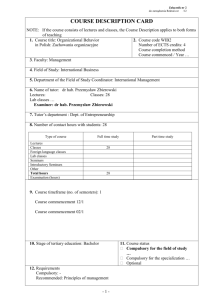
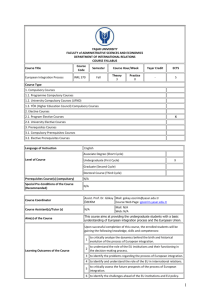
English Language Courses Offered at the AOU
advertisement

Student Guide For Undergraduate Degrees 2011-2012 Academic Year 2011-2012 1 Table of Contents Preface 5 The Arab Open University: the Beginnings 6 University Mission, Vision and Goals 6 1 Mission Statement 6 2 The AOU’s Vision 6 3 The AOU’s Goals 7 4 Reasons for Joining the AOU 7 5 Partnership with The Open University, UK 7 A System of Integrated Open Learning 8 1 The Student Learning Package 8 2 Tutorial Sessions 8 3 Student Attendance 9 4 Office Hours 9 Resources 9 1 Learning Resources 9 2 Computer Laboratories 9 3 Other Facilities 9 AOU Branches 10 Quality Assurance 10 1 Designing Learning Materials 10 2 Managing and Monitoring of Tutors 10 3 Assessment 11 Admission Requirements 12 Language Placement Tests 13 English Language Levels Offered at the AOU 13 2 Credit Transfer (Course Equivalence) 14 Academic Degrees Offered at the AOU 14 1 BA (Honours) in Business Studies 15 2 BA (Honours) in English Language and Literature 15 3 BSc (Honours) in Information Technology and Computing 16 4 Academic Programmes Offered by the Faculty of Education 16 4.1 Bachelor of Education (BEd) in Elementary Education 16 16 4.2 Postgraduate Diploma in Education 4.3 Bachelor Degree (BEd) in Special Education 16 4.3.1 Specialization: Mental Retardation 4.3.2 Specialization: Learning Difficulties 4.4 Diploma in Special Education (Mental Retardation) 16 4.5 BEd for Intermediate and Secondary Stages 5 Faculty of General Studies 17 5.1 Compulsory and Elective Courses 17 5.2 Exemption from Arabic Language Skills Courses 18 5.3 Non-Native Speakers of Arabic 18 6 Exit Awards 18 6.1 English Language and Literature Exit Awards 7 Future Developments 18 19 Key University Regulations and Policies 20 1 Students with Special Needs 20 2 Student Appeals 20 3 Cheating and Plagiarism 20 4 Inability to Take the Final Examination 21 5 Repeating Courses 21 6 Attendance at Tutorials 22 3 7 Duration of Study and Study Load 22 8 Prerequisites 22 9 Postponement, Suspension and Withdrawal 22 10 Granting the Bachelor’s Degree 23 11 Award/Grade Classification 23 12 Study Fees 24 13 Student Transfer 25 Transfer Between Academic Programmes 25 Transfer Between Branches 25 14 Student Conduct, By-laws and Disciplinary Procedure 26 15 University Website and Addresses 28 16 University Headquarters and Branches 29 Appendix 1 30 Appendix 2 41 Appendix 3 47 Appendix 4 50 Appendix 5 54 4 Preface Dear Student Welcome to the Arab Open University. This is our student guide: the Arab Open University (AOU) is not only the perfect choice for high quality education and training, but also your gateway to future career opportunities. It gives you all the information you need to understand what the AOU can do for you: details of entry requirements for the different academic specializations, and general course requirements which show how the University will help you develop your language and computing skills and improve your knowledge of Arabic and Islamic civilization. The guide gives you an overview of the University: its foundation, objectives, programmes and general rules and systems of learning and teaching. It introduces you to the courses, examinations, and assessment systems and answers many frequently asked questions. Your tutors will be your main link with the University so do not hesitate to get in touch with them if you need help – they will be able to put you on the right track. Our administrative staff is also here to help and support you. In return, what we expect from you is commitment to the ethos of the AOU, to its academic achievements and to its high standards. The AOU is a partner of The Open University, UK (www.open.ac.uk). The AOU student guide and th OU’s “ Student’s guide to studying on a programme validated by The Open University” complement each other and should be read by all AOU students and staff. Both guides are available on our website www.arabou.edu.kw. More information about validation by The Open University .UK, can be found at www.open.ac.uk/validate. We look forward to seeing you at the Arab Open University. 5 The Arab Open University: the Beginnings The AOU: A Brief History In 1996, the chairman of the Arab Gulf Programme for United Nations Development Organizations (AGFUND), HRH Prince Talal Bin Abel Aziz, took steps towards establishing the Arab Open University as a pan-Arab project. A working group was established under the chairmanship of HRH Prince Talal to create a development plan and leading international consultants Arthur Andersen were contracted to conduct a comprehensive feasibility study. The concept of the Arab Open University (AOU) was formally presented to a UNESCO regional conference held in Beirut in March 1998 and subsequently to a UNESCO international conference in Paris, in October of that year. Five Arab states – Bahrain, Egypt, Jordan, Kuwait and Lebanon – offered to host the AOU’s headquarters and a decision was made in December 2000 for the headquarters and a branch to be located in Kuwait. At the same time, branches were established in Bahrain, Egypt, Jordan, Lebanon and Saudi Arabia and a seventh branch, which started operating in September 2007, was opened in the Sultanate of Oman. As part of its long-term plans, the AOU intends to open two more branches in Palestine and Yemen, in collaboration with local authorities, and hopes to establish further branches, particularly in Syria and Sudan. Teaching at the AOU started in early October 2002 in the Kuwait, Jordan and Lebanon branches. Instruction in the Bahrain, Saudi Arabia and Egypt branches commenced in the fall semester of the academic year 2002/2003, while it started in the second/spring semester of the academic year 2007/2008 in the new Oman branch. University Mission, Vision, and Goals 1. Mission Statement The AOU is a higher education institution delivering an open education system of learning. The University is mandated to serve local and regional communities by offering marketdriven programmes of study and research at a pan-Arab level. The University, which is student-centred, promotes education for all and seeks to disseminate knowledge through carefully chosen undergraduate and graduate programmes delivered by highly qualified academics and supported by state of the art technology. 2. The AOU’s Vision The AOU is realising HRH Prince Talal Bin Abel Aziz’s vision of a sustainable education project by extending its services, and opening opportunities, in as many Arab countries as possible. The AOU seeks to offer opportunities to those who would not otherwise have access to higher education. It is committed to offering high quality programmes which respond to the market needs of the Arab world in education, health, engineering, business and other key sectors. Consistent with its mission and driven by the concept of lifelong learning, the AOU offers a platform for continuing education through a combined approach in which learning is implemented through online interactive learning. 6 3. The AOU’s Goals Based on the vision stated above, the AOU has adopted a set of objectives for its mission. These include: Offering opportunities of high quality higher education to a large and diverse population of students Developing a centre of excellence for open education and distance learning Providing a forum for continuing education across the region which will meet the needs of individuals and local communities Providing opportunities for professional training according to market demands Providing special opportunities in higher education to disadvantaged groups of potential students (e.g. women and those residing in remote areas) Participating, as a contributing partner, in promoting research and scholarly activities in areas of special concern to Arab society Promoting humanitarian and Islamic values and ethics. 4. Reasons for Joining the AOU The AOU is unique in the Arab world by virtue of its partnership with The Open University (UK), where its graduates receive two degrees, one from the AOU and a validated award from the OU (UK). Furthermore: The learning system of the AOU is a blend of face-to-face tutoring and self-instructional textbooks designed for distance learning by the OUUK, and uses the latest applications of electronic technology in teaching and learning (e-learning) High quality academic programmes are carefully selected and designed to meet the needs of both local and international markets Only 25% student attendance is required, compared to traditional modes of higher education which helps students who have time constraints, and other commitments such as family obligations (e.g. children), or who have disabilities Courses are designed to accommodate working students and those commuting from remote areas High quality interactive educational materials are employed Mobility and opportunities for credit transfer across branches are possible. The AOU encourages its students to become independent learners whereby self-learning is emphasized throughout their studies. This enables students to become lifelong learners beyond graduation. The language of instruction at the AOU is English, which not only improves students' proficiency in the English language, but also ensures better job opportunities after graduation. 5. Partnership with the Open University UK The AOU is approved by The Open University as an appropriate organization to offer higher education programmes leading to Open University validated awards. OU validated awards have parity of esteem with similar awards offered throughout UK higher education. A validated award 7 is exactly the same as an OU direct award in terms of employment or application for postgraduate study. Under this partnership, the OU (UK) provides the following to the AOU: Programmes and courses. Learning materials (textbooks, DVDs, etc.). Programme monitoring, external examining. Dual awards (BA/BSC), exit awards (diplomas and certificates) together with the AOU. A System of Integrated Learning The AOU learning and teaching model is based on high quality educational materials. The Open University-based courses offered at the AOU are taught in English and are licensed from the OU(UK). The following is a brief description of the model: 1. Students are allocated to an individual subject tutor in the ratio of 25:1 Learning is facilitated through a university-wide electronic Learning Management System (LMS) All branches are equipped with multimedia and computing laboratories to support students Student assessment is carried out through two main components: o Continuous assessment, i.e. Mid-Term Assessments (MTA) and Tutor Marked Assignments – (TMAs), and o Formal end of semester examinations Where each component comprises 50% of the overall assessment score. Tutors provide comprehensive feedback on students' TMAs to direct them towards better understanding of the subject matter, and to enhance their learning experience. The Student Learning Package This package, purchased from the student’s AOU branch, contains: Core teaching materials specially prepared for active, independent study A number of other items that vary slightly depending on the particular course requirements, e.g. further reading material in the form of set books, supporting notes, or study guides Audio-visual aids in the form of cassettes and CD-ROMs. The package contains most of the student’s needs for the study of his/her chosen courses. 2. Tutorial Sessions Tutorial sessions are designed to provide a forum for interaction between tutors and students on the one hand, and between the students themselves on the other. Tutorial sessions are scheduled on a weekly basis and are conducted by highly qualified and well trained tutors. These sessions are meant to be discussion forums covering the main topics for the study week ahead as identified in the course calendars. Tutors utilize these sessions in innovative ways that help students interact and learn more efficiently and effectively. 8 3. Student Attendance Required attendance varies depending on the number of credit hours taken per semester. On average: Students attend 4-8 hours per week English orientation courses require 8 hours of attendance weekly. These sessions are not intended to serve as classroom-style lectures. Students are expected to take responsibility for their own learning by studying the course materials according to the schedule provided in the course calendar. Attending face-to-face tutorial sessions of the registered course is mandatory by the student whose absence from such tutorials may not exceed 25% of the prescribed tutorials as stated in the approved University Calendar. 4. Office Hours Tutors maintain scheduled weekly office hours which are intended to provide a more informal environment for academic support. Students are advised to take advantage of these office hours for assistance with academic problems as needed. Resources 1. Learning Resources Each branch offers a variety of learning resources such as textbooks, IT resources, etc. to support the AOU academic programmes, students and tutors. All students have access to a variety of course- and programme-related resources accessible through the internet, collectively referred to as the e-library. Specifically, Moodle-based software, called LMS (Learning Management System), provides access to all electronic resources to which the AOU subscribes and is available to students and faculties in every branch. 2. Computer Laboratories Some courses require access to computing facilities and all such facilities are provided at various computer laboratories in each branch. Some courses have mandatory online components as part of the course materials or supporting materials intended to help learners: all materials of such kinds can be accessed in the computer laboratories. Electronic support for all courses is provided through the University’s Learning Management System (LMS), which also includes a teleconferencing facility. The AOU is moving towards electronic submission of all student assignments. 3. Other Facilities Most AOU branches offer additional facilities such as those listed below: • Student cafeteria • Entertainment rooms 9 • • • • Prayer rooms Some parking space Lifts for easy access to the upper floors of the branch buildings Some provisions for students with special needs, such as ramps. AOU Branches Each AOU branch is the main source of support for its students. It provides: Advice and guidance on how to study effectively in the AOU and which courses or programmes to study Induction to the AOU and to the mode of instruction employed Allocation to a subject specialist tutor who will provide face-to-face tuition, mark assignments, and be available during office hours A range of other resources and support services (please see your AOU branch website). Quality Assurance To ensure a high quality learning experience for students, the AOU monitors and evaluates its procedures, practices and student services on a systematic and regular basis. The AOU will ensure that its materials are of the highest quality. 1. Designing Learning Materials The design of course learning materials is the direct responsibility of the deans of the respective faculties. Academic teams from inside and outside the AOU are usually tasked with producing the required learning materials for newly designed courses. The production of required learning materials is achieved in accordance with certain specifications and methodologies of implementation. External assessors from other universities are involved in the process to ensure that the courses produced are of a high academic standard, comparable to those taught in campus-based institutions. At present, the three programmes, namely English Language Studies, Business Studies, and IT and Computing Studies, which are all taught in English, use courses produced according to the very high standard of the OU(UK). Wherever necessary, such courses are adapted to ensure that the learning materials, in written and audio-visual forms, adhere to the Arab-Islamic values. The Faculty of Education programmes have also been developed to meet local accreditation requirements. In addition, some of the programmes have been subjected to validation through the Open University Validation Services. 2. Managing and Monitoring of Tutors Because tutors are the interface between the University and its student body, care is taken to ensure that they deliver a high quality experience to students. Upon appointment, tutors are trained both in the generic skills necessary for them to teach effectively in the AOU system and in the specifics of the courses they will be tutoring: 10 Each tutor is assigned 20-25 students Their face-to-face tutoring is monitored by a full-time course coordinator in the branch The grading and the quality of the feedback given to students on Tutor Marked Assignments (TMAs) are also monitored Students have the chance to evaluate the performance of their tutors on a semester basis via a specially designed questionnaire The branch director will take appropriate action when inadequate performance is detected. 3. Assessment The academic staff of the relevant faculty sets all assessment material. However, before a given assignment or examination is approved for use, the questions and model answers must be approved by external assessors (external examiners in the case of the programmes validated by the OU (UK). The AOU adopts a rigorous policy for the assessment of student achievement in courses and programmes of study. The policy aims to create a robust and fair system of evaluation of achievement. Each component of the system of assessment is also intended to serve a learning need within the overall learning process. 3.1 Tutor Marked Assignments (TMAs) Each course requires students to complete a number of TMAs during a given semester; the number depends on the level and credit rating of the course. These assignments are spread out over the duration of the course. At higher levels of study, some TMAs are set as thematic projects and require students to read widely and assemble rational arguments from many information sources. TMAs are marked by the student's subject tutor and contribute to the total grade for the course. 3.1.1 Submission and Marking of Tutor Marked Assignments TMAs are submitted in soft (LMS) and hard copies on the specified dates according to the approved course calendar The numerical mark of zero (0) shall be recorded for each TMA not submitted by the cut-off date unless the student provides within three days of the cut-off date evidence of a medical report or extraordinary circumstances which are beyond his/her control. The reason for nonsubmission of the assignment has to be reported to the relevant course coordinator based on a recommendation by the student's tutor If the case is approved then, depending on the circumstances, the TMA may be submitted up to three weeks after the cut-off date The final TMA for a course must be submitted by its cut-off date unless there are extraordinary circumstances approved by the programme coordinator based on a recommendation from the tutor and the course coordinator concerned. . 3.2 Mid-Term Assessments (MTAs) MTAs are another means of monitoring the progress of students during the course and are carried out during tutorial sessions or possibly at a separate time if there is more than one section of the course. They are therefore prepared by course 11 Coordinators at each branch and approved by the dean. 3.3 Final Examinations This is the third component of student assessment. These exams are designed under the direct supervision of the dean of the faculty and are approved by the external examiners. The same examination is given at the same time in all AOU branches. 3.4 Assessment and Examination Policy The AOU adopts various methods to assess the rate of students’ progress towards achieving the programme’s objectives. The assessment strategy may vary from one course to another, but usually includes the following elements: 50% of the final total mark is allotted for continuous assessment during the semester (TMAs 20% and MID-TERM ASSESSMENT(MTAs 30%) The other 50% is allotted for the final exam - this is held at the end of the semester. i. For a student to pass a course, he/she must achieve an overall score of 50% in the final examination and continuous assessment, combined i.e. he/she should score a minimum of 20 % in the continuous assessment and 30% in the final examination or vice versa. ii. The classification of the degree award for the programmes validated by The Open University (Uk) is calculated on the basis of the student’s average grade in his/her best 32 credit hours of courses in Level 2 and the best 32 credit hours in Level 3 iii. All students taking a course (across the AOU branches) must sit for the same final examination, and must present identification in order to enter the examination room • Students’ final examination scripts are marked at the relevant branch under the supervision of the branch director in coordination with the dean concerned • Students' final examination scripts shall be anonymous and identified by code not by the student’s name vi. A student unable to sit the final examination due to an acceptable medical report or a force majeure, will be given a grade of “Incomplete” (I), and shall be allowed to sit for a makeup final examination in the nearest semester when that course is offered; otherwise, he/she shall receive a grade of Fail (F). Admission Requirements To be admitted to any BA/BSc programme, the student should meet the following conditions: Have a general secondary school certificate or its equivalent Fulfill any other conditions determined by the AOU or competent authorities of the branch country. This is because there may be special admission requirements of the local Ministry of Higher Education in some AOU countries. Students are advised to contact the local AOU branch for more information about admission requirements. The Branch Council shall devise and approve a specific admission policy pursuant to admission requirements in the branch country. The documents to be attached to the application form may vary from one branch to another, but all branches require the following: A copy of the student's high school certificate or its equivalent 12 A copy of ID or passport/labour card Passport-size photos. Language Placement Tests The AOU administers Language Placement Tests in both Arabic and English, not as admission requirements but as indicators to help place students at the appropriate level of language development. Based on the test scores, students will be assigned courses which aim to develop the students' proficiency in English/Arabic in order to undertake the full course load in their respective areas of specialization. English Language Courses Offered at the AOU The undergraduate programmes based on courses licensed from the OUUK are taught in English. Therefore the AOU has developed a number of language competency courses These courses which are not validated by by the OU (UK), are delivered by the Faculty of Language Studies (FLS) and are aimed at developing the students proficiency in English. Currently the AOU offers courses the following five courses: • • The English Orientation Programme (EOP) comprises three non-credit courses (EL097, EL098 and EL099), which target students with low levels of proficiency. The English Communication Skills Programme (ECS) 1, and 2, comprises two threecredit hour courses of compulsory university requirements: EL111 and EL112 1. Course Assignment Prospective students are assigned to the above courses on the basis of their scores in the English Placement Test (Oxford Online Placement Test (OOPT)) .Five levels of English integrated skills courses are available to incoming students: 1. EL097 Beginner 2.EL098 Elementary 3.EL099 Pre-Intermediate 4.EL111 Intermediate 5.EL112 Upper-Intermediate 2. Course Details The programme offers significant face-to-face interaction at each level as language skills development is best done by direct contact between the student and the tutor Four two-hour tutorials are assigned weekly in each level of the English Orientation Programme Credit courses have a total of 32 contact hours a semester (a two-hour tutorial per week) Students registered in the first, second, or third levels of the programme are not permitted to study more than two courses during the semester. 3. Exemption from Foundation Programme Courses (EL111 and EL112) A student will be exempted from EL111 if he/she gets an IELTS score of band 5.5 and below 7, or a score of 500 to 549 in TOEFL completed within 2 years prior to admission to the University. 13 A student will be exempted from EL112 if he/she gets an IELTS score of 7 or above or a TOEFL score of 550 or above, completed within 2 years prior to admission to the University. Credit Transfer (Course Equivalence) The current University policy allows a student who has been admitted to an academic programme to apply for credit transfer against courses at Level 1 only. Admitted students may thereafter submit appropriate documents in order to gain proper credit transfer for courses completed successfully at other recognized institutions of higher education. This is achieved by submitting details of the courses that he/she wishes to be considered as equivalent. Each application must include a detailed description of each course that has been completed successfully, together with an official transcript showing the number of credit hours and marks earned. The course should be at least equivalent in its academic content and number of credit hours to the course offered by the AOU. Credit transfer/course equivalence cannot exceed 14 credit hours at Level 1. Applications for credit transfer are carefully scrutinized in accordance with the approved University criteria. (See the BA/BSc Degree Requirements By-laws, Appendix 1). Academic Degrees Offered at the AOU THE AOU comprises five faculties: Faculty of Business Studies, Faculty of Computer Studies, Faculty of Education Studies, Faculty of General Studies, and Faculty of Language Studies, four of which have their programmes validated by the OU (UK). However, only some of the Faculty of Education Studies programmes are partially validated by the OU (UK). These programmes are: Bachelor degree in Business Studies (Systems, Economics, Marketing, Accounting).( BA (Honours) in Business Studies Programme) Bachelor degree in Information Technology and Computing, Information and Communications Technology, Computing, Computing with Business(BSc (Honours) in Information Technology and Computing (ITC)) Bachelor of Arts in English Language and Literature, English Language and Literature with Business Studies(BA (Honours) in English Language and Literature) Bachelor of Education (BEd) for Intermediate and Secondary Stages. It should be noted that the OU (UK) follows the credit points system. However, the AOU follows the credit hour system. The following table shows the credit point/credit hour equivalence: Credit Hours Credit Points 8 30 5 20 4 15 3 10 14 A detailed description of the four AOU progammes is given below. (Please also see Appendices 1, 2, 3, 4, 5.) 1.BA (Honours) in Business Studies Programme: New Study Plan Degree Requirements The BA degree in Business Studies has been developed and is delivered by the AOU. It has been validated through a process of external peer review by OUUK as being of an appropriate standard and quality to lead to the Open University validated award of BA (Hons). The degree comprises 128-135 credit hours (as per local accreditation requirements) which can be completed over a four-year period of full-time study. The breakdown of credit hours and courses needed to complete the programme, as well as the graduation plan for Business Studies are presented below: Number 1 2 3 Category Mandatory General University Requirements Faculty Requirements and University Electives Core Programme Specialized Courses Total Credit Hours 18 14-21 96 128-135 For additional progamme details, please see Appendix 2. 2. BA (Honours) in English Language and Literature: New Study Plan Degree Requirements The BA programme in English Language and Literature, BA (Hons) ELL, has been developed and is delivered by the AOU. It has been validated through a process of external peer review by the OUUK as being of an appropriate standard and quality to lead to the Open University validated award of BA (Hons) ELL. The programme is offered in two tracks: (i) (ii) English Language and Literature, leading to the BA degree in English Language and Literature, BA (Hons) ELL, and English Language and Literature with Business Studies (ELL with BS) leading to the BA degree in English Language and Literature (ELL) with Business Studies (BS), BA (Hons) ELL with BS. 15 The degree comprises 128-142 credit hours which can be completed over a four-year period of full-time study. The number of credit hours selected within this range is determined by the track the student takes, and local accreditation requirements. The breakdown of credit hours and courses needed to complete the programme, as well as the graduation plan for ELL are presented below: Number 1 2 3 Category Mandatory General University Requirements Faculty Requirements and University Electives Core Programme Specialized Courses Total Credit Hours 18 14-28 96 128-142 3. BSc (Honours) in Information Technology and Computing (ITC): New Study Plan Degree Requirements The BSc programme in Information Technology and Computing, BSc (Hons) ITC, has been developed and will be delivered by the AOU. It has been validated through a process of external peer review by the OUUK as being of an appropriate standard and quality to lead to the Open University validated award of BSc (Hons) ITC (OUVA). The programme comprises 131-135 credit hours, as per local accreditation requirements, which can be completed over a four-year period of full-time study. The breakdown of credit hours and courses needed to complete the programme is as follows: Number 1 2 3 Categories Mandatory University Requirements Faculty Requirements and University Electives Core Programme (Specialization) Requirements Total Credit Hours 18 17-21 96 131-135 For additional programme details, please see Appendix 4. 4. Academic Programmes Offered by the Faculty of Education The Faculty of Education Studies (FES) is currently offering the following programmes: 4.1 Bachelor of Education (BEd) in Elementary Education 4.2 Postgraduate Diploma in Education 4.3 Bachelor Degree (BEd) in Special Education - 4.3.1 Specialization: Mental Retardation - 4.3.2 Specialization: Learning Difficulties 16 4.4 Diploma in Special Education (Mental Retardation) 4.5 BEd for Intermediate and Secondary Stages FES has also developed a bachelor degree (BEd) for Intermediate and Secondary Stages. It is offered with six specializations: Arabic Language, English Language, Mathematics, Computing, Geography and History. This programme is validated by the OUVS. Note: (1) An Education programme is currently offered at the Jordan, Kuwait, Lebanon and Saudi Arabia branches of the AOU according to local needs. (2) Most courses in Education are offered in Arabic only. For additional programme details, please see Appendix 5. 5. Faculty of General Studies As shown in the table below, the Faculty of General Studies (FGS) offers a range of largely skills-based compulsory courses and electives, which cover Arabic and Islamic civilization and issues and problems of development. The AOU attaches special significance to the role of such studies in the make-up of its programmes. In particular, it views their role as significant in developing in students a broader perspective on life in general, and enriching personal development in particular. FGS offers the following courses: 5.1 Compulsory and Elective Courses A) Compulsory Courses (9 Credit Hours) Course Code Course Title GR101 AR111 AR112 Self-Learning Skills Arabic Communication Skills (I) Arabic Communication Skills (II) B) Elective Courses Course Code GR111 GR112 GR115 GR131 Credit Hours 3 3 3 (12 Credit Hours) Course Title Arab Islamic Civilization Issues and Problems of Development in the Arab Region Current International Issues and Problems History &Civilization of the (state) a -Branch Requirement 17 Credit Hours 3 3 3 3 5.2 Exemption from Arabic Language Skills Courses i. ii. A student who passes the Arabic Language Placement Test with an average of 60% or above is exempted from studying Arabic Language Communication Skills 1 (AR111) A student who passes the Arabic Language Placement Test with 90% or above is exempted from studying Arabic Language Communication Skills 2 (AR112). 5.3 Non-Native Speakers of Arabic Students who apply to be exempted from studying the Arabic Language Courses (AR111 or AR112), and whose mother tongue is not Arabic, must have studied and passed Arabic Language Courses for non-speakers (AFL111/AFL112) in an accredited university and with credit equivalent to at least six (6) credit hours. 6. Exit Awards The rationale behind exit awards is to provide opportunities for students at the AOU to obtain certificates or diplomas after completing the requirements of the particular exit award. The exit awards are part of the BA/BSc (Hons) degree programmes at the AOU. The general requirements for the award of a certificate are the successful completion of 60 credit points of study at Level 1, whereas the general requirements for the award of a diploma are the successful completion of 120 points of study at Level 2 or higher levels. It is possible that more exit awards will be offered in the future, for example in Computing. At the present, the only exit award offered is by the faculty of English Language and Literature as follows: 6.1 English Language and Literature Exit Awards Certificate in Humanities [Cert in Humanities (OUVA)] Award Requirements A student will be eligible for the undergraduate Certificate in Humanities if he/she successfully completes the following two courses from the BA programme in ELL totaling 16 credit hours: Course Code A123A A123B Course Title An Introduction to the Humanities (I) An Introduction to the Humanities (II) Total 18 Credit Hours 8 8 16 Diploma in English Literature [Dip in EL (OUVA)] Award Requirements A student will be eligible for the undergraduate Diploma in English Literature if he/she successfully completes the following Level 2 and Level 3 OU-based courses from the BA programme in ELL totaling 32 credit hours: Course Code A210A A210B Course Title Approaching Literature (I): The Realist Novel and Shakespeare and the Canon Approaching Literature (II): Romantic Writings Credit Hours 8 A319A Literature in the Modern World (I) 8 A319B Literature in the Modern World (II) Total 8 32 8 Diploma in English Language Studies [Dip ELS (OUVA)] Award Requirements A student will be eligible for the undergraduate Diploma in English Language Studies if he/she successfully completes the following Level 2 and Level 3 OU-based courses from the BA pogramme in ELL totaling 32 credit hours: Course Code Course Title U210A The English Language: Past, Present, and Future (I) U210B E303A E303B The English Language: Past, Present, and Future (II) English Grammar in Context (I) English Grammar in Context (II) Total Credit Hours 8 8 8 8 32 7. Future Developments New specialization tracks will be added to suit student and market demands in AOU branch countries Postgraduate programmes will be introduced in all faculties according to market demands. 19 Key University Regulations and Policies 1. Students with Special Needs i. ii. iii. 2. i. ii. iii. iv. v. vi. Students with special needs who feel that certain circumstances have impacted negatively on their performance when completing their assignments should submit proof of this to their tutor who will discuss the matter with the appropriate authority Students with special needs who need particular support should present their case to their tutor who will discuss the matter with the appropriate authority Students requiring an extension to the examination time must submit their needs not less than three weeks before the date of the examination or the due date of submitting the research/project. Student Appeals Students may appeal their final grade to the Branch Examination Committee within one week from announcement of course results The Branch Examination Committee ensures that the marks have been compiled properly. It also ensures that all answer scripts have been marked and verified and notifies the student of the acceptance or rejection of his/her appeal. If the appeal is rejected, students may then appeal the branch committee decision to the Faculty Examination Committee through the Branch director within one week after notification by the branch committee. Reasons for appeal together with supporting documents must be provided. The appeal is then forwarded for review by the Faculty Examination Committee The decision of the examination committee is final but however if students who wish to pursue their appeal beyond this point should do so within one week from the date of notification of the Faculty Examination Committee findings. In such cases, the committee looks into the appeal once again and this time its decision is considered final and irrevocable. The student shall be notified of the decision through the branch within one week of its being made In all cases, if a grade is modified as a result of an appeal then all examination committees must be informed. If the student is not satisfied with the outcome of the entire appeal process, the student may appeal to the University Rector or to the OUVS. 3. Cheating and Plagiarism Any student caught cheating or found to have committed an act of plagiarism shall be referred to the competent Branch Disciplinary Committee, which shall take its decisions as per rules in effect at the AOU. Punishment, if warranted, may include dismissal from the University. The following are considered acts of cheating and plagiarism: i. ii. iii. iv. v. Copying printed material and submitting it as part of TMAs, or examination scripts without proper acknowledgement and documentation Copying material from the internet, including tables and pictures without proper acknowledgement Copying other students' work Using material prepared for the student by individuals or institutions, i.e. material which is not the student's own work Taking unauthorized material into the examination room. 20 4. Inability to Take the Final Examination The following cases shall be observed when the student is unable to take the final examination at the fixed time and place: i. A student who cannot take the final examination or submit a report/project which is considered a main component of the assessment, must submit a medical report or a force majeure to the Students’ Affairs Office which will forward it to the competent authority ii. The case must be submitted within three days of the date of the final examination iii. If the Branch Examination Committee accepts the case, the student is awarded I (Incomplete) and the student may take the examination with all other students studying the course at the end of the next semester or academic year iv. If the Branch Examination Committee rejects the excuse, the student is awarded a zero (0) in this examination v. A student, who cannot take a final examination of a course with accepted reasons, can take that examination again on the next occasion that the examination for the same course is held. 5. Repeating Courses a) The student may not retake any course in which he obtains grade (C) or above. b) The student who fails in an elective course may retake the same course or any other elective course for the purpose of completing the programme’s approved study plan requirements. The student’s new grade resulting from such repeat courses shall be included in his semester and cumulative averages. However, in case of a student’s fail mark, the number of course hours shall be excluded from his cumulative average, provided that no modification should occur in the semester average pertaining to the semester in which he failed. c) The student who fails in a compulsory course must retake the same course in a subsequent semester. The student’s grade resulting from such repeat course shall be entered in his record. However, in case he fails therein, the number of course hours shall be excluded from his cumulative average, provided that no modification should occur in the semester average for the semester in which he failed. d) For the purposes of raising the student’s cumulative average to the required limit for graduation purposes only, the student may retake any course in his Study Plan other than OUUK courses. The student’s new grade, whether higher or lower than the previous grade, shall be included in his cumulative average. The student’s number of points obtained the first time as well as the number of course hours shall be excluded when computing his new cumulative average. e) For the purpose of raising the student’s cumulative average to the required limit for graduation purposes only, the student may retake any OUUK course included in his programme’s study plan in which he had previously obtained a (D) grade, provided that the ceiling of the student’s new grade shall be (C). The student’s number of points obtained the first 21 time as well as the number of course hours shall be excluded when computing his new cumulative average. 6. Attendance at Tutorials With due regard to local accreditation conditions required from each university branch: i. Face-to-face classroom meeting hours allocated for tutorials in each course during the single semester shall be 4 classroom hours against each credit hour allotted to the course, pursuant to arrangements made by the concerned branch which suit its circumstances ii. Face-to-face tutorial classroom hours may be increased in case of certain courses having special nature pursuant to ratio to be determined by the competent faculty or branch with a view to fulfilling local accreditation requirements iii. Attending face-to-face tutorial sessions of the registered course is mandatory by the student whose absence from such tutorials may not exceed 25% of the prescribed tutorials as stated in the approved university calendar. 7. Duration of Study and Study Load i. ii. iii. iv. v. vi. The academic year consists of two semesters, each of which lasts for sixteen (16) weeks The summer session lasts for eight (8) weeks The University Council approves the university calendar for each academic year. The calendar includes dates for the beginning of semesters, adding and dropping courses, final examinations, etc. The minimum load of a regular student is eight (8) credit hours. (Bahrain branch requires a minimum of 12 credit hours.) The maximum is twenty-one (21) credit hours per semester in all branches Students with a cumulative average of less than 2 points shall not be allowed to register for more than 12 credit hours The maximum period of study at the AOU is sixteen (16) semesters, equivalent to eight (8) academic years. (Summer semesters are not included.) 8. Prerequisites i. ii. 9. The study plan shows the prerequisites of each course A student may not register on any course without taking the prerequisite for that course. Postponement, Suspension and Withdrawal i. ii. A continuing student may submit an application within two weeks of the beginning of the semester to postpone his/her study. Such a postponement period should not exceed two years (four semesters) whether continuous or interrupted. The postponement period shall not be included within the maximum period required for graduation During the add and drop period, the student may withdraw from study after the approval of the competent party at the branch. • A student who does not register in a certain semester is considered suspended. If he/she submits subsequently an acceptable excuse before the end of the semester, the suspension period is considered a postponement 22 • iii. If the student resumes study after a period of postponement or suspension with an acceptable excuse, he/she can complete the study of the second part of the course provided that he/she has satisfied the requirements of the first part of the course. The marks obtained in the first part will contribute to the final grade of the course provided that the period of postponement or suspension does not exceed four semesters. A student’s enrolment shall be cancelled if he/she fails to register for any course during the first semester following his/her first enrolment at the University and/or not registering in any course for three consecutive semesters without valid excuse. 10. Granting the Bachelor’s Degree The bachelor’s degree is granted after completing the following graduation requirements: i. Passing all courses required for graduation pursuant to the study plan approved for the bachelor’s degree in the concerned programme ii. Achieving a cumulative average of not less than 2 points iii. Not exceeding the maximum period of study iv. Finishing any other requirements stated inside or outside the study plan v. The OU validated award is classified on the basis of the student's grade point average in the best 32 credit hours at Level 2 and the best 32 credit hours at Level 3. 11.Award/Grades Classification Awards The classification of the student's certificate as derived from the OUUK shall be as follows: First class Second class (1st Division) AOU Rating/ Cumulative Average Excellent Very good Second class (2nd Division) Third class Good Pass Classification, OU (UK) Grades Final grades for each course as letter grades shall correspond to the following points: Letter Grade A B+ B C+ C D F Points 4 3.5 3. 2.5 2 1.5 0. 23 Grade D is considered as the minimum passing grade for a student’s successful completion of the course. 12. Study Fees The AOU is a non-profit university and aims to keep its fee levels as low as possible, consistent with the need to offer a high quality learning experience for its students. The study fees differ depending on the nature of courses and the living standards of the Arab country where the university branch exists. The university also has a fund called “AOU student fund” for the purpose of financially supporting the students in need as well honoring the distinguished students by giving them grants and subsidies or returnable loans. 24 13. Student Transfer 13.1 Transfers Between Academic Programmes A student is eligible to transfer from one programme to another provided that he/she fulfils the admission requirements of the programme to which he/she wishes to transfer and that the transfer takes place at the beginning of the semester following the one in which he/she has been admitted. In this case, all the courses that the student has already completed successfully and which correspond with the requirements of the new programme will be taken into account. The number of course hours which do not belong to the study plan of the programme to which the student has transferred, as well as the points he/she has attained against such courses, shall be excluded from his/her cumulative average. The student should fill in a special form during the period announced in the university calendar. The transfer is subject to the following conditions: i. ii. iii. iv. The availability of a vacant place in the programme The student’s average in the secondary school certificate should not be less than the average announced and accepted by the programme into which the student wishes to transfer Satisfying any other academic qualifications required by the programme when submitting the application Passing any examination(s) required by the programme to which the student wants to transfer. 13.2 Transfer Between Branches A student who is registered in one branch of the University is eligible to transfer to another branch, but normally only at the beginning of the semester. In this case, all completed courses are taken into account for the student. However transfer between branches is subject to local requirements i.e. additional local requirements might need to be met. The tuition fees for the new courses are calculated according to the fees of the new branch. Transfer is dependent on the following: i. ii. iii. iv. v. vi. vii. The availability of space for an extra student in the programme and fulfillment of local requirements The student’s average in the secondary school certificates should not be less than the average required by the programme to which the student is applying to transfer When applying for transfer from a branch, the student should be registered in that branch without any disciplinary issues outstanding The student shall fill in a special form before the end of the semester, stating the reasons for his/her transfer In certain circumstances, a student may apply for transfer from one branch to another during the semester provided that he/she can provide a valid reason for transfer. In this case, the tutorials, examinations and other study requirements are not affected The student shall pay the appropriate transfer fee when filing the application. If the application is rejected, the student has the right to receive a refund of the money Normally, transfer should occur within the same programme in which the student is registered. If not, admission to a different programme should be done simultaneously with the transfer application 25 viii. ix. x. 14. Where necessary, it is the student’s responsibility to get a residence permit in the branch country to which he/she wants to transfer When a transfer has been approved by the two branches, the student’s file is sent to the new branch Before joining the new branch, the student should be informed about any admission conditions or requirements observed in the new branch so that he/she can fulfill these conditions either before or after joining the new branch. Student Conduct, By-laws and Disciplinary Procedure First These by-laws shall cover all university-registered students regarding any violation of the University rules, regulations and by-laws. In particular, they cover the following violations: i. ii. iii. iv. v. vi. vii. Any act incompatible with honour and dignity or breaching good conduct inside or outside the University Any act leading to the damage of the University premises and properties Cheating or attempting to cheat in examinations Cheating in carrying out assignments and reports or any other duties required in this regard Organization of non-academic societies and meetings inside the University without the prior approval of the competent University administration Circulation of publications, newsletters, or posters, or collecting signatures for any purpose, without permission from the competent party in the University Any “sit-in” strike inside the University premises or participation in any demonstration incompatible with the University rules and values in force. Second A student who attempts to cheat or does cheat in the examination, as described in a report signed by the head invigilator or the examination supervisor, may be subjected to the following punishments, separately or collectively, following investigation by the Branch Disciplinary Council: i. ii. iii. iv. v. vi. Verbal or written notice Warning Final warning Failure in the examination and concerned course Dismissal from the University for one semester or more Total and final dismissal from the University Any punishment imposed will be recorded in the student's file. Third A student may submit an appeal against the decision taken by the Disciplinary Committee or the Disciplinary Council within fifteen days from the date of being informed of the decision. The decision of the Higher Disciplinary Board is then final and binding. 26 14.1 Student Grievance Procedures Branch authorities look into each grievance and usually respond to the student concerned within a week. There are different types of grievances (appeals, complaints) and there are specific procedures for their submission and processing. 14.2 Procedures for Appeals and Complaints Appeals Students may appeal their final course grades by filling the online appeals form within 7 days from the announcement of the final course results. The student can also attach any relevant documents. Copies of the appeal form will automatically be sent to the Branch Examination Committee and concerned departments. The BEC will consider the appeal and if the appeal is valid a copy of the BEC recommendation will be sent to the Vice Rector for Academic Affairs (VRAA).. The VRAA will send its recommendation that the appeal is upheld to the Central examination Committee (CEC). The grade will only be changed after the approval of the CEC. The CEC decision will be communicated to the BEC with a copy to Student Affairs Office to inform the student and the student Affairs Office will notify the student with the decision. If the appeal is rejected and the student is dissatisfied with the decision to dismiss the appeal, he or she may take the appeal to a higher level by appealing to the Faculty Examination Committee (FEC) through the Branch Director within 7 days of notification of the decision to reject the appeal. If the student is still not satisfied with the FEC decision, he/she may appeal to the Rector of the University or to Open University Validation Services (OUVS). Complaints The student may lodge a complaint any time during the academic year, by completing the University formal student complaints form. The student must state the grounds for complaint, giving detailed reasons to support his or her case. A copy will be automatically forwarded to the concerned department and to Student Affairs Office. The concerned department will examine the complaint and it may consult other members of University staff or departments if it is deemed appropriate in particular cases. The Concerned department may find grounds for complaint and produce a report on the case setting out its recommendations and the documentations considered. 27 The Report will be sent to the Assistant Director for Administration and Finance or Assistant Director for Academic Affairs based on the nature and subject of the complaints for approval. Upon the approval of the concerned Assistant director, the Student Affairs Office will notify the final outcome of the complaint to the student. If the student is dissatisfied with the decision, he or she may appeal through the Branch Director to Vice Rector for Academic affairs (VRAA) or Vice rector for administrative and financial affairs (VRAF) within 7 days of notification of the decision to reject the complaint. The student will be informed through the Branch Director with the decision of the respective Vice Rector. The student may also complaint to the University Rector and to OUVS if he/she is not satisfied with the decision of the VRAA or VRAF. 15. University Websites and Addresses To facilitate the educational process and achieve comprehensive and meaningful results, the AOU has established websites on the internet as a means of providing information on its various programmes and activities for the common good of the students and other interested parties. These websites are in English unless otherwise noted: 1. Business Studies Programme: http://arabou.edu.kw/index.php?option=com_k2&view=item&layout=item&id=30&Itemid= 124&lang=en 2. Computing and Information Technology Programme: http://arabou.edu.kw/index.php?option=com_k2&view=item&layout=item&id=31&Itemid= 125&lang=en 3. Language Studies Programme: http://arabou.edu.kw/index.php?option=com_k2&view=item&layout=item&id=32&Itemid= 126&lang=en 4. An Education website will be launched soon after the Education Programmes receive validation from the OUVS. The AOU also has comprehensive websites set up at most of its branches, in English unless otherwise noted: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Bahrain: http://arabou.edu.kw/ Egypt: http://arabou.edu.kw/ Jordan: http://arabou.edu.kw/ Kuwait: http://arabou.edu.kw/ Lebanon: http://arabou.edu.kw/ Saudi Arabia: http://arabou.edu.kw/ Oman: http://arabou.edu.kw/ 28 16. University Headquarters and Branches Headquarters Bahrain Branch Egypt Branch Jordan Branch Kuwait Branch Lebanon Branch Oman Branch Saudi Arabia Branch Arab Open University - Headquarters PO Box 3322 Safat - Postal Code 13033 State of Kuwait Tel: (00965) 25329013/8 Fax: (00965) 25321318 Email: info@arabou.edu.kw University website (Arabic and English): http://www.arabou.edu.kw Bahrain - Al Haram Plaza, Al Salah Street Kingdom of Bahrain PO Box 18211 - Manama - Bahrain Tel: (0097317) 407088/407077 Fax: (0097317) 400916 Email: student-affairs@aou.org.bh Cairo - Arab Council for Childhood and Development Building Intersection of Makram Ebeid Street and Abd Al-Razeq Al-Sanhoury Street, Nasr City, Cairo Tel: (00202) 6711870/67 Fax: (00202) 6711868 Email: info@aou.edu.eg Behind Queen Alia Hospital and close to Association of Arab University – Tareq Area, PO Box 1339 Amman – Postal Code 11953 Amman - Jordan Tel: (00962) 6 5630630 Fax: (00962) 6 5630610 Email: director@aou.edu.jo Khaitan - Area 2- Zaid Bin Khail Street Tel: (00965) 24767166 Fax: (00965) 24767436 PO Box 3322 Safat - Postal Code 13033 State of Kuwait Email: info@arabou.edu.kw Omar Bayham Street- Al Hursh Area 20584518 - Beirut Lebanon Tel: (00961) 1392139-45 Fax: (00961)1392146 Email: admin@aou.edu.lb Qurum 16,Way No 234, Building No 3490 PO Box 1596, PC 130 Muscat Sultanate of Oman. Tel: (00968 24699444) Fax: (00968 24699669) Email: info@aouoman.org Al Riyadh - Al Falah District opposite Imam Mohamad Bin Saud University opposite Gate no.2 - southern part PO Box 84901 – Riyadh 11681- Kingdom of Saudi Arabia Tel: (00966) 12742277 Fax: (00966) 12742696 Email: support@arabou.edu.sa 29 Appendix 1 BA Award Requirements Bylaws At Arab Open University Approved by University Council in its meeting No. 28, February 23, 2009 Article I A) The present bylaws shall be called “BA Award Requirements Bylaws at Arab Open University” and shall be in force from the date of approval thereof by the University Council. B) The following words and expressions shall have the meanings specified hereunder unless the context indicates otherwise: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. University Rector Dean Branch Academic Committee 6. Programme 7. Tutorial 8. Study Plan : : : : : The Arab Open University The University Rector The Dean of Academic Programme The University branch established in any country. A permanent committee formed by the University Council. : Academic major accredited for BA Award : One hour during which a face-to-face meeting takes place between the student and the tutor. : Distribution of courses pursuant to the components of the accredited academic programme. Article 2 The present bylaws shall apply to all academic programmes offered by the University at the BA level pursuant to the academic programme’s approved study plan. Article 3 Study Plans A) The University Council shall approve the BA Programme Study Plans pursuant to the recommendation of the competent Faculty Council and endorsement of the Academic Committee. B) Academic Programme Study Plans shall be based on the credit hour system. C) The total of credit hours required for obtaining a BA award in any programme shall not be less than (128) credit hours distributed as follows: A minimum of (18) credit hours of compulsory general university requirements. 30 80-100 credit hours of programme’s major requirements. A minimum of 14 credit hours of Faculty requirements and the elective courses specified in the approved study plan of the Academic Programme. Article 4 Academic Year A) The academic year shall consist of two semesters, each having a duration of 16 weeks including the final examinations period. The summer semester is optional, and shall cover a duration of 8 weeks including the final examinations period. B) The commencement of the academic year and semesters as well as examination dates shall be determined pursuant to University Calendar as approved by the University Council. Article 5 Admission A) To be admitted in any BA programme the student should fulfill the following conditions: Obtain a general secondary school certificate or equivalent. Fulfill any other conditions determined by the University or competent authorities of the Branch country. B) The Branch Council shall devise and approve a specific admissions policy pursuant to admissions requirements in the Branch country. Article 6 Language Placement Test A) All freshmen shall submit the Language Placement Test in Arabic and English pursuant to standards approved by the University Council. B) Non-Arabic speaking Freshmen shall be exempt from the Arabic Placement Test and shall be treated pursuant to standards approved by the University Council. C) Freshmen attaining a minimum of (500) score in the TOEFL hard copy version, equivalent score in the soft copy version, or the equivalent score thereof in the IELTS shall be exempt from the English Placement Test, provided that their scores have been obtained within the two years preceding their admission to the University. D) Students may be exempt from pursuing one or more Arabic or English compulsory University required courses or both pursuant to scores obtained in Arabic and English 31 Placement Tests, TOEFL or IELTS in accordance with the standards approved by the University Council. E) The freshmen’s academic record shall, on entry, contain a record of all courses from which the freshmen has been exempted as a result of his performance at both placement tests. Such exempt courses shall be marked (CR). However, the credit hours due to such courses shall not be included in his cumulative averages. Article 7 Study Duration The maximum duration for obtaining a BA award shall be sixteen semesters adjustable to the local accreditation requirements of the country branch of operation. Article 8 Study Load and Registration With due regard to local accreditation requirements applied to each Branch: A) The minimum study load per student shall be 8 credit hours per semester. B) The maximum study load per student shall be 21 credit hours per semester. C) Student with cumulative average less than 2 points shall not be permitted to register for more than 12 credit hours. D) “A maximum of eight credit hours can be taken during the summer sessions, provided that this does not conflict with the OUVS regulations.” E) “OU-based courses may be offered during the summer session, based on the Branch’s demand and in coordination with the relevant Deans. Sample will be sent to the EE accordingly.” Article 9 The student may register for any course offered by the University, which course is not included in the Study Plan of the Programme in which he is enrolled provided that such course credit hours shall not be included within the credit hours required for graduation. Further, they shall not be part of student’s semester or cumulative averages. 32 Article 10 The duly registered student in a University branch may study courses falling within his Study Plan at another Branch pursuant to the approval of the Directors of both concerned branches. The Director of Admissions and Registration shall be notified therewith. Article 11 The student shall not be permitted to register for any course without studying its pre-requisite, if any, pursuant to Study Plan. Article 12 Drop and Add A) Without prejudice to the provisions of Article 8 hereof, the student may drop and add certain courses included in the Study Plan within the statutory Drop and Add period declared in the University Calendar. B) Letter (W) – symbol indicating Withdrawal – shall be entered in the student’s academic record upon withdrawal from any course after the Drop and Add period up to one week prior to the final examinations date, provided that such withdrawn course hours are not included in the student’s semester and cumulative averages. Article 13 Postponement of Study The continuing student (non-freshmen) may postpone his study within a period not exceeding two weeks from the commencement of the semester, provided that such postponement does not exceed four consecutive or interrupted semesters. Such postponement shall not be included within the maximum study duration limit allowed for completion of graduation requirements. Article 14 Discontinuing of Studies The student shall be deemed a discontinuing student should he fail to register in any course during any semester. Such semester shall be included in the allowed study duration limit unless a force-majeure excuse is submitted by the student and approved by Branch Director. In case of such approval, the student shall be deemed to have postponed his studies for the relevant semester. 33 Article 15 Cancellation of enrollment A) Student’s enrollment shall be cancelled in the following cases: Upon personally filing an application of withdrawal from the University. If he fails to register for any course during the first semester following enrollment at the University. Should he discontinue his studies for three consecutive semesters without valid excuse. B) Student with cancelled enrollment due to discontinued studies may apply for re-enrollment in the same academic programme which he discontinued, or any other programme provided he fulfills the conditions of enrollment therein. Article 16 Tutorials With due regard to local accreditation conditions required from each University Branch: A) Face-to-face classroom meeting hours allocated for tutorials in each course during the single semester shall be 4 classroom hours against each credit hour allotted to the course, pursuant to arrangements made by the concerned Branch which suit its circumstances. B) Face-to-face tutorial classroom hours may be increased in case of certain courses having special nature pursuant to ratio to be determined by the competent Faculty or branch with a view to fulfill local accreditation requirements. C) Attending face-to-face tutorial sessions of the registered course is mandatory by the student whose absence from such tutorials may not exceed 25% of the prescribed tutorials as stated in the approved University Calendar. Article 17 Course Assessment A) Each course shall have the final mark out of (100) marks to be equally distributed between the Continuous Assessment and the Final Examinations. This distribution may be adjusted either by increasing or decreasing the ratio of each component according to the nature of the course following the approval of the concerned Faculty Council and the endorsement of the Academic Committee. B) The Continuous Assessment’s (50) marks shall be allotted as follows: (20) marks shall be assigned for Tutor Marked Assignments (TMAs) specified in the Course Calendar. (30) marks shall be allotted to Midterm Assessment. C) The concerned Faculty may exclude any course from the marks distribution stipulated in para (b) above following the approval of the Academic Committee. 34 D) The number of TMAs in any given course is a minimum of one per semester, and that number is determined by the deanship concerned. E) A maximum of two Midterm Assessments per course may be held during the semester. F) - “A unified mid-term examination is held to all groups of a given course at the branch level; however, the concerned deanship may unify the content and time of exams in all branches. In all cases the mid-term examination should be approved by the concerned dean. G) “A student’s grades in the continuous assessment (TMAs and MTAs) of each course should be entered in the Student Information System (SIS) of the respective branch without delay so that the student’s grade record is completed at most one week before the beginning of the final exams.” Article 18 Students Final Examinations answer books shall be kept at branches for reference purposes for a period of two semesters following which they shall be destroyed. Article 19 The student who is absent from the Final Examinations shall earn a (0-zero) mark unless he submits a force majeure excuse within three days from the Final Examinations convening date. In case the excuse was accepted, letter (I) – symbol for Incomplete – shall be entered in the student’s academic record, and shall be permitted to re-sit for the examination on its first subsequent session. In such case, course’s credit hours shall be excluded from the student’s semester and cumulative averages. Should the student fail to submit the examination on its first subsequent session, the symbol (I) shall be replaced by letter (F) – Fail – in his academic record. Article 20 The Student may sit for the Final Examinations in the courses in which he is registered at any other Branch pursuant to the approval of the directors both concerned branches. Article 21 A) Final grades for each course as letter grades shall correspond to the following points: Letter grade A B+ B Points 4 3.5 3.0 35 C+ C D F 2.5 2.0 1.5 0.0 B) Grade D is considered as the minimum passing grade for student’s successful completion of the course. Article 22 The student shall fail the course in any of the following cases: A) If the student’s mark in Continuous Assessment was less than (20) out of (50) marks. In this case, FC grade - (Failed in Continuous Assessment) - shall be entered in his record. B) If the student’s mark in the Final Examinations was less than (20) out of (50) marks. In this case, (FF) grade – Failed in the Final Examinations – shall be entered in his record. C) If the student’s final mark, being the total marks obtained in the Continuous Assessment and the Final Examinations was less than (50%), in this case, letter (F) – symbol for Fail – shall be entered in his record. Article 23 Credit hours of the student’s failed course, pursuant to any said cases, shall be included in the student’s semester and cumulative averages. Article 24 The final course results shall be approved by the Central Examinations Committee pursuant to a recommendation submitted by the Examinations Committee of the concerned Faculty. Article 25 Objection to Results and Modification Thereof A) The student may request a review of his final mark in any course through applying to the Branch Examination Committee within one week of announcing the course’s approved results. B) The Branch Examinations Committee shall study the student’s objection, verify absence of error in adding or entering of the student’s marks in the course, as well as the absence of 36 unmarked questions. The student shall be notified of the Committee’s decision within one week of his application date. C) The student may object to the Branch Examinations Committee’s decision through applying to the competent Faculty Examinations Committee within one week of the Branch Examinations Committee’s decision date. D) The Faculty Examinations Committee shall study the student’s objection and render its final and irrevocable decision thereon. The student shall be notified of its decision within one week of receipt of his objection. E) Student’s result in any course shall become final following the lapse of one semester, and may not be modified under any circumstance. Moreover, the graduate’s grade in any course may not be modified following the lapse of two weeks on the announcement date thereof. Article 26 Semester and Cumulative Averages A) The semester average shall be computed pursuant to dividing student’s total number of points earned during the semester by the total number of credit hours of courses studied during the same semester. This should take into consideration that the number of points obtained by the student in each course is the result of multiplying the hours assigned to the relevant course by the number of points corresponding to the grade obtained by the student as stipulated by the provisions of Article 21 hereof. B) With due regard to the provisions of Articles (12 – para b) and (19), computation of the relevant semester average shall include all courses pursued by the student in the semester pursuant to the Study Plan, including failed or successfully completed courses. C) In exception of the stipulations of Articles (6 para e), (12 para b), (19) and (29 para b) hereof, the cumulative average shall be computed pursuant to dividing the student’s total number of points earned in all courses studied since his enrolment at the University according to the Study Plan, by the total number of such course hours,. D) The semester or cumulative averages, shall be approximated to the nearest two decimal points. Article 27 Warning and Dismissal A) A warning shall be issued to the student whose cumulative average is less than 2 points at the end of any semester excluding the summer semester. B) The student shall be dismissed from the University if he receives four warnings within four consecutive semesters excluding the summer semester. 37 C) The student who has been dismissed from the University for academic reasons related to the cumulative average may re-apply for enrolment in any University program excluding the one from which he was dismissed. Article 28 Repeat Courses A) The student may not retake any course in which he obtains grade (C) or above. B) The student who fails in an elective course may retake the same course or any other elective course for the purpose of completing the programme’s approved Study Plan requirements. The student’s new grade resulting from such repeat courses shall be included in his semester and cumulative averages. However, in case of student’s fail mark, the number of course hours shall be excluded from his cumulative average, provided that no modification should occur in the semester average pertaining to the semester in which he failed. C) The student who fails in a compulsory course must retake the same course in a subsequent semester. The student’s grade resulting from such repeat course shall be entered in his record. However, in case he fails therein, the number of course hours shall be excluded from his cumulative average, provided that no modification should occur in the semester average for the semester in which he failed. D) For the purposes of raising the student’s cumulative average to the required limit for graduation purposes only, the student may retake any course in his Study Plan other than UKOU courses. The student’s new grade, whether higher or lesser than the previous grade, shall be included in his cumulative average. The student’s number of points obtained in the first time as well as the number of course hours shall be excluded when computing his new cumulative average. E) For the purpose of raising the student’s cumulative average to the required limit for graduation purposes only, the student may retake any UKOU course included in his programme’s Study Plan in which he had previously obtained a (D) grade, provided that the ceiling of the student’s new grade shall be (C). The student’s number of points obtained in the first time as well as the number of course hours shall be excluded when computing his new cumulative average. Article 29 Equivalency of Courses A) Courses completed by the student in another recognized educational institution existing in the AOU Branch country may be equated pursuant to the Criteria for Course Equivalence as approved by the University Council. C) Duly equated courses shall be entered in the student’s academic record together with course number and hours. Letter (T) shall be entered opposite such course to indicate (Equated). The total hours of such courses shall be excluded from the student’s cumulative average. 38 Article 30 Transfer Between Programs A) The student may transfer from the programme in which he is enrolled into another programme pursuant to criteria and procedures approved by the University Council. B) Upon the student’s transfer from one programme into another, the number of course hours which do not belong to the Study Plan of the programme to which he has transferred, as well as points he attained against such courses shall be excluded from his cumulative average. Article 31 Transfer Between Branches The student may transfer from the branch in which he is enrolled into any other branch pursuant to the criteria and procedures approved by University Council. Article 32 Graduation A) The University awards shall be conferred pursuant to University Council decision, following the recommendation of the competent Faculty Examinations Committee and the Central Examinations Committee. B) The Bachelor award shall be conferred following the student’s successful completion of all courses included in his programme’s Study Plan provided that his cumulative average is not below (2) points. C) “Exit Awards might be offered to students who do not fulfill graduation requirements from the programme in which they are enrolled provided that they satisfy the conditions specified by the concerned faculty for such awards.” Article 33 The graduating student’s award grades shall be pursuant to the cumulative average of all Study Plan courses as follows: Cumulative Average 4 - 3.67 3.66 - 3 2.99 – 2.33 2.32 - 2 Grade Excellent Very Good Good Pass 39 Article 34 General Provisions A) The present bylaws shall abrogate all previous bylaws regulating requirements for the BA award at the University. B) The University Council shall decide on all cases not covered by the provisions of present bylaws and shall resolve any conflicts arising from their implementation. C) Deans, Branch Directors, and Director of Admissions and Registration shall be responsible for implementing the present bylaws. 40 Appendix 2 BA (Hons) Business Studies Programme: New Study Plan 1. Mandatory General University Requirements (18 credit hours) The following courses comprise the Mandatory General University Requirements: Course Code Course Title Credit Hours Prerequisites AR111 Arabic Communication Skills (I) 3 AR112 Arabic Communication Skills (II) 3 EL111 English Communication Skills (I) 3 EL112 English Communication Skills (II) 3 GR101 Self-Learning Skills 3 TU170 Learning Online 3 Total AR111 EL111 18 2. Faculty Requirements and University Electives (14-21 credit hours) A minimum of 14 and a maximum of 21 credits (as per local accreditation requirements) are to be taken from the following list: Course Code Credit Hours Course Title Prerequisite s GR111 Arab Islamic Civilization 3 GR112 Issues and Problems of Development in the Arab World 3 GR131 Branch Requirement 3 BE200 Marketing Management 3 BE201 Consumer Behaviour 3 BE300 Marketing Research 3 BE210 Financial Accounting 3 BE211 Managerial Accounting 3 BE210 BE310 Cost Accounting 3 BE210 BE220 Money and Banking 3 41 BE201 Remarks Obligatory faculty requireme nt for the marketing track Obligatory faculty requireme nt for the accounting track BE230 Financial Institutions 3 BE231 Financial Management 3 BE320 Islamic Finance 3 BE321 Taxation 3 BE322 Small Business Management 3 BU130 Managing in the Workplace 8 M150A M150B Data, Computing and Information (I) Data, Computing and Information (II) 4 M150A 4 Notes: i. Obligatory courses in a certain track can be taken as elective courses in other tracks ii. BE stands for "Business Essentials" iii. Core programme (specialized) courses (64 credit hours). The Business Programme is offered in five tracks as follows: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. BA (Hons) Business Studies with Systems Practice BA (Hons) Business Studies with Economics BA (Hons) Business Studies with Accounting BA (Hons) Business Studies with Marketing BA (Hons) Business Studies All tracks have a common core of specialized courses totaling (64) credit hours as in the following table: Course Code B120 Course Title Credit Hours Prerequisites An Introduction to Business Studies 8 EL111 LB160 Business English Communication 8 EL111 B200A Understanding Business Behaviour: Business Environments and Markets (I) Understanding Business Behaviour: Business Processes and Organizations (II) 8 B120 8 B200A B202A Understanding Business Functions (I) 8 B120 B202B Understanding Business Functions (II) 8 B202A B300A Business Behaviour in a Changing World (I) Business Behaviour in a Changing World (II) Total 8 B120 8 B300A B200B B300B 42 64 Note: The two courses B200 and B202 will be replaced by B201 and B203 respectively if and when available. 3. Core Track (Specialized) Courses (32 credit hours each track as in the table below): Note: The course T205 will be replaced by T214 if and when available. Course Code Tracks and Course Titles Credit Hours Prerequisites BA (Hons) Business Studies with Systems Practice T205A Systems Thinking: Theory and Practice (I) 8 B120 T205B Systems Thinking: Theory & Practice (II) 8 T205A T306A Managing Complexity: A Systems Approach (I) 8 B120 8 T306A Managing Complexity: A Systems Approach (II) BA (Hons) Business Studies with Economics T306B DD202A Economics and Economic Change (I) (Microeconomics) 8 B120 DD202B Economics and Economic Change (II) (Macroeconomics) 8 DD202A D319A Understanding Economic Behaviour (I) 8 B120 D319B Understanding Economic Behaviour (II) BA (Hons) Business Studies with Accounting 8 D319A B680A Certificate in Accounting (I): (Financial Accounting and Reporting) 8 B120 B680B Certificate in Accounting (II) (Cost and Management Accounting) 8 B680A Accounting for Strategy Implementation 8 B120 B321 M248 Data Analysis BA (Hons) Business Studies with Marketing 8 B322 Investigating Entrepreneurial Opportunities 8 B120 B324 Marketing and Society Networked Living: Exploring Information and Communication Technologies (I) Networked Living: Exploring Information and Communication Technologies (II) 8 B120 4 TU170 4 T175A T175A T175B M248 Data Analysis BA (Hons) Business Studies B321 B322 T175A 8 Accounting for Strategy Implementation Investigating Entrepreneurial Opportunities Networked Living: Exploring Information 43 8 B120 8 4 B120 TU170 T175B M248 and Communication Technologies (I) Networked Living: Exploring Information and Communication Technologies (II) 4 Data Analysis T175A 8 Note: course B680 will be replaced by B291 & B292 if and when necessary. 4. Correspondences Between Courses in the Old Study Plan and the New Study Plan New Study Plan New Courses Course Code B200A B200B B202A B202B B300A B300B DD202A DD202B D319A D319B T205A Course Title Credit Hours Understanding Business Behaviour: Business Environments and Markets (I) Understanding Business Behaviour: Business Processes and Organizations (II) Understanding Business Functions (I) Equivalent Courses in the Old Study Plan Course Credit Course Title Code Hours 8 B200 Understandin g Business Behaviour: 16 B202 Understandin g Business Functions 16 B300 Business Behaviour in a Changing World 16 D202 Economics and Economic Change 16 D319 Understandin g Economic Behaviour 16 T205 Systems Thinking: Theory and 16 8 8 Understanding Business Functions (II) 8 Business Behaviour in a Changing World (I) Business Behaviour in a Changing World (II) Economics and Economic Change (I) (Microeconomics) Economics and Economic Change (II) (Macroeconomics) Understanding Economic Behaviour (I) Understanding Economic Behaviour (II) Systems Thinking: Theory and Practice (I) 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 44 T205B T306A T306B Systems Thinking: Theory and Practice (II) Managing Complexity: A Systems Approach (I) Managing Complexity: A Systems Approach (II) Practice 8 8 T306 8 45 Managing Complexity: A Systems Approach 16 5. OU (UK) Validated Courses that were Phased Out and their Replacements The following list includes some of the phased-out OU-based courses and their replacements in the new Validated Programme: Phased Out Courses Credit Course Code and Title Hours DD121 Introduction to 8 the Social Sciences (1) 8 DD122 Introduction to the Social Sciences (II) 8 T171 You, Your Computer, and the Net 8 T172 Working With Our Environment New Courses Course Code and Title B120 An Introduction to Business Studies LB160 Business English Communication OR T175A Networked Living: Exploring Information and Communication Technologies (I) AND T175B Networked Living: Exploring Information and Communication Technologies (II) T175A Networked Living: Exploring Information and Communication Technologies (I) AND T175B Networked Living: Exploring Information and Communication Technologies (II) B120 An Introduction to Business Studies OR LB160 Business English Communication OR T175A Networked Living: Exploring Information and Communication Technologies (I) AND T175B Networked Living: Exploring Information and Communication Technologies (II) 46 Credit Hours 8 8 4 4 4 4 8 8 4 4 Appendix 3 BA (Hons) English Language and Literature: New Study Plan 1. Mandatory General University Requirements (18 credit hours) The following six courses comprise the Mandatory General University Requirements: Course Code AR111 AR112 EL111 EL112 GR101 TU170 Course Title Arabic Communication Skills (I) Arabic Communication Skills (II) English Communication Skills (I) English Communication Skills (II) Self-Learning Skills Learning Online Credit Hours 3 3 3 Prerequisites AR111 EL111 3 3 3 2. Faculty requirements and university electives to be taken from the table below: (i) (ii) ELL track: 14-20 credit hours according to local accreditation requirements ELL track with BS: 22-28 credit hours according to local accreditation requirements. Course Code B120 Credit Prerequisites Hours Course Title An Introduction to Business Studies 8 EL111 EL120 English Phonetics and Linguistics 4 EL111 EL121 The Short Story and Essay Writing 4 EL111 EL230 EL320 American Literature Translation Teaching English as a Foreign Language Networked Living: Exploring Information and Communication Technologies (I) Networked Living: Exploring Information and Communication Technologies (II) Arab Islamic Civilization Branch Requirement Business English Communication An Introduction to the Social Sciences (I) 4 4 EL121 EL120 4 U210B 4 TU170 4 T175A 3 3 8 - 8 - EL340 T175A T175B GR111 GR131 LB160 DD121 47 Remarks Obligatory faculty requirement for ELL with BS Obligatory faculty requirement for the two tracks 3. Core programme (specialization) courses 96 credit hours for each track Symbol X denotes an obligatory course for the track: Course Code and Title Credit Hours Prerequisites A123A An Introduction to the Humanities (I) 8 A123B An Introduction to the Humanities (II) Tracks ELL ELL with BS EL112 & EL121 X X 8 A123A X X A210A Approaching Literature (I): The Realist Novel and Shakespeare and the Canon 8 A123B X X A210B Approaching Literature (II): Romantic Writings 8 A123B X X U210A The English Language: Past, Present and Future (I) 8 EL112 & EL120 X X U210B The English Language: Past, Present and Future (II) 8 EL112 & EL120 X X E300A English Language and Literacy (I) 8 U210B X - E300B English Language and Literacy (II) 8 E300A X - E303A English Grammar in Context (I) 8 U210B X E303B English Grammar in Context (II) 8 E303A X Both (I) & (II) OR A319A Literature in the Modern World (I) 8 A210A X A319B Literature in the Modern World (II) B202A Understanding Business Functions (I) 8 8 A319A X B120 - X B202B Understanding Business Functions (II) 8 B202A - X B300A Business Behaviour in a Changing World (I) B300B Business Behaviour in a Changing World (II) Total 8 B120 - X 8 B300A - X 96 96 48 Both (I) & (II) 3.1 Correspondences between courses in the old study plan and courses in the new study plan Course No EL120 EL121 II. NEW STUDY PLAN NEW COURSES Course Title Credit Hours English Phonetics and Linguistics 4 The Short Story and Essay Writing 4 A123A An Introduction to the Humanities (I) 8 A123B An Introduction to the Humanities (II) 8 A210A A210B U210A U210B E303A E303B E300A E300B A319A A319B B202A B202B B300A B300B Approaching Literature (I): The Realist Novel and Shakespeare and the Canon Approaching Literature (II): Romantic Writings The English Language: Past, Present and Future (I) The English Language: Past, Present and Future (II) EQUIVALENT COURSES IN THE OLD STUDY PLAN Course No and Credit Title Hours 8 University Electives at least List University Electives List A123 An Introduction to the Humanities 16 A210 Approaching Literature 16 SAME COURSE: NO CHANGE SAME COURSE: NO CHANGE 8 E303 English Grammar in Context 16 E300 English Language and Literacy 16 A319 Literature in the Modern World 16 8 8 8 8 English Grammar in Context (I) 8 English Grammar in Context (II) 8 English Language and Literacy (I) 8 English Language and Literacy (II) 8 Literature in the Modern World (I) 8 Literature in the Modern World (II) 8 Understanding Business Functions (I) Understanding Business Functions (II) Business Behaviour in a Changing World (I) Business Behaviour in a Changing World (II) 49 8 8 8 8 8 B202 Understanding Business Functions 16 B300 Business Behaviour in a Changing World 16 Appendix 4 BSc (Hons) Information Technology and Computing – ITC 1. Mandatory University Requirements (18 credit hours) The following six courses comprise the Mandatory General University Requirements. Course Code Course Title Credit Hours Prerequisites AR111 Arabic Communication Skills (I) 3 __ AR112 Arabic Communication Skills (II) 3 AR111 EL111 English Communication Skills (I) 3 __ EL112 English Communication Skills (II) 3 EL111 GR101 Self-Learning Skills 3 __ TU170 Learning Online 3 __ Total 18 2. Faculty Requirements & University Electives (17-21 credit hours) Students should take 17-21credit hours from the following list, as per local accreditation requirements, including the two courses M131 and T490 which are the faculty requirements (six credit hours). Course Code Credit Hours 3 Course Title M131 Discrete Mathematics T490 Selected Topics in Computer Science MS101 GR111 GR131 M105 M132 M133 M211 M350 MU120A Physics for Computer Students Arab Islamic Civilization Branch Requirement Introduction to Programming Linear Algebra Numerical Analysis Fundamentals of Algorithms and Data Structures Operating System Concepts Open Mathematics (I) 50 Prerequisites Remark Obligatory faculty requirement s for all tracks 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 4 M132 MU120B T103 Open Mathematics (II) Computer Architecture 4 3 MU120A 3. Core Programme (Specialization) Courses (96 credit hours) The ITC programme is offered in four tracks, with 96 credit hours each. The core specialization courses for the four tracks are presented below. The symbol X means obligatory for the track. 1. ITC Track: Information Technology and Computing 2. ICT Track: Information and Communication Technologies 3. C Track: Computing 4. CwB Track: Computing with Business Course Code B120 B202 A B202 B B300 A B300 B M150A M150B M253 M255 M256 M257 M263 M359 M362 M363 M366 MST121A MST121B MT262A Credit Hours 8 Course Title An Introduction to Business Studies Understanding Business Functions Understanding Business Functions Business Behaviour in a Changing World Business Behaviour in a Changing World Data, Computing and Information (I) Data, Computing and Information (II) Team Working in Distributed Environment Object Oriented Programming with Java Software Development with Java Putting Java to Work Building Blocks of Software Relational Data Base: Theory and Practice Developing Concurrent Distributed Systems Software Engineering with Objects Natural and Artificial Intelligence Using Mathematics (I) Using Mathematics (II) Putting Computer System to Work (I) 51 Prerequisites Tracks ITC ICT C CwB X 8 B120 X 8 B120 X 8 B120 X 8 B120 X 4 EL111 X X X X 4 M150A X X X X 3 M150B X X X 8 M150B X X X 8 M257 X X X 5 8 8 X X X X X 8 M255 M150B M255 or MT262B M257 8 M256 X 8 M255 4 4 4 MST121A M150B X X X X X X X X X X X X X MT262B T175A T175B T209A T209B T224 T320 T324 T325 T471 Putting Computer System to Work (II) Networked Living: Exploring Information and Communicattions Technologies (I) Networked Living: Exploring Information and Communications Technologies (II) Telematics (I) Telematics (II) Computers and Processors Business Technologies Keeping Ahead in ICT Technologies for Digital Media Telematics Project Total 4 MT262A X X 4 TU170 X X X 4 T175A X X X 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 T175B T209A M150B T209B T209B T209B M359 X X X X X X X X X 96 X 96 X X 96 X 96 Note: Courses that are obligatory for a certain track may be taken as electives in other tracks. 4. Correspondences between courses in the old study plan and courses in the new study plan New Study Plan Equivalent Courses in the Old Study Plan New Courses Course Code Course Title Credit Hours T103 Computer Architecture, Logic and Information Processing 3 CS103 3 CS105 M105 Introduction to Computer Programming MU120A MU120B MST121A MST121B Open Mathematics (I) Open Mathematics (II) 4 Using Mathematics (I) Using Mathematics (II) 4 MU120 4 MST121 4 Discrete Mathematics M131 Course Code CS131 3 52 Course Title Computer Architecture , Logic and Information Processing Introduction to Computer Programmin g Open Mathematic s Using Mathematic s Discrete Mathematic s Credit Hours 3 3 8 8 3 M150A M150B T175A Data, Computing and Information (I) Data, Computing and Information (II) Networked Living: Exploring Information and Communicattions Technologies (I) Networked Living: Exploring Information and Communicattions Technologies (II) T175B 4 M150 4 4 T175 4 Data, Computing and Information Networked Living: Exploring Information and Communica tion Technologie s 8 8 Is equivalent to T171 T209A T209B M255 M256 MT262A MT262B M362 M363 T324 T325 T490 Telematics (I) Telematics (II) Object Oriented Programming with Java Software Development with Java Putting Computer System to Work (I) Putting Computer System to Work (II) Developing Concurrent Distributed Systems Software Engineering with Objects 8 8 Keeping Ahead in ICT Technologies for Digital Media Selected Topics in Computer Science 8 T209 8 M206 8 4 MT262 4 8 M301 8 T305 8 CS490 3 53 Telematics Computing, An Object Oriented Approach Putting Computer Systems to Work Software Systems and their Developme nt Digital Communica tions Selected Topics in Computer Science 16 16 8 16 16 3 Appendix 5 Bachelor of Education Program (B.Ed.) in Elementary Education 4.1 Bachelor of Education (B Ed.) in Elementary Education This is a full four-year program (eight semesters) that seeks to qualify holders of a secondary school certificate or its equivalent as elementary (primary) school teachers. This degree requires the successful completion of 128 credit hours minimum of the prescribed courses as follows: i. ii. General Studies (University Requirements): Courses in General Studies constitute 30 credit hours. Courses in language, computer and internet skills, and Self-Learning skills form the mandatory portion of these requirements. Courses in the Humanities form the elective portion of these requirements. Discipline-based Studies: These courses constitute 98 credit hours, comprising both compulsory core courses (54 credit hours) and electives (44 credit hours). Requirements of the Program University Requirements Behavioral and Professional Requirements Compulsory Requirements (specialization) Total Credit Hours 30 Credit Hours 54 Credit Hours 44 Credit Hours 128 Credit Hours 1. University Requirements Course Code Course Title GR101 GR100 AR111 AR112 EL111 EL112 GR111 GR112 GR115 GR131 Self-Learning Skills Computer and Internet Skills Arabic Communication Skills (1) Arabic Communication Skills (2) English Communication Skills (1) English Communication Skills (2) Islamic and Arab Civilization Developmental Issues and Problems in the Arab World Contemporary International Issues and Problems Branch Requirement 54 Credit Points 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 Prerequisites AR111 EL111 - 3 3 - 3 - 8. Behavioral and Professional Requirements These requirements aim at providing the student with the necessary theoretical knowledge and practical skills to enable him/her to contribute effectively to the education process. These requirements consist of 16 compulsory courses with a total of 54 credit hours. These courses are: Course Code ED111 ED212 ED313 ED221 ED121 ED422 ED323 ED324 ED423 ED331 ED241 ED332 ED431 ED442 ED441 ED449 3. Course Title Introduction to Education Elementary Education Class Management and Learning Environment Teaching and Learning Psychology Developmental Psychology (Childhood) Principles of Guidance and Counseling Children with Special Needs Education Learning Disabilities Measurement, Evaluation and Setting of School Tests Educational Technology Curricula and General Teaching Methods Computer Assisted Teaching Designing and Producing Educational Software Research Methodology Teaching Practice (1) Teaching Practice (2) Credit Hours 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 6 6 Academic Specialization Requirements These requirements aim at providing the student with the theoretical knowledge and practical skills needed for teaching the major subjects in the curricula of the first four classes (levels) in the elementary stage. These courses include 11 compulsory courses with a total of 44 credit hours. Course Code ED251 ED252 ED353 ED354 ED255 ED256 ED253 ED254 ED363 ED364 Course Title Islamic Studies for Elementary Level Teachers Islamic Studies Teaching Methods in Elementary Schools Arabic Language for Elementary School Teachers Arabic Language Teaching Methods in Elementary Schools English Language for Elementary School Teachers* English Language Teaching Methods in Elementary Schools* Social Studies for Elementary School Teachers Social Studies Teaching Methods for Elementary Schools Mathematics for Elementary School Teachers Mathematics Teaching Methods for Elementary Schools 55 Credit Hours 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 ED467 ED468 ED482 Science for Elementary School Teachers (1) Science for Elementary School Teachers (2) Environmental and Health Sciences 4 4 4 * Registration in courses ED255 and ED256 can be done as an alternative for the Islamic Studies courses (ED251 and ED252) for non-Muslims. 4.2 Postgraduate Diploma in Education Program Requirements: Students are required to complete 36 credit hours to get the postgraduate diploma. Due to the nature of the open education system adopted by the AOU, the student is not obliged to complete the program within a specific period of time. The student registers the credit hours pursuant to his/her circumstances and conditions (whether social or practical). The program requirements are grouped as follows: (i) University General Requirements (6 credit hours) These requirements aim at developing the students' skills in the independent learning fields and the use of the computer and internet. These requirements are compulsory and include two courses of 3 credit hours each, with a total of 6 credit hours. These courses are: Course Code GR100 GR101 (ii) Course Title Skills of Using the Computer and Internet Self-Learning Skills Total Credit Hours 3 3 6 Domain Requirements (12 credit hours) The domain requirements are linked directly to the program objectives which aim to provide the student with the necessary theoretical knowledge and practical skills to enable him/her to contribute effectively to the educational and teaching process. These requirements include nine compulsory courses with a total of 27 credit hours. These courses are divided into educational and psychology courses (12 credit hours) and behavioural and professional courses (15 credit hours), as follows: Educational and Psychology Courses Course Code ED321 ED511 ED521 ED523 (12 credit hours) Course Title Teaching and Learning Psychology Introduction to Education Developmental Psychology (Adolescence) Measurement and Evaluation and Setting of School Tests Total 56 Credit Hours 3 3 3 3 12 Behavioural and Professional Courses Course Code ED433 ED531 ED534 ED536 ED533* ED535* ED537* ED538* ED532* ED539* Course Title Credit Hours 3 3 4 2 3 3 3 3 3 3 30 Educational Technology Curricula and Teaching Methods Teaching Practice Research Methodology Islamic Studies Curricula and Teaching Methods English Language Curricula and Teaching Methods Natural Sciences Curricula and Teaching Methods Mathematics Curricula and Teaching Methods Arabic Language Curricula and Teaching Methods Social Studies Curricula and Teaching Methods Total * One course according to specialization. (iii) Electives (2 credit hours) These electives include a group of courses, two credit hours each. The student must choose one course only. Course Code ED422 ED512 ED513 Credit Hours Principles of School Guidance and Counseling 2 International Educational Innovations 2 Systems and Problems of Education in the Arab States 2 Total 2* * Please note there are slight differences in different branches according to local requirements. 4.3 Course Title Bachelor Degree (B.Ed.) in Special Education This degree requires the successful completion of 132 credit hours. Mandatory Courses Semester One Course Code GR100 GR101 AR111 EL111 Course Title Computer and Internet Studies Self-Study Learning? Skills Arabic Communication Skills Communication Skills in No. of Units 3 Theoretical Practical Prerequisite 3 - - 3 3 - - 3 3 - - 3 3 - - 57 English (1) Introduction to Special 3 SP100 Education* Total 15 ** SP100 is compulsory for all specializations Semester Two Course Code GR111 AR112 EL112 SP111 ED121 ED241 Course Title History of Islamic Culture Communication Skills in Arabic (2) Communication Skills in English (2) Special Art Education Developmental Psychology (Childhood Curricula and Methods of Instruction Total No. of Units 3 3 3 - - 15 Theoretical Practical Prerequisite 3 3 - AR111 3 3 - EL111 2 3 3 3 - - 3 3 - - 17 17 - Semester Three Course Code SP202 SP205 SP210 SP112 ED313 ED363 Course Title Early Intervention in Special Education Evaluation and Diagnosis in Special Education Intellectual Capabilities/Theories of Mental Formation Special Physical Education Classroom Management and Learning Environment Mathematics for Teachers of Special Education Total No. of Units Theoretical Practical Prerequisite 3 3 - - 3 3 - - 3 3 - - 2 2 - - 3 3 - - 4 4 - - 18 18 58 Semester Four Course Code Course Title No. of Units Theoretical Practical Prerequisite 3 3 - - SP233 Introduction to Rehabilitation of Persons with Special Needs Communication Disorders Building and Modifying Behaviour 3 3 3 3 - - SP235 Emotional Behavioural Disorders and Autism 3 3 - - ED221 Psychology of Learning and Instruction 3 3 - - ED482 Health and Environmental Sciences 4 4 19 19 SP211 SP230 Total 4.3.1 Specialization: Mental Retardation Semester Five Course Code Course Title No. of Units Theoretica l Practica l Prerequisit e SP301 Introduction to Mental Retardation 3 3 - - SP305 Introduction to Multiple Disability 3 3 - - SP315 Theories of Mental Retardation 2 2 - - ED320 Individual Education Programme 3 3 - - ED332 Computer Assisted Learning 3 3 - - AR325 Arabic for Special Education Teachers 3 3 - - 17 17 - Total 59 Semester Six Course Code Course Title No. of Units Theoretical Practical Prerequisite SP330 Computer Applications for the Mentally Retarded 3 2 1 ED332 SP333 Teaching Methods for the Mentally Retarded 3 3 - - SP335 Designing Curricula for Persons with Special Needs 3 3 - - SP340 Working with Families of Persons with Special Needs 3 3 - - ED345 Adaptive Behaviour Skills 3 2 1 - ED364 Teaching Methods of Mathematics 4 4 19 17 Total 2 Semester Seven Course Code SP401 SP405 SP410 SP415 ED420 ED431 Course Title Case Study in Mental Retardation Contemporary Issues in Special Education Administration and Supervision in Special Education Integrating and Other Educational Alternatives Science for Special Education Teachers Designing and Producing Educational Software Total 60 No. of Units Theoretica l Practica l Prerequisit e 2 1 1 SP333 3 3 - - 3 3 - - 3 3 - - 3 3 - - 3 2 1 - 17 15 2 Semester Eight Course Code SP444 Course Title No. of Units Practicum in Mental Retardation Total Theoretical 10 Practical Prerequisite 10 SP333 - 10 10 4.3.2 Specialization: Learning Difficulties Semester Five Course Code SP302 SP305 SP316 SP321 ED332 AR325 Course Title Introduction to Learning Difficulties Introduction to Multiple Disability Theories of Learning Difficulties Learning Difficulties in Reading and Writing Computer Assisted Learning Arabic for Special Education Teachers Total No. of Units 3 Theoretical Practical Prerequisite 3 - - 3 3 - - 2 2 - - 3 3 - - 3 3 3 3 - - 17 17 - - Semester Six Course Code SP331 SP334 SP336 SP340 SP345 SP364 Course Title Using Computers in Learning Difficulties Teaching Methods of Learning Difficulties Developmental Learning Difficulties Working with Families of Persons with Special Needs Adapted Behaviour Skills Teaching Methods of Mathematics Total No. of Units 3 Theoretical Practical Prerequisite 3 - - 3 3 - - 3 3 - - 3 3 - - 3 4 3 4 - - 19 19 61 Semester Seven Course Code SP402 SP405 SP410 SP415 SP420 SP431 Course Title Case Study of Learning Difficulties Contemporary Issues in Special Education Administration and Supervision in Special Needs Integrating and Other Educational Alternatives Science for Special Education Teachers Designing and Producing Educational Software Total No. of Units 2 Theoretical Practical 1 1 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 2 17 15 Prerequisite 1 Semester Eight Course Code SP477 4.4 Course Title Practicum (Field Training) in Learning Difficulties Total No. of Units 10 Theoretic al - Practical Prerequisite 10 - 10 Diploma in Special Education (Mental Retardation) Mandatory Courses Semester One Course Code GR100 GR101 ED322 ED332 SP550 SP555 (18 Credit Hours) Course Title Computer and Internet Skills Self-Learning Skills Developmental (Childhood) Psychology Computer Assisted Learning Introduction to Special Education Building and Modifying Behaviour Total credit hours of Level 1 62 Credit Hours 3 3 3 3 3 3 18 Semester Two: Mental Retardation Track Course Code SP564 SP565 SP566 SP567 SP568 SP569 (17 Credit Hours) Course Title Introduction to Mental Retardation Evaluation and Diagnosis in Special Education Individual Programmes for the Mentally Retarded Adaptive Behaviour for the Mentally Retarded Teaching Methods for the Mentally Retarded Administration and Supervision in Special Education Total credit hours Credit Hours 3 3 3 3 3 2 17 Semester Three Course Code SP575 SP576 SP577 Course Title Working with the Families of People with Special Needs Integrating Students with Special Needs in Ordinary Schools Practicum Total credit hours Credit Hours 2 2 5 9 4.5 BEd for Intermediate and Secondary Stages The Bachelor of Education for Intermediate and Secondary Stages (BEd) comprises six specializations (Arabic Language, English Language, Mathematics, Computing, Geography, History). Programme Aims and Objectives The Faculty of Education Studies (FES) has developed the BEd for Intermediate and Secondary Stages in order to: Contribute towards the achievement of the mission and objectives of the Arab Open University, dissemination of knowledge and contribution to human development in the Arab states Meet the high demand in the Arab world for intermediate and secondary school teachers Enhance the quality of teacher preparation and training and thereby contribute to the development and improvement of intermediate and secondary education in the Arab states. Its aims and objectives are to: 63 Provide students with high quality instruction and training in education Offer a programme of distance learning that addresses the academic and professional needs of students and the community Provide a supportive environment that will help students develop sound theoretical and practical competencies that will serve them well in their professional lives Develop students’ creative and critical thinking and communication skills Prepare students for further and more advanced studies Prepare and qualify students as teachers in intermediate and secondary schools or for careers in the human and social development sectors Develop students’ knowledge of, and interest in, the teaching profession Provide students with the appropriate academic knowledge and professional training in order to provide children with appropriate learning opportunities Encourage students to develop their self-reflective and independent learning skills in preparation for lifelong learning. The BEd programme will: Provide students with the knowledge, skills, expertise and commitment required to develop in? the teaching profession and to become effective teachers at the intermediate and secondary stages Prepare and train teachers to deal successfully with the demands and challenges of the teaching profession in the twenty-first century Contribute towards meeting the demand for teachers in the Arab states especially in those where the AOU operates Offer opportunities to others (non-teachers) to pursue their university studies in education. Programme Structure The total number of credit points required for the degree is 440, divided as follows: 1- University Requirements (90 Credit Points) These requirements focus on providing the student with practical skills, particularly communication skills and include eight compulsory courses with a total of 80 credit points and one elective course with a total of 10 credit points. These courses are: Compulsory courses Course Code AR111 AR112 EL111 EL112 GR100 GR101 GR131 ED482 (80 Credit Points) Course Title Arabic Communication Skills (I) Arabic Communication Skills (II) English Communication Skills (I) English Communication Skills (II) Computer and Internet Skills Self-Learning Skills Branch Requirement Environmental and Health Sciences 64 Credit Points 10 10 10 10 10 10 10 10 Prerequisites AR111 EL111 - Elective Courses One from the following: Course Code GR112 GR111 (10 Credit Points) Course Title Contemporary International Issues and Problems Arab and Islamic Culture Credit Points Prerequisites 10 - 10 - 2. General Education Requirements (160 Credit Points) These requirements aim at providing the student with the theoretical knowledge and practical skills necessary to contribute effectively to pupils' learning. These include 12 compulsory courses with a total of 140 credit points and two elective courses with a total of 20 credit points. Course Code ED112 ED120 ED122 ED140 ED242 ED113 ED231 ED227 ED123 ED245 Course Title Credit Points Foundations of Education Developmental Psychology Educational Psychology Curriculum Teaching Strategy Class Management and Learning Environment Educational Technology Principles of Guidance and Counselling Measurement, Evaluation and Setting of School Tests Research Methodology Teaching Practice (I) ED343 ED349 10 10 10 10 10 10 10 10 10 10 30 Teaching Practice (II) 30 65 Prerequisites ED120 ED140 ED140 ED122 ED122 ED123 ED113 ED123 ED227 ED231 ED242 ED245 EE, EA, EM, EH, EG225 ED243 Elective Courses (20 Credit Points) Two from the following: Course Code ED223 ED132 ED213 ED224 ED244 ED344 Course Title Mental Health Psychology Computer Assisted Teaching ** School Administration Education of Students with Special Needs Sociology of Education Comparative Education Credit Points 10 10 10 10 10 10 Prerequisites ED122 ED112 ED122 ED122 ED112 * The total credit points for the Computing Programme and English Language Programme is 470. **This course is compulsory for computing pathway. 2. Academic Specialization (190 Credit Points) These requirements aim to provide the student with the theoretical knowledge and practical skills needed to teach the following subjects: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Arabic Language English Language Mathematics Computing Geography History Students will follow one of these pathways as follows. (i) Arabic Language Specialization: Study Plan According to Levels 66 Foundation Level (100 Credit Points) No. Course Title 1 2 3 4 English Communication Skills (I) Arabic Communication Skills (I) Computer and Internet Skills Independent Study Skills English Communication Skills (II) Environmental and Health Sciences Foundations of Education Arabic Communication Skills (II) Elective Course from University Requirements Kuwait Branch Requirement 5 6 7 8 9 10 Course Code EL111 AR111 GR100 GR101 Credit Points 10 10 10 10 Course Type Compulsory Compulsory Compulsory Compulsory EL112 10 Compulsory EL111 ED482 10 Compulsory - ED112 AR112 10 10 Compulsory Compulsory AR111 GR000 10 Elective - GR131 10 Compulsory - Course Code ED123 Credit Points Course Type Prerequisites 10 Compulsory ED122 ED120 ED122 ED140 10 10 10 Compulsory Compulsory Compulsory ED120 - ED113 10 Compulsory - ED000 10 Elective - EA000 10 Elective - EA110 EA111 EA112 EA113 EA114 10 10 10 10 10 Compulsory Compulsory Compulsory Compulsory Compulsory EA111 Prerequisites - Level 1 (120 Credit Points) No. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Course Title Measurement, Evaluation and Setting of School Tests Developmental Psychology Educational Psychology Curriculum Classroom Management and Learning Environment Elective from Education Elective Course from Specialization Introduction to Linguistics Morphology and Syntax (I) Arabic Rhetoric Pre-Islamic Poetry Morphology and Syntax (II) 67 Level 2 (120 Credit Points) No. 1 2 3 Course Title Teaching Strategy Elective from Education Educational Technology Principles of Guidance and Counselling 4 Course Code ED242 ED000 ED231 Credit Points 10 10 10 Course Type Compulsory Elective Compulsory ED227 10 Compulsory Prerequisites ED140 ED140 ED122 ED242 5 Special Teaching Methods EA225 10 Compulsory 6 Research Methodology Elective Course from Specialization Islamic and Umayyad Poetry Literary Criticism Prosody Abbassiyad Poetry Morphology and Syntax (II) ED245 10 Compulsory ED123 EA000 10 Elective - EA220 EA222 EA224 EA226 EA228 10 10 10 10 10 Compulsory Compulsory Compulsory Compulsory Compulsory EA113 EA220 EA114 Course Code Credit Points Course Type Prerequisites 7 8 9 10 11 12 Level 3 (120 Credit Points) No. Course Title 1 Teaching Practice (I) ED343 30 Compulsory 2 Teaching Practice (II) Elective Course from Specialization Modern Arabic Poetry Modern Arabic Prose Applications in Arabic Syntax Seminar on Research Methodology in Arabic Language Comparative Literature ED349 30 Compulsory EA000 10 Elective EA330 EA333 EA336 EA339 10 10 10 Compulsory Compulsory Compulsory Compulsory 3 4 5 6 7 8 10 EA342 68 10 ED113 ED123 ED227 ED231 ED242 EA225 ED343 EA226 EA228 EA228 Compulsory EA330 (ii) English Language Specialization: Study Plan according to Levels Foundation Level No. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 (110 Credit Points) Course Title English Communication Skills (I) Arabic Communication Skills (I) Computer and Internet Skills Independent Study Skills English Communication Skills (II) Environmental and Health Sciences Foundations of Education Arabic Communication Skills (II) Elective Course from University Requirements Kuwait Branch Requirement English Phonetics and Linguistics Course Code Credit Points Course Type Prerequisites EL111 10 Compulsory - AR111 GR100 GR101 10 10 10 Compulsory Compulsory Compulsory - EL112 10 Compulsory EL111 ED482 10 Compulsory - ED112 10 Compulsory - AR112 10 Compulsory AR111 GR000 10 Elective - GR131 10 Compulsory - EL120 10 Compulsory - 69 Level1 No. 1 (120 Credit Points) Course Title Measurement, Evaluation and Setting of School Tests Developmental Psychology Educational Psychology Curriculum Classroom Management and Learning Environment Elective from Education 2 3 4 5 6 Elective Course from Specialization Elective from Education The English Language: Past, Present and the Future (I) 7 8 9 The Short Story and Essay Writing Elective Course from 11 Specialization Level 2 (120 Credit Points) 10 Credit Points Course Type Prerequisites 10 Compulsory ED122 ED120 ED122 ED140 10 10 10 Compulsory Compulsory Compulsory ED120 - ED113 10 Compulsory - Elective - Course Code ED123 ED000 10 EE000 10 Elective - ED000 10 Elective - U210A 20 Compulsory - 10 Compulsory 10 Elective EL121 EE000 EL120 - No. Course Title Course Code Credit Points 1 3 Teaching Strategy Educational Technology Principles of Guidance and Counseling Research Methodology Approaching Literature (I): The Realist Novel and Shakespeare and the Canon The English Language: Past, Present and the Future (II) English Language Teaching Methods ED242 ED231 10 10 Course Type Compulsory Compulsory ED227 10 Compulsory ED122 ED245 10 Compulsory ED140 20 Compulsory - U210B 30 Compulsory U210A EE225 30 Compulsory ED242 4 5 6 7 8 Level 3 No. A210A Prerequisites ED140 ED242 (120 Credit Points) Course Title Course Code Credit Points Course Type ED343 70 Prerequisites ED113 30 1 Teaching Practice (I) 2 Teaching Practice (II) 3 English Language and Literacy English Grammar in Context 4 (iii) Course Title 1 2 3 4 English Communication Skills (I) Arabic Communication Skills (I) Computer and Internet Skills Self-Learning Skills English Communication Skills (II) Environmental and Health Sciences Foundations of Education Arabic Communication Skills (II) Elective Course from University Requirements Kuwait Branch Requirement Learning Online 7 8 9 10 11 30 Compulsory ED343 ED300A 30 Compulsory U210A E303A 30 Compulsory U210A (110 Credit Points) No. 6 ED349 Computing Specialization: Study Plan According to Levels Foundation Level 5 Compulsory ED123 ED227 ED231 ED242 ED245 EE225 Course Code EL111 AR111 GR100 GR101 Credit Points 10 10 10 10 Course Type Compulsory Compulsory Compulsory Compulsory Prerequisite s - EL112 10 Compulsory EL111 ED482 10 Compulsory - ED112 AR112 10 10 Compulsory Compulsory AR111 GR000 10 Elective - GR131 TU170 10 10 Compulsory Compulsory - 71 Level1 No. Course Title Measurement, Evaluation and Setting of School Tests Developmental Psychology Educational Psychology Computer Assisted Teaching* Curriculum Classroom Management and Learning Environment Data, Computing and Information Networked Living: Exploring Information and Communication Technologies Learning Online 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Level 2 No. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 120 Credit Points Course Code Credit Points Course Type Prerequisite s ED123 10 Compulsory ED122 ED120 ED122 ED132 ED140 10 10 10 10 Compulsory Compulsory Compulsory Compulsory ED120 - ED113 10 Compulsory - M150 30 Compulsory - 30 Compulsory - 10 Compulsory - T175 TU170 (120 Credit Points) Course Title Teaching Strategy Research Methodology Educational Technology Principles of Guidance and Counseling Object Oriented Programming with Java Multimedia Programming with Java Elective Course from Specialization* Elective from Education Course Code ED242 ED245 ED231 Credit Points 10 10 10 Course Type Compulsory Compulsory Compulsory ED227 10 Compulsory M255 30 Compulsory 10 Compulsory - 30 Elective - 10 Elective - M300 M000 or T000 ED000 Prerequisites ED140 ED140 ED122 M150 *The student can register either a 30 credit-hour elective course or two, or 15 credit-hour elective courses. 72 Level 3 No. (120 Credit Points) Course Title Course Code Credit Points Course Type 1 Teaching Practice (1) ED343 30 Compulsory 2 Teaching Practice (2) Relational Database Theory and Practice Project ED349 M359 30 Compulsory 30 Compulsory T471 30 Compulsory 3 4 (iv) Mathematics Specialization: Study Plan According to Levels 73 Prerequisites ED113 ED123 ED227 ED231 ED242 ED245 ED343 M255 M359 Foundation Level (100 Credit Points) Course Code Credit Points Course Type No. Course Title 1 English Communication Skills (1) EL111 10 Compulsory - 2 Arabic Communication Skills (1) AR111 10 Compulsory - 3 Computer and Internet Skills GR100 10 Compulsory - 4 Self-Learning Skills GR101 10 Compulsory - 5 English Communication Skills (2) EL112 10 Compulsory EL111 6 Environmental and Health Sciences ED482 10 Compulsory - 7 Foundations of Education ED112 10 Compulsory - 8 Arabic Communication Skills (2) AR112 10 Compulsory AR111 9 Elective Course from University Requirements GR000 10 Elective - 10 Kuwait Branch Requirement GR131 10 Compulsory - Level 1 (120 Credit Points) 74 Prerequisites No. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Course Title Course Code Measurement, Evaluation and Setting of School Tests Credit Points Course Type Prerequisites 10 Compulsory ED122 ED123 ED120 ED122 ED140 10 10 10 Compulsory Compulsory Compulsory ED120 - Developmental Psychology Educational Psychology Curriculum Classroom Management and Learning Environment Elective from Education Calculus I Calculus II ED113 10 Compulsory - ED000 EM110 EM120 Elective Compulsory Compulsory EM110 Linear Algebra I EM112 10 10 10 10 Compulsory Physics Principles of Statistics Probability Theory EM113 EM117 EM118 10 10 10 Compulsory Compulsory Compulsory - Course Code ED242 ED000 ED231 Credit Points 10 10 10 Course Type Compulsory Elective Compulsory ED227 10 Compulsory ED122 EM225 10 Compulsory ED242 ED245 10 Compulsory - EM222 10 Compulsory EM120 EM216 10 Compulsory - EM214 10 Compulsory EM120 EM217 10 Compulsory - EM265 10 Compulsory EM120 EM000 10 Elective - - Level 2 (120 Credit Points) No. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Course Title Teaching Strategy Elective from Education Educational Technology Principles of Guidance and Counseling Special Teaching Methods Research Methodology Calculus Foundation of Mathematics Geometry Ordinary Differential Equations Real Analysis Elective Course from Specialization* 75 Prerequisites ED140 ED140 Level 3 (120 Credit Points) No. Course Title Course Code Credit Points Course Type Prerequisites ED113 ED123 ED227 ED231 ED242 EM225 ED343 1 Teaching Practice (I) ED343 30 Compulsory 2 Teaching Practice (II) ED349 30 Compulsory 3 4 Number Theory Abstract Algebra I Elective Course from Specialization * Elective Course from Specialization * Complex Analysis Introduction to Topology EM315 EM310 10 10 Compulsory Compulsory - EM000 10 Elective - EM000 10 Elective - EM336 EM369 10 10 Compulsory Compulsory EM265 - 5 6 7 8 (v) Geography Specialization: Study Plan According to Levels Foundation Level No. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 (100 Credit Points) Course Title English Communication Skills (I) Arabic Communication Skills (I) Computer and Internet Skills Self-Learning Skills English Communication Skills (II) Environmental and Health Sciences Foundations of Education Arabic Communication Skills (II) Elective Course from University Requirements Kuwait Branch Requirement Course Code Credit Points Course Type Prerequisites EL111 10 Compulsory - AR111 GR100 GR101 10 10 10 Compulsory Compulsory Compulsory - EL112 10 Compulsory EL111 ED482 10 Compulsory - ED112 AR112 10 10 Compulsory Compulsory AR111 GR000 10 Elective - GR131 10 Compulsory - Level 1 (120 Credit Points) 76 No. 1 Course Title Course Code ED123 Credit Points Course Type Prerequisites 10 Compulsory ED122 ED120 ED122 ED140 10 10 10 Compulsory Compulsory Compulsory ED120 - ED113 10 Compulsory - ED000 EG109 EG110 10 10 10 Elective Compulsory - 6 7 8 Measurement, Evaluation and Setting of School Tests Developmental Psychology Educational Psychology Curriculum Classroom Management and Learning Environment Elective from Education General Geography Introduction to Mapping 9 10 Physical Geography Regional Geography EG111 EG112 10 10 11 12 Human Geography EG113 10 Elective Specialization EG000 10 Course Code ED242 ED000 ED231 Credit Points 10 10 10 ED227 2 3 4 5 Compulsory Compulsory Compulsory - Compulsory Elective - Course Type Prerequisites Compulsory Elective Compulsory ED140 ED140 10 Compulsory ED122 Level 2 (120 Credit Points) No. 1 2 3 Course Title Teaching Strategy Elective from Education Educational Technology Principles of Guidance and Counseling 4 5 Special teaching Methods EG225 10 Compulsory 6 7 8 9 Research Methodology Geography of Population ED245 EG214 Geography of Settlements Economic Geography EG215 EG216 10 10 10 10 10 Climatology EG217 10 Compulsory Compulsory Compulsory Compulsory Compulsory 11 Geography of Kuwait EG222 10 12 Elective Specialization EG000 10 Level 3 (120 Credit Points) 77 Compulsory Elective ED242 ED123 EG113 EG113 EG111 EG112 EG112 EG113 - No. Course Title Course Code Credit Points Course Type 1 Teaching Practice (I) ED343 30 Compulsory 2 Teaching Practice (II) ED349 30 Compulsory EH301 4 Modern and Contemporary History of Kuwait Distribution Maps EG311 10 5 Geography of Arab Region EG313 10 Interpretation of Maps and Air Photos Seminar on Research Methodology in Geography Elective Specialization EG314 3 6 7 8 EG316 EG000 10 10 10 10 Compulsory Compulsory Compulsory Compulsory Compulsory Prerequisites ED113 ED123 ED227 ED231 ED242 EG225 ED343 EG112 EG112 EG110 EG225 Elective - (vi) History Specialization: Study Plan According to Levels Foundation Level No. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 (100 Credit Points) Course Title English Communication Skills (I) Arabic Communication Skills (I) Computer and Internet Skills Self-Learning Skills English Communication Skills (II) Environmental and Health Sciences Foundations of Education Arabic Communication Skills (II) Elective Course from University Requirements Kuwait Branch Requirement Course Code Credit Points Course Type Prerequisites EL111 10 Compulsory - AR111 10 Compulsory - GR100 GR101 10 10 Compulsory Compulsory - EL112 10 Compulsory EL111 ED482 10 Compulsory - ED112 10 Compulsory - AR112 10 Compulsory AR111 GR000 10 Elective - GR131 10 Compulsory - Level 1 (120 Credit Points) 78 Credit Points Course Type Prerequisite s 10 Compulsory ED122 ED120 ED122 ED140 10 10 10 Compulsory Compulsory Compulsory ED120 - ED113 10 Compulsory - ED000 EH109 10 10 Elective Compulsory - EH110 10 Compulsory - Early Islamic History Umayyad Reign EH111 EH112 10 10 Compulsory - Compulsory The Abbasid EH113 10 Elective from Specialization EH000 10 Compulsory Elective EH111 EH111 - Course Code Credit Points 10 10 10 10 Course Type Prerequisites Compulsory Elective Compulsory Compulsory ED140 ED140 ED122 10 10 10 10 Compulsory Compulsory Compulsory Compulsory ED242 ED123 EH112 EH112 Compulsory Compulsory EH113 No. Course Title Course Code 1 Measurement, Evaluation and Setting of School Tests Developmental Psychology Educational Psychology Curriculum Classroom Management and Learning Environment Elective from Education Ancient History of the Arabs Ancient History of the Arabian Peninsula ED123 9 10 11 12 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Level 2 (120 Credit Points) No. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Course Title Teaching Strategy Elective from Education Educational Technology Principles of Guidance and Counseling Special Teaching Methods Research Methodology History of Islamic Maghreb ED242 ED000 ED231 ED227 History of Andalusia Medieval History of Europe EH215 EH216 Ottoman Empire Modern and Contemporary History of Arabs Elective from Specialization EH217 10 10 EH222 10 Compulsory EH109 EH000 10 Elective - EH225 ED245 EH214 Level 3 (120 Credit Points) 79 No . 1 Course Title Course Code Credit Points Course Type Prerequisites Teaching Practice (I) ED343 30 Compulsory 2 Teaching Practice (II) ED349 30 Compulsory ED113 ED123 ED227 ED231 ED242 EH225 ED343 3 Modern and Contemporary History of the Arabian Gulf Modern and Contemporary History of Kuwait Geography of the Arab Region Modern and Contemporary History of Europe Seminar on Research Methodology in History Elective from Specialization EH300 10 Compulsory - EH301 10 Compulsory - EG313 EH315 10 10 Compulsory Compulsory EH216 EH316 10 Compulsory EH225 EG000 10 Elective - 4 5 6 7 8 80