Worms - local.brookings.k12.sd.us
advertisement

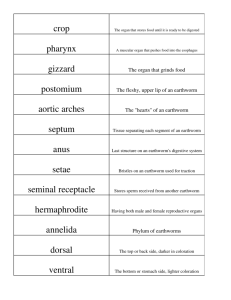
Protective outer layer MADE OF CELLS on flukes & tapeworms that protects against the host’s digestive enzymes & immune system TEGUMENT Earthworms belong to this phylum. Annelida This organ in the earthworm’s digestive system stores food before it is digested. CROP In an earthworm this digestive organ grinds the food. GIZZARD Hooks and suckers at the anterior end of a tapeworm which help it hold onto its host are called the ____________ SCOLEX The nervous system in an earthworm consists of a ventral nerve cord and two cerebral __________________ GANGLIA Protective NON-CELLULAR outer covering on earthworms & roundworms CUTICLE Earthworms belong to this CLASS Oligochaeta This ridge inside an earthworm’s intestine increases surface area so more nutrients can be absorbed TYPHLOSOLE In an earthworm this tube connects the pharynx to the crop ESOPHAGUS The intermediate host is the animal in which the ____________ form of a parasitic worm lives. LARVA ADULT The primary host is the animal in which the __________ form of a parasitic worm lives and reproduces. LARVA ADULT The excretory organs in an earthworm are called ____________________ Excretory organs in FLAT & ROUNDWORMS are called _________ NEPHRIDIA FLAME CELLS In the life cycle of the beef tapeworm, the worm larvae form ___________ in the muscles of the cows they infect. CYSTS Planaria, flukes, and tapeworms are examples of this group of worms. Flat A hermaphroditic reproductive section from a tapeworm which is released in the feces is called a ________________ Round Segmented Type of coelom found in FLATWORMS acoelom pseudocoelom eucoelom PROGLOTTID A true body cavity lined with mesoderm on both sides is called a _______________. EUCOELOM Type of coelom found in ROUND WORMS acoelom Type of coelom found in Segmented worms pseudocoelom eucoelom Hookworms, pinworms, and filarial worms are examples of _________ worms Acoelom Pseudocoelom Eucoelom FLAT Name the flatworm with no mouth, no anus, and no digestive organs. Planaria Tapeworm Fluke ROUND SEGMENTED All worms are ___________________ VERTEBRATES INVERTEBRATES Type of worm which has a scolex Planaria Tapeworm Fluke Organisms with a pseudocoelom are missing which germ layer around their internal organs? MESODERM All worms are ____________________ DEUTEROSTOMES PROTOSTOMES Type of symmetry seen in worms asymmetry These bristle-like structures on the ventral side of an earthworm give it traction. SETAE Radial Bilateral To which PHYLUM do FLATWORMS belong?____________ Annelida Platyhelminthes Nematoda The pharynx, crop, and gizzard are all parts of the _____________ system in an earthworm. Digestive To which PHYLUM do round worms belong? To which PHYLUM do SEGMENTED WORMS belong? Name 4 characteristics shared by ALL WORMS Annelida Platyhelminthes Nematoda A one opening digestive cavity seen in Planaria and flukes is called a ____________________________. GASTROVASCULAR CAVITY Annelida Platyhelminthes Nematoda Invertebrate protostomes, bilateral symmetry, elongated bodies, cephalization, cerebral ganglia, breathe through skin In the lifecycle of the beef tapeworm, the intermediate host is a ___________ Human snail cow Tapeworms live in which body organ? Type of worm that is spread to humans through insect bites. INTESTINES FILARIAL The _______ is the intermediate host for the larval form of the Schistosomiasis blood fluke. Human snail cow Type of reproduction seen in earthworms Sexual Asexual An organism that has BOTH male and female sex organs is called Humans are the __________ host in the life cycle of Schistosomiasis blood fluke. Primary Type of circulatory system seen in earthworms OPEN Direct Indirect The outer covering on an earthworm that protects it from losing moisture is called __________________ CUTICLE CLOSED The ability to regrow lost body parts is called __________________ HERMAPHRODITE Type of development seen in earthworms intermediate REGENERATION Most invertebrates are _____________ except echinoderms. protostomes deuterostomes An earthworm has ________ openings to its digestive system. 1 2 none A Planaria has ____ opening(s) to its digestive system. 1 2 Name a kind of worm that infects humans by burrowing through the skin none Blood fluke OR hookworms Nephridia and flame cells belong to which body system? Name a kind of worm that infects humans by eating undercooked meat containing cysts Excretory Beef or pork tapeworm OR Trichina pork roundworm Seminal vesicles are part of the _________________ system. Reproductive The aortic arches in an earthworm are part of the ____________system. Circulatory The ringed swelling on the body of an earthworm that produces mucous during reproduction =? CLITELLUM In an earthworm the _____________ store sperm made by the worm itself. Seminal vesicles Humans are infected by Ascaris intestinal round worms by __________ Ingesting contaminated food or water Flap of tissue that overhangs an earthworm’s mouth and senses food, light, & vibration = ? PROSTOMIUM Which worm that you learned about can reproduce asexually? PLANARIA How are a tegument and cuticle different? Tegument = made of cells Cuticle = noncellular In an earthworm this body part stores sperm received from other worms during sex SEMINAL RECEPTACLES Type of worm you would expect to have proglottids TAPEWORM ROUND CLITELLUM Type of worm you would expect to have a gastrovascular cavity Planaria OR Fluke Leeches and earthworms are examples of ____________ worms. FLAT In an earthworm this body part makes mucous to help exchange sperm SEGMENTED The part of an earthworm that acts as its heart to pump blood =? AORTIC ARCHES Tell one adaptation earthworms have to help it absorb nutrients from soil. really long intestine OR typhlosole Type of skeleton seen in earthworms fluid in coelom (hydrostatic skeleton) ________________ is the most common parasitic worm infection worldwide. Ascaris The part in a earthworm that acts as its brain = ? CEREBRAL GANGLIA Type of fertilization seen in earthworms. INTERNAL EXTERNAL In Latin the name Annelida means “little rings” Muscular part that pulls food into an earthworm’s digestive system =? PHARYNX The concentration of nervous and sensory organs in the head end of an animal is called ______________ Thin membranes that divide the coelom of an earthworm into compartments = ? SEPTA Tell how Elephantiasis is transmitted to humans Mosquito bites CEPHALIZATION Tell how beef tapeworm is transmitted to humans Eating undercooked meat containing cysts Tell how blood flukes are transmitted to humans Larvae burrow through skin Most common parasitic worm in the United States Pinworms In Latin the name Oligochaeta means “few bristles” Tell how hookworms are transmitted to humans larvae burrow through skin Tell how pinworms are transmitted to humans ingesting eggs from hands Name a worm with INDIRECT development. blood fluke (Schistosoma); Trichinella; Beef/pork tapeworm; dog heart worm Earthworms belong in this Kingdom ANIMALIA Give an example of a round worm: Pinworm, Ascaris, Trichinella Hookworms, filarial worms Earthworm part that stores sperm made to give away Seminal vesicles What disease is caused by blood flukes in which irritation, bleeding, and tissue decay result from blocked blood vessels? SCHISTOSOMIASIS Filarial worms that cause Elephantiasis live in the human _____________ system. Give the Kingdom, Phylum, and class for earthworms K: Animalia P: Annelida C: Oligochaeta What is the advantage of having a 2 opening digestive system? Can start to specialize organs “Different parts do different jobs” What roundworm disease caused by a Trichinella worm results in muscle pain, and stiffness when larvae make cysts in your muscle? TRICHINOSIS Earthworm part that makes sperm TESTES LYMPHATIC Earthworm part that makes eggs. OVARY The anus is the exit opening for the _____________ system. DIGESTIVE Earthworm part where digestion is completed and nutrients are absorbed INTESTINE Which body system collects and removes nitrogen waste & carries out osmoregulation? EXCRETORY Which body system deals with exchange of gases with the atmosphere? How do earthworms breathe? Gas exchange through their skin RESPIRATORY Give a function for Nephridia Collect/remove nitrogen waste; osmoregulation Earthworm part that stores sperm received from other worms Seminal receptacles Maintaining the balance of water and ions in the body is called ? OSMOREGULATION What form of nitrogen waste is excreted by earthworms? UREA All invertebrates have a _____________ heart & a _____________ nerve cord. (Use dorsal & ventral) All vertebrates have a _______________ heart and a _______________ nerve cord. (Use dorsal & ventral) Dorsal Heart/ventral nerve cord Ventral Heart/dorsal nerve cord Tell how the digestive system in a tapeworm is different from other kinds of flatworms. In an earthworm, the exit openings for sperm leaving the seminal vesicles is called the _____________________ Tapeworms have no anus, mouth, or digestive organs; other flatworms have a gastro-vascular cavity In an earthworm nitrogen waste is collected by _____________ & exits through pores in the _____________ nephridia ; skin Male genital pores The exit opening for digestive waste in earthworms is called the ____________ anus Tell one way digestive waste and Nitrogen waste are different. Digestive: comes from undigested food, Removed as feces by digestive system Excretory: made by body cells during metabolism: removed as urea, uric acid, or ammonia by Excretory system Body system to which cerebral ganglia and ventral nerve cord belong. NERVOUS Body system to which pharynx, crop, and gizzard belong. DIGESTIVE Give the function for the GIZZARD GRIND FOOD Give the function for the CLITELLUM Make mucous for reproduction Give the function for the INTESTINE Absorb nutrients Give the function for SETAE TRACTION Body system to which nephridia and flame cells belong. EXCRETORY Body system to which aortic arches belong CIRCULATORY Give the function for the CROP STORE FOOD Give the function for the PHARYNX Pull food iuto the digestive system Give the function for the CUTICLE protection; prevent water loss Give the function for the TYPHLOSOLE Give the function for the PROSTOMIUM Increase surface area to absorb nutrients cover/protect mouth; sense light/dark, food, & vibrations