Power System Analysis Homework: Transformers & Generators
advertisement

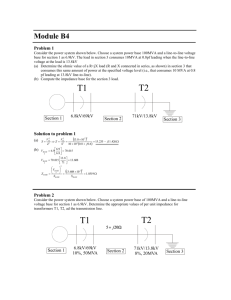
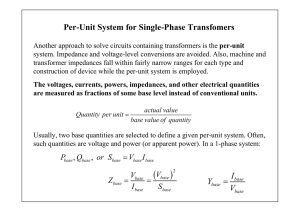
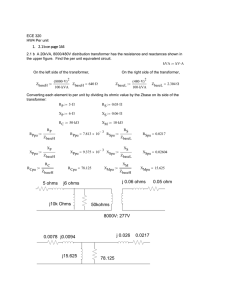
EENG 457 Power System Analysis I HOMEWORK 2 1. A single-phase 50-kVA, 2400/240 V, 50 Hz transformer is used as a step-down transformer at the load end of a line whose series impedance is Zline = 1.0 + j 2.0 . The equivalent series impedance of the transformer is 1.2 + j 2.4 referred to the high-voltage (primary) side. The transformer is delivering rated power at 0.8 power factor lagging and at rated secondary voltage. Determine (a) the voltage at the primary side of the transformer. (b) the voltage at the source end of the line. (c) the real and reactive power delivered by the source. 2. Consider the single-phase transformer circuit shown below. Transformer ratings and reactances are: Transformer A Transformer B : 30 kVA , 240 / 480 V, X = 0.10 p.u. : 20 kVA , 460 / 115 V, X = 0.10 p.u. The transmission line can be represented as a series impedance Zline =j 2 . The load impedance is Zload = 0.9 + j 0.2 . Choose a base of 30 kVA, 240 V in the voltage source ( Vs ) circuit. (a) Draw the impedance diagram for this circuit, with all impedances in per unit. (b) The source voltage is given as VS =2200 V. Find the load current both in per-unit and in amperes. (c) Find the source current (Is) in per-unit and in amperes. Is + Vs A transmission line (Zline = j 2 Ω) IL B Zload =0.9+j0.2 Ω 3-) A 500 MVA 200/20 kV three-phase Y- transformer has an equivalent impedance of 1.2 + j 4 per phase referred to the high-voltage side (Y). The transformer is supplying a three-phase load of 450 MVA, 0.8 power factor lagging at a terminal voltage of 20 kV on the low voltage side ( ). The primary is supplied from a transmission line with an impedance of 0.8 + j 1.2 per phase. Determine (a) the line-to-line voltage at the high-voltage terminals of the transformer. (b) the total complex power delivered by the source at the sending end of the transmission line. 4-) A 50 MVA, 24-kV three-phase 50-Hz synchronous generator has a synchronous reactance of 8 per phase and negligible armature resistance. The generator is delivering rated power at 0.8 power factor lagging at rated terminal voltage to an infinite bus. (a) Calculate the internal voltage Ef per phase and the power angle . (b) With the internal voltage held constant at the value in part (a), the shaft torque is reduced until the generator delivers 28 MW. Find the armature current and the power factor at the infinite bus. 5-) A three-phase synchronous generator, rated 18 kV and 150 MVA, has synchronous reactance of 1.5 per-unit. It is operated on an infinite bus of voltage 16 kV and delivers 120 MVA at 0.8 power-factor lagging. (a) Calculate the internal voltage Ef, the power angle and the armature current. (b) If the field current of the machine is reduced by 10%, while the prime mover power is maintained constant, find the new value of and the new power factor at the infinite bus. SOLUTION 1. (a) Calculations in per-unit with base: Sbase 50 kVA, Vbase 2400 V on high voltage side of transformer (H ) Z base 2 Vbase 24002 115.2 Sbase 50 103 Line and transformer impedances in per-unit: Z line 0.0087 j 0.0174 pu., Z tr 0.0104 j 0.0208 pu. Current base on primary side: I base Sbase 50 103 20.833 A 2400 Vbase Zline + Ztr I V1 Vs Vload Load (a) Vload 1.000 pu., I 1.0 cos 1 (0.8) 1.0 36.870 pu. V1 Vload Ztr I 1.0 (0.0104 j 0.0208) 1.0 36.870 1.0208 j 0.0104 pu. 1.02090.580 pu. V1 2400 1.0209 2450.2 V (b) Vs V1 Zline I 1.0209 0.580 (0.0087 j0.0174) 1.0 36.87 0 1.0382 j 0.0191 1.03841.0540 pu. Vs 2400 1.0384 2492.2 V (c) The complex power supplied by the source: S Vs I * 1.03841.0540 1.036.870 1.038437.9240 pu. 0.8191 j 0.6382 pu. Ps 50 0.8191 40.956 kW 2-) Qs 50 0.6382 31.91 kVar (a) Base voltages, Vb, B 480 V Base impedances, Zb, B , Vb,C 120 V 4802 1202 7.68 , Z 0.48 b , C 30 103 30 103 Impedances in per-unit 0.9 j 0.2 Z load 1.875 j 0.4167 0.48 p.u., ZTL 2 XT ,A 30 240 0.1 0.1 30 240 j2 j 0.2604 7.68 p.u 2 p.u, X T ,B 30 460 0.1 0.1378 20 480 Impedance diagram, j0.1 j0.2604 j0.1378 + Vs 1.875+j0.4167 p.u (b) Vs (220 / 240)0 p.u. 0.91670 p.u. IL 0.9167 Z total Z total 1.875 j 0.9149 I L 0.4394 p.u., I base (C ) p.u. I L 0.3949 j 0.1927 p.u. Sb 30 103 250 A I L 0.4394 250 109.85 A Vb (C ) 120 (c) Ibase ( A) Sb 30 103 62.5 A I L 0.4394 62.5 27.46 A Vb ( A) 480 3-) (a) Calculations in per-unit with base: Sbase 500 MVA, Vb( H ) 200 kV on high-voltage side of transformer, Vb( L ) 20 kV on low-voltage side of transformer (H ) Z base (Vb( H ) ) 2 2002 80 , Sbase 500 (L) Z base (Vb( L ) ) 2 202 0.80 Sbase 500 Line and transformer impedances in per-unit: Z line 0.01 j 0.015 pu., Z tr 0.015 j 0.05 pu. Load impedance: Z load 2 Vload 202 0.888 Sload 450 Z load 0.888 36.87 0.711 j 0.533 Z load 1.111 36.87 pu. Zline Impedance diagram: + I VH Vs Let Vload 1.00 pu. Ztr I Vload Vload 0.9 36.87 Zload VH Vload Ztr I 1.0378 j 0.0279 pu. Load pu. VH 207.64 kV line-to-line. (b) Vs VH Z line I 1.0531 j 0.0333 pu. S source Vs I * 0.7402 j 0.5927 pu. S source 370.12 j 296.33 MVA 4-) Let Vt 24 3 0 kV 13.860 kV line-to-neutral Ia 50 1.203 kA I a 1.203 36.87 kA 3 24 E f Vt jX s I a 13.86 j8 1.203 36.87 kV 19.634 j 7.698 kV line-to-neutral Generator current, E f 36.53 kV line-to-line, tan 1 (7.698 /19.634) 21.4 (b) P E f . Vt Xs sin( ) 28 MW, 3 E f E f Vt jI a X s , Let I a I a E f cos( ) 13.86 8 I a cos( ) E f sin( ) 8 I a sin( ) 39.522 28 8 E f 21.09 kV from part (a) sin 1 14.8 3 21.09 13.86 Ia tan( ) 21.09sin( ) 0.825 21.09 cos( ) 13.86 21.09sin( ) 1.0582 kA 8sin( ) 5-) Let Sbase 150 MVA, Vbase 18 kV, 120 0.8 pu. Vt I a 150 Real power: P 0.64 pu. SG Ia Vt 16 0 pu. 0.88880 pu. 18 0.8 0.9 pu., I a 0.9 36.87 pu 0.8888 (a) E f Vt jX s I a 0.8888 j1.5 0.9 36.87 1.699 j1.08 pu. 2.01332.45 pu. 32.45 . (b) E f 0.9 2.013 1.8117 pu. From part(a), prime mover power P 0.64 pu. Vt E f Xs sin( ) 0.64 1.5 0.5963 36.6 E f 1.811736.6 pu. 1.454 j1.08 0.8888 1.8117 E f Vt 0.454 j1.08 Ia 0.72 j 0.3027 pu. cos( ) 0.922 jX s j1.5 sin( )