Section 2: Cell Membrane
advertisement

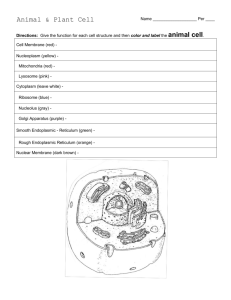
Unit 2 Name _______________________________ # ________ Section 1: Introduction to Cells 1. What scientist named cells? What kind of cells was he looking at? 2. List each of the parts of the cell theory. 3. What are the differences between prokaryotes and eukaryotes? Section 2: Cell Membrane 1. Which macromolecule do each of the following components belong to? a. Phospholipid _________________ b. Cholesterol (steroid) _________________ c. Membrane proteins _________________ d. Carbohydrate chains _________________ 2. Draw a phospholipid. Label the polar (hydrophilic) end and the non-polar (hydrophobic) end. 3. What are the functions of the cell membrane? 4. What is the function of the membrane proteins? 5. What is the function of the cholesterol? 6. What is the function of the carbohydrate chains? 7. What are two other names that refer to the cell membrane? 8. On the diagram below, color all phospholipid heads one color and the tails another color. Use a third color for all the membrane proteins. Use a forth color for carbohydrate chains, and a fifth color for cholesterol. Label all of the letters. Section 3: Diffusion 1. Is diffusion an example of active or passive transport? Why? 2. In what direction do particles move during diffusion? 3. What is the difference between simple diffusion and facilitated diffusion? Section 4: Osmosis 1. Is osmosis an example of active or passive transport? Why? 2. In what direction does water move during osmosis? 3. What is the difference between a hypotonic, isotonic, and hypertonic solution? Section 5: Active Transport 1. What makes active transport different than passive transport? 2. What is the difference between pinocytosis and phagocytosis? Section 6: Movement Across the Membrane In the pictures below, the cell on the left is permeable to the solute but not water, and the cell on the right is permeable to water but not the solute. Draw an arrow to show the direction of the net movement of the solute or the water. If there is no net movement draw an equal sign. Label each row as isotonic, hypotonic, or hypertonic. In each of the pictures below, draw an arrow to show the direction of solute movement through the transmembrane (integral) protein. Determine if the process requires energy or not, and circle the correct response. Facilitated Diffusion Requires Energy Yes Active Transport No Requires Energy Yes No Draw endocytosis and exocytosis. (Hint: You only need one picture.) Label the cell membrane, interstitial fluid, intracellular fluid, particle, and vesicle with particle. Section 7: Nucleus and Cytoplasm 1. What is the function of each of the following? a. Nucleus b. Nucleolus c. Ribosome d. Rough endoplasmic reticulum e. Smooth endoplasmic reticulum f. Golgi apparatus g. Lysosome h. Vacuole i. Mitochondria j. Chloroplast k. Cytoskeleton l. Cilia m. Flagella n. Centriole 2. Choose a color for each of the parts below and fill in the square with the color of your choice. Color the cell part to match. Cell Membrane Nucleolus Ribosome Microtubules (Cytoskeleton) Cytoplasm Golgi Apparatus Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Nuclear Membrane Nucleoplasm Flagella Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Lysosome Mitochondria 3. Choose a color for each of the parts below and fill in the square with the color of your choice. Color the cell part to match. Nucleolus Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Microtubules Cytoplasm Golgi Apparatus Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Cell Wall Nucleoplasm Vacuole Mitochondria Ribosome Nuclear Membrane Cell Membrane Chloroplasts 4. Which cell represents an animal cell? How do you know? 5. Which cell represents a plant cell? How do you know? Section 8: Cell Specialization 1. What are the differences between a unicellular and multicellular organism? 2. What is cell specialization? 3. Give an example of each of the following levels of organization. a. Atom b. Molecule c. Macromolecule d. Organelle e. Cell f. Tissue g. Organ h. Organ system i. Organism