Properties of Organic Compounds
advertisement
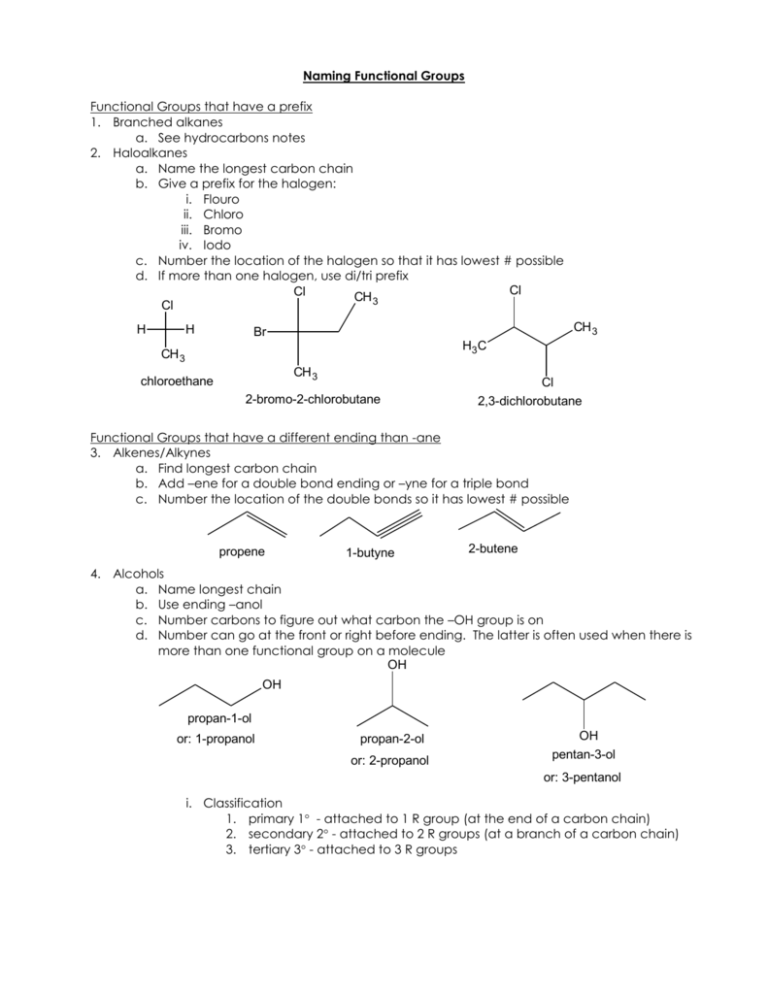
Naming Functional Groups Functional Groups that have a prefix 1. Branched alkanes a. See hydrocarbons notes 2. Haloalkanes a. Name the longest carbon chain b. Give a prefix for the halogen: i. Flouro ii. Chloro iii. Bromo iv. Iodo c. Number the location of the halogen so that it has lowest # possible d. If more than one halogen, use di/tri prefix Cl Cl CH 3 Cl H H CH 3 Br H3C CH 3 CH 3 chloroethane 2-bromo-2-chlorobutane Cl 2,3-dichlorobutane Functional Groups that have a different ending than -ane 3. Alkenes/Alkynes a. Find longest carbon chain b. Add –ene for a double bond ending or –yne for a triple bond c. Number the location of the double bonds so it has lowest # possible propene 1-butyne 2-butene 4. Alcohols a. Name longest chain b. Use ending –anol c. Number carbons to figure out what carbon the –OH group is on d. Number can go at the front or right before ending. The latter is often used when there is more than one functional group on a molecule OH OH propan-1-ol or: 1-propanol propan-2-ol or: 2-propanol OH pentan-3-ol or: 3-pentanol i. Classification 1. primary 1 - attached to 1 R group (at the end of a carbon chain) 2. secondary 2 - attached to 2 R groups (at a branch of a carbon chain) 3. tertiary 3 - attached to 3 R groups R R H R C O H H H C O R primary secondary H R C O R H tertiary 5. Ethers a. Naming (easy) i. Identify the carbon chains on either side of the oxygen ii. Name in alphabetical order or use di/tri prefix iii. Put “ether” on the end CH 3 O H3 C CH 3 H3 C dimethyl ether O ethyl methyl ether b. Naming (when ether is a substituent) i. Name longest carbon chain ii. Name other carbon chain attached to O and add –oxy ending iii. Number comes from carbon that O is attached to on longest carbon chain O CH 3 H3C CH 3 2-methoxypropane 6. Amines a. Name longest carbon chain b. Add –anamine ending c. If more than one chain attached to N, use branching rules as with alkanes but use N instead of number of carbon to show alkyl group is attached to nitrogen. CH3 NH2 H3C methanamine N CH3 H3C NH N-methylethanamine H3C CH3 N-ethyl-N-methylpropan-1-amine 7. Aldehydes/Ketones a. Name longest chain b. If carbonyl (C=O) is i. on the end: Use ending –anal 1. no number needed unless higher priority functional group is on molecule ii. in the middle: Use ending -anone 1. Number carbons to figure out what carbon the C=O group is on 2. Number can go at the front or right before ending. The latter is often used when there is more than one functional group on a molecule O O H3 C CH 3 H propanal ethanal 2-propanone Aldehyde Ketone 8. Carboxylic Acids a. Name longest chain b. Use ending –anoic acid O O H3 C OH ethanoic acid OH propanoic acid 9. Esters a. Count number of carbons in chain attached to carbonyl (C=O) including carbonyl’s carbon b. Add –anoate ending c. Name alkyl group attached to O and add as prefix O O H3C H3C O O CH 3 ethyl propaonate methylethanoate 10. Amides a. Name longest carbon chain b. Add –anamide ending c. If Nitrogen has substituents, use “N-(substituent)” name and add as prefix O O H3C H3C NH2 ethanamide NH N-ethylpropanamide CH 3