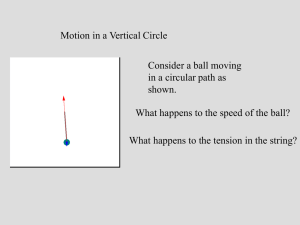
A ball on the end of a string is swung in a vertical circle
advertisement

AP Physics Name___________________ Mrs. Tsarevsky Circular Motion Quiz 4-1 A ball on the end of a string is swung in a vertical circle. The mass m of the ball is 0.25 kg and the radius of the circle R = 0.75 m. The position of the ball is marked every quarter of a revolution in the diagram below. (a) On the diagram below, draw all of the forces acting on the ball when it is at position IV. Be sure and label each force. (b) When the ball is at position IV, the tension force in the string is twice as great as the weight of the ball. Determine the speed of the ball at position IV. (c) On the diagrams below, draw and label the forces acting on the ball i. at the top of the circle (position I) and ii. at the bottom of the circle (position III). 1 AP Physics Name___________________ Mrs. Tsarevsky (d) The speed of the ball at position III (the bottom of the circle) is 5 m/s. Determine the tension force in the string as the ball passes through position III. (e) Suppose the string breaks just as the ball is at position IV. i. Describe the subsequent motion of the ball. ii. Use the speed you calculated in part (b) to determine the maximum height the ball reaches after the string breaks. 2 AP Physics Name___________________ Mrs. Tsarevsky Problem2. The Solar Maximum Mission Satellite was placed in a circular orbit about 150 mi above Earth. a) determine the orbital speed of the satellite b) the time required for one complete revolution. 3 AP Physics Name___________________ Mrs. Tsarevsky Circular Motion Quiz 4-1 ____ 1. The second hand on a watch has a length of 4.50 mm and makes one revolution in 60.00 s. What is the speed of the end of the second hand as it moves in uniform circular motion? a) 9.42 104 m/s d) 4.71 104 m/s b) 2.67 103 m/s e) 2.36 105 m/s c) 5.34 103 m/s ____ 2. A racecar is traveling at constant speed around a circular track. What happens to the centripetal acceleration of the car if the speed is doubled? a) It remains the same. b) It increases by a factor of 2. c) It increases by a factor of 4. d) It is decreased by a factor of one-half. e) It is decreased by a factor of one-fourth. ____ 3. A 0.25-kg ball attached to a string is rotating in a horizontal circle of radius 0.5 m. If the ball revolves twice every second, what is the tension in the sting? a) 2 N b) 5 N c) 7 N d) 10 N e) 20 N ____ 4. A certain string just breaks when it is under 400 N of tension. A boy uses this string to whirl a 10-kg stone in a horizontal circle of radius 10 m. The boy continuously increases the speed of the stone. At approximately what speed will the string break? a) 10 m/s b) 20 m/s c) 80 m/s d) 100 m/s e) 400 m/s ____ 5. In an amusement park ride, a small child stands against the wall of a cylindrical room that is then made to rotate. The floor drops downward and the child remains pinned against the wall. If the radius of the device is 2.15 m and the relevant coefficient of friction between the child and the wall is 0.400, with what minimum speed is the child moving if he is to remain pinned against the wall? a) 7.26 m/s b) 3.93 m/s c) 12.1 m/s d) 5.18 m/s e) 9.80 m/s ____ 6. Which force is responsible for holding a car in a frictionless banked curve? a) the reaction force to the car's weight b) the vertical component of the car's weight c) the vertical component of the normal force d) the horizontal component of the car's weight e) the horizontal component of the normal force ____ 7. Which force is responsible for holding a car in an unbanked curve? a) the car's weight b) the force of friction c) the reaction force to the car's weight d) the vertical component of the normal force 4 AP Physics Name___________________ Mrs. Tsarevsky e) the horizontal component of the normal force ____ 8. The earth exerts the necessary centripetal force on an orbiting satellite to keep it moving in a circle at constant speed. Which statement best explains why the speed of the satellite does not change even though there is a net force exerted on it? a) The satellite is in equilibrium. b) The acceleration of the satellite is 0 m/s2. c) The centripetal force has magnitude mv2/r. d) The centripetal force is canceled by the reaction force. e) The centripetal force is always perpendicular to the velocity. ____ 9. Consider a hypothetical planet in our solar system whose average distance from the Sun is about four times that of Earth. Determine the orbital period for this hypothetical planet. a) 0.25 year b) 2.5 years c) 4 years d) 8 years e) 16 years Use the following to answer questions 10-12: A 2400-kg satellite is in a circular orbit around a planet. The satellite travels with a constant speed of 6.67 103 m/s. The radius of the circular orbit is 8.92 106 m. ____10. At the instant shown in the figure, which arrow indicates the direction of the net force on the satellite? ____ 11. What is the acceleration of the satellite? a) 2.5 m/s2 b) 21 m/s2 c) 9.8 m/s2 d) 5.0 m/s2 e) zero m/s2 ____ 12. Determine the magnitude of the gravitational force exerted on the satellite by the planet. a) 1.2 104 N b) 2.4 104 N c) 5.0 103 N d) 7.5 104 N e) This cannot be determined since the mass and radius of the planet are not 5 AP Physics Name___________________ Mrs. Tsarevsky specified. ____ 13. A plane is traveling at 200 m/s following the arc of a vertical circle of radius R. At the top of its path, the passengers experience "weightlessness." To one significant figure, what is the value of R? a) 200 m b) 1000 m c) 2000 m d) 4000 m e) 40 000 m ____ 14. A 25-kg box is sliding down an ice-covered hill. When it reaches point A, the box is moving at 11 m/s. Point A is at the bottom of a circular arc that has a radius R = 7.5 m. What is the magnitude of the normal force on the box at Point A? a) 250 N b) 280 N c) 400 N d) 650 N e) 900 N ____15. Which of the following statements is one of Kepler's three laws of planetary motion? A) A line joining any planet to the sun sweeps out equal areas in equal times. B) Only an odd number of planets can orbit the sun. C) The period of any planet about the sun is proportional to the planet's distance from the sun. D) All planets move in elliptical orbits with the earth at one focus. E) F = GMm/R2 _______16. Suppose a planet exists that has half the mass of earth and half its radius. On the surface of that planet, the acceleration due to gravity is A) twice that on earth. D) one-fourth that on earth. B) the same as that on earth. E) none of these. C) half that on earth. ______17. 6 AP Physics Name___________________ Mrs. Tsarevsky Of the satellites shown revolving around the earth, the one with the greatest speed is A) 1 B) 2 C) 3 D) 4 E) 5 _______18. Two planets have masses M and m, and the ratio M/m = 25. The distance between the planets is R. The point P is between the planets as shown, and the distance between M and P is x. At P the gravitational forces on an object due to M and m are equal in magnitude. The value of x is A) 5R/6 B) 25R/36 C) R/25 D) 6R/5 E) None of these is correct. _____19. Newton's law of gravity is F = GMm/r2. What are the SI units of the gravitational constant G? A) G has no dimensions. D) kg2/N · m2 B) N · kg2/m2 E) None of these is correct. C) N · m2/kg2 ______20. The mean radius of the earth is about 6.436 × 106 m. A satellite in a circular orbit 3.20 × 106 m above the surface of the earth has an acceleration of approximately A) 39.2 m/s2 B) 22.1 m/s2 C) 14.2 m/s2 D) 6.54 m/s2 E) 4.36 m/s2 ______21. 7 AP Physics Name___________________ Mrs. Tsarevsky Five homogeneous planets have relative masses and sizes as shown in the figure. A body of mass m would weigh least on which planet? A) 1 B) 2 C) 3 D) 4 E) 5 8 AP Physics Name___________________ Mrs. Tsarevsky Answer Key -- Description 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16 17 18 19 20 21 d c e b a e b e d A d a d d A A c A c E E 9 AP Physics Name___________________ Mrs. Tsarevsky ____ 9. A car enters a horizontal, curved roadbed of radius 50 m. The coefficient of static friction between the tires and the roadbed is 0.20. What is the maximum speed with which the car can safely negotiate the unbanked curve? a) 5 m/s b) 10 m/s c) 20 m/s d) 40 m/s e) 100 m/s Answer: 9. b 12.A satellite in orbit around the earth has a period of one hour. An identical satellite is placed in an orbit having a radius that is nine times larger than the first satellite. What is the period of the second satellite? a) 0.04 h b) 3 h c) 4 h d) 9 h e) 27 h Answer 12. e 10