File
advertisement

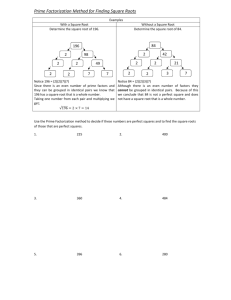
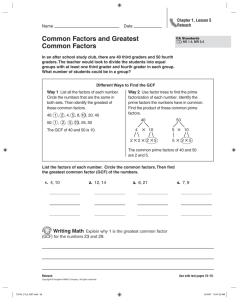
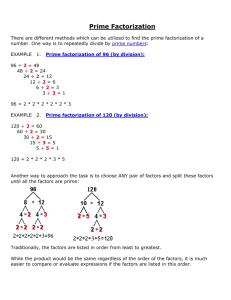
Notes 7 – 1 Factoring a Monomial and Greatest Common Factors Date ________ Algebra 1 Objective: At the end of this lesson, students will be able to factor a monomial and find the greatest common factor (GCF) of a set of monomials. Chapter 7 is titled, Factoring, so before we get into it, we need to figure out what that means. Let’s start with the word, factor. What is a factor? ________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ So then, what is factoring? _______________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ Example 1 – What are factors of 16? Since there are different options for factoring a number like 16, we need to be a little more specific. Many times when we factor a number, we are asked to find the prime factorization. Again, before we do this, let’s figure out what it means!! What does prime mean? _________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ So then, what is prime factorization? _____________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ There are two main ways for finding the prime factorization of a number. Prime Factorization Method 1 – Factor Tree Step 1 – Break the composite number (________________) into two factors. Step 2 – Look at the two factors. If both numbers are prime, you’re done! If one or both of the numbers are composite, break it into two factors. Step 3 – Continue this process until you are left with all prime factors!! Example 2 – Find the prime factorization of each number by making a Factor Tree. a. 48 b. 50 Prime Factorization Method 2 – Cake Method (named by Mr. Bechtel) Step 1 – Find the smallest prime number that goes into the composite number. Then divide the composite number by that number. Step 2 – Look at the resulting number. If the number is prime, you’re done! If the number is composite, repeat Step 1 until the resulting number is prime. Example 3 – Find the prime factorization of each number using the Cake Method. a. 45 b. 60 In Chapter 6, we worked with variables and exponents, and since we can find the prime factorization of a number, we can factor a monomial!! Example 4 – Factor 60a3b2 Keep going with this!! Now that we know how to factor a monomial, we are going to find the greatest common factor of two (or three) monomials. What is the greatest common factor (GCF)? _______________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ The good news is that to find the GCF, we can use the Cake method of prime factorization for two monomials at the same time!! Example 5 – Find the GCF of the two monomials. a. 18 and 30 b. 12x2y and 20xy2 Example 6 – Find the GCF of the three monomials. a. 24m, 36, 84m