SBA Semester 2
advertisement

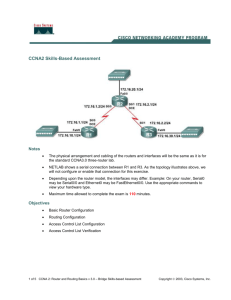
1 of 6 CCNA2 Bridge Skills-based Assessment Notes The physical arrangement and cabling of the routers and interfaces matches the standard CCNA3.0 three-router lab. Depending upon the router model, the interfaces may differ. Example: On your router, Serial0 may be Serial0/0 and Ethernet0 may be FastEthernet0/0. Use the appropriate commands to view your hardware type. Maximum time allowed to complete the exam is 110 minutes. Objectives Basic Router Configuration Routing Configuration Access Control List Configuration Access Control List Verification CCNA 2: Router and Routing Basics v 3.0 – Bridge Skills-based Assessment Adapted 23 March 2004 Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. 106759321 2 of 6 Preconfigs The following items need to be firstly pre-configured on all three routers: Hostnames on all routers IP addresses and interface descriptions on all interfaces All configured interfaces enabled Clock rates on DCE interfaces The topology cabling The console, vty and privilege passwords on routers IP host tables configured Following are the preconfigs: Router R1 hostname R1 ! enable secret class ! ip host R2 172.16.1.2 172.16.2.1 172.16.20.1 ip host R3 172.16.3.1 172.16.2.2 172.16.30.1 ! interface FastEthernet0/0 description R1 LAN ip address 172.16.10.1 255.255.255.0 no shutdown ! interface Serial0/0 description WAN link to R2 ip address 172.16.1.1 255.255.255.0 clockrate 56000 no shutdown ! ip classless ! line con 0 exec-timeout 0 0 password cisco logging synchronous login line aux 0 line vty 0 4 password cisco login Router R2 hostname R2 ! enable secret class ! ip host R1 172.16.1.1 172.16.3.2 172.16.10.1 ip host R3 172.16.3.1 172.16.2.2 172.16.30.1 CCNA 2: Router and Routing Basics v 3.0 – Bridge Skills-based Assessment Adapted 23 March 2004 Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. 106759321 3 of 6 ! interface FastEthernet0/0 description R2 LAN ip address 172.16.20.1 255.255.255.0 no shutdown ! interface Serial0/0 description WAN link to R1 ip address 172.16.1.2 255.255.255.0 no shutdown ! interface Serial0/1 description WAN link to R3 ip address 172.16.2.1 255.255.255.0 clockrate 56000 no shutdown ! ip classless ! line con 0 exec-timeout 0 0 password cisco logging synchronous login line aux 0 line vty 0 4 password cisco login Router R3 hostname R3 ! enable secret class ! ip host R1 172.16.1.1 172.16.3.2 172.16.10.1 ip host R2 172.16.1.2 172.16.2.1 172.16.20.1 ! interface FastEthernet0/0 description R3 LAN ip address 172.16.30.1 255.255.255.0 no shutdown ! interface Serial0/1 description WAN link to R2 ip address 172.16.2.2 255.255.255.0 no shutdown ! ip classless ! line con 0 exec-timeout 0 0 password cisco logging synchronous login line aux 0 line vty 0 4 password cisco login CCNA 2: Router and Routing Basics v 3.0 – Bridge Skills-based Assessment Adapted 23 March 2004 Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. 106759321 4 of 6 Configuration Tasks Basic Router Configuration Using the Preconfigs above, configure the three routers. You should verify direct connections between all interfaces before continuing. Add two loopback interfaces (loopback0 & loopback1) to router R2. These loopback interfaces will function as virtual devices in this exercise. These devices will be referred to as R2L0 and R2L1 for clarity. The syntax of commands for configuring a loopback interface: R2(config)#interface loopback number R2(config-if)#ip address ip-address subnet-mask Give R2L0 the IP address of 172.16.21.1/24. Give R2L1 the IP address of 172.16.22.1/24. Add one loopback interface to router R3. This loopback will function as a virtual device. This device will be referred to as R3L0. Give R3L0 the IP address of 172.16.31.1/24 Routing Configuration Enable IGRP on all three routers to route all network traffic. Show and analyze the routing table to ensure IGRP is working correctly. Test connectivity from R1 to R3. From R3L0, test ping and telnet connectivity to R2L0 and R2L1. Access Control List Configuration Create a named access-list that denies telnet and ping from R3L0 to R2L0 and R2L1. (You might think of this as blocking a student workstation, R3L0, from telnet and ping to your file servers, R2L0 and R2L1.) You should always be able to telnet and ping to the serial interfaces on router R2 from any source. You should also be able to telnet and ping to R2L0 and R2L1 from any source other than R3L0. Access Control List Verification Verify each configured access list to ensure that the appropriate traffic is blocked, while other traffic is permitted. Use the ip telnet source-interface command for verifying the access list with respect to that traffic. o Use this command to set the IP address of an interface as the source for all Telnet connections. If the specified interface is not up, the Cisco IOS software selects the address of the interface closest to the destination as the source address. This command is applied in the Global configuration mode. The syntax for this command is: ip telnet source-interface interface CCNA 2: Router and Routing Basics v 3.0 – Bridge Skills-based Assessment Adapted 23 March 2004 Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. 106759321 5 of 6 o Example: The following example forces the IP address for FastEthernet interface 1 as the source address for Telnet connections: o To reset the source address to the default for each connection, use the no form of this command. Router(config)# ip telnet source-interface FastEthernet1 The syntax for this command is: no ip telnet source-interface Use the extended ping command for verifying the access list with respect to that traffic. o When a normal ping command is sent from a router, the source address of the ping is the IP address of the interface that the packet uses to exit the router. If an extended ping command is used, the source IP address can be changed to any IP address on the router. The extended ping is used to perform a more advanced check of host reachability and network connectivity. The extended ping command works only at the privileged EXEC command line. The normal ping works both in the user EXEC mode and the privileged EXEC mode. To use this feature, enter ping at the command line and press "Return". You are prompted for fields as given in the example below. o With extended ping, we get the option to specify the source address of the ping packet, as shown below. Router A>enable Router A#ping Protocol [ip]: Target IP address: 192.168.40.1 !--- The address to ping. Repeat count [5]: Datagram size [100]: Timeout in seconds [2]: Extended commands [n]: y Source address or interface: 172.16.23.2 !---Ping packets will be sourced from this address. Type of service [0]: Set DF bit in IP header? [no]: Validate reply data? [no]: Data pattern [0xABCD]: Loose, Strict, Record, Timestamp, Verbose[none]: Sweep range of sizes [n]: Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 162.108.21.8, timeout is 2 seconds: !!!!! Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 36/97/132 ms !--- Ping is successful. Router A# CCNA 2: Router and Routing Basics v 3.0 – Bridge Skills-based Assessment Adapted 23 March 2004 Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. 106759321 6 of 6 The following table is provided for you to document your testing for your confirmation. If the access list fails to control the traffic, consider revising the configuration(s). Packet Type Ping From Router/Interface To Router/Interface Results router R3/Loopback0 router R2/Serial0 success Approach to this SBA Practice this assessment at your Academy. When you attend your nominated lab day follow these steps. o On each of the three routers execute the erase start and reload commands. o Perform a show run command on each router to confirm that there is no pre-existing configuration. o Work through the pre-configuration process for each router and verify the operation of the network. o Work through and verify the access list configuration portion of this SBA. o Capture and save to a diskette all commands and results (from erase start onwards) executed in the terminal session for each router as R1commands.txt, R2commands.txt and R3commands.txt. o Capture and save to the same diskette the configuration of each router as R1config.txt, R2config.txt and R3config.txt o The diskette, labeled with your name, is to be submitted at the conclusion of the SBA session. CCNA 2: Router and Routing Basics v 3.0 – Bridge Skills-based Assessment Adapted 23 March 2004 Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. 106759321