The Components of GDP Case Study
advertisement

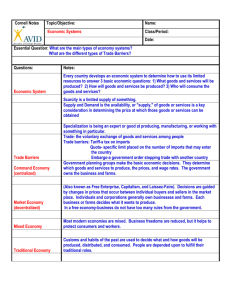
Tonya Blevins, ECO2072 Summer 2011 Case Study: The Components of GDP The Components of GDP (Gross Domestic Product) This Case study is about Gross Domestic Products (GDP) and its components. Gross Domestic Product is a measure of all of the goods and services produced in the nation during a given time period. GDP is a measure of the total income of the nation as well as the total expenditures on the economy’s output of goods and services. GDP is broken into four components. They are: consumption, investments. government purchases, and net exports. Economists study Gross Domestic Product, along with various spending, hence the reason GDP is broken down into four components, consumption, investments, government purchases, and net exports. GDP is broken into an identity equation (Y=C+I+G+NX) because the monies allocated into the four components equals the GDP. Consumption is the first component of GDP. Consumption is considered to be the spending of funds on household goods and services. Consumption excludes the purchasing of new housing. Consumption can also be durable or non-durable, which includes appliances and food. Intangible items includes item such as medical care. The second component, Investments, is goods that may be used in the future to produce more goods. Investments include the purchasing of new housing. Government purchases, the third component, are considered to be spending on goods and services by the local, state, and federal government. This includes items such as: government salaries and expenditures on public works. The last component is Net Exports. Net Exports is when monies are allocated on domestic goods by foreigners (which are exports) minus the spending on goods produced by domestic residents, which are imports. Gross Domestic Product relates to economics because its components were used to calculate the growth of the economy in the United States from 1965 to 2010. GDP has grown in the United States at a rate of about 3% per year, which allows society to enjoy a more prosperous life than most countries with a lower GDP. GDP is not always rising; periods where GDP declines is called a recession, in which incomes decreases, along with other forms of distress to include: bankruptcy and unemployment. GDP relates to economics because statistics show that countries with a larger GDP tend to have a better way of life. In short, GDP is the measure of all goods and services produced in the nation during a given time period. GDP also measure the total income of the nation, as well as the total expenditures on the economy’s output of goods and services. GDP is broken into four components: consumption, investments, government purchases, and net exports. All of those components make up the GDP or a country. Countries with a higher GDP, such as the United States have a better way of life.