Shoulder/Elbow/Wrist Tests
advertisement

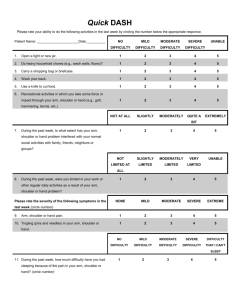
(P= procedure; += positive finding; C=condition) Tests for the Shoulder: 1) Rotator Cuff Lesion: Empty Can Test (to isolate supraspinatus) P: Arm in Flexion and Abducted 45º (scaption) with thumb down Therapist stabilizes pt’s shoulder and pushes down on elbow; patient resists +: Pain during resistance C: Supraspinatus mm. lesion/ Rotator Cuff Lesion Drop Arm Test (Codman’s Test) P: Passive 90º ABduction of arm. Pt then slowly (and in control) lowers arm +: Pt is unable to lower arm slowly or severe pain is felt during test C: Rotator Cuff Lesion -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------2) Bicipital Tendinitis: Speed’s Test (getting Biceps to contract) P: Shoulder flexed 90º, elbow extended, and forearm supinated Therapist stabilizes shoulder (other hand on ant. elbow); Pt flexes arm against resisitance +: Pain and/or weakness during movement C: Biceps Tendinitis (lesion of biceps tendon) Yergason’s Test P: Pt’s arm along side of body, elbow flexed 90º, and forearm pronated Pt laterally rotates arm and supinates forearm against therapist’s resistance +: Pain in bicipital groove or tendon may pop out of groove C: Bicipital Tendinitis -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------3) Impingement Syndrome: Painful Arc Test P: Active ABduction of arm +: Pain between 60º-130º of ABduction indicates impingement of supraspinatus tendon or infraspinatus, or a subacromial bursa problem C: Impingement Syndrome -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 4) Dislocations/Separations: Shoulder Apprehension Test (dislocation) P: Passive ABduction of arm and flexion on elbow, both to 90º Therapist then slowly laterally rotates shoulder +: Look/feeling of apprehension on pt’s face and pt’s resistance C: Anterior Dislocation Acromioclavicular Shear Test (separation) P: Therapist cups hands over deltoids, one hand over clavicle, one over spine of scapula. Therapist squeezes hands together. +: Pain or abnormal movement at the AC joint C: Shoulder Separation/AC Joint Injury -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------No Special Regionalized Test For: Frozen Shoulder (Adhesive Capsulitis)- mm’s not involved Acute Bursitis- look for signs of inflammation (P= procedure; += positive finding; C=condition) Tests for the Elbow: 1) Lateral Epicondylitis: Police Stop Sign P: Active flexion of arm, extended elbow, and extend wrist +: Pain over lateral epicondlye and lateral forearm C: Lateral Epidcondylitis -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------2) Medial Epicondylitis: Medical Epicondylitis (Golfer’s Elbow) Test P: Therapist palpates medial epicondlye, then passively supinates forearm and extends elbow and wrist +: Pain at medial epicondyle C: Medial Epicondylitis -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------3) Ligament Sprains: Valgus/Varus Stress Test P: Therapist supports supinated and flexed arm To test lateral (valgus): push against med. elbow to stress lateral To test medial (varus): push against lat. elbow to stress medial +: Pain or abnormal movement laterally or medially C: Ligament Sprains/Instability -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------4) Ulnar Nerve Entrapment at the Cubital Tunnel: Tinel’s Sign (for any nerve problem) P: Pt’s elbow slightly flexed. Therapist taps ulnar groove between olecranon process and medial epicondyle +: Tingling sensation in ulnar distribution (medial forearm to last 2 fingers) C: Ulnar Nerve Entrapment (P= procedure; += positive finding; C=condition) Tests for the Wrist and Fingers: 1) Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: Phalen’s Test (commonly correlated w/ carpal tunnel) P: Pt places dorsal hands together, then presses them together for 30 or 60 seconds (keep arms parallel) +: Numbness and tingling in distribution of median nerve (ant. palm to first 3 ½ fingers) C: Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Tinel’s Sign P: Therapist supports pt’s loosely flexed/supinated arm and taps the area of the carpal tunnel +: Numbness and tingling in distribution of median nerve (ant. palm to first 3 ½ fingers) C: Carpal Tunnel Syndrome O-Ring Test P: Active opposition. Therapist attempts to open the “O” with their finger +: Marked weakness of thenar muscles C: Carpal Tunnel Syndrome -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------2) De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis: Finkelstein’s Test P: Pt makes a fist with their thumb inside and ulnar deviates (isolates and stretches) +: Pain at lateral wrist/ region of “snuff box” C: De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------No Special Regionalized Test For: Dupuytren’s Contracture ORTHOPEDIC TESTS: PAINFUL ARC Active AB of shoulder + : Supraspinatus, Infra, bursa EMPTY CAN Scaption poition (abduct arm & medially rotate) w/ resistance + : Supraspinatus Lesion SPEEDS Flex shoulder against resist + : Bicep Tendinitis YERGASONS Ltrl rotate & supinate against ressitance + : Bicipital groove or tendon AC JOINT COMPRESSION Compress scap spine & clavicle + : AC joint pathology DROP ARM/CODMAN’S Actively lower arm + : instability of RTC tear/lesion… POLICE STOP SIGN Flex shoulder, extend elbow, extend wrist + : Ltrl Epicondylitis GOLFER’S ELBOW Palpate med epi. – Supinate forearm, extend elbow & wrist + : Medial epicondylitis TINELS SIGN Tap Ulnar groove + : tingling = ulnar nerve PHALENS (carpals tunnel syn) Actively place dorsal hands together. Press for 60 secs + : numb/tingle indicate median nerve disturbed TINELS Passively tap carpel tunnel area + : numb/tingle = median nerve disturbed “O” RING Actively oppose thumb & pinky together. Passivley attempt to open + : wkness of thumb mm = Carpel Tunnel Syndrome FINKLESTEIN’S (DE QUERVAIN’S TENOSYNOVITIS Actively flex thumb, wrap fingers, ulnar deviate + : pn in lateral wrist (anatomical snuff) = De Quer Tenso.