Department: Electrical and Electronic Engineering
advertisement
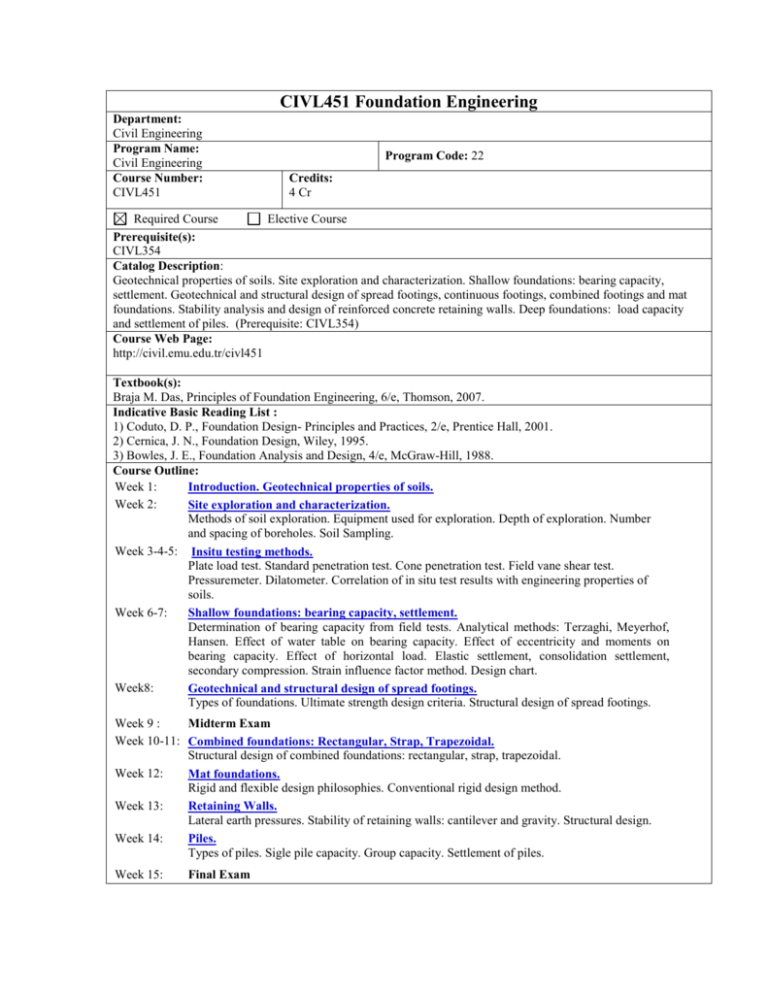
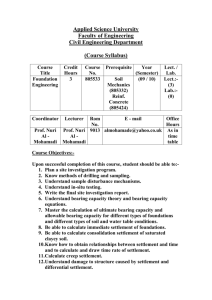
CIVL451 Foundation Engineering Department: Civil Engineering Program Name: Civil Engineering Course Number: CIVL451 Program Code: 22 Credits: 4 Cr Required Course Elective Course Prerequisite(s): CIVL354 Catalog Description: Geotechnical properties of soils. Site exploration and characterization. Shallow foundations: bearing capacity, settlement. Geotechnical and structural design of spread footings, continuous footings, combined footings and mat foundations. Stability analysis and design of reinforced concrete retaining walls. Deep foundations: load capacity and settlement of piles. (Prerequisite: CIVL354) Course Web Page: http://civil.emu.edu.tr/civl451 Textbook(s): Braja M. Das, Principles of Foundation Engineering, 6/e, Thomson, 2007. Indicative Basic Reading List : 1) Coduto, D. P., Foundation Design- Principles and Practices, 2/e, Prentice Hall, 2001. 2) Cernica, J. N., Foundation Design, Wiley, 1995. 3) Bowles, J. E., Foundation Analysis and Design, 4/e, McGraw-Hill, 1988. Course Outline: Week 1: Introduction. Geotechnical properties of soils. Week 2: Site exploration and characterization. Methods of soil exploration. Equipment used for exploration. Depth of exploration. Number and spacing of boreholes. Soil Sampling. Week 3-4-5: Insitu testing methods. Plate load test. Standard penetration test. Cone penetration test. Field vane shear test. Pressuremeter. Dilatometer. Correlation of in situ test results with engineering properties of soils. Week 6-7: Shallow foundations: bearing capacity, settlement. Determination of bearing capacity from field tests. Analytical methods: Terzaghi, Meyerhof, Hansen. Effect of water table on bearing capacity. Effect of eccentricity and moments on bearing capacity. Effect of horizontal load. Elastic settlement, consolidation settlement, secondary compression. Strain influence factor method. Design chart. Week8: Geotechnical and structural design of spread footings. Types of foundations. Ultimate strength design criteria. Structural design of spread footings. Week 9 : Midterm Exam Week 10-11: Combined foundations: Rectangular, Strap, Trapezoidal. Structural design of combined foundations: rectangular, strap, trapezoidal. Week 12: Mat foundations. Rigid and flexible design philosophies. Conventional rigid design method. Week 13: Retaining Walls. Lateral earth pressures. Stability of retaining walls: cantilever and gravity. Structural design. Week 14: Piles. Types of piles. Sigle pile capacity. Group capacity. Settlement of piles. Week 15: Final Exam Course Learning Outcomes: On successful completion of this course, all students will have developed knowledge and understanding of: (a) Exploration, sampling, and in situ soil measurements. (b) Analysis of bearing capacity and settlement of foundations. (c) Evaluation of factors considered in design of shallow foundations. (d) Structural design of shallow foundations. (e) Determination of lateral earth pressures and stability of retaining walls. (f) Determination of load capacity and settlement of deep foundations. On successful completion of this course, all students will have developed their skills in: (a) Engineering fundamentals (b) In-depth technical competence (c) Problem identification, formulation and solution (d) Professional responsibilities Class Schedule: Tutorial/Quiz/Laboratory Schedule: 4 hrs of lectures per week 1 hr of tutorial/quiz/laboratory per week Method Midterm Exam Lab/Field Work/Presentation Assessment Quizzes Homework Final Examination Contribution of Course to Criterion 5 No 1 1 3-4 5 1 Percentage 30% 5% 10% 15% 40% Credit Hours for: Mathematics & Basic Science : 0 Engineering Design : 4 General Education : 0 Relationship of Course to Program Outcomes The course has been designed to contribute to the following program outcomes: (a) an ability to apply knowledge of mathematics, science, and engineering. (b) an ability to design a system, component, social, political, ethical, health and safety, manufacturability, and sustainability. (c) an ability to identify , formulate and solve engineering problems. (d) an understanding of professional and ethical responsibility. (e) an ability to use the techniques, skills, and modern engineering tools necessary for engineering practice. (f) a recognition of the need for, and an ability to engage in life-long learning. Prepared by: Huriye Bilsel Date Prepared: 18 May 2010