Final Exam - La Salle University
advertisement

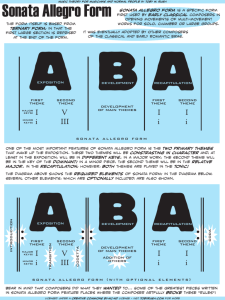
La Salle University MUS 150 Art of Listening Final Exam Name ______________________________ I. Listening Excerpt One: Elvis Costello and the Brodsky Quartet: “For Other Eyes” 1. Which of the following terms best defines the texture of this example? a. monophonic b. polyphonic c. homophonic d popophonic 2. Which of the following sections in the form of this selection are you hearing? a. B1A1 b. B1C1 c. AA1 d. C1A e. CB1 3. Which of the following describes the meter of this example? a. 2 b. 3 c. 4 d. non-metric e. no meter 4. When the B section starts, what changes? a. the rhythm b. the timbre c. the melody d. the text pattern e. no texture e. all of the above 5. When the meaning of the lyrics are portrayed in the music, it is known as ____________ . a. word painting b. illustrative c. conceptual d. cryptic e. picturesque Bonus 1: (After #71 on the Answer Sheet) Specific timbre of this example? Excerpt Two: Bonus: J. Rodrigo: “En los Trigales” 6. What is the form of this selection? a. ACBC b. BCAC c. AACB d. ABA e. CBAA 7. The rhythmic motive in this example is: a. repeated b. developed c. the basis for the entire work d. stated in the introduction e. all of the above 8. Which of the following describes the meter of this example? a. 2 b. 3 c. 4 d. non-metric e. no meter 9. Which of the following terms best defines the texture of this example? a. monophonic b. polyphonic c. homophonic d popophonic e. no texture 10. This work is describing something. What is it? a. traffic b. mountains c. people working in wheat fields d. animals at play e. a Shakespeare play 11. When music has a story or something descriptive, it is known as ____________ music. a. adventure b. illustrative c. concept d. program e. picture Bonus 2: (After #71 on the Answer Sheet) Specific timbre of this example? Excerpt Three: Sammartini: “Symphony In F Major” , first movement 12. Which of the following illustrates a basic idea of the overall form of this movement? a. AABB b. AABABA c. AA1A2A3 d. ABABAB e. ABCDE 13. This work is from the Roccoco period. What is the name I use to refer to this period? a. Common practice b. Three strikes c. Ugly Duckling d. Pre Hip Hop d. all of the above 14. The larger work that this selection is taken from is classified as a(n) a. opera. b. symphony. c. song. d. suite. e. short story 15. Which family of instruments is prominently featured in this example? a. electronic b. keyboard c. string d. percussion e. voice Bonus 3: (After #71 on the Answer Sheet) Specific timbre of this example? Excerpt Four: J.S. Bach “Bourree” 16. The larger work that this selection is taken from is classified as a(n) a. opera. b. symphony. c. song. d. suite. e. short story 17. The solo instrument is a a. violin b. guitar c. percussion d. trumpet e. pianoforte 18. Which of the following illustrates a basic idea of the overall form of this movement? a. AABB b. AAAA c. AA1A2A3 d. ABABAB e. ABCDE 19. This work is based on the form and rhythms of a: a. story b. text c. dance d. song e. all of the above Bonus 4: (After #71 on the Answer Sheet) Meter of this example? Excerpt Five: W.A. Mozart: “Symphony No. 40 In G Minor, K. 550, first movement” 20. The texture of this part of the work is: a. monophonic b. homophonic c. polyphonic d. no texture e. all of the above 21. Which family of instruments is prominently featured in this example? a. electronic b. keyboard c. string d. percussion e. voice 22. If you listen to this work as “absolute” music, what is taking place in this excerpt? a. Theme One b. the Exposition c. the Home Key d. all of the above 23. Which of the following refers to the TIMBRE of this example? a. moderately fast meter in 4 b. gradual changes from soft to loud c. a full orchestra d. consonant and dissonant e. homophonic and polyphonic texture 24. Which of the following illustrates a basic idea of the overall form of this movement? a. AABA b. ABACADA c. AA1A2A3 d. ABABAB e. ABCDE Bonus 5: (After #71 on the Answer Sheet) Meter of this example? II. Multiple Choice 25. Which of the following classifications refers to one who relies more on emotion, drama, flexibility in structure, and effect in their art? a. bohemian b. foreign c. classic d. romantic e. pedantic 26. Which of the following terms means “instrumental work in a fast tempo”? a. concerto b. sonata allegro c. symphony d. song e. movement 27. When listening to music, the “home sound” with a common center of stability is called the: a. meter b. key c. measure d. scale e. dynamic 28. Which of the following terms best defines a singing style? a. sonata b. movement c. bel canto d cadenza e. texture 29. In the Recapitulation of Sonata Allegro form, for the first time, theme 2 is? a. repeated b. louder c. faster d. in the home key e. absent 30. In any piece of music, the beat will always be played by the: a. drums b. bass c. cymbals d. violins e. it might not be played at all 31. Which of the following is not required to fit our definition of music? a. time b. organization c. singing d. sound 32. Which of the following terms is describing timbre? a. printed music b. fast c. solo guitar d soft e. texture 33. Which of the following refers to a short, instantly recognizable musical idea or fragment? a. theme b. motive c. sequence d. ostinato e. drone 34. A ____ is a resting place in music, and may be either temporary (incomplete) or permanent (complete). a. pitch b. cadence c. rhythm d. dynamic e. mezzo soprano 35. Which of the following refers to the melody in a “serious” musical composition? a. theme b. motive c. sequence d. ostinato e. drone 36. Which of the following classifications refers to more of an adherence to balance, structure, and formal considerations in their art? a. bohemian b. foreign c. classic d. romantic e. pedantic 37. Which of the following terms refers to a series of dances? a. concerto b. sonata c. symphony d. song 38. Which of the following does NOT begin in the year 1600. a. opera b. Classical Period c. Baroque Period d. Common Practice Period e. suite 39. Which of the following terms is a description of the tempo of a musical example? a. loud b. homophonic c. fast d four e. violin 40. Which of the following accurately describes the speed plan of each of the movements of a “typical” symphony from the Classical period? a. fast fast slow slow c. fast slow fast slow e. fast dancelike slow fast b. dancelike fast fast slow d. fast slow dancelike fast 41. The twelve-tone system of composition is a concept that was created and developed by: a. Bach b. Beethoven c. Schoenberg d. Miles Davis 42. In a sitcom on television, when three characters are all talking at the same time for a comic effect, this is the same as what texture in music? a. monophonic b. homophonic c. polyphonic d. unison e. pteraphonic 43. In much of the music that we hear, the beat is something that is typically: a. clearly heard b. missing c. implied d. played by one person 44. What does the term “modulate” mean? a. change speed b. change key c. change theme e. sung d. change song 45. How many movements are contained in Beethoven’s “Symphony No. 5 in C Minor, Op. 67”? a. 2 b. 3 c. 4 d 5 e. 1 46. Which of the following terms best defines the meter of a musical example? a. loud b. homophonic c. fast d four e. violin 47. In a “typical” example of Sonata Allegro form, the Coda section contains only a: a. new movement b. new theme c. new key d. big cadence e. repeated note 48. Which of the following does not typically happen to signify the end of the Development / beginning of the Recapitulation? a. running out of “steam” b. a new key c. the home key d. Theme 1 49. Which of the following occurs in the Development of Sonata-Allegro form? a. we hear the home key d. we hear the second theme in the home key b. we hear the first theme in the home key e. the themes are fragmented and modulate constantly c. the movement comes to an end 50. Which of the following terms refers to a piece of music with singing? a. concerto b. sonata c. symphony d. song e. suite 51. Which of the following terms best defines the texture of a musical example? a. loud b. homophonic c. fast d four e. violin 52. Where is the first time that you will hear Theme 2 in the Home Key in Sonata Allegro form? a. Exposition b. Development c. Recapitulation d. Coda e. Theme 2 is never heard in the home key 53. Which of the following sections is repeated? a. Exposition b. Development c. Recapitulation d. Coda 54. Which of the following does not happen in the Exposition of Sonata Allegro Form? a. a modulation b. a coda c. two themes d. the home key e. a new key 55. Classical period music will often announce "This Is The End" when approaching: a. the first Exposition b. a concerto c. a cadence d. a texture e. a beat 56. Which movement of a composition will you typically find in Sonata Allegro form? a. first b. second c. third d. fourth e. all 57. What would you NOT expect to hear in a Development section? a. home key b. polyphonic texture c. intensity d. motives e. modulation 58. Program music is a. music that is associated with an extra musical idea, person, concept. b. music that is found in a recital program c. music that is used to begin important events d. music that is not meant to be performed live 59. Which of the following do we hear at the beginning of the Recapitulation in Sonata Allegro form? a. first theme in the home key d. bridge (transition or moving music) modulating b. second theme in the home key e. second theme in a new key c. a singer’s cadenza 60. Which of the following terms best defines the dynamics of a musical example? a. loud b. homophonic c. fast d four e. violin 61. Which of the following would you expect in the first movement of a work from the Classical Period? a. it is slow b. it features dancing c. it is in Sonata Allegro form d. it is short e. it does not end 62. The term for music that contains no program and is to be enjoyed for its own sake is: a. single b. instrumental c. basic d. absolute e. dramatic 63. How many themes are usually contained in Sonata Allegro form? a. one b. two c. three d. four e. five III. Matching 64. _______ Word painting A. Energy present in the flow of music 65. _______ 66. _______ SonaSuite B. How the beats are grouped (usually 2, 3, or 4) C. Pattern of shorts and longs 67. _______ 68. _______ Rhythm Meter D. Two Sections, each repeated: AABB E. Referring to voices 69. _______ Groove F. Using musical means to illustrate the text 70. _______ 71. _______ Binary Form Cant- or Chant- G. Referring to instruments H. Collection of dances Answer Sheet and Part II Name ______________________ 1 . _____ 21. _____ 41. _____ 61. _____ 2 . _____ 22. _____ 42. _____ 62. _____ 3 . _____ 23. _____ 43. _____ 63. _____ 4 . _____ 24. _____ 44. _____ 64. _____ 5 . _____ 25. _____ 45. _____ 65. _____ 6 . _____ 26. _____ 46. _____ 66. _____ 7 . _____ 27. _____ 47. _____ 67. _____ 8 . _____ 28. _____ 48. _____ 68. _____ 9 . _____ 29. _____ 49. _____ 69. _____ 10 . _____ 30. _____ 50. _____ 70. _____ 11 . _____ 31. _____ 51. _____ 71. _____ 12 . _____ 32. _____ 52. _____ Bonus 1:__________ 13 . _____ 33. _____ 53. _____ Bonus 2:__________ 14 . _____ 34. _____ 54. _____ Bonus 3:__________ 15 . _____ 35. _____ 55. _____ Bonus 4:__________ 16 . _____ 36. _____ 56. _____ Bonus 5:__________ 17 . _____ 37. _____ 57. _____ 18 . _____ 38. _____ 58. _____ 19 . _____ 39. _____ 59. _____ 20 . _____ 40. _____ 60. _____ II. True or False. For each statement, indicate if it is true or false. *BONUS - change each false statement to make it read true. 72. _____ The term absolute music refers to a piece of music with a story. 73. _____ The Recapitulation generally does not change key, but stays in the home key. 74. _____ A symphony is a multi-movement work for orchestra with a solo instrument. 75. _____ The Exposition is the first time you will hear Theme 2 in the home key. 76. ______The most common meter you will encounter in music is four. 77. _____ "Serious" music that centers around a key is said to be from the "Common Practice" period. 78. ______ The Common Practice Period was from 1700-1800. 79. _____ Romantic composers faithfully followed the rules that Mozart set. 80. _____ Polyphonic texture contains harmony. 81. _____ The start of the Development section occurs when the music runs out of steam, and we hear the home key and theme 1 again. 82. _____ All "twelve-tone "music is atonal. 83. _____ All atonal music is "twelve-tone ". 84. _____ A "classic" sensibility stresses an awareness of form and balance. 85. _____ Romanticism displays an interest in the individual, drama, expression, and freedom. 86. _____ The end of the Common Practice Period occurs with the loss of rhythm and form. 87. _____ Any work that is in sonata allegro form is automatically the first movement. 88. _____ The Italian term "bel canto" probably refers to instrumental program music. 89. _____ It is generally unacceptable to applaud between movements of a composition. 90. _____ The art music of the twentieth century is characterized by a strengthening of tonality, reinforcing a central "key", and following all rules of the “Common Practice Period”. 91. _____ A work called a cantata is probably performed without singing. 92. _____ The first movement of most all works from the Classical period is in sonata allegro form. 93. _____ The term program music refers to a piece of music with a story. *Bonus: Please feel free to add an extra page to answer these questions if you need more room! *Follow the example that compares the plot of The Wizard of Oz to Sonata Allegro form. Use examples from the drama, and give the structural names from the form. **Double bonus: Follow the same example, but use a different dramatic work of your choosing. *Describe the organization and order of the movements of a symphony (how many, speed plan). *List the 3 Bs of music. *What is the name I use for the Rococo Period and why? *Describe Arnold Schoenberg’s 12-tone method of composition *Discuss any of the works on the program of the in-class guitar recital. Use relevant terminology. Please submit the last two pages (completed) to me by 5:00 pm on Friday, December 14. Be sure your name is on the first answer sheet! Thanks for a great semester! Best of luck for the remainder of your academic pursuits!!!