coded to function 7900. 8100 Maintenance of Plant. Consists of activities that are concerned with keeping the grounds, buildings and equipment at an acceptable level of efficiency through repairs or preventative maintenance. NOTE: Equipment repair services which are direct costs of specific programs within the FEFP shall be charged to the function of Instruction when the amount of such services is material in relation to the cost of the programs. Equipment repair services rendered for the functions of Pupil Transportation (7800) and Food Services (7600) are to be charged to these functions. Routine maintenance of audio visual equipment is to be charged to Instructional Media Services (6200). All other equipment repairs may be charged to 8100. If the maintenance labor force is used to construct facilities, the costs should be reclassified to function 7400. 8200 Administrative Technology Services. Activities concerned with supporting the school district’s information technology systems, including supporting administrative networks, maintaining administrative information systems, and processing data for administrative and managerial purposes. These activities include expenditures for internal technology support, as well as support provided by external vendors using operating funds. These activities include costs associated with the administration and supervision of technology personnel, systems planning and analysis, systems application development, systems operations, network support services, hardware maintenance and support services, and other technology-related administrative costs. 9100 Community Services. Community Services consist of those activities that are not related to providing education for pupils in a school system. These include services provided by the school system for the community as a whole or some segment of the community, such as community recreation programs, civic activities, public libraries, programs of custody and care of children, and community welfare activities. Does not include instructional programs. Fee supported instructional programs should be coded to 5500. 62 4 Expenditure Accounts 9200 Debt Service. Payments of principal and interest for the retirement of debt. 9299 Discounts/Payments to Refund Bond Escrow Agent 9300 Other Capital Outlay (Other than Facilities Acquisition and Construction). School bus purchases, computer purchases, furniture, etc. 9700 Transfers. Nonreciprocal interfund activity represented by disbursement of cash or goods from one fund within the district to another fund without an equivalent return and without a requirement for repayment. FACILITY Florida law requires financial reporting on a school basis. By statute, a school is defined as, ". . . an organization of pupils for instructional purposes on an elementary, secondary or other public school level, approved under regulations of the State Board of Education." In many instances, "Facility" is synonymous with "school." Accounting for the financial transactions of a school district will require the identification of a number of facilities or cost centers which are not schools, however, the operating costs associated with such centers will be attributed to schools on program cost reports. The four digit numbers for schools are assigned by the Department of Education. Administrative departments are designated by the 9000 series of numbers. PROGRAM Section 237.34, Florida Statutes, requires program cost reporting. This reporting is to be accomplished as described in Chapter 5 of this manual. FISCAL YEAR Fiscal year denotes a twelve-month period of time to which the annual budget applies and at the end of which a school system determines its financial position and the results of its operations. In transmitting records to DOE, fiscal year shall be identified as illustrated here: 01 for FY 2000-2001 00 for FY 1999-2000 GRANT Grant numbers are assigned by DOE to control reporting of expenditures for state and federal grants. This is a five character reporting field. Districts may elect to crosswalk from a locally designed code structure. PROJECT/REPORTING This dimension is used to account for expenditures on specific projects funded through grants and to account for construction projects. This is a five character field. Districts may elect to crosswalk from a locally designed code structure. NOTE: The expenditure of money received and recorded under revenue account code 3344, District 63 4 Expenditure Accounts Discretionary Lottery Funds, shall be recorded and reported through Grant and Project/Reporting. Expenditures recorded must be consistent with policies and procedures established by the district to define enhancement and expenditures consistent with that definition. 64 4 Expenditure Accounts Chapter Five Program Cost Accounting and Reporting Section 237.34, Florida Statutes requires program cost accounting and reporting on a school-by-school basis. Cost reporting has two central elements: 1. 2. Identification of direct program costs and aggregation of these costs by program, and Attribution of indirect costs to programs on an appropriate basis. Program costing is not accomplished solely by the day-to-day transactions as recorded on the district's accounting records. In fact, such a transaction-based system is difficult and expensive to manage since many transactions involve more than one program and the attributed indirect costs would have to be adjusted several times during the fiscal year. Effective budgetary control, an essential component of the accounting system, becomes an increasingly complex matter under such a system. This is particularly true in Florida’s structure where statute directs that funded programs are to be costed. Beginning with the 1997-98 fiscal year, exceptional education program funding follows the student into all classes, not just special education classes. Students identified as needing English for Speakers of Other Languages (ESOL) programming are generally taught in Basic Programs funded classes (which also may have exceptional education students in membership). The financial accounting system provides the foundation for program costing. However, this system probably precludes capturing all funding and cost at the program level. At the time program costs are prepared, certain cost accounting procedures must be applied to the amounts produced by the financial accounting system. These procedures are applied on a systematic basis and are documented for audit trail purposes. The following sections detail Florida's program costing procedures. COSTS TO BE REPORTED With the exception of capital object expenditures for land, land improvements, buildings and fixed equipment and remodeling/renovations, ALL function 5000-8100 expenditures from the General Fund and Special Revenue Funds will be included in program costs (except function 5500). Two separate cost reports, by school, are to be produced; one for General Fund expenditures and one for Special Revenue Funds expenditures. Each set of school reports will be aggregated to produce a report for the General Fund and a report for the Special Revenue Funds. The aggregate reports will include the following items to reconcile to the annual financial report expenditure totals from the General and Special Revenue Funds: Recreation & Enrichment Programs Other Specified Programs Non-Program Capital Expenditures Community Services (Function 9100) Debt Service (Function 9200) Transportation and Food Services will be reported on a school-by-school basis, but will not be attributed as costs of programs. COST ELEMENTS Cost reporting elements include direct and indirect costs. Direct costs are classified into major objects. 65 5 Program Cost Accounting & Reporting Indirect costs are classified as school level or district level. State Board of Education Rule 6A-1.014 distinguishes costs as school or district level. The distinction is made on the nature of the cost, rather than the cost center to which the expenditure is charged. The major objects of direct cost are: Salaries (Object 100 as defined in the Red Book) Benefits (Object 200) Purchased Services (Object 300)/Energy Services (Object 400) Materials and Supplies (Object 500) Other Expenses (Object 700) Capital Outlay (Object 600 except Buildings and Fixed Equipment (630), Land (660), Land Improvements (670), and Remodeling/Renovation (680)) Direct costs of programs are those costs identified with the function 5000, (except function 5500) Instruction. Direct costs include the above objects under the function, Instruction. Direct salaries and benefits are the largest cost elements to be considered in program costing. In those instances in which a teacher serves more than one program, it is necessary to divide the total salary accurately between programs. The following procedure will be used: (1) The number of periods or instructional modules for each instructor will be determined. (2) The instructor's salary will be divided by the number of periods or time modules. (3) In the case of Special Programs (Exceptional, At-Risk, Vocational, or Adult) the salary for each program is the product of the number of periods in each of the designated programs and the period salary. Exceptions occur in that a vocational class may include high school and adult students. In this situation, it is necessary to consider the number of students and the relative time of instruction in each reporting category. (4) In the case of Basic Programs, it is necessary to examine the class grade level composition since the student's grade level determines FTE earnings. If there are students from two grade groups (4-8) and (9-12), it is necessary to split the period salary accordingly. An example of the procedure discussed above would be a teacher earning $21,000.00 and having the following time schedule and Basic Program pupil load: Time Module 1 2 3 4 5 6 Number of Students Assignment 8th Grade Planning XXX Vocational (6-12) XXX Vocational (6-12) XXX English 16 English 10 English 12 9th Grade XXX XXX XXX 16 20 14 In the illustration above, $4,200.00 will be assigned to each student contact period or time module ($21,000.00 x .20). Vocational (6-12) is a category in itself. Grade levels for these periods are ignored $8,400.00 will be assigned to Vocational (6-12) for this teacher. The $4,200 assigned 4th period will be prorated equally to the 4-8th grade program and the 9-12th grade program ($2,100.00 each). 66 5 Program Cost Accounting & Reporting The $4,200.00 assigned 5th period will be prorated as follows: one-third (10/30) to 4-8th grade program = $1,400.00 two-thirds (20/30) to 9-12th grade program = $2,800.00 The $4,200 assigned sixth period will be prorated as follows: 12/26 or 46% = $1,932.00 salary for the 4-8th grade program 14/26 or 54% = $2,268.00 salary for the 9-12th grade program The $21,000 will therefore be prorated as follows: Vocational (6-12) = Basic, 4-8 = Basic, 9-12 = $8,400.00 5,432.00 7,168.00 $21,000.00 This information will also be used to determine full-time equivalent staff positions for the staff attribution schedule. Indirect costs are attributed on three bases: Staff (number of teachers), FTE students, and Time/Space. For this purpose, full-time equivalent teachers by program are determined concurrently with salaries by program. 40 percent or .40 FTE staff positions will be assigned to Vocational (6-12) program for this teacher. period 2 period 3 .20 .20 .26 FTE staff positions will be assigned to the 4-8 grades category. period 4 period 5 period 6 .10 .07 .09 .34 FTE staff positions will be assigned to the 9-12 grades category. period 4 period 5 period 6 .10 .13 .11 The Program Cost Reporting System attributes salaries to programs and computes the full-time equivalent staff positions by program when assignment data by period, annual salary data, and days worked of annual contract period, are input for each teacher. The other objects of Function 5000 are a relatively small part of total program costs. These costs may be specifically identified to particular programs or attributed on the following bases: Purchased Services (FTE), Materials and Supplies (FTE), Capital Outlay (FTE), and Other Expenses (Staff). Indirect costs (functions 6100-8100) are those which are of such nature they cannot be readily or accurately identified with a program or the instructional function. For example, the custodial staff of a school may clean areas used jointly by individuals performing under Instruction, Instructional Support or General Support functions. 67 5 Program Cost Accounting & Reporting ATTRIBUTION OF COSTS Three bases are used for attributing indirect costs to the instructional programs. FTE students for those costs which tend to increase or decrease with the number of students or which are otherwise related to students. Staff (number of full-time equivalent teachers paid from General Fund and Special Revenue Funds) for those costs which tend to increase or decrease with the number of teachers or which are otherwise more related to staff than students. Time and Space are used for those costs which vary with the amount of space used by programs. These bases are related to Instructional Support and General Support functions as follows: FTE Students Pupil Personnel Services, Instructional Media, Food Service, Pupil Transportation Services, and Board. Staff Instruction and Curriculum Development, Instructional Staff Training Services, General Administration, School Administration, Fiscal Services, and Central Services. Instructional Time/Space Operation of Plant, Maintenance of Plant, and Facilities Acquisition and Construction. RATIONALE FOR ATTRIBUTION Two factors are involved in determination of required attribution basis: (1) The causal relationship between the expense item and the programs benefited. There are certain expenditures which tend to increase or decrease as the number of students or staff, or other factors vary. (2) Cost involved in employing a particular attribution basis. A basis may be preferred in terms of causal relationship, but the cost of securing data for its use may not be justified by the additional degree of accuracy derived. Florida specifies a basis for each support function. Some activities within a particular function may be more appropriately attributed on a different basis than other activities of the same function. However, practicality (cost) dictates that all costs of the function be attributed in accordance with the most significant causal relationship. The following paragraphs address each support function and the attribution basis to be used. Pupil Personnel Services include Attendance and Social Work, Guidance Services, Health Services and Psychological Services provided to pupils. The attribution base selected for Pupil Personnel Services is FTE Students. Although the provision of services to teachers is an important part of Instructional Media Services, the service of librarians to pupils is the predominant activity. This activity would increase or decrease relative to the increase or decrease of students. The factor of FTE students was selected to prorate these services to program categories. 68 5 Program Cost Accounting & Reporting Instruction and Curriculum Development and Instructional Staff Training Services are almost entirely involved in instructional staff activities. These services should be attributed on an instructional staff basis. The Board is involved in many activities involving service to students and staff. For purposes of Cost Reporting, these services should be attributed on an FTE student basis. The majority of activity in General Administration involves managing personnel. Although it is recognized that many other activities are carried on which are pupil and space related, this function should be attributed on an instructional staff basis. To attribute costs on a total staff basis would involve a secondary attribution that could result in additional expense but may not increase the accuracy of the attribution. Under the description of activities involved in the function, School Administration, many are involved with the instructional staff of the school. Because of their heavy involvement with students, a split between attribution bases may be warranted. For the present, this function should be attributed on a staff basis, due to the efforts necessary in making this split. Facilities Acquisition and Construction, Operation of Plant, and Maintenance of Plant consist mostly of acquiring, cleaning and maintaining space. To visualize the inadequacies of attributing indirect operation and maintenance cost on an FTE or Staff basis, the following diagram is offered: K-12 BASIC CLASSROOM* Typical Structure 1 Teacher 27 FTE Students 750 Square Feet VOCATIONAL LAB* Typical Structure 1 Teacher 18 FTE Students 1500 Square Feet SPEECH THERAPY SPACE* Typical Structure 1 Teacher 3 FTE Students 100 Square Feet *Not to scale The Program Cost Reporting System provides for inputting each teacher’s space from existing district systems. Alternatively, models of space usage may be used. 69 5 Program Cost Accounting & Reporting In reviewing attribution of maintenance and operation in cost accounting literature, space is the most recommended basis. Consultation with school facilities personnel also indicates that space would be the better of the alternatives. Maintenance costs should be recorded as direct to program categories when the cost is a result of the characteristics of the program. For example: a maintenance contract on typewriters used for a vocational program. Where possible, other maintenance costs should be recorded by building. Any remaining maintenance costs should be attributed to schools and programs on a space basis. Fiscal Services and Central Services involve budgeting, receiving, disbursing, payroll, buying, storing, etc. These activities increase or decrease in relationship to the numbers of staff served. Fiscal Services and Central Services should therefore be attributed on the basis of instructional staff. As in the case of similar functions, a primary and secondary attribution (involving total staff) might be warranted if not for the expense involved in making such an attribution. Food and Transportation services increase or decrease in relation to the number of students served. These costs should be attributed on the basis of FTE students. Food Service costs by school center and district-wide costs shall be attributed on FTE. While Food Service and Transportation are not to be attributed to programs, it is necessary to report these costs by school. SOURCES OF ATTRIBUTION FACTORS Annual FTE by school and by program is to be taken from the FTE submitted to the Department of Education. The Staff figures are based on the full-time equivalent teachers by program. Full-time is defined as a teacher serving a regular teaching contract for the school year. Short course and summer courses must be equated to the regular term. The Florida Inventory of School Houses (FISH) reports all spaces for each school. Time usage of space must be established with reference to the class schedule. Districts may use space models in which a typical program space is used for each teacher identified with the program. ATTRIBUTION TABLES The attribution factors (FTE, Staff, and Space) of all programs constitute the overall attribution table for indirect costs. These factors provide for the attribution of indirect costs for both school and district level expenditures. One attribution table is not adequate for accurate distribution of all expenditures. For example, a district's General Fund is involved with all schools and all programs, while compensatory expenditures are to be made only for certain target schools and programs. Thus, School/Program tables are used to attribute indirect costs and prorate certain residual direct costs. All costs must be associated with a school/program table. Each district designates the school/program tables needed to accurately cost its program. For example: General Fund 70 5 Program Cost Accounting & Reporting General Fund expenditures except those specified to other tables. This table includes all schools and programs. Transportation Expenditures. Exclude schools and programs not served, such as Adult Education. Special Revenue Funds Food Service Expenditures. Include schools having Food Service and exclude non-participating programs such as Adult Education. Migrant Program Expenditures. Include only schools and programs served. Vocational Project Expenditures. Include only schools and programs served. Adult Basic Education Project Expenditures. Include only schools and programs served. Exceptional Student Education, Federal Project Expenditures. Include only schools served. Districts will have more tables than illustrated here. The number of tables will vary based on the district's program and the identification of programs in its accounting system. SPECIAL CONSIDERATIONS 1. Aides exclusively assigned to particular programs shall be identified to those programs. 2. Contracted services expenditures which have been handled at the district level, but which are incurred for specific programs, shall be reported as direct costs for the specific programs. For example, a school board may have contracted for services for students reported in Physical or Occupational Therapy program, but because the contract was developed by the district office, the expenditure may not have been reported as a direct program cost for ESE. Contractual expenditures which are similar to the cited example shall be reported as costs of the program benefited. This can be accomplished through use of special tables in the cost reporting system. 3. Exceptional Student Education Programs (beginning 1997-98) a. Students receiving exceptional education service are reported in ESE for the full day. Therefore, all Basic, Vocational, and At-Risk teachers with ESE students in their classes are to be reported as ESE in proportion to the number of ESE students to all students in their classes (period by period). b. All ESE teaching personnel (team teachers, co-teachers, facilitators, consulting teachers, and lab teachers) are to be reported as ESE direct costs. 4. Adult Education 71 5 Program Cost Accounting & Reporting a. Plant Operating Costs - When separate school numbers are assigned to day and evening programs conducted in the same plant, operating costs (utilities, custodial and maintenance) shall be attributed to both schools. b. Director of Adult Education Costs - When the Director of Adult Education also performs the function of principal of an adult school, administrative costs shall be split between school level and district level indirect. COMPUTER PROGRAMS FOR COST ACCOUNTING The Automated Cost Reporting System was developed to accomplish the large number of mathematical calculations required for distributing salaries to programs served, developing indirect cost attribution factors and attributing indirect costs to these factors. Phase I of the system distributes salary and develops Staff and Time/Space factors as described. The second phase creates attribution tables. The third and final phase uses the results of the preceding phases plus additional expenditure data in the production of the required reports and supplemental cost analysis reports. The program logic of the Automated Cost Reporting System is consistent with the requirements found in this chapter. COST REPORTING PROCESS Direct salaries for teachers must be determined programmatically by the process described earlier and summarized in the following sentence. If a teacher teaches more than one time module and different programs are involved in each time module, the year-to-date salary of the teacher first should be divided by the number of time modules taught and then multiplied by the percent of students in the categories within the time modules. Direct salaries for substitute teachers (when not specifically identified to a program because of the nature of the substitute service) are to be attributed on a Staff basis. Direct Salaries for classroom aides serving more than one program are to be attributed on a Staff basis, if the time of service for each program is not readily determinable. Salary supplements generally should be distributed in the same manner as regular pay. However, when the supplement is not related to regular duties, a Staff attribution should be used to distribute the supplement. Other salary amounts paid to teachers (conversion of sick leave on retirement and sabbatical leave) should be handled on a district-wide staff attribution. Employee benefits are calculated based on a district or school percentage of benefits paid to salaries paid (option 1) or through direct input to programs (option 2). Option 1 is preferred over handling benefits by transaction because of the detail involved in tracing by transaction. The percent of variance for groups of teachers is not of enough significance to justify the detail necessary in handling by transaction. This is also likely true of benefits by school. Unless there is an unusual benefit variance by school, it is recommended that Option 1 users select the district level (by table) calculations. Direct purchased services may be recorded from transactions for programs. The balance of direct purchased services, after deduction of transactions identified to specific programs is prorated on an FTE basis, either through school or district proration. 72 5 Program Cost Accounting & Reporting Other expenses may be recorded directly from transactions for programs. The balance of direct other expenses, after deduction of transactions identified to specific programs, is prorated on a Staff basis, either through school or district proration. Capital Outlay expenses may be recorded directly from transactions for programs. The balance of direct capital outlay, after deductions for transactions identified to specific programs, is prorated on an FTE basis, either through school or district proration. Indirect school costs are those indirect costs which are either identified to the school by transaction or are prorated to the school on an approved basis. These school indirect costs are attributed to cost programs within the school on either the number of full-time equivalent (FTE) students in the program, the number of full-time equivalent staff members in the program or the space used by the program. Indirect district-wide costs are those indirect costs which are identified to district-wide support activities. These indirect district-wide costs are attributed to programs within schools based either on FTE students, FTE staff members or space used by the programs. District indirect costs applicable to all programs are distributed to all programs. Indirect cost applicable only to one program or to a subset of programs are distributed only to those program(s) through use of a school/program table for that purpose. DESCRIPTION OF ATTRIBUTION PROCESS Attribution bases are applied to indirect cost function codes as follows: FTE 6100 6200 7100 7600 7800 STAFF 6300 6400 7200 7300 7500 7700 SPACE 7400 7900 8100 Direct costs which cannot be identified to specific programs will be attributed by object of expenditure as follows: FTE STAFF Purchased Services Salaries (residual amounts only) Materials/Supplies Benefits (residual amounts only) Capital Outlay Other Expenses Salaries and Benefits are to be directly identified to a program, however, salary amounts for instructional aides (not exclusively assigned to particular programs) and substitutes plus some supplemental salary payments as described previously may be attributed. These small amounts not directly identified with a program are termed residual amounts in that they are direct in nature, but identification stops short of a program (school or district level). The other objects of direct costs constitute about five percent of program costs. The nature of a large portion of these items is such that direct identification to programs is impractical. Accordingly, these objects are frequently recorded only to the school level. 73 5 Program Cost Accounting & Reporting CALCULATION Within each school/program table the calculation of attributed amounts are the same. The school/program table defines the schools and programs within schools for which attribution factors are to be included in the distribution of costs associated with the school/program table. Calculations for each attribution base (FTE, Staff, and Space) are handled identically. (1) District level indirect costs attributable to all schools and programs. An example would be Function 7100 (Board). This cost should be in the "ALL" school/program table. The amount would be attributed to all programs at all schools. For each program at each school the amount would be the product of multiplying the dollar amount of Function 7100 by a fraction – the numerator of which is the FTE of the program at the school and the denominator is the FTE of all programs at all schools. (2) District level indirect costs attributable to a group of programs only. An example would be the costs of supporting the office of the Assistant Superintendent for Vocational Education. These costs are a part of Function 7200, General Administration, but the benefit is limited to vocational education. This cost should be attributed only to vocational programs. Accordingly, through use of a table devoted to vocational programs, the cost is distributed to each vocational program at each school by a fraction in which the numerator is the staff of the particular vocational program at that school and the denominator is the staff of all vocational programs in the district. (3) District level indirect costs attributable only to a single program. An example would be the salary and benefits of a Program Coordinator (Function 6300) who serves only one program. This situation would call for use of a special table devoted to the program. The numerator of the fraction used to distribute this cost to each school would be the staff of the program at the school and the denominator would be the staff of the program for the district. (4) School indirect costs recorded to school level. The amount attributed to each program at that school would be determined by the factor (FTE, Staff or Space determined by the function) for each program relative to the aggregate of that factor for all programs at the school. For example, one teacher is employed in the Exceptional Student Education (ESE) program of a school and there are nine other full-time teachers. One-tenth of school indirect costs to be attributed on a Staff basis would be attributed to ESE. (5) School indirect costs recorded at district level. These amounts are school level by State Board Rule 6A-1.014. Practicality requires recording at district level. An example of such costs would be maintenance labor. These amounts are attributed in the same manner as district indirect costs, but reported as additions to school indirect. See controls 2000, 2001, and 2002 for the correct entry of this data. (6) Residual direct amounts. The nature of these items is described in the preceding section. These amounts are attributed in the same manner as district or school indirects except that the amounts are added to the particular object of direct costs. 74 5 Program Cost Accounting & Reporting (7) Food Service and Transportation. These amounts are not attributed to programs, but are based on each school's share of FTE exclusive of Adult Education programs and offcampus vocational programs. Schools not served should be deleted from the tables needed for the functions. 75 5 Program Cost Accounting & Reporting Chapter Six Internal Service Funds Internal service funds are established to account for any activity that provides goods or services to other funds, departments, or agencies of the primary government and its component units, or to other governments, on a cost-reimbursement basis. An internal service fund should be used only when the reporting government is the predominant participant in the activity. Otherwise, the activity should be reported as an enterprise fund. (Statement 34, paragraph 68) As a proprietary fund, an internal service fund utilizes the total economic resources measurement focus and the accrual basis of accounting. Therefore, revenues are recognized in the accounting period in which they are earned and expenses are recognized when incurred, regardless of the timing of the related cash flows. Although generally accepted accounting principles do not require the use of an internal service fund, SBE Rule 6A-1.099, requires the use of an internal service fund for all educational consortia activities. The authorizing statute is Section 230.23(12), F.S., which states that school boards "may establish and participate in educational consortia which are designed to provide joint programs and services to cooperating school districts, consistent with the provisions of s. 4(b), Art. IX of the State Constitution." The following principles regarding internal service funds (or enterprise funds required for self-insurance pools) apply to educational consortia are: a. All monies received by a consortium shall be deposited to the official accounts of the host district (recipient agency) and shall be separately accounted for in an internal service fund. b. All transactions for the consortium shall be recorded in the proper account within the fund. Projects submitted on behalf of the consortium shall be recorded directly in the internal service fund. Revenues generated by billing to participating districts shall be recorded directly in the internal service fund. c. Expenditures for operating costs of the consortium, including any rent or service charge due the host district's general fund, shall be charged to the fund. Contractual services performed by the consortium for the host district shall be accounted for in the same manner as those for other consortium members; i.e., there would be an expenditure charged to the general or special revenue fund of the school district receiving services and revenue credited to the internal service fund. Amounts charged by the consortium shall be sufficient to cover all costs of goods or services provided to member districts. Records of the consortium shall be in sufficient detail to determine that member districts receive full value of purchased goods or services. For instance, if a member district pays $10,000 for goods or services from the consortium, the records of the consortium shall reflect that $10,000 of goods or services were provided to the member district. d. The disposition of unexpended cash balances at the end of each fiscal year should be by refund to the participating consortia members; however, the host district may, with the consent of the participating members, carry forward cash balances for use in the ensuing fiscal year. 76 6 Internal Service Funds e. Districts that serve as the host district for more than one consortium shall maintain separate records for each consortium. f. The account that a consortium should use when revenues are recognized from member districts is 3481, Charges for Services. The initial receipt of money from member districts shall be handled on the books of the host district as deferred revenue. The participation member district shall record disbursements to the consortium as a receivable until goods or services are received. At that time an expenditure shall be recorded on the accounts of the member district and revenue shall be recognized on host district's accounts. Contracted services and activities rendered by an educational consortium may include, but not be limited to, bidding, contracting and purchasing arrangements for the purpose of implementing the following examples of the types of programs or functions provided. 1. Programs: a. b. c. d. e. Teacher Education Center Inservice Training for Non-instructional Personnel Federal Programs Student Testing State and Federal Mandated Programs 2. Functions: a. b. c. d. e. f. g. Instructional Services Fiscal Services Data Processing and Management Information Services Pupil Personnel Services Purchasing Printing Media Center Any other services to member districts deemed necessary by the Board of Directors of the consortium may also be rendered. Additional information regarding the account structure necessary to record the activity described above can be found in Chapters 2, 3, and 4 of this manual. 77 6 Internal Service Funds Chapter Seven School Internal Funds SECTION I – PRINCIPLES 1. The school board shall be responsible for administration and control of internal funds of the district school system, and in connection therewith shall: a. adopt written rules governing the receipt and disbursement of all internal funds and for the accounting for property pursuant to Florida Statutes. b. provide for an annual audit of internal funds in accordance with Rule 6A-1.087, FAC. 2. The financial transactions of school organizations shall be accounted for in the school internal funds. All funds handled by school board employees during normal working hours shall be included in and become part of the internal funds of the school unless accounted for in the district level accounting system. All organizations of the school, or operating in the name of the school, which obtain moneys from the public shall be accountable to the board for receipt and expenditure of those funds in the manner prescribed by the board. If authorized by school board rule, a school based direct support organization as authorized by Section 237.40, F.S., may have all financial transactions accounted for in school internal funds. 3. Funds collected by and used for the benefit of faculty and staff may be exempt from the preceding requirements at the option of the school board. 4. School internal account funds shall be used to benefit activities authorized by the district school board. 5. Student participation in fundraising activities shall not be in conflict with the program as administered by the school board. 6. The objective of fundraising activities by the school, by any group within, or in the name of the school shall not conflict with programs as administered by the school board. 7. Funds collected shall be expended to benefit those students in school unless those funds are being collected for a specific documented purpose or are generated by vocational production shops. Vocational production revenue shall benefit the students or program that generated the funds or the student body. Those internal account funds designated for general purposes shall be used to benefit the student body. 8. Collecting and expending of school internal account funds shall be in accordance with the Florida Constitution, Florida Statutes, State Board of Education rules, and school board rules. Sound business practices should be observed in all transactions. 9. Each school organization should operate within a budget formulated by the organization members. The format of the budget shall be prescribed by the principal if not prescribed by school board rule. 78 8 Fiduciary Funds 10. Purchases from internal accounts shall not exceed the resources of the applicable student activity/project account, except for items acquired for resale or items authorized by school board rule. Purchases to support instructional programs may be made from revenue derived from production work of vocational programs. 11. An adequate system of internal controls shall be maintained in order to safeguard the assets of the school internal funds. SECTION II - GENERAL PRACTICES 1. All employees having responsibility for handling and recording internal funds financial transactions shall be bonded through the district. 2. Purchases from internal funds must be authorized in writing by the principal or designee. Neither the school nor the school board shall be liable for any purchase made in the name of the school without express written approval. 3. District approved pre-numbered receipt forms shall be used as the means of recording cash received, and as the basis for entries to the accounting records. 4. Approved pre-numbered checks shall be used as the means for disbursing funds, and as the basis for accounting entries, with the exception of disbursements from properly established petty cash funds. 5. Promissory notes, installment contracts or lease purchase agreements shall not be executed in the name of a school or any school organization except as authorized by the school board. 6. Internal funds shall not be used to cash checks to accommodate individuals, make any kind of loans, pay any form of compensation directly to employees, or extend credit. Employees of the district who are compensated for additional services, such as game personnel to work at athletic events, shall be paid through the district payroll department or when appropriate as prescribed by school board rule. Designated area vocational technical centers may cash checks and make loans as necessary to administer student grant and loan programs funded by federal, state, or private sources. 7. Internal funds shall be accounted for on the same fiscal year basis as all other school district funds. No school organization shall make expenditures that exceed the cash resources available to that organization. All accounts payable shall be disclosed to the school board at year end. 8. Bank statements shall be reconciled as soon as received, preferably by a person other than the person who receipts and disburses funds. 9. Monthly financial reports shall be made in approved written form to provide the school's administration with financial information necessary for decision making. An annual report will provide data for inclusion of internal funds in the district's annual financial statement. 10. Account balances shall be subject to limits which the school board may prescribe. 79 8 Fiduciary Funds SECTION III - STANDARDS, PRACTICES AND PROCEDURES 1.0 CONTROL OF CASH RESOURCES 1.1 DEPOSITORIES FOR INTERNAL FUNDS Depositories in which internal funds are kept must be qualified public depositories, approved by the school board, and required to furnish the same type of security for deposits as is required for other district school board funds. 1.2 BANK ACCOUNTS Each school shall have only one checking account which shall be entitled "(SCHOOL NAME) Internal Fund, The School District of ________ County Florida," or alternative which clearly identifies the school and school district. This account title must be imprinted on all internal fund checks and deposit slips. All monies received by the school will be deposited intact as collected into this account and all disbursements will be made by checks drawn on this account. Savings or investment accounts shall be titled in the same manner. Additional checking accounts may be utilized by designated area vocational technical centers if required in the administration of student grant or loan programs. The name of such program shall be incorporated in the account title. 1.3 CHECK SIGNATURES (a) Each account shall have at least two authorized check signers, one of whom must be the principal. These names shall be kept on file for audit. All checks must be signed with two signatures as prescribed by the principal if not prescribed by school board rule. 1.4 (b) The principal is responsible for all financial transactions and proper check signatures. (c) Under no circumstances shall checks be presigned. CASH COLLECTIONS AND DEPOSITS (a) All money collected by the school must be substantiated by pre-numbered receipts, consecutively numbered class receipt records, reports of monies collected, pre-numbered tickets, reports of tickets issued and sold or other auditable records. (b) Insofar as is practicable, all money should be collected in the school office. Collections made outside of the school office must be turned in to the school office no later than the next business day. (c) All money collected must be deposited intact to a depository as frequently as feasible and as dictated by sound business practices. IN ANY EVENT, FUNDS COLLECTED MUST BE DEPOSITED WITHIN FIVE (5) WORKING DAYS AFTER RECEIPT. (d) All deposits must equal the total amount of money taken in and recorded on receipts for the period covered by the deposit. Deposit slips shall be made in the number of copies necessary to meet the approved accounting procedures. All checks received shall be deposited with a restrictive endorsement of for deposit only and specifying the account title and number. (e) The principal or designee shall be notified immediately of any errors in deposits or disbursements and shall take appropriate action to effect correction. 80 8 Fiduciary Funds (f) 1.5 INVESTMENTS (a) The school board shall adopt policies pertaining to the investment of school funds not needed for immediate expenditures. The adopted policies shall make provisions for investing or placing on deposit all such funds in order to earn the maximum possible yield under the circumstances. (Section 230.23(10)(k), F. S.) (b) 1.6 All checks, receipt forms and tickets shall be pre-numbered and perpetual inventories of each shall be maintained. Inventories shall show the beginning and ending numbers of all documents acquired and issued. In all cases where tickets are used, ticket reports and unsold tickets must be available for audit. Any pre-numbered documents shall be accompanied by a certified statement of the numbers received. Internal funds which are temporarily idle shall, as required by law, be invested pursuant to policies of the school board using any medium of investment legal for public funds, and may not exceed insurance protection or other legal collateral limits. (Rule 6A-1.085, FAC) COLLECTION OF WORTHLESS CHECKS (a) The principal is responsible for seeking reimbursement for any unpaid check returned by the bank. (b) A check can be declared uncollectable and written off the books only by action of the school board or designated officer. This action will be taken only after every legal and reasonable effort at collection by the principal has been exhausted. (c) The school principal may require payment for school obligations in cash, money order, or other form of guaranteed payment if it is deemed necessary. 2.0 STUDENT ACTIVITY/PROJECTS 2.1 ATHLETICS All revenue and expenditures involving athletic business transacted at the school level shall be recorded in accounts in this classification. 2.2 MUSIC (a) Proceeds from activities of musical organizations; donations to these groups; and their expenses for supplies and trips shall be recorded in this classification. (b) 2.3 Collections from students for rental or maintenance of uniforms or instruments shall be recorded in separate accounts in this classification, or in trust if restricted as to use. CLASSES, CLUBS AND DEPARTMENTS (a) Class and club accounts are those which support a group of students within a community of interest with a roster of members, officers, and a sponsor. Approval for the existence of all club and class activities is the responsibility of the principal. (b) The sponsor of each school club or organization is responsible for providing adequate financial documents and records to the principal and is responsible for retaining 81 8 Fiduciary Funds duplicates of said documents and records. These records may include an organization budget; duplicate receipts for all income from dues, fund-raising activities, entertainments, assessments, or donations; and approved requests for payments. (c) All collections received by any club or school organization must be deposited in the school internal fund. (d) All disbursements by any club or school organization must be made by an internal fund check, or from an approved petty cash fund. Disbursements shall be approved by the appropriate organization officer, when the organization has officers, the sponsor and the principal. (e) A financial report shall be filed with the principal's office at the close of each fundraising activity. To accommodate collection of data for this report a separate account for the activity may be established. The organization sponsor shall participate, along with the finance clerk, in the designation of transactions to be recorded in each of the organization's accounts. (f) Class and club monies shall be expended for the benefit of the class or club or for purposes designated by the class or club that participated in generation of the revenue. (g) 2.4 (1) Any remaining balance in the account of a class that has graduated shall be transferred to the general miscellaneous account at the discretion of the principal. (2) Any remaining balance in the account of an inactive student organization shall be considered as belonging to the general miscellaneous account and shall be closed at the end of the following school year. Departments may be structured similar to classes and shall conduct financial activities subject to the above. TRUST (a) Funds collected for a specific, restricted purpose shall be accounted for in a trust account. (b) Trust funds shall be expended only for the purpose for which collected. When the purpose of the trust fund has been accomplished or becomes inoperative, unused trust funds shall be returned to the person(s) from whom collected, if practicable. Donors may designate an alternative purpose. Funds which can not be returned shall be handled in accordance with school board policy. (c) At no time shall a trust account have a deficit. (d) If a school organization undertakes a project extending beyond the current fiscal year, or receives a restricted donation to be used over a period of time beyond the year in which received, approval must be granted in accordance with school board rules, and the funds held in a trust account. 82 8 Fiduciary Funds 2.5 (e) Collections for the school board, such as out-of-state tuition, adult matriculation and tuition fees, course fees, reimbursement for damages, or telephone charges are trust funds. Sales tax collected for the State is also a trust account. (f) Collections for parking decals issued by secondary schools and vocational schools may be restricted by the school board as to use, and if so, should be accounted for separately in a trust account. (g) Funds collected from students as deposits for use of locks, and restricted by the school board as to use, shall be accounted for separately in a trust account. GENERAL (a) This category encompasses all other accounts for funds which are to be utilized for the general welfare of the student body. (b) Separate accounts shall be maintained for activities such as the school store and other activities when it is good business practice to separately monitor the financial status of the activity. Activities not accounted for separately shall be recorded in a miscellaneous account. 3.0 PURCHASING 3.1 REQUIREMENTS (a) The requirements pertaining to purchases and securing bids on purchases made from public tax funds shall be observed when purchases are made from internal funds except that: (b) 3.2 (1) School board approval of internal account vouchers is not required unless specifically provided for by school board rule. (2) School board requirements for internal funds may be more strict than those required for tax funds. (Rule 6A-1.091, FAC) Insofar as is possible, purchases of the same or a similar nature to be used in more than one school should be combined and purchased only after approval of the school board. (Rule 6A-1.091, FAC). RESPONSIBILITY (a) The school principal is fully responsible for all purchases and purchase commitments requiring present or future disbursements of internal fund monies. A signed commitment from the principal or designee(s) must be on file before any purchase is made. Vendors shall be notified of this policy. No purchase shall be made unless sufficient resources are available, except items for resale. (b) The school board may delegate by rule to such individuals as it may deem appropriate, the making of purchases from internal funds and the securing of quotations and awarding of contracts. (Rule 6A-1.091, FAC) (c) No person, unless authorized to do so under regulations of the school board, may make any purchase involving the use of school funds. (Rule 6A-1.012, FAC) 83 8 Fiduciary Funds 3.3 BIDS (a) Bids shall be requested from three or more sources for any authorized purchase exceeding amounts set forth in a scale of district sizes and purchase amounts. (Rule 6A1.012, FAC) (b) The school board shall have authority to reject any or all bids and request new bids. In acceptance of bids, the school board shall accept the lowest and best bid. (Rule 6A1.012, FAC) (c) School boards may establish more strict requirements for bids. (d) School boards may establish procedures requiring competitive quotations for all or selected types of purchases in amounts under the board adopted bid requirement. Such quotations shall be documented. (e) Proposed purchases in excess of the district bid limit must comply with bid requirements of Florida Statutes, State Board of Education Rules, and school board rules. These will be referred to the district purchasing department for development of specifications, bids, advertising and processing. (f) When the district has a bid in effect, purchases of items covered must be made from the approved vendor unless the same item may be purchased elsewhere at a lower cost. 3.4 PETTY CASH If authorized by school board rule, petty cash funds may be established for internal funds. 3.5 RESTRICTED EXPENDITURES (a) The following expenditures from internal funds are deemed inappropriate and shall not be made except from trust funds collected for a specifically identified purpose. (1) Equipment, supplies, forms, and postage for curricular or classroom use for which school board funds are available. However, revenue derived from vocational education production shops may be used for these purposes. (2) Curricular-related travel; professional, technical, or consultant services; or other items for which school board funds are available. However, revenue derived from vocational education production shops may be used for these purposes. (3) Articles for the personal use of any student, employee, or other person; except those items which are identifiable as being in recognition of service or promotion of school activities and those items identified under Rule 6A-1.043, FAC, Promotion and Public Relations Expenditures. (4) Personal memberships or subscriptions. (5) Salaries or other compensation for duties or assignments which are the responsibility of the school district. (6) Loans, credit, or accommodation purchases for anyone. 84 8 Fiduciary Funds (7) 3.6 Repairs and maintenance of school board equipment for which school board funds are available. However, revenue derived from vocational education production shops may be used for these purposes. PROPERTY ACQUISITION AND CONTROL (a) Tangible personal property as defined in Chapter 274.01, F.S., purchased or acquired by donation becomes the property of the school board and is subject to the board's procedures for property control. (b) Notification to the appropriate district office is required when items that meet the criteria for fixed assets are purchased or received as a donation. A full description of any equipment or property acquired by a school must be given, including make, model, serial number, date acquired and total cost, or fair market value for donated property. (c) Expenditures for buildings, remodeling, renovation, repairs, or alteration to the facilities, or any property involving risk must have prior written approval of the superintendent or designee. (d) Approval must be obtained from the superintendent or designee to change, alter, or attach permanent fixtures to school property; or to utilize more than the ordinary amount of utilities. 4.0 GENERAL STANDARDS, PRACTICES AND PROCEDURES 4.1 REPORTS (a) The principal's financial report and any other interim reports shall be prepared and submitted according to the schedule and format prescribed in district adopted procedures. (b) 4.2 AUDITS (a) The school board shall provide for an annual audit of internal funds. (b) 4.3 At the close of the school year the annual report shall be prepared as district procedures provide, and shall be attested to by the principal and the preparer by their signatures as to its accuracy in reflecting the year's activity and year-end balances to be included in the District Annual Financial Report. In accordance with Rule 6A-1.087(2), FAC, the signed, written report of the audit shall include notations of any failure to comply with Florida Statutes, State Board of Education Rules and rules of the school board. The report, which must also provide commentary as to financial management and irregularities, shall be presented to the school board while in session and filed as a part of the public record. COOPERATIVE ACTIVITIES (a) A cooperative activity is one in which the school participates with outside groups such as the P.T.A. or booster clubs through planning, staging, or conducting school-related activities. Such activities may be held on or off the school grounds and will usually take the form of fund-raising events such as carnivals, paid entertainments, or food sales. 85 8 Fiduciary Funds (b) 4.4 4.5 Such activities must be approved by the principal and be beneficial to students. District procedures shall be followed to provide appropriate accounting for funds and to ensure compliance with policies contained herein. If a share of the proceeds is to be disbursed to the cooperating group, a prior written agreement should be executed. FUNDRAISING (a) Each fundraising activity shall be planned to finance a specified objective. (b) Each fundraising activity shall have the approval of the organization sponsor and the principal. (c) The principal shall control the fundraising activities conducted in the name of the school, and assure that the purposes are worthwhile. (1) Raffles and other activities of chance shall not be conducted for school connected activities. (2) Fundraising activities for which students are charged an admission shall not be presented during school hours. (d) When any school organization or group is involved in a fundraising activity or any function exposing the school board to extraordinary liability, approval must be obtained in advance from the superintendent or designee. (e) Collections for all school sponsored fundraising activities must be deposited in the internal fund, and all transactions in connection with the activity conducted in accordance with school board rules. RETENTION OF RECORDS (a) Chapters 119 and 267, F.S., provide that no public official may mutilate, destroy, sell, loan or otherwise dispose of any public record without the consent of the Bureau of Records and Information Management of the Department of State. Provided applicable audits have been released, records may be disposed of in accordance with procedures established by Department of Records and Forms Management. Examples of such records for internal funds could include check requisitions and documentation, canceled checks, recap of collections, journals, ledgers, financial reports, purchase orders, payroll records, and serialized forms. (b) Procedures for destruction of records shall be in accordance with Chapters 119 and 267, F.S. 4.6 SALES OF FOOD AND BEVERAGES The sale of food or beverages to students by direct sale or through vending machines shall be in accordance with Rule 6A-7.042, FAC. 5.0 MODIFICATION OF CHAPTER PROVISIONS 5.1 CENTRALIZED ACCOUNTING SYSTEMS Districts which utilize centralized accounting systems for internal funds may apply to the Commissioner of Education for modification of the policies and procedures in this chapter. 86 8 Fiduciary Funds 5.2 EMERGENCY MODIFICATIONS Districts may apply to the Commissioner of Education for modification of the policies and procedures in this chapter. Such application shall state the specific provision herein and the emergency or reason for which relief is sought. Approval of any modification shall be valid up to one year. 5.3 VOCATIONAL CENTERS The director of a designated area vocational technical center shall assume the duties and responsibilities assigned to the position of principal by this chapter. 5.4 ECONOMIC EDUCATION PROJECTS Economic Education Projects may be exempted from Sections I-IV at the discretion of school boards with the following stipulations: 1. 2. 3. 4. That administrative oversight continues to assure that activities are in the best interest f the students and the school. That involved employees are bonded. That checks drawn on bank accounts be controlled so that a teacher or sponsor's authorization is required, and That bank statements are currently reconciled and reviewed by the principal. Economic Education projects include Junior Achievement programs and similar programs which link the curriculum with appropriate economic education activities. SECTION IV CHART OF ACCOUNTS SCHOOL INTERNAL FUNDS Fund Group (Trust and Agency Funds) Balance Sheet Accounts Revenue Accounts Student Activity/Project 800 As provided in Chapter 2 3900 10000 Athletics 20000 Music 30000 Classes 40000 Clubs 50000 Departments 60000 Trust 70000 General Expenditure Accounts Function Object Student Activity/Project 9800 As provided in Chapter 4 10000 Athletics 20000 Music 30000 Classes 40000 Clubs 50000 Departments 60000 Trust 70000 General 87 8 Fiduciary Funds SECTION V - SCHOOL INTERNAL FUND DEFINITIONS This section contains definitions of terms used in this guide and such additional terms as seem necessary to achieve common understandings concerning financial accounting procedures for internal funds. Internal funds are defined as all local school funds derived by any public school from all activities or sources. The glossary is arranged alphabetically with appropriate cross-referencing where necessary. Some of the definitions shown are taken or adapted from the recommendations of the National Committee on Governmental Accounting. Others have been taken or adapted from Handbook I and Handbook II in the State Education Records and Reports Series. Account - A record of financial transactions that are similar in terms of a given frame of reference, such as purpose, objective, or source. Accounting Period - A period of time for which financial statements are prepared. (i.e., July 1 through June 30). Accounts Payable - Unpaid balances or invoices against an internal fund which are owed. Accounts Receivable - Amounts owed to the internal funds. Accrual Basis - Recording of revenues and expenditures at the time revenue is earned or at the time an expenditure results in a liability regardless of when the actual cash receipt or disbursement occurs. Asset - Something of value that is owned by an entity. Assets, Current - Cash and other assets readily converted into cash, such as accounts receivable, inventory, and some prepaid expenses. Assets, Fixed - Land, buildings, machinery, furniture, and other equipment which the school system intends to hold or continue in use over a long period of time. "Fixed" denotes probability of intent to continue use or possession, and does not indicate immobility of an asset. Audit - An examination of records and documents by an auditor in the process of securing evidence for one or more of the following purposes: (a) determining the propriety of completed transactions, (b) ascertaining whether all transactions have been recorded, (c) determining whether transactions are accurately recorded in the accounts and in the statements drawn from the accounts. Balance - The difference between the total debits and the total credits of an account; the total of an account containing only debits or only credits. Bank Deposit - The total amount of money taken in and recorded on receipts for a specified time period and deposited intact with a depository. Capital Outlay - Expenditures for land or existing buildings, improvement of grounds, construction of buildings, additions to buildings, remodeling of buildings, or equipment. Cash - Currency, checks, postal and express money orders, and bank deposits including certificates of deposit. 88 8 Fiduciary Funds Cash Basis - The basis of accounting under which revenues are recorded only when actually received and only cash disbursements are recorded as expenditures. Cash Discount - An allowance received or given if payment is completed within a stated period. The term is not to be confused with "trade discount". Change Fund - An amount of money obtained by issuing a check to a designated individual for the purpose of making change for a specific event. No expenditures are to be made from these monies. Check - A written order on a bank to pay on demand a specified sum of money to a named person, to his order, or to bearer from money on deposit to the credit of the maker. It is canceled when it has been paid by the bank and thus "cleared" and returned to the writer. Closing the Books - The process of putting the account books in order at the end of a month, or a fiscal period, so that a trial balance and financial reports may be prepared. Commemorative Item - Personalized articles such as class jewelry, announcements, caps and gowns, yearbooks, cards and invitations, insignia, and school pictures. Commission - A share of sale proceeds from any company or individual given the school in return for the sale, rental, or promotion of any items within the school. Concession - The act of granting to an individual or group a right that resides with the school. Deficit - The excess of the obligations of an account over its resources. Deposit in Transit - A deposit which has been transmitted to the bank and recorded in the school ledgers but was not reflected on the monthly bank statement because it was not received before the bank's preparation of the statement. Deposit, Property - Money collected from students and held in a school account for return at a designated time for the purpose of covering losses or damages to school-owned supply and equipment items while being used by the students. Depositories - Banks or savings and loan institutions where schools conduct the business of depositing and withdrawing money. Disbursements - Money paid out. Double Entry - A system of bookkeeping which requires for every entry made to the debit side of an account or accounts, an entry for the corresponding amount or amounts must be made to the credit side of another account or accounts. Dues - A regular charge made to students for the privilege of being a member of a particular club or student body organization. Encumbrance - A restriction of available money by issuance of a purchase order. 89 8 Fiduciary Funds Equipment - A material item of a non-expendable nature, such as a built-in facility, a movable or fixed unit of furniture or furnishings, an instrument or apparatus, a machine (including attachments), instructional skill-training device, or a set of small articles whose parts are replaceable or repairable, the whole retaining its identity and utility over a period of time which is characteristic for items of its class. Expenditures - Decreases in net financial resources. If accounts are kept on the accrual basis, this includes total charges incurred, whether paid or unpaid. On the cash bases, payments are termed disbursements. Expense, Travel - Expenses incurred by students and sponsors of a school activity in connection with travel related to the activity other than those expenses directly chargeable to student transportation. Fidelity Bond - A bond guaranteeing the school board against losses resulting from the dishonest actions of employees. Finance Clerk - Person assigned responsibilities for internal accounts bookkeeping. Financial Statement - A formal written presentation which sets forth information concerning the financial condition of the school internal funds. Fiscal Period - Any period at the end of which a school determines its financial condition and the results of its operations, and closes its books. Fiscal Year - As it pertains to internal funds, July 1 through June 30. General Ledger - A book, file, or other device in which accounts are kept to the degree of detail necessary to summarize the financial transactions of the school. General ledger accounts may be kept for any group of receipts or expenditures on which an administrative officer wishes to maintain fiscal control. Gift - Something of value received for which no repayment or special service to the contributor is expected. Grant - Money received by a school activity for which no repayment is expected but for which certain conditions exist relative to the disbursement of funds. Inactive Account - An account is considered inactive upon declaration of the principal when; (1) no financial transactions have occurred within one year and the need for the organization has passed; or (2) a class has graduated. Intact, or Deposit Intact - The practice in which money is presented to a bank or bookkeeper for the credit of the school's internal fund in the same form as received. This means that any receipt of funds in the form of cash shall be deposited as cash. The cashing of a check from funds on hand would be a violation of this concept as would be the substitution of a check for cash. Internal Control - A plan of organization under which employees' duties are so arranged, and records and procedures so designed, as to make it possible to exercise effective accounting control over assets, liabilities, revenues, and expenditures. For example, under such a system, work is subdivided so that no one employee performs a complete cycle of operations. The procedures to be followed are definitely laid down and such procedures call for proper authorizations by designated officials for all actions to be taken. 90 8 Fiduciary Funds Inventory - The cost of supplies and equipment on hand not yet distributed to requisitioning units. Inventory Record - A detailed list or record showing quantities, descriptions, values, units of measure, and unit prices. Investments - Temporarily idle funds placed in interest earning accounts. Invoice - A vendor's notification of merchandise provided or services rendered to a purchaser with the quantity, prices, and charges stated. Other information customarily shown on the invoice are the customer's order number, order date, date of delivery or shipping, and terms of payment. Journal - The accounting record in which financial transactions of the school are formally recorded for the first time. Liabilities - Debt or other legal obligations arising out of transactions which are payable but not necessarily due. (Encumbrances are not liabilities, they become liabilities when the services or materials for which the encumbrance was established have been rendered or received.) Memoranda (Memo) Account - An informal record of an internal fund transaction that cannot be recorded under the regular financial accounts but for which a record is desired. (i.e. ENCUMBRANCES) Outstanding Check - A check issued and recorded by the school which has not been presented to the bank for payment prior to issuance of the monthly bank statement. Outstanding Deposit - (See Deposit in Transit) Overdrawn - A situation in which a check has been written for an amount in excess of that on deposit. An overdraft is the amount by which withdrawals exceed the depositor's available balance. Perpetual Inventory - An inventory system which is initiated by a physical inventory and perpetuated by entry of receipts and withdrawals, thereby reflecting current balances on hand for each item. Petty Cash - Cash paid out in small amounts for authorized expenditures. Petty cash may be used to reimburse persons or to make a direct purchase. (Petty cash funds must be authorized.) Payments must be evidenced by petty cash vouchers which are signed receipts that show the purpose, date, and amount. Posting - The act of recording to an account in a ledger the detailed or summarized data contained in the documents of original entry. Pre-Numbered Documents - Checks, receipt forms, tickets, and similar items which have been consecutively numbered and controlled before use. Prior Authorization - A written approval granting authority to enter into a contract, to obligate funds for a purchase, or to receive a benefit, before such an action occurs. Purchase Order - A document issued to a vendor authorizing the delivery of goods or services which implies the obligation of funds. 91 8 Fiduciary Funds Reconciliation of Bank Statement - A statement of the details of the differences between the bank statement and the cash account record to show agreement of the adjusted balances. Refund - An amount paid back or credit allowed. Reimbursement - Repayment of authorized expenditures made on behalf of the school's internal fund. Repairs, Minor - The restoration to a usable condition of a given piece of equipment, building, or grounds. Cost of new construction, renovating, and remodeling are not included here but are considered capital outlay. Reports - Written statements of information which are made by a person, unit, or organization for the use of some other person, unit, or organization. Requisition - A written request, usually from one department to the purchasing officer or to another department, for specified articles or services. Student Activities - Direct and personal services for public school students, such as interscholastic athletics, entertainments, publications, clubs, band, or orchestra, that are managed or operated by students under the guidance and direction of authorized adults, and are not part of the regular instructional program. Student Organization - Any group of students organized on campus into a single body for the purpose of pursuing common goals and objectives. This includes the various types of student clubs and class organizations which, with proper approval by school authorities, are managed and operated by students under the direction or supervision of authorized adults. Subsidiary Ledger - A record of the financial transactions of a given activity showing the receipts, expenditures, transfers, adjustments, and balances for the activity's account. Supply - An item of expendable nature that is consumed, worn out, or deteriorated in use; or one that loses its identity through fabrication or incorporation into a different or more complex unit or substance. Supporting Documentation - Evidence attesting to the authenticity, accuracy and authority of a financial transaction. Surety Bond - A written promise to pay damages or to indemnify against losses caused by the party or parties named in the document, through non-performance or through defalcation. For example, a surety bond may be required of a contractor or an official handling cash or securities. Trade Discount - An allowance made to those engaged in certain businesses and allowable irrespective of the time when the account is paid. The term should not be confused with "Cash Discount". Transfer - Money which is taken from one account and added to another account. Transfers are not receipts or expenditures. Trust and Agency Funds - Funds used to account for money and property held by a governmental unit in the capacity of trustee, custodian, or agent. 92 8 Fiduciary Funds Voided Check - A check which has been declared void. A check on which an error has been made in writing, such as an incorrect amount, signature, or a discrepancy in the information included. The check is made void by mutilating the signature space and the check is retained. 93 8 Fiduciary Funds Chapter Eight Fiduciary Funds Fiduciary funds should be used to report assets held in trustee or agency capacity for others and therefore, can not be used to support the government’s own programs. Fiduciary funds should be reported using the economic resources measurement focus and the accrual basis of accounting, except for the recognition of certain liabilities of defined benefit pension plans and certain postemployment healthcare plans. (Statement 34, paragraph 107) Statement 34 specifically excludes fiduciary funds from presentation in the government-wide financial statements, but requires fiduciary fund financial statements to be reported by fund type. Statement 34 identifies fiduciary funds as pension trust funds, investment trust funds, private-purpose trust funds, and agency funds. Trust funds are used to report resources held and administered by the reporting government when it is acting in a fiduciary capacity for individuals, private organizations, or other governments. Trust funds are distinguished from agency funds generally by the existence of a trust agreement that effects the degree of management involvement and the length of time that the resources are held. (Statement 34, paragraph 69) Pension Trust Funds should be used to report resources that are required to be held in trust for the members and beneficiaries of defined benefit pension plans, defined contribution plans, other postemployment benefit plans, or other employee benefit plans. (Statement 34, paragraph 70) Investment Trust Funds should be used to report the external portion of investment pools reported by the school district. (Statement 34, paragraph 71) Private-purpose Trust Funds should be used to report all other trust arrangements under which principal and/or income benefit individuals, private organizations or other governments. Specifically, scholarship trust funds should be classified as private-purpose trusts. (Statement 34, paragraph 72) Agency Funds should be used to report resources held by the school district in a purely custodial capacity (assets equal liabilities). Agency funds typically involve only the receipt, temporary investment, and remittance of fiduciary resources to individuals, private organizations, or other governments. (Statement 34, paragraph 73) 94 8 Fiduciary Funds Appendix A Supplies and Equipment In this section criteria are provided for the solution of the ever present problem in financial accounting distinguishing between supplies and equipment. These guides consist of criteria for classifying an item as supply and criteria for classifying an item as equipment. Equipment built-in or fixed to the building or grounds is considered a part of the building or land improvement, and is to be charged to those respective accounts. CRITERIA FOR SUPPLY ITEMS A supply item is any article or material which meets any one or more of the following conditions: 1. It is consumed in use. 2. It loses its original shape or appearance with use. 3. It is expendable, that is, if the article is damaged or some of its parts are lost or worn out, it is usually more feasible to replace it with an entirely new unit rather than repair it. 4. It is an inexpensive item, having characteristics of equipment, whose small unit cost makes it inadvisable to capitalize the item. It loses its identity through incorporation into a different or more complex unit or substance. 5. CRITERIA FOR EQUIPMENT ITEMS An equipment item is a material unit which meets all of the following conditions: 1. It retains its original shape and appearance with use. 2. It is nonexpendable, that is usually more feasible to repair it rather than replace it with an entirely new unit. 3. It represents an investment of money which makes it feasible and advisable to capitalize the item. 3. It does not lose its identity through incorporation into a different or more complex unit or substance. 4. Criterion number 4 is very important, especially if capital outlay expenditures are to be depreciated, in memorandum accounting, to arrive at equipment use cost. 95 A Supplies & Equipment Appendix B Optional Object Codes The optional third digit object account shown below is compatible with the current automated state data bases as adopted. Districts may elect to use this third digit in order to provide information requested in the automated state data base system. SALARIES 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Regular Pay Overtime Pay Supplements Terminal Pay - (payment for unused annual leave) Sick Leave Buy Back - (payment for unused sick leave) Sabbatical Leave Merit Pay (Not assigned) Other (e.g., uniform allowance, etc.) BENEFITS 1. 2. 3. 4. 9. Health and Hospitalizations Life Insurance Commercial or Merit and Insurance Annuity Plan Cafeteria Plan Other LIBRARY BOOKS (Object 610 Only) 1. 2. New Libraries Existing Libraries B Optional Object Codes Appendix C Alphabetical List of Supplies, Equipment, AV A Abrasives - S Absorbent Cotton - S Account Book - S Accounting Forms - S Accounting Machine - E Acetylene - S Achievement Test - S Acid - S Adaptors - S Adaptors for Computer - E Adding Machine - E Adding Machine Ribbon - S Adding Machine Tape - S Addressing Machine - E Addressing Machine Plate - S Addressing Machine Ribbon - S Addressing Machine Stencils - S Adhesive Tape - S Adzes - S Air Compressor - E Air Conditioning Unit, Casement - E Air Gauge, Tire - S Air Hoist - E Air, Compressed - S Alarm Door - E Album - S Alidade, Telescopic - E Alignment Gauge, Camber, Toe-in Etc. - E Ammonia - S Ampoule - S Anatomical Chart - AV Anatomical Model - E Andiron - E Anemometer - E Anesthetic - S Aniline Dye - S Animal Box - S Ant Colony - S Antenna, Mobile, Truck - E Anti-Freeze - S Antiseptic - S Antiseptic Gauze - S Antitoxin - S Anvil - E Apparatus Cabinet - E Applicator, Throat - S Apron - S Aquarium - E Arc Welding Apparatus - E Arch Support - S Archery Set - S Architect’s Scale, 1 in. meas. - S Armature Growler - E Arrows - S Art Canvas - S Art Crayons - S Art Eraser - S Art Paint - S Art Paper - S Asbestos - S Ash Can - S Asphalt - S Asphalt Roofing and Siding - S Astringent - S Astrograph, Wall - E Athletic Uniform - S Atlas - S Atomizer - S Audiometer - E Auger - S Auger Bit - S Autoclave - E Automatic Regulating Valve - S Automobile - E Automobile Control for Handicap - S Automobile Defroster - S Automobile Fuel Tank - S Automobile Heater - S Automobile Lift - E Automobile Signal - S Automobile Tires and Tubes - S Awl - S Axe - S Supplies, Equipment, AV List B Babbit Metal - S Baby Dolls Computerized - E Badge - S Badminton Racket - S Bag, Camera - S Bag, Courier/Canvas - S Bag, Laundry - S Bags, Golf, Leather - E Baking Pan - S Baking Powder - S Baking Soda - S Balance, Beam - E Balance, Small Spring - S Baling Press, Compression Molding - E Ball - S Ball Bearings - S Ball Cages - S Ball Peen Hammer - S Ballast - E Balloon - S Ballot Box - S Band Instrument - E Band Saw - E Band Saw Blade - S Bandage - S Bands, Rubber - S Banner - S Bar, Horizontal, Portable - E Barbell - E Barbell Set - E Barber Shop Tools, Electrical - E Barber Shop Tools, Hand - S Barber Type Furniture - E Barograph - E Barometer - E Barrel - S Base, Baseball - S Base, Electric Lamp - S Baseball - S Basin, Portable - S Basket, Container - S Basketball - S Basketball Shoes - S Bass Drum Hoops - S Bat - S Bath Curtain - S Bath Mat - S Bath Robe - S Bathtub Fittings - S Baton - S Batons for Police Academy - E Batteries - S Batteries, Electric - S Battery Chargers - E Battery Crimper - E Battery Elements - S Batting Tee - S Batting, Cotton - S Beads, Arts and Crafts - S Beaker - S Beanbag - S Beanbag Chair - E Bearings, Ball - S Bearings, Roller - S Beater, Egg, Electric - E Beater, Egg, Hand - S Beauty Class Furniture - E Bed - E Bed Pan - S Bed Spread - S Bed Springs - S Bed, Day - E Bedding - S Beef Extract - S Beeswax - S Bell, Small Hand or Desk - S Bellow, Hand - S Bellow, Power - E Belt Dressing - S Bench - E Bench Stops - S Benzene - S Bevel - S Bicycle - E Bicycle Rack, Portable - E Billhead - S Billing Machine - E Binder, Agricultural - E Binder, Loose-leaf - S Binding Cloth - S Biological Chart - AV Biological Model - E Biology Specimen - S Supplies, Equipment, AV List Bit - S Bit Brace - S Bit Tools - S Bits in a set - S Blackboard Pointer - S Blackboard, Portable - E Blackboard, Small Slate - S Bladder - S Blade, Saw - S Blanket - S Blanket, Fire - E Blanks, Printed - S Bleach - S Bleacher, Portable - E Blender - E Blinds, Mini - S Block, Hat - S Block, Kindergarten - S Block, Surface Hardened - S Block, Terminal - S Blood Analysis Apparatus, Complete - E Blood Plasma Cabinet - E Blood Pressure Apparatus - E Blotter - S Blotter Holder - S Blotter Pad - S Blowpipe - S Blue Print Machine - E Blue Print Paper - S Bluing - S Board, Bread - S Board, Bulletin, Portable - E Board, Carom - S Board, Checker - S Board, Cork - S Board, Drawing - S Board, Dry Erase - E Board, Emery - S Board, Flannel - S Board, Highlight - E Board, Ironing - S Board, Lumber - S Board, Mounting - S Board, Sandwich - S Board, Wash - S Boat or Canoe - E Bobbin - S Bodkin - S Body, Bus - E Body, Truck - E Boiler Cleaner - S Boiler Compound - S Boiler Firing Tools - S Bolt - S Bolt Cutter - S Bond Paper - S Book Card - S Book Cloth - S Book Ends - S Book Jacket - S Book Plate - S Book Pocket - S Book Record - S Book Stacks - E Book Truck - E Book, Cash - S Book, Composition - S Book, Library - E Book, Loose-leaf Note - S Book, Records - S Book, Text - S Bookbinding Machinery - E Bookcase, Sectional - E Bookcover - S Bookkeeping Forms - S Bookkeeping Machine - E Boomwacker - E Boring Machine, Precision Table or Vertical Types -E Bosing Ring, Complete - E Bottle - S Bottle Siphon - S Bow, Archery - S Bowl - S Bowl, Water Closet - S Bowling Alley Pin - S Box File, Cardboard - S Box, Electrical - S Boxing Gloves - S Boyle's Law Apparatus, Complete - E Brackets - S Brake Lining Machine - E Brakes & Folders, Hand or Power - E Brakes, Complete Replacement Unit - S Braking Lining - S Supplies, Equipment, AV List Brass Polish - S Brass Rod - S Brass Sheet - S Bread Board - S Bread Knife - S Bread Pan - S Bread Slicer, Electrical - E Bread Slicer, Mechanical - E Breaker, Circuit - S Bricks - S Bridges, Wheatstone and Similar - E Bridle - S Briefcase - S Broiler, Electric - E Brushes - S Bug Spray - S Bulb, Electric Light - S Bulb, Flower - S Bulletin Board, Portable - E Bunting - S Burettes - S Burlap - S Burner, Bunsen - S Bus Accessories - S Bus Repair Parts - S Bus Ticket - S Bus Tires & Tubes - S Bus Token - S Bus Wagon - E Busing - S Butter Spreader - S Buttons - S Buttons, Push - S Buzzer - S Supplies, Equipment, AV List C Cabinet, Apparatus - E Cabinet, Beverage Cooling, Ice/Elec - E Cabinet, Filing - E Cabinet, Frozen Food Storage - E Cabinet, Ice Cream, Ice/Electric - E Cabinet, Laboratory - E Cabinet, Lantern Slide - E Cabinet, Print, Drafting - E Cabinet, Printers, Galley - E Cabinet, Printers, Type - E Cabinet, Supply - E Cables - S Cage, Ball - S Cage, Hamster - E Cake Knife - S Cake Pan - S Cake Soap - S Calcimine - S Calculating Machine - E Calculator, Pocket - S Calendar - S Calendar Pad - S Calendar Stand - S Calico - S Caliper - S Call Bell - S Calorimeter, Continuous Flow - E Calorimeter, Electric - E Camera, Motion Picture - E Camera, Still - E Can Cover - S Can Opener, Hand - S Can, Ash - S Can, Gas - S Candle - S Candlestick - S Cane - S Canner - E Canoe - E Canvas - S Canvas Bag - S Cap, Metal - S Car Seat - E Carbide - S Carbon Dioxide - S Carbon Paper & Ribbon - S Carborundum Stone - S Carburetor - S Card - S Card Holder - S Card Punching & Sorting Device - E Card Rack - E Card Table - E Card, Computer - E Cardboard - S Cardboard Box - S Carpenters' Square - S Carpet - E Carpet Beater - S Carrom Board - S Carrom Cues - S Carrom Rings - S Cart, Game, Leap Pad - S Carving Knife - S Case, Brief - S Case, Cardboard - S Case, Display - E Case, File - E Case, Laboratory - E Case, Supply, Cloth - S Case, Supply, Hard - E Case, Type - E Cash Box - S Cash Register - E Cassette Player - E Casting Bronze - S Catalogue Card - S Catches - S Cattle - E Caulking Compound - S Caulking Iron, All Sizes - S Caustic - S Cellophane - S Celluloid - S Cement, Construction - S Cement, Liquid - S Centering Machine - E Centrifuge - E Certificate - S Chafing Dish - S Chain - S Chain Hoist - E Supplies, Equipment, AV List Chain, Tire - S Chair - E Chair Mat - E Chair Pad - S Chair, Beanbag - E Chair, Folding - E Chalk - S Chamois - S Change Holder - S Charcoal - S Charge Slips - S Charger, Battery - E Chart - AV Chart Rack - E Chart Stand - E Chart, Eye - AV Chart, Flip - AV Chassis, Bus - E Chassis, Truck - E Check Handling Machine - E Check Writer - E Check, Brass - S Checkbook - S Checker Board - S Checkers - S Cheesecloth - S Chemicals - S Chemistry Glassware - S Chemistry Rubber Goods - S Chinaware - S Chisel, not in Sets - S Chisels, in Sets - E Chopper, Food, Hand - S Chopper, Food, Power - E Choral Robes - S Circuit Breakers - S Clamp - S Clay - S Clay, Modeling Tool - S Cleaner, Flue - S Cleaner, Steam Vapor - E Cleaner, Vacuum - E Cleaning Compound - S Clinometers, Photoelectric - E Clip - S Clippers, Hair, Electric - E Clippers, Hair, Hand - S Clock, Desk - S Clock, Wall - E Cloth - S Cloth Cutting Machine - E Cloth Net - S Clothes Basket - S Clothes Brush - S Clothes Dryer - E Clothes Hook - S Clothesline - S Clothespins - S Club, Golf, Individual - E Clubs, Golf, Set - E Clutch Rebuilding Apparatus - E Coal - S Coal Bag - S Coal Hods - S Coal Screen - S Coal Scuttle - S Coal Shovel - S Coat Hanger - S Coat Hook - S Cocoa Mat - S Coffee Can - S Coffee Grinder - E Coffee Percolator, Electric - E Coffee Pot - S Coffee Urn - E Coin, Currency & Check Handling Machine - E Coke - S Colander - S Collapsible Table - E Collator, Metal - E Colony, Ant - S Colored Pencils - S Colorimeter - E Coloring Dye - S Comb - S Combine - E Combustion Analyzer - E Comealong - E Comparator - E Compass, Blackboard - S Compass, Drawing - S Compass, Magnetic - E Compass, Magnetic, Pocket - S Compound, Chemical - S Compound, Cleaning - S Compound, Grinding - S Compound, Patching - S Compressed Air - S Compressor, Air - E Supplies, Equipment, AV List Computer Adapter - E Computer Cables - S Computer Cards - E Computer Glare Screen - E Computing Machine - E Condenser, Electronic - E Condenser, Ignition Distribution - S Condiment - S Conduit Box - S Conduits and Fittings - S Connecting Rod Align - E Connecting Rod Boring Machine - E Connecting Rod Rebabbiting Jig - E Connector, Phone Net - S Connector, Wire - S Construction Paper - S Container - S Converter Toi - S Conveyor - E Cooker, Pressure - E Cooking Stove - E Cooking Utensil - S Cooler, Igloo - E Cooler, Styrofoam - S Cooler, Water - E Coping Saw Blade - S Copper - S Copper, Soldering - S Copyholder - S Cord - S Cord, Electric - S Cores, Valve - S Cork - S Corkboard - S Corkscrew - S Cornice, Metal - S Correction Fluid, Stencil - S Corrosive - S Corrugated Paper - S Costume, Cloth - S Costume, Theatrical - S Cot - S Cotter Pin - S Cotton Gauze - S Cotton, Absorbent - S Couch - E Counter Freezer - E Counter, Revolution & Stroke - S Countersink - S Coupling - S Courier Bag - S Cover - S Coverall - S Covers, Toilet Seat - S Crayons - S Creeper - E Crib - E Crimper, Battery - E Crock - S Crockery - S Cross- Section Paper - S Crucible - S Crude 0il - S Crushed Rock - S Crutches - S Crystal, Watch - S Cue, Carrom - S Cultivator - E Culvert, Sheet Metal - S Cup - S Cup Award - S Cup Grease - S Cup Hook - S Cupboard - E Curling Iron - S Curtain Rod - S Curtain, Shower & Window - S Cuticle Pusher - S Cutlery - S Cutter, Glass - S Cutter, Mat - E Cutter, Pastry - S Cutter, Pipe - E Cutter, Plane - S Cylinder Boring Machine - E Cylinder Oil - S Cylinder, Dictating Machines - S Cylinder, Gas - E Cylinder, Hydrometer Jar - S Cylinder, Mailing - S Supplies, Equipment, AV List D Damper - S Date Stamp - S Dater - S Dating Machine - E Daybed - E Daybed Mattress - S Decorations - S Deep Fat Fryer - E Deep Freezer - E Dental Abrasive Points - S Dental Bench - E Dental Cabinet - E Dental Chair - E Dental Chart - S Dental Drill - S Dental Drilling Apparatus - E Dental Instruments, Small - S Deodorizer - S Desk - E Desk Blotter - S Desk Lamp - S Desk Letter Basket - S Desk Pad - S Developer, Photographic - S Developing Tank - S Dextrin - S Dextrose - S Diaper Genie - S Diapers - S Diary - S Dictating Machine - E Dictating Machine Cylinder - S Dictionary Stand - E Dictionary, Abridged - S Dictionary, Large Unabridged - E Dies, in Sets - E Dies, not in Sets - S Diesel Engine for Classroom Use - E Diesel Engine, Integral Parts of Larger Units - S Digger, Posthole - S Diploma - S Diploma Cover - S Diploma Ribbon - S Diploma Seal - S Disc, Optical - E Disc, Phonograph - S Dish Brush - S Dish Cloth - S Dish Pan - S Dish Truck - E Dishes - S Dishwashing Machine - E Disinfectant - S Disk, Laser - AV Dispenser, Paper Towel - E Dispenser, Sanitary Napkin - E Dispenser, Soap - S Dispenser, Toilet Seat - E Display Case - E Display Mount - S Dissecting Set - S Distilled Water - S Distilling Apparatus - E Distributor - S Distributor Box - E Ditto Machine - E Dividers - S Doilies - S Doll - S Doll, Baby, Computerized - E Dolly, Trash Can - E Door - S Door Mat - S Door, Alarm - E Dowel - S Drafting Machine - E Dragline - S Drain Cleaners - S Drain Pan - S Drain Plugs - S Drain Plunger - S Drain Tile - S Drainpipe Flusher - S Drapery Cloth - S Drapes - S Supplies, Equipment, AV List Drawing Board - S Drawing Compass - S Drawing Instruments - S Drawing Paper - S Drawing Pen - S Drawing Table - E Dresser, Emery Wheel - S Dressing, Belt - S Drier, Ink - S Drier, Paint - S Drier, Varnish - S Drift Meter - E Drift Pins, all sizes - S Drill Bits - S Drill Bits Set - S Drill Points - S Drill Press, Bench, Floor/Radial - E Drill, Hand - S Drill, Power - E Drinking Water Cooler, Elec/Ice - E Drugs - S Drum, Bass, Hoops - S Drum, Bass, Kettle, Snare - E Drum, Fiber - S Drum, Metal - S Drumheads - S Drumstick - S Dry Cells - S Dry Erase Board = E Dry Goods - S Dry Measures - S Dryer, Clothes - E Dryer, Hair - E Drying Unit, Infra-red - E Dumbbells - S Duplicating Machine - E Duplicating Machine Brush - S Duplicating Machine Ink - S Duplicating Machine Paper - S Duplicating Machine Parts - S Duplicating Machine Roll - S Dust Cloth - S Duster - S Dustpan - S Dye - S Supplies, Equipment, AV List E Earthenware - S Easel - E Edge Toots, Except Cutting Dies - S Educational Test - S Eggbeater, Electric - E Eggbeater, Hand - S Elastic - S Electric Batteries - S Electric Box - S Electric Clippers, Sheep, Horse - E Electric Cord - S Electric Dishwasher - E Electric Floor Scrubber - E Electric Fuse - S Electric Games - E Electric Hole Punch - E Electric Hot Plate - E Electric Iron - E Electric Lamp Base - S Electric Light Bulb - S Electric Mixer - E Electric Sanding Machine - E Electric Stapler - E Electric Switch - S Electric Toaster - E Electric Tube Tester - E Electric Vacuum Cleaner - E Electric Waxing Machine - E Electric Welding Apparatus - E Electric Wire - S Electrode - S Electrolysis Apparatus - E Electromagnet, Laboratory - S Electronic Component - S Electronic Deviation Meter - E Electronic Frequency Meter - E Electronic Power Supply & Voltage Regulators- E Electronic Tube - S Electronic Volt-Ohmmeter - E Element, Battery - S Embosser - E Embossing Fluid - S Embossing Pan - S Emery Board - S Emery Cloth - S Emery Powder - S Emery Wheel - S Emery Wheel Dresser - S Enamel- S Enameled Ware - S End Table - E Engine Flushing Machine - E Engine, for Classroom Use - E Engine, Integral Parts for Larger Unit - S Engineer’s Scales, Measure - S Enlarger - E Envelope - S Envelope Sealer - E Epsom Salts - S Eradicator, Ink - S Eraser, Electric - E Eraser, Hand - S Essences - S Exhibit Case - E Exposure Meter, Camera - E Extensometer - E Extinguisher, Fire - E Extract - S Extractor - E Eye Chart - AV Eyelet - S Supplies, Equipment, AV List F Fabric - S Face & Eye Shield - S Face, Archery - S Falling Weight Rammer - E Fan, Electric, Portable - E Fastener - S Fastener, Apparel - S Faucet, Combination & Single - S Feldspar - S Felt - S Fencing Foil - S Ferrule - S Fertilizer - S Fiber Rod - S Fiber Sheet - S Fiber Tube - S Fiberboard - S Figures, Geometrical, Models, in sets - E File Box - S File Card, S File Folder - S File, Wood & Metal Working - S Filing Cabinet - E Filing Machine - E Filings - S Filler, Battery - S Filler, Ink - S Filler, Paint - S Filler, Wood - S Film - S Film Cement - S Filter Paper - S Filter, Small - S Fingers, Rubber - S Fire Axe - S Fire Blanket - E Fire Blanket - E Fire Extinguisher - E Fire Extinguisher Refill - S Fire Hook - S Fire Shovel - S Fire Tongs - S Fireplace Fixtures - E First Aid Kit - S Fittings, Lubrication - S Flag - S Flannel Board - S Flashlight - S Flask - S Flat Iron, Electric - E Flavoring - S Flaxseed - S Flexible Cord Set - S Flexible Metal Hose - S Flexible Metal Tubing - S Flip Chart - AV Float, Hydrometer - S Float, Plumbing - S Floor Oil - S Floor Scrubber, Electric - E Floor Wax - S Flour - S Flower Bulb - S Flowerpot - S Flowers - S Flue Cleaner - S Fluorescent lamp - S Fluorescent Starter - S Fluoroscope - E Flush Valve - S Flusher, Drainpipe -S Flux - S Fly Spray - S Flypaper - S Folder - S Folding Chair - E Folding Table - E Food - S Football - S Football Dummies, Tackling - S Football Helmet - S Football Shoes - S Football Uniform - S Forceps - S Forges - E Fork, Mulch - S Fork, Silverware - S Fork, Spading - S Fork, Tuning - S Forklift - E Supplies, Equipment, AV List Form, Dress - E Form, Geometrical, Model. in sets - E Form, Printed - S Formaldehyde - S Fossil in Rock - AV Foundry Machinery - E Frame, Blueprint - E Frame, Doors - S Frame, Mirror - S Frame, Ophthalmic - S Frame, Picture - S Frame, Saw - S Frame, Window - S Freezer - E Freezer, Ice Cream - E Frequency Meter - E Friction Tape - E Fruit - S Fuel - S Fumigant - S Fungicide - S Funnel - S Furnace, Heat Treating - E Furnace, laboratory - E Furnace, Remelting, Type Metal - E Furniture - E Furniture Polish - S Fuse - S Supplies, Equipment, AV List G Galvanometer - E Galvanoscope - E Game Cart, Leap Pad - S Game Cartridge - S Game, Electronic - E Game, Handheld - S Games - S Garbage Can - S Garden Hose - S Garden Tools - S Garment - S Garnet Paper - S Gas - S Gas Can - S Gas Compressor - E Gas Cylinder - E Gas Mantel - S Gas Meter, Laboratory Type - E Gas Plate - E Gas Stove - E Gasket - S Gasoline - S Gasoline Dispensing Pump, Elec. - E Gasoline Dispensing Pump, Hand - S Gauge - S Gauge, Tire - S Gauze - S Gear Cutting Machine - E Gears - S Gelatin - S Gelatin Duplicator - E Gelatin Pad - S Generator, Integral Part of Larger Unit - S Generator, Not integral Part of Larger Unit - E Geographic Globe, Large Stand Type - E Geographic Globe, Small Desk - S Glass - S Glass Cutter - S Glass Wool - S Glass, Plexiglas - S Glass, Watch - S Glasses, Drinking - S Glasses, Magnifying - S Glasses, Ophthalmic - S Glassware - S Glaze - S Glides - S Globe, Geographic, Large Stand - AV Globe, Geographic, Small Desk - AV Gloves, Rubber - S Glue - S Gluegun - S Glycerin - S Goggles - S Golf Bag, Leather - E Golf Club, Individual - S Golf Clubs, Set - E Graduated Measures - S Graph Paper - S Graphite - S Grass Seed - S Grass Shears, Hand Operated - S Grass Shears, Power Operated - E Grate, Stove - S Gravel - S Grease - S Grease Gun, Air, Gun Only - S Grease Gun, Hand - S Grinder, Hand Operated - S Grinder, Power Operated - E Grinding Compound - S Grinding Wheel - S Groceries - S Guard, Arm - S Guard, Lamp - S Guard, Shin - S Gummed Cloth - S Gummed Figures - S Gummed Labels - S Gummed Seals - S Gummed Tape - S Gun, Starting - E Gym Shoes - S Gypsum - S Supplies, Equipment, AV List H Hacksaw - S Hair Clippers, Electric - E Hair Clippers, Hand - S Hair Dryer - E Hairpins - S Hall Tree - E Hammer, Autobody, Pneumatic, Etc. E Hammer, Ball Peen - S Hammer, Electric, Hand - E Hammer, Light Forged - S Hammer, Sledge - S Hamper - S Hamster Cage - E Hand Bag - S Hand Saw - S Hand Stamp - S Hand Tools, in sets - E Hand Tools, Power Driven, Pneumatic&Elect- E Hand Truck - E Handball - S Handbook - S Handcuffs - E Handheld Games - S Handle - S Handscrew, Wood & Iron - S Hanger, Clothing - S Hanger, Hardware - S Hanger, Rug - E Hardware - S Harness - E Harrow - E Hat Block- S Hatchet - S Headlight - S Headphones - S Headset, over $150 - E Heater, Portable - E Heating Pad - S Hectograph - E Helmet, Football - S Hemp Fiber - S Henna - S Highlight Board - E Hinge - S Hods, Coal - S Hoes, Garden - S Hoist, Electric & Pneumatic - E Holder, Blotter - S Holder, Change - S Holder, Change - S Holder, Copy - S Holder, Dictionary - E Hole Punch, Electric - E Hooks - S Hoops, Bass Drum - S Horn, Motor Vehicles - S Horse - E Horses, Gym Equipment - E Horseshoes - S Hose Nozzle - S Hose, Apparel - S Hose, Clamp - S Hose, Garden - S Hose. Flexible Metal - S Hot Plate - E Hot Water Bottle - S Hurdle - E Hydraulic Jack, Garage Type - E Hydraulic Wheels - S Hydrometer - S Hydrometer Float - S Hygrometer - S Hypodermic Needle - S Hypodermic Syringe - S Supplies, Equipment, AV List I Ice - S Ice Bag - S Ice Cream Freezer - E Idoform - S Ignition Coil - S Incandescent Lamp, Bulb - S Index Cards - S Index Labels - S Index Tabs - S Indian Clubs - S Inductance Standards - E Ink Drier - S Ink Eradicator - S Ink Pad - S Ink- S Inkwell and Parts - S Inner Tube, Auto - S Insect Net - S Insect Screening - S Insecticide - S Insignia - S Instrument, Band & Musical - E Instrument, Dental, Small - S Instrument, Drafting - S Instrument, Medical, Small - S Instrument, Musical - E Instrument, Recording, Elec. - E Instrument, Surgical, Small - S Insulator - S Intelligence Test - S Interferometer - E Interval Timer - S Iodine - S Iron Filings - S Iron Gauze - S Iron Wedge - S Iron, Electric - E Iron, Sheet - S Ironer - E Ironing Board - S J Jack, Garage Type, Hydraulic - E Jack, Mechanical - S Jacket, Book - S Jar - S Jointer - E Joints, Plumbing - S Juice Extractor, Electric - E Jump Standards - E Jumper Cables - S K Kerosene - S Kettle - S Key - S Key Rack - E Key Ring - S Keyboard, Piano, Paper - S Keyhole Saw - S Kiln - E Kit, First Aid - S Kitchen Table - E Kitchen Utensils - S Knee Pad - S Knife - S Supplies, Equipment, AV List L Labels - S Laboratory Balance, Beam - E Laboratory Fittings, Plumbing - S Laboratory Furniture - E Laboratory Glassware - S Laboratory Model - E Laboratory Mount - S Laboratory Tools, Small Hand - S Lacing - S Lacquers - S Lactose - S Ladder - E Ladle - S Lag Screw - S Lamp Base - S Lamp Bulb - S Lamp, Desk - S Lamp, Drafting Table - S Lamp, Electric Floor - E Lantern - S Lantern Slide - S Lantern Slide Cabinet - E Laser Disk - AV Laser Pointer - E Lath - S Lathe, Brake Drum - E Lathe, Engine - E Lathe, TurreVAutomatic Screw Machines - E Lathe, Wood Turning - E Lawn Mower - E Lawn Roller - E Lawn Sprinkler, Movable - S Lead - S Lead Pencil - S Lead, Red - S Lead, Slug & Rule Casting Machine, Elrod - E Leap Pad Cart - S Leap Pad Machine - E Leather - S Leather Briefcase - S Leather Working Tool, Hand - S Lectern - E Ledger - S Lens - S Letter Basket - S Letter File - S Letter Opener - S Letter Press - E Letter Scales - S Letterhead - S Lettering Pen - S Level, Precision Machinist - S Level, Small or Carpenter - S Library Furniture - E Library Truck - E Lift, Vehicle - E Light Bulb - S Light Globe - S Lighting Unit, Blueprinting - E Lime - S Line Marker, Large Push Type - E Line Marker, Small - S Linens - S Liner, Staff, Music - S Liner, Type - S Lining, Brake - S Lining, Cloth - S Linoleum - S Linotype - E Linotype Metal - S Linseed Oil - S Liquid Bronzing - S Liquid Polish - S Liquid Soap - S Litmus Paper - S Livestock - E Loam - S Lock, Small, not built-in - S Locker, not built-in - E Locknut - S Loom - E Loose-leaf Notebook - S Lubricant - S Lubricating Oil - S Lubrication Fitting - S Lug, Soldering - S Lumber - S Supplies, Equipment, AV List M Machine Tools - E Machine, Adding - E Machine, Addressing - E Machine, Billing - E Machine, Bookkeeping - E Machine, Brake Lining –E Machine, Calculating - E Machine, Check Handling - E Machine, Coin Handling - E Machine, Coin Operated - E Machine, Dating, Power - E Machine, Dating, Small Hand - S Machine, Dictating - E Machine, Dishwashing - E Machine, Drafting - E Machine, Dry Cleaning - E Machine, Duplicating - E Machine, Laundry - E Machine, Leap Pad - E Machine, Mimeograph - E Machine, Mixing - E Machine, Numbering, Power - E Machine, Numbering, Small Hand - S Machine, Polishing - E Machine, Pressing - E Machine, Sanding - E Machine, Scrubbing - E Machine, Sewing - E Machine, Stamping, Power - E Machine, Stamping, Small Hand - S Machine, Tabulating - E Machine, Washing - E Machine, Waxing - E Machinery, Canning - E Machinery, Cement Making - E Magazine Cover - S Magazine Rack, Large Stand - E Magnet, Laboratory - S Magnifying Glass - S Mail Box - S Mallet - S Manicuring Tool - S Manila File - S Manila Folder - S Manila Rope - S Mannequin - E Map - AV Map Tracks - S Markers, Line, Large Push - E Markers, Line, Small - S Mat Cutter - E Mat, Chair - E Mat, Door & Bath - S Mat, Floor - S Mat, Gymnasium, Tumbling, Wrestling - E Matches - S Matrix, Type - S Mattocks - S Mattress - S Mattress, Daybed - S Mauls - S Meal - S Meat - S Mechanical Drawing Instrument - S Mechanical Pencil - S Medal - S Medical Instrument, small – S Medicine - S Medicine Balls - S Medicine Case - E Megaphone - S Memo Book - S Memory Chip - E Mending Materials - S Mesh, Steel Wire - S Metabolism Apparatus - E Metal Polish - S Metal Stud Punch - E Metal Working Machinery - E Metal Working Tool, Small Hand - S Metal, Laboratory - S Metal, Linotype - S Metals, Die Casting - S Meter Stick - S Meter, Watt, Laboratory Type - E Microfiche - AV Microfilm Reader & Viewer - E Micrometer, in sets - E Micrometer, not in sets - S Microphone - E Microprojector - E Supplies, Equipment, AV List Microscope - E Milk Can - S Milking Machine - E Milliammeter - E Milling Machines, Bench/Floor - E Millivoltmeter - E Mimeograph Machine - E Mimeograph Paper - S Mineral Wool - S Minerals, Laboratory - S Mini Blinds - S Minute Book - S· Mirror Frame S Mirror, Large Wall - E Mirror, Small - S Miter Box - E Mixer, Electric - E Mobiles - S Model, Shop & Laboratory - E Modeling Clay - S Modeling Tool - S Molding, Metal - S Mop - S Mop Pail - S Mop Truck - E Mop Wringer - S Mortar - S Mortiser - E Moss - S Motion Picture Projector - E Motor Analyzer - E Motor Generator Set - E Motor Vehicle Parts - S Motor Vehicles - E Motor, Integral Part of Larger Unit - S Motor, Not Integral Part of Larger Unit - E Motorcycle - E Mounting Boards - S Mouse Balls - S Mouse Trap - S Mouse, Computer - E Mowers, Lawn - E Mucilage - S Mulch Fork - S Music Sheet - S Music Stand - E Musical Instruments - E Muslin - S Mustard - S Supplies, Equipment, AV List N Nail Polish - S Nails - S Napkins - S Napkins, Sanitary - S Neatsfoot Oil - S Needles - S Needles, Hypodermic - S Negative Rack - S Negative Tank - S Net, Cloth - S Net, Steel- E Newspaper - S Nibbling Machine - E Niffy Nabber - S Noise &. Field Strength Meter - E Notebook Cover - S Nozzle, Hose - S Numbering Machine, Power - E Numbering Machine, Small Hand - S Nuts - S O Oakum - S Oars - S Office Composing Machine - E Office Furniture - E Ohmmeter - E Oil - S Oil Can - S Oilcloth - S Ointment - S Oleomargarine - S Openers, Letter - S Ophthalmic Frames - S Optical Disc - E Organ - E Oscillograph - E Outlet, Electrical - S Outline Map - S Output Meter - E Oven - E Ovenware Dishes - S Oxygen - S Supplies, Equipment, AV List P Packing - S Pad, Desk - S Pad, Ink - S Pad, Shoulder - S Pad, Stamp - S Pad, Typewriter - S Pad, Writing - S Padding - S Padlocks - S Pads, Chair - S Pail - S Paint - S Paint Brush - S Paint Drier - S Paint Remover - S Paint Spraying Outfit - E Palette - S Pamphlet - S Pan - S Pantograph - S Paper - S Paper Clips - S Paper Cups - S Paper Cutter - E Paper Fasteners - S Paper Napkins - S Paper Punch - S Paper Towel - S Paper Towel Dispenser - E Parachute - S Paraffin - S Parts, Radio, Resistors, Tubes, Transformers - S Parts, Repair - S Paste - S Paste Brush - S Pasteboard - S Pasteboard Box - S Pastries - S Pastry Cutter - S Patching Compound - S Pattern - S Peat Moss - S Pedal, Foot - E Peeler, Electrical - E Pen Point - S Pencil - S Pencil Sharpener - S Pencil, Mechanical - S Penholder - S Penknife - S Pennant - S Pens - S Percolator, Coffee, Electric - E Periodical - S Permanent Waving Machine - E Pestle - S Phonograph - E Phonograph Needle - S Phonograph Record - S Phonograph Record Album - S Photocopying Apparatus - E Photoelectric Cell - S Photoengraving Apparatus - E Photograph - S Photograph Mount - S Photographic Lens - S Photometer - E Piano - E Piano Parts - S Picks - S Picture - E Picture Frame - S Picture Wire - S Picture, Large Wall - E Pigment - S Pillow - S Ping Pong Set - S Pinking Shears - S Pins - S Pipe - S Pipe Cutter - E Pipe Dies, in set - E Pipe Dies, not in sets - S Pipe Fitting - S Pipe, Steel - S Pipette - S Piston - S Piston Ring - S Pitch Pipe - S Pitcher - S Pitchfork - S Supplies, Equipment, AV List Plane Cutter - S Planer, Power - E Planing Machine, Photengravers - E Plaque, Permanent - E Plaster - S Plaster, Adhesive - S Plastic Wood - S Plate Glass - S Plate, Addressing Machine - S Plate, Battery - S Plate, Bench - E Plate, Book - S Plate, Hot - E Plate, Lantern Slice - S Plate, Photographic - S Plates - S Platform - E Player, Cassette - E Plexiglas - S Pliers - S Plow, Field - E Plow, Snow - E Plug, Drain S Plug, Spark - S Plumb - S Plumbing & Heating Valve - S Plumbing Fixture Fittings & Trim - S Plunger, Drain - S Pocket Calculator - S Pocket Chart, Plain - S Pocketbook - S Pointer - S Pointer, Laser - E Points, Drill - S Polarimeter - E Polariscope - E Pole - S Pole, Climbing - S Polish - S Portfolio, Leather - S Post - S Postal Meter - E Poster - S Posthole Digger - S Pot - S Pot Cleaner - S Potato Peeler, Large Machine - E Pottery - S Powder - S Power Sprayer & Duster - E Powersurge Strip - S Preservative - S Press, Arbor - E Press, Book, Bookbinders - E Press, Cylinder, Flat Bed, Printing - E Press, Engraving - E Press, Letter - E Press, Lithographic/Offset Print - E Press, Power - E Press, Punch, Foot Power - E Printed Material - S Printing Case - E Printing Frame - E Printing Ink - S Printing Materials - S Printing Press - E Printing Set, Rubber - S Printing Type - S Prism - S Projector, Motion Picture - E Projector, Still - E Protractor - S Pruner, Hand - S Pruner, Power - E Psychrometer - S Public Address System, Portable - E Pulley - S Pumice - S Pump - E Punch - S Puppet - S Push Buttons - S Push Cart - E Putty - S Pyrometer - E Q Quinine - S Quiver, Arrow - S Supplies, Equipment, AV List R Rack, Chart - E Rack, Wire Display - E Racket, Badminton - S Racket, Tennis - S Radio Receiving Set - E Radio Transmitter - E Radio Tube - S Raffia - S Rags - S Rake, Garden - S Rake, Window - E Range, Cooking - E Rasps - S Ratchet, Air - E Rattan - S Reamers - S Receptacles - S Record Book - S Record Forms - S Record Player - E Record, Phonograph - S Recorder, Sound - E Recording Tape & Wire - S Reeds - S Reel, Motion Picture Film - S Reels, Hose - S Reference Book - E Reflector, Parabolic - S Refracting Apparatus - E Refrigerator, Electric/Ice not built in - E Register, Cash - E Register, Printed - S Regulating Valve - S Regulator, Voltage - S Relief Map - S Remote Control - E Repair Parts - S Report Form - S Resistor - S Respirator - S Restocking Fee - same obj as item Retort, Glass Laboratory - S Ribbon, Adding Machines - S Ribbon, Addressing Machine - S Ribbon, Cloth - S Ribbon, Typewriter - S Rifles, ROTC - S Ring Toss Game - S Ring, Carrom - S Ring, Flying - E Ring, Key - S Rivets - S Robe, Choral - S Robot - E Rock & Fossil Collection - AV Rock, Crushed - S Roller Bearings - S Roller, Ink - S Roller, Lawn - E Rolodex Heavy Duty - E Roofing Materials - S Rope - S Rosin - S ROTC Guidon/Sphere - E ROTC Rifles - s Rotten Stone - S Rouge - S Router, Plate, Photoengraving - E Rowboat - E Rubber Goods - S Rubbish Can - S Rug Hanger - E Rug, Room Size - E Rug, Scatter - S Ruler - S Rules, Shrink & Circumference - S Supplies, Equipment, AV List S Saccharimeter - E Safe - E Safety Glass - S Safety Pins - S Salt - S Sand - S Sanding Machine - E Sandpaper - S Sandwich Board - S Sanitary Napkin Dispenser - E Sanitary Napkins- S Sash Cord - S Sash, Combination Screen & Storm - S Sash, Screen - S Sash, Storm - S Saucer - S Saw Blade - S Saw Frame - S Saw, Band - E Saw, Circular - E Saw, Hand - S Saw, Poeer Hack - E Sawdust - S Scales, Bean Balance - E Scales, Draftsmen's - S Scales, Plastic Balance - S Scales, Platform - E Scales, Spring - S Scalpel - S Scissors - S Scoop Shovel, Hand - S Scooter - E Scouring Powder - S Scraper, Hand - S Screen Door - S Screen, Computer Glare - E Screen, Projection, Portable - E Screen, Window - S Screw Extractor - S Screw Eyes - S Screw Hooks - S Screwdriver - S Screwdriver Set - E Screws - S Scrubbing Compound - S Scrubbing Machine - E Scythe - S Sealer, Envelopes - E Seasoning - S Seat - E Sectional Bookcase - E Sedative - S Seed, Grass - S Separator, Battery - S Serum - S Serving Tray - S Settee - E Sewing Machine - E Shaker, Laboratory - E Shampoo - S Shaper & Router - E Shaper, Bench & Floor - E Shears, Hand-Operated - S Shears, Power-Operated - E Sheaves - S Sheet Metal - S Sheeting - S Shellac - S Shelves, Steel - E Shelving Materials - S Shingles - S Shock Absorber - S Shoes & Boots - S Shopcoat - S Shorthand Writing Machine - E Shovel, Hand - S Shower Fittings - S Shrubs - S Shuffleboard Set - S Shuttlecock - S Siding, Sheet Metal - S Sifter - S Signs - S Silk Screen Printing Apparatus - S Silver Polish - S Silverware - S Sink Fittings - S Supplies, Equipment, AV List Skeleton, Plastic - E Skelton, Cardboard - S Skillet - S Skis - S Slats - S Sledge Hammer - S Slicer, Bread, Mechanical - E Slide Rule - S Slides, Lantern - S Slides, Microscope, Blank - S Slides, Microscope, Things on Slide - AV Slides, Projector - S Snaps - S Sneakers - S Snips - S Snow Shovel, Hand - S Soap - S Soap Dispenser - S Soccer Ball - S Soccer Shoes - S Socket Wrench - S Socket Wrench Set - E Socks, Pair - S Sod - S Soda, Baking - S Softball - S Softener, Water, Chemical - S Soil - S Soil Penetrometer - E Soil Test Mold - E Soldering Copper - S Soldering Materials - S Solvent - S Sound Recorder - E Spade - S Spading Fork - S Spark Plug Cleaning Machine - E Spark Plugs - S Spatula - S Speakers - E Specimen, Laboratory - S Spectroscope - E Sphygmomanometer - E Spikes - S Spirits - S Spirometer - E Splint - S Spokes - S Spokeshaves - S Sponge - S Spoon - S Spotlight - S Spray Mixture - S Sprayer, Power - E Spread, Bed - S Spreader, Manure - E Spreader, Tire - E Springs - S Springs, Furniture - S Sprinkler, Lawn, Movable - S Sprocket - S Squares - S Squeegee - S Stack, Book - E Stadia Rod - E Stadiometer - E Staff Liner, Music - S Stain Remover - S Stainer - S Stains - S Stakes - S Stamp Pad - S Stamp, Rubber - S Stamping Machine, Power - E Stamping Machine, Small Hand - S Stand, Calendars - S Stand, Chart - E Stand, Engine Repair - E Stand, Music - E Stand, Umbrella - E Standards, Jump - E Stapler, Electric - E Stapler, Foot, Power Operated - E Stapler, Heavy Duty - E Stapler, Small Hand - S Staples - S Starch - S Starter, Electric - S Stationery - S Statuary - E Steam Packing - S Steel Measuring Tape - S Steel Shelves - E Steel Wool - S Steel, Sheet - S Supplies, Equipment, AV List Stencil Correction Fluid - S Stencils - S Stenographer Notebook - S Stereoscope - E Sterile Gauze - S Sterilizer - E Stethoscope - S Stick, Composing - S Stick, Hockey - S Stilt, Sport - S Stitchers - E Stock Record - S Stockings - S Stone, Printers - E Stool - E Stop Watch - S Stop, Bench - S Stopper - S Storage Battery - S Storage Rack - E Stove - E Straight Edge - S Straw, Drinking - S Stretcher - S Striking Bag Outfit - E String - S Stud Punch, Metal - E Stylus - S Sunglass Frame - S Sunglasses - S Supply Case - E Support, Back, Belt - S Supporter, Athletic - S Surface Hardened Block - S Surge Protector - S Surgical Instrument, Small - S Surgical Powder - S Swage - S Switch Box - S Switch, Electric - S Synchronizer, Camera - S Syringe - S Syrup - S Supplies, Equipment, AV List T Table - E Table Protector - S Table Tennis Ball - S Table Tennis Racket - S Table, Computing - S Tablecloth - S Tablet, Medicinal - S Tablet, Writing - S Tabs, Index - S Tabulating Machine - E Tack Hammer - S Tacks - S Tags - S Talcum Powder - S Tank, Bulk Storage, not Integral Part of Buildings or Building Services - E Tank, Carpet Shampooer - S Tape - S Tape Measure - S Taps - S Tar Roofing and Siding - S Target, Archery - S Team Uniform - S Tee, Batting - S Teeth Dinosaur - E Telephone - E Telescopic Pole - E Television Set - E Television Tube - S Television Wall Mount - E Tennis Ball - S Tennis Court Net, Cord - S Tennis Court Net, Steel - E Tennis Racket - S Tent Wall - E Tent, Shelter - S Terminal, Battery - S Test Tube - S Test Tube Brush - S Test Tube Rack - S Test, Achievement - S Textbook - S Theatrical Costume - S Theodolites & Tripods - E Thermograph - E Thermometer - S Thermometer, Ear, Digital - E Thermostat - S Thimble - S Thinner - S Thread - S Throat Applicator - S Thumb Tacks - S Tickets - S Tile, Drain - S Timer - S Tin Can - S Tin Cutters - S Tinware - S Tire Chains - S Tire Iron - E Tires & -Tubes - S Tissues, Cleansing - S Toaster, Electric - E Toggle Bolt - S Toilet Paper - S Toilet Seat Covers - S Toilet Seat Dispenser - E Tokens - S Tongs - S Tongue Depressors - S Tool Set, Hand - E Toolbox, Heavy-duty - E Tools, Hand, not in sets - S Topsoil - S Tow Bar - S Towels - S Toys - S Toys, Riding - E Tracing Cloth - S Tracing Paper - S Tractor - E Tractor Set - E Trammel - S Transformer, Laboratory - S Transmission, Integral Parts of Larger Units - E Transmission, Not Integral Part of Larger Units - E Supplies, Equipment, AV List Trash Can Dolly - E Triangle, Drafting - S Trimmer, Hedge, Hand - S Trimmer, Hedge, Power - E Tripod, Camera - E Trophy - S Trowel - S Truck, Hand - E Truck, Motor - E Tube, Inner - S Tube, Radio - S Tube, Television - S Tubing Material - S Tumbler, Glass - S Tuning Fork - S Tunnel, Models, Wind - E Turpentine - S Tweezers - S Twine - S Type Case - E Type Casting Machine - E Type Cleaner - S Type Liners - S Type Matrix - S Type, Printing - S Typewriter - E Typewriter Brush - S Typewriter Cover - S Typewriter Desk - E Typewriter Ribbon - S U Ultrasonic Cleaner - E Umbrella, Hand – S Umbrella, Large - E Umbrella Stand - E Unguent - S Uniform - S Upholstering Material - S UPS Power Supply - E Urn, Coffee - E Urn, Flower - S Utensils - S V Vacuum Beater Bar - S Vacuum Bottle - S Vacuum Cleaner - E Vacuum Tube Voltmeter - E Valve - S Valve Part - S Vaporizer, Electric - S Varnish - S Varnish Drier - S Varnish Remover - S Vase - S Vaulting Pole - S Vegetables - S Vending Machine - E Vibrograph - E Vines - S Vise, Bench - E Vise, Small Hand - S Vision Chart - AV Volleyball Net - S Volleyballs - S Voltmeter - E Supplies, Equipment, AV List W Wackers - E Wagon - E Wall Brush - S Wall Mount - E Wall Rocks - E Wall Screen - E Wallboard - S Wallpaper - S Washbasin - S Washcloth - S Washer & Dryer, Photographic - E Washers, Rubber & Leather - S Washing Machine - E Washing Powder - S Washtub - S Waste, Machinists, Etc. - S Wastebasket - S Watch Crystal - S Watch, Stop - S Watchmen's Time Clock - E Water Color Brush - S Water Cooler - E Water Glass - S Water Meter, Laboratory Type - E Water Softener - S Water, Distilled - S Watts Meter, Laboratory Type - E Wave Meter & Wave Analyzer - E Wax Crayons - S Wax, Liquid - S Wax, Paste - S Wax, Sealing - S Waxing Machine - E Weaving Machine - E Weighing Scale, Beam - E Weighing Scale, Small Spring - S Weight Set - E Weights - S Welding Apparatus - E Welding Rod - S Wheel Straightening Apparatus - E Wheel, Automobile - S Wheel, Emery - S Wheel, Hydraulic - S Wheel, Lawn Mower - S Wheel, Pottery - E Wheelbarrow - E Whetstone - S Whiskbroom - S Whistles - S Window Glass - S Window Screen - S Window Shade - S Window Working Safety Belt - S Wipers - S Wire - S Wood Filler - S Wood Preservative - S Wood Stain - S Wood, Plastic - S Wool - S Wool, Glass - S Wool, Steel - S Work Bench - E Work Table - E Wrapping Paper - S Wrench, in sets - E Wrench, not in sets - S Writing Paper - S X X-Ray Machine - E Y Yard Bench - E Yard Brooms - S Yardstick - S Yarn - S Z Zinc - S Supplies, Equipment, AV List Index Accounting Standards ................................... 4 Accounts Payable ........................................ 18 Accounts Receivable ..................................... 8 Accrued Interest Payable ............................. 21 Accumulated Depreciation .......................... 14 Administrative Technology Services Function ................................................................. 62 Adult General Education ............................. 29 After School Snack Reimbursement ........... 29 Appropriations ............................................. 25 ARRA Economic Stimulus Capital Projects 44 ARRA Fiscal Stimulation............................ 29 Assets ............................................................ 6 Attribution of Costs ..................................... 68 Audio Visual Materials ............................... 15 Balance Sheet Accounts .............................. 6 Board Function ............................................ 60 Bond Anticipation Notes ............................. 23 Bond Reserve .............................................. 26 Bonds Payable ............................................. 23 Budgetary Credits ........................................ 25 Budgetary Debits ......................................... 17 Buildings and Fixed Equipment .................. 14 Capital Assets .............................................. 13 Cash ............................................................... 6 Cash - Interest Earning Deposits ................... 7 Cash Change Funds ....................................... 7 Cash in Lieu of Donated Foods ................... 30 Cash on Demand Deposit .............................. 6 Cash on Hand ................................................ 7 Cash with Fiscal/Service Agents ................... 7 Categorical State Sources ............................ 31 Central Services ........................................... 61 Certificates of Participation Payable. .......... 24 Child Care Food Program ........................... 29 Community Action Programs ...................... 28 Community Services ..................................... 3 Community Services Function .................... 62 Computer Software ..................................... 15 Construction in Progress ............................. 15 Cost Elements .............................................. 65 Cost Reporting Process ............................... 72 Current Assets ............................................... 6 Current Liabilities ........................................ 17 Debt Service Function.................................. 63 Debt Service Funds ...................................... 42 Deferred Revenues ....................................... 24 Deposits Payable .......................................... 21 District Bonds Payable ................................. 23 Drug Free Schools........................................ 29 Due From Budgetary Funds ........................... 9 Due From Internal Funds ............................... 9 Due From Other Funds .................................. 9 Due from Reinsurer...................................... 12 Due to Fiscal Agent ..................................... 22 Due to Other Agencies ................................. 21 Eisenhower Math and Science ..................... 29 Elementary and Secondary Education Act, Title I........................................................ 29 Encumbrances .............................................. 17 Endowments ................................................. 25 Enterprise Funds .......................................... 46 Equipment Criteria .................................... 95 Estimated Liability for Arbitrage Rebate ..... 22 Estimated Liability for Claim Adjustment Expenses .................................................. 22 Estimated Liability for Long-Term Claims . 24 Estimated Liability for Self-Insurance Program .................................................... 22 Estimated PECO Advance Payable ............. 24 Estimated Revenues ..................................... 17 Estimated Unpaid Claims- Self-Insurance Program .................................................... 22 Expenditures .................................................. 3 Facilities Acquisition and Construction Function ................................................... 61 Facility ........................................................... 3 Federal Direct. Revenue............................... 28 Federal Impact Funds ................................... 28 FEFP ............................................................ 30 Fiduciary Funds ......................................... 94 Fiscal Services Function .............................. 61 Fiscal Year ..................................................... 4 Fixed Assets ................................................. 13 Florida Education Finance Program ............ 30 Food Service ................................................ 35 Index Food Services .............................................. 61 Function ......................................................... 3 Fund ............................................................... 2 Fund Equity ................................................. 25 General Administration Function ................ 60 General Fund ............................................... 41 General Support Services .............................. 3 General Support Services Function ............. 60 Gifts, Grants, and Bequests ......................... 35 Governmental Accounting Standards Board . 4 Grant ............................................................ 63 Improvements Other Than Buildings .......... 14 Individuals with Disabilities Education ...... 29 Information Services Function .................... 61 Instruction...................................................... 3 Instruction Function .................................... 58 Instructional Support Services....................... 3 Instructional Support Services Function ..... 58 Interest Receivable on Investments ............. 12 Internal Accounts Payable ........................... 22 Internal Funds ........................................... 78 Internal Service Funds .............................. 76 Internal Services Function ........................... 62 Inventory ..................................................... 11 Investments.................................................. 11 Investments - SBE/COBI Bonds ................. 12 Investments - Section 237.161 Loans ......... 12 Investments - State Board of Administration ................................................................. 12 Investments - U. S. Government Securities 11 Land ............................................................. 13 Liability for Compensated Absences .......... 24 Loans ........................................................... 39 Long-term Debt Proceeds and Sales of Capital Assets .......................................... 38 Long-Term Liabilities ................................. 22 Maintenance of Plant Function ................... 62 Matured Bonds Payable .............................. 21 Matured Interest Payable ............................. 21 MD&A .......................................................... 5 Medicaid ...................................................... 28 Motor Vehicle License Revenue Bonds Payable .................................................... 24 Motor Vehicles ............................................ 15 National Forest Funds ................................. 29 National School Lunch Act ......................... 29 Net Assets, Held in Trust ............................ 27 Net Assets, Restricted .................................. 27 Notes Payable............................................... 23 Nutrition Education and Training Program . 30 Object ............................................................. 3 Object Codes ................................................ 46 Obligations Under Capital Leases ............... 23 Operation of Plant Function ......................... 62 Optional Object Codes .............................. 96 Other Current Assets .................................... 12 Payroll Deductions and Withholdings ......... 21 Permanent Funds .......................................... 41 Petty Cash ...................................................... 6 Planning, Research, Development, and Evaluation Services .................................. 61 Program .......................................................... 3 Program Cost Accounting and Reporting .................................................................. 65 Project ............................................................ 4 Property under Capital Lease ....................... 15 R.O.T.C. ....................................................... 28 Racing Commission Funds .......................... 32 Reserved for Debt Service ........................... 26 Reserved for Encumbrances ........................ 25 Reserved for Ending Cash Balance.............. 26 Reserved for Endowments ........................... 25 Reserved for Inventory ................................ 26 Reserved for State Required Carryover Programs .................................................. 25 Revenue Accounts ...................................... 28 Revenues ........................................................ 2 Sale of Bonds ............................................... 38 Sales Tax Payable ........................................ 22 SBE/COBI Bonds ........................................ 12 School Administration Function .................. 60 School Breakfast Reimbursement ................ 29 School Internal Funds................................ 78 School Lunch Reimbursement ..................... 29 Section 237.151 Notes Payable.................... 22 Section 237.161 Loans ................................. 12 Section 237.161/237.162 Notes Payable ..... 23 Sinking Fund .............................................. 26 Special Act Bonds Payable .......................... 24 Special Revenue Funds ................................ 44 Staff Services Function ................................ 61 State Auto License ....................................... 31 State Board of Administration ..................... 12 Index State Board of Education/Capital Outlay Bond Indebtedness .................................. 23 State Fiscal Stimulation Funds .................... 28 State Required Carryover Programs ............ 25 Statistical Services Function ....................... 61 Student Fees ................................................ 35 Summer Food Service Program .................. 30 Supplies Criteria ........................................ 95 Taxes Receivable........................................... 7 Transfers ...................................................... 37 Transfers Function ....................................... 63 Transportation Services Function ................ 62 Travel ........................................................... 48 U. S. Government Securities ........................ 11 U.S.D.A. Donated Commodities.................. 29 Unreserved Fund Balance ............................ 26 Vocational Education Acts .......................... 28 Vocational Rehabilitation ............................ 29 Workforce Development .............................. 30 Workforce Investment Act ........................... 28 Index