Metamorphic Rock-rocks buried deep in the Earth that are changed
advertisement
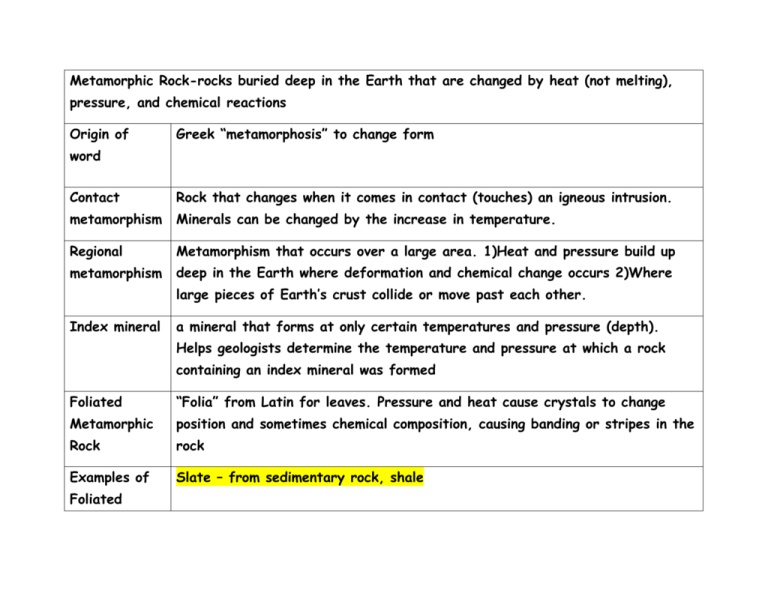
Metamorphic Rock-rocks buried deep in the Earth that are changed by heat (not melting), pressure, and chemical reactions Origin of Greek “metamorphosis” to change form word Contact Rock that changes when it comes in contact (touches) an igneous intrusion. metamorphism Minerals can be changed by the increase in temperature. Regional Metamorphism that occurs over a large area. 1)Heat and pressure build up metamorphism deep in the Earth where deformation and chemical change occurs 2)Where large pieces of Earth’s crust collide or move past each other. Index mineral a mineral that forms at only certain temperatures and pressure (depth). Helps geologists determine the temperature and pressure at which a rock containing an index mineral was formed Foliated “Folia” from Latin for leaves. Pressure and heat cause crystals to change Metamorphic position and sometimes chemical composition, causing banding or stripes in the Rock rock Examples of Slate – from sedimentary rock, shale Foliated Metamorphic Rock Schist – from igneous rock granite Gneiss – from igneous rock granite Nonfoliated Rock changed by heat and pressure. Rock has no banding or stripes, but the Metamorphic crystals may have enlarge during metamorphism. Rock Examples of Nonfoliated Metamorphic Rock Marble - from sedimentary limestone Quartzite – from sedimentary sandstone Hornfels - fine-grained. Hornfels is a rock that was "baked" while near a heat source such as a magma chamber, sill or dike. Deformation Change in shape of a rock caused by a force placed on it such as stretching or squeezing.






