PC3243 Photonics
advertisement

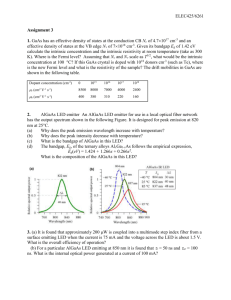
PC3243 Photonics Tutorial 3 - 2006 1. In a GaAs sample at 300K, using Joyce-Dixon approximation, a) if the Fermi level coincides with the valence band edge, calculate the hole density and hence the electron density using the law of mass action. b) if equal concentrations of electrons and holes are injected with carrier density n = p = 1017 cm-3, calculate the quasi-Fermi levels. 2. Consider an In 0.53Ga 0.47As sample at 300K in which excess electrons and holes are injected at low density of 1015 cm-3. Calculate the carrier recombination lifrtime r. Assume the same refractive index as GaAs and that the p.A matrix element is similar in form to that of GaAs. Eg = 0.8 eV me* = 0.042 mo mh* = 0.40mo 3. Sketch the absorption coefficient for GaAs as a function of photon energy in the range 1.6 – 2.2 eV. Calculate the cut-off wavelength beyond which is zero. 4. In a p-type GaAs doped with Na = 1018cm-3, electrons are injected to produce a minority carrier concentration of 1015 cm-3. What is the rate of photo emission assuming that all e-h recombination is due to photo emission? What is the optical output power? The photon energy is 1.4 eV. 5. In a GaAs sample the electrons are moving under an electric field of 5 kVcm-1 and the carrier concentration is uniform at 1016 cm-3. The electron velocity is the saturated velocity of 107 cm/s. Calculate the drift current density. If the diffusion current has the same magnitude, calculate the concentration gradient needed. Assume a diffusion coefficient of 100 cm2/s 6. An abrupt GaAs pn diode has Na = 1017 cm-3 and Nd = 1015 cm-3. a) b) c) d) Calculate the Fermi levels at 300K in the p and n regions Determine the contact potential Vbi. Calculate the depletion widths in the n and p regions The diode is under a forward bias of Vf = 0.5V. Calculate the new depletion width.