Grad project rk
advertisement

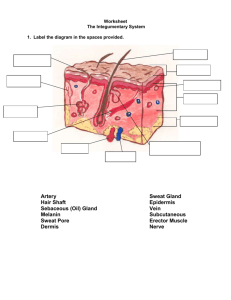
Robert Aversa Graduation Project 11th grade Hypothermia Intro The purpose of this paper is to illustrate and exemplify the details of hypothermia. Though everyone might have a general idea about what hypothermia is, my interest in the topic was stimulated when I had an experience one frigid morning this school year. Though many people sided with my vague understanding of hypothermia, I’m obliged to investigate the ins and outs of my topic in order to accomplish this project which is imperative to my graduation, and to prove my hypothesis which was opposed during the happenings of my experience. I chose hypothermia to be my topic when my homeroom teacher took the class outside in the cold one morning where we remained for several minutes shivering. On the way back inside, I sparked a discussion with my teacher about how if we would have remained outside in those conditions long enough, we were bound to suffer from hypothermia. My teacher begged to differ and opposed my skeptical statement. Thus I designated the purpose of this project to the use of proving my point, and learning about the complexities of hypothermia. Background What is Hypothermia? Hypo is a Greek root word that means “under” or “less than normal” and thermia carries the meaning “temperature”. Thus by oblivious reasons, hypothermia can be understood to mean, less than normal temperature, which is exactly what it is. There are several different stages of Hypothermia.1 The human body has an average temperature of 98.6°F. Hypothermia is the condition where the core body temperature is considerably lower than this. The first stage of hypothermia is not uncommon, and many people have probably experienced this at some point in their life. In this stage the body’s temperature drops about three degrees to around 96.5°F - 95°F. Symptoms of stage on include: goose mumps, mild shivering, and numbness in hands, blue coloring in lips. 2 Many children experience this when they are in water that is too cold to be in. This stage is not dangerous, though it may be very uncomfortable. However, if it is left untreated, it may progress into the next stages and prove to be destructive. Stage two of Hypothermia is marked by body temperature between 95°F and 91.4°F. This stage is considered to be dangerous. Symptoms may include: impaired muscle use, confusion, complete numbness in extremities, paleness in skin, blue coloring in lips and extremities, and shivering is usually extreme.3 1 “What is Hypothermia?" WiseGEEK: clear answers for common questions. Web. 03 Jan. 2010. <http://www.wisegeek.com/what-is-hypothermia.htm> 2 3 “What is Hypothermia?" “What is Hypothermia?" Body temperature of 90°F or less is defined as stage three of Hypothermia. Symptoms may include: difficulty moving, high heart rate, confusion, and failure of organs. Stage three Hypothermia is extremely dangerous and requires immediate help. “Without treatment, hypothermia at this stage is fatal.”4 Causes There are many causes for hypothermia, while some might seem oblivious, other may be obscure to the uneducated. Hypothermia is not only a condition on its own, but it can also be a symptom. Some of the most common causes of hypothermia include: Cold exposure, alcohol consumption/poisoning, exposure to cold outdoors, bacterial infections/diseases, immersion in cold water, drug overdose, or malnutrition.5 There are many other causes of hypothermia, many of which are due to a preexisting disease or condition; this is called secondary hypothermia.6 The severity of hypothermia is usually determined by the exposure to the cause. For instance, if someone were to jump into cold water and get out quickly into a warmer, drier environment, they would probably 4 5 “What is Hypothermia?" "Causes of Hypothermia - WrongDiagnosis.com." Wrong Diagnosis. Web. 03 Jan. 2010. <http://www.wrongdiagnosis.com/h/hypothermia/causes.htm> 6 "Hypothermia." Web. 03 Jan. 2010. <http://www.emedicinehealth.com/hypothermia/article_em.htm> experience only first stage at the most. But if someone were to remain in cold water, they could end up experiencing second or ever third stage hypothermia. There are three main ways your body loses heat: Radiated heat, direct contact, and wind. Heat radiates, or is emitted, from uncovered surfaces on your body. Your head is accountable for more than half of your body’s heat loss. Direct contact is when your body loses heat by being in direct contact with someone cold and thus transferring its thermal energy, such as being in a tub of cold water. The wind is also a big factor in heat loss. It carries away the warm layer of air that surrounds your skin, and this chills your outer body and requiring your body to produce more heat. The wind chill factor and be a huge impact, especially if you are wet. 7 Treatment If someone is experiencing or seems to have symptoms of hypothermia, close attention must be paid to treat it properly. There are several steps that should be taken and performed for anyone who might be experiencing hypothermia. 1) The first step is to stop further heat loss; this means removing the victim from the cold and cover and/or dry the victim.8 2) The second step is to 7 "Hypothermia: Causes - MayoClinic.com." Mayo Clinic medical information and tools for healthy living - MayoClinic.com. Web. 03 Jan. 2010. <http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/hypothermia/DS00333/DSECTION=causes> 8 Hood, Ron. "Hypothermia and Exposure." The Sanders Family Home Page. Web. 03 Jan. 2010. add heat; best case scenario would be to bring the victim inside to warm environment.9 3) The third step: add fuel to the victim; hot liquids such as soup and warm drinks are ideal, but caffeine and alcohol should be avoided at all costs.10 These steps are most effective during the earlier stages of hypothermia. If the victim is in the later stages, greater measures must be taken in order or ensure the victims health and safety. For more severe cases of hypothermia, CPR must be used accordingly. A victims breathing, pulse, and consciousness should always be monitored. If the victim becomes unconscious or has difficulty breathing, 911 must be called and the victim’s vitals must be carefully monitored. Since hypothermia is extremely dangerous and hard to treat during the later stages, it is imperative for hypothermia to be recognized and treated in the early stages before it is too late.11 Prevention measures should always be taken in order to avoid hypothermia: Make sure you are healthy and well rested, don’t travel alone, wear multiple layers, cover head, neck, hands, and feet, keep dry, and be aware of wind and wet weather.12 Risks <http://www.theozarks.com/Hypothermia_2.htm> 9 Hood, Ron Hood, Ron 11 Hood, Ron 10 12 "Hypothermia." There are many risks that can lead to hypothermia that should be recognized by everyone every time. People of older age are much more susceptible to becoming victims of hypothermia. The body’s ability to sense cold and to regulate itself may decrease with age and should be compensated for. Very young age is also a risk factor. Children lose heat faster than adults do and are less responsible when it comes to taking care of themselves. Mental illnesses are also a huge risk factor. People with mental illnesses may not be able to judge the appropriate precautions and procedures that should be taken. Alcohol and drug use are risks that include multiple factors. Alcohol and some drugs dull the body’s ability to determine safe temperatures and also impairs judgment. Certain medical conditions and medications can affect the body’s ability to heat itself and thus should be taken into account. 13 Effects Effects of hypothermia are generally active and not passive. Hypothermia affects both the mind and the rest of the body. One of the biggest affects hypothermia has on the mind is inducing confusion. A victim might not understand the situation he or she is in if the condition progresses to that state. Sometimes a victim might try to remove clothing because of confusing the feeling 13 "Hypothermia: Causes - MayoClinic.com." of cold with warmth. In the later stages of hypothermia, a victim is more likely to feel drowsy or even lose consciousness.14 The effects hypothermia has on the body are just as dangerous if not more so. Shivering and slurred speech are big signs of early hypothermia. Hypothermia also effects a person’s coordination, and often people become clumsy. 15 Perhaps the most dangerous and important affects of hypothermia is abnormal heart rate and respiration. During the early stages of hypothermia, heart rate, breathing and blood pressure increase and the body shivers to regain heat. This increase is not dangerous. However, during the later stages of hypothermia, heart rate and breathing decrease which is dangerous. Immobility follows these affects.16 In late third stage hypothermia, the heart begins irregular rhythms and brain activity is dulled, which can leave the victim seeming comatose or dead. 17 As this happens, the victim advances towards death. Conclusion As mentioned in the earlier sections, first stage hypothermia is not uncommon. Shivering is a major indicator of early hypothermia, which is experienced by many people in poor conditions. However, if early stages are left untreated, hypothermia will progress into the later stages and prove to be very harmful and even life threatening. If a person was left in a condition where they 14 Hood, Ron "Hypothermia: Causes - MayoClinic.com." 16 Hood, Ron 17 "Hypothermia." 15 began to shiver, and did not receive proper treatment steps that were explained in the Treatment sections, they would end up losing more heat, and eventually their condition would advance to the later, more serious stages of hypothermia. Works Cited "Causes of Hypothermia - WrongDiagnosis.com." Wrong Diagnosis. Web. 03 Jan. 2010. <http://www.wrongdiagnosis.com/h/hypothermia/causes.htm> Hood, Ron. "Hypothermia and Exposure." The Sanders Family Home Page. Web. 03 Jan. 2010. <http://www.theozarks.com/Hypothermia_2.htm> "Hypothermia." Web. 03 Jan. 2010. <http://www.emedicinehealth.com/hypothermia/article_em.htm> "Hypothermia: Causes - MayoClinic.com." Mayo Clinic medical information and tools for healthy living - MayoClinic.com. Web. 03 Jan. 2010. <http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/hypothermia/DS00333/DSECTION=causes> "What is Hypothermia?" WiseGEEK: clear answers for common questions. Web. 03 Jan. 2010. <http://www.wisegeek.com/what-is-hypothermia.htm>