Identity, College Adjustment and Student Success
advertisement
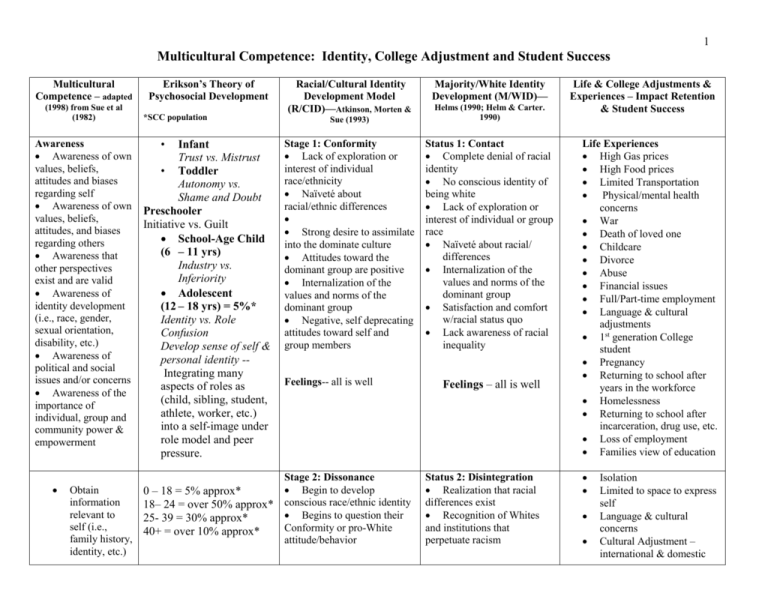
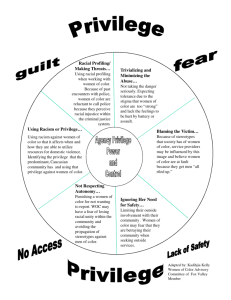
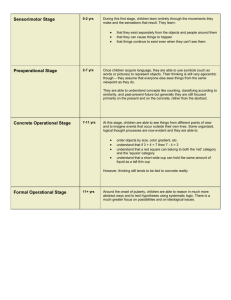
1 Multicultural Competence: Identity, College Adjustment and Student Success Multicultural Competence – adapted (1998) from Sue et al (1982) Awareness Awareness of own values, beliefs, attitudes and biases regarding self Awareness of own values, beliefs, attitudes, and biases regarding others Awareness that other perspectives exist and are valid Awareness of identity development (i.e., race, gender, sexual orientation, disability, etc.) Awareness of political and social issues and/or concerns Awareness of the importance of individual, group and community power & empowerment Obtain information relevant to self (i.e., family history, identity, etc.) Erikson’s Theory of Psychosocial Development *SCC population • Infant Trust vs. Mistrust • Toddler Autonomy vs. Shame and Doubt Preschooler Initiative vs. Guilt School-Age Child (6 – 11 yrs) Industry vs. Inferiority Adolescent (12 – 18 yrs) = 5%* Identity vs. Role Confusion Develop sense of self & personal identity -Integrating many aspects of roles as (child, sibling, student, athlete, worker, etc.) into a self-image under role model and peer pressure. 0 – 18 = 5% approx* 18– 24 = over 50% approx* 25- 39 = 30% approx* 40+ = over 10% approx* Racial/Cultural Identity Development Model (R/CID)—Atkinson, Morten & Majority/White Identity Development (M/WID)— Sue (1993) Helms (1990; Helm & Carter. 1990) Stage 1: Conformity Lack of exploration or interest of individual race/ethnicity Naïveté about racial/ethnic differences Strong desire to assimilate into the dominate culture Attitudes toward the dominant group are positive Internalization of the values and norms of the dominant group Negative, self deprecating attitudes toward self and group members Status 1: Contact Complete denial of racial identity No conscious identity of being white Lack of exploration or interest of individual or group race Naïveté about racial/ differences Internalization of the values and norms of the dominant group Satisfaction and comfort w/racial status quo Lack awareness of racial inequality Feelings-- all is well Stage 2: Dissonance Begin to develop conscious race/ethnic identity Begins to question their Conformity or pro-White attitude/behavior Feelings – all is well Status 2: Disintegration Realization that racial differences exist Recognition of Whites and institutions that perpetuate racism Life & College Adjustments & Experiences – Impact Retention & Student Success Life Experiences High Gas prices High Food prices Limited Transportation Physical/mental health concerns War Death of loved one Childcare Divorce Abuse Financial issues Full/Part-time employment Language & cultural adjustments 1st generation College student Pregnancy Returning to school after years in the workforce Homelessness Returning to school after incarceration, drug use, etc. Loss of employment Families view of education Isolation Limited to space to express self Language & cultural concerns Cultural Adjustment – international & domestic 2 Knowledge Obtain information relevant to others (i.e., gender, race, disability, etc.) Obtain information related to social issues/concerns relevant to self and others Gather information about political, religious, educational and economic structures Obtain information regarding the strengths and power of groups and communities Developmental Stages Young Adult (19 – 40 yrs) = 80%+* Intimacy vs. Isolation Form intimate relationships; make personal commitments to others Middle-Age Adult (40 – 64 yrs) = over 10%* Generativity vs. Stagnation Creating or nurturing things that produce feelings of accomplishment or usefulness Seeks satisfaction through productivity in career, family, and community & civic interests. Older Adult (65 yrs– death) Integrity vs. Despair Reflect on life accomplishments and disappointments, deal with losses; and begin to confront death R/CID (cont) M/WID –(cont) Stage 2: Dissonance Alternate between selfand-group appreciation and depreciating attitudes and behaviors Status 2: Disintegration Reality of white privilege Question status quo Feelings: anxiety, anger, conflict, guilt Feelings: Conflict, distrust, anger Adjustments & Experiences Campus Experiences (Transition: Something Happens) (Transition: Something Happens) Limited relationships Identity concerns Difficulty fitting in Limited time to use campus resources Limited number of people of color in classroom Limited number of faculty & staff of color Limited “romance” opportunities Inappropriate communication on campus Difficulty understanding college system Difficulty w/classes Inappropriate instructor &/or student comments Incorrect course selection Pre-college courses Limited financial resources Pressure to declare a major Lack of relationship with advisor or faculty Lack of student relationships 3 Skills Apply appropriate awareness and knowledge to a given situation Develop appropriate skills (i.e., intercultural communicatio ns, facilitating discussions; teaching, critical thinking, etc.) Develop the ability to identify and analyze institutional inequality Develop appropriate skills to be an ally Engage in reciprocal dialog with diverse groups of people Use appropriate multicultural interventions R/CID (cont) M/WID –(cont) Stage 3: Resistance and Immersion Embrace own racial/ethnic group completely Blind endorsement of one’s group -culturocentrism Accept racism and oppression as a reality Rejection of the values and norms of the dominant group Status 3: Reintegration Support internalized belief that people of color are inferior and Whites superior Acknowledge the status quo is what’s due White people Assert that Whites contributions to society have earned them power, privilege and preferences Support stereotypes of groups of People of Color Feelings: Shame, guilt, Anger, rage, conflict, distrust, pride Feelings: Ethnocentrisms, blame, pride, power, superiority (Transition: Something Happens) Adjustments & Experiences Campus Experiences Students Feelings: Confusion, anger, blame, frustration, excitement, pride, superiority, determination, helplessness, despair, joy, contentment –you name it. 4 Skills (cont) R/CID (cont) M/WID (cont) Stage 4: Introspection Develop a security in their racial identity Re-direct anger/negativity toward “White system” to exploration of individual and group identity issues Conflict between allegiance to one’s own racial/ethnic group Acknowledge there is variation amongst all groups of people Status 4: Pseudo independence Begin to acknowledge racist identity Begin to abandon racist identity Begin to develop a positive White identity Recognize Blacks and People of color are not inferior and White superior Challenge distortions of Blacks and People of Color Develop inclusive thinking that leads to putting awareness & knowledge into action Learn ways to discuss the politics of the environment (i.e., hiring, enrollment, student success, etc.) Apply appropriate skills that support empowering groups and communities Feelings: stress, conflict, confidence, hope/resolve Feelings: stress, conflict, shame, blame (Transition: Something Happens) (Transition: Something Happens) 5 Social Action/ Social Justice Take action that incorporates a social action framework Take action that “challenges” institutional inequality (i.e., polices, procedures, laws, etc.) Participate in the politics of the environment (i.e., community organizations, schools, etc.) to make change Take action that will benefit members of a particular group or groups Take action that supports the empowerment of groups and communities Take action that supports social change and justice –become an ally R/CID (cont) M/WID (cont) Stage 5: Integrative Awareness –Final Stage Confident and secure in racial identity Desire to eliminate all forms of oppression High positive regard toward self and towards one’s group Respect and appreciation for other racial/cultural groups Integration of social and personal identity –gender, religion class, etc. Openness to constructive elements of dominant culture Commitment to eliminate oppression Status 5: Immersion Revise thoughts and images about Blacks and other People of Color Self exploration of what it means to be white or have a white identity? Critical questioning about race, racism, power and privilege Internalize positive White identity Search for accurate information and understanding Feelings: Respect, trust, appreciation, pride, confidence Feelings: Conflict, some resolve, respect, appreciation 6 M/WID (cont) Status 6: Emersion Critically think about new information and impact on self and group Focus on obtaining knowledge about self and other diverse groups Immerse self in diverse communities Immerse self with other Whites that support values and views Feelings: respect, pride, confidence, peace, joy Status 7: Autonomy- Final Status Acknowledge complexities of race and identities Able to establish authentic relationships with People of Color Practice maintaining transformation Commit to eradicating racism and other “isms” No longer feel the need to oppress others Feelings: Respect, appreciation, trust, peace