Equilibrium - SpongeOfKnowledge
advertisement

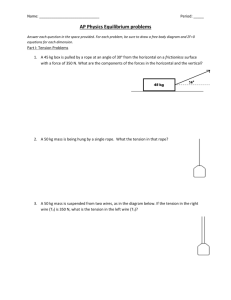
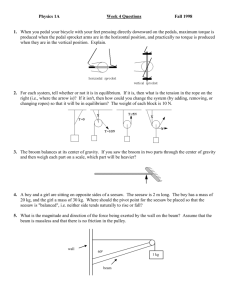
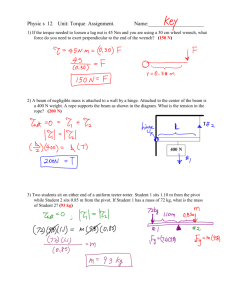
Equilibrium 4. Release 07/08 1. An object is supported by two cords as shown. The tension in the horizontal cord is 320 N. What is the mass m? (a) 26 kg (c) 53 kg 2. If the load on the uniform beam shown below is moved to the left, how doe the tension force T and the magnitude of the vertical force Fv exerted by the wall on the hinge change? (b) 42 kg (d) 250 kg A post of negligible mass is supported by two cables as shown. Release 06/07 5. Which of the following is a torque expression? (a) (c) What is the force exerted by the post on point X? (a) 1100 N (b) 2600 N (c) 2900 N (d) 5100 N 3. 6. ma v sin (b) (d) mv F sin d A 45 N block is suspended as shown in the diagram. A uniform 45 kg beam of length 3.0 m is supported as shown. What is the tension, T, in the horizontal cable? (a) 19 N (b) 21 N (c) 23 N (d) 97 N What is the tension T in the cable? (a) 220 N (b) 280 N (c) 290 N (d) 370 N 7. A uniform 2.4 m long beam with a mass of 25 kg is kept horizontal by a force F. What is the magnitude of the force F? (a) 1.2 x 102 N (b) 1.4 x 102 N 2 (c) 2.5 x 10 N (d) 4.9 x 102 N 8. A uniform plank, 5.0 m long and with a mass of 15 kg, rests on two supports as shown. 10. A mass is suspended by two ropes from a ceiling and a wall. Determine the mass m. (a) 13 kg (c) 26 kg (b) 17 kg (d) 39 kg 11. A force is used to rotate a beam. As the beam rotates, the direction of the force changes but its magnitude does not. What force does the left-handed support exert on the plank? (a) 74 N (b) 88 N (c) 123 N (d) 147 N Release 05/06 9. A force is used to apply a torque to a beam as shown. What happens to the torque on the beam due to this force as the beam is rotated from position 1 to position 4? (a) always increases (b) always decreases (c) increases then decreases (d) decreases then increases 12. Two young children are playing on a seesaw. Which of the following is a correct equation for finding the torque about the fulcrum due to this force? (a) (c) F F cos (b) (d) F / F sin What is the magnitude of the net torque, due to the two children, about the seesaw pivot in the position shown? (a) 220 N·m (b) 230 N·m (c) 1400 N·m (d) 1500 N·m 16. A 1.6 kg ball is held in the hand of a fully extended 11.2 kg arm as shown. (cg = centre of gravity) Release 04/05 13. Which of the following demonstrates the application of torque? (a) Pulling a block across a floor. (b) Pushing a block up an incline. (c) Using a screwdriver to turn a screw. (d) Stopping a block from sliding down an incline. 14. What are the tensions T1 and T2 in the two ropes holding the 36 kg mass as shown? What is the total torque about the shoulder joint due to the ball and to this arm? (a) 17 N·m (b) 19 N·m (c) 35 N·m (d) 38 N·m Aug 04 17. In which direction should a force act on the boom so that it creates a minimum torque about the hinge? (a) T1 = 180 N; T2 = 180 N (c) T1 = 350 N; T2 = 180 N (b) T1 = 180 N; T2 = 270 N (d) T1 = 350 N; T2 = 350 N 15. Two cables are used to support a 24 kg mass on a 1.6 m long 8.0 kg uniform horizontal beam as shown. (a) W (c) Y (b) X (d) Z 18. A 5.0 kg mass is suspended by a rope. A horizontally directed force F is applied to the mass. What is the tension T in the right cable? (a) 130 N (b) 150 N (c) 190 N (d) 300 N What magnitude of force is needed to produce an angle of θ = 65º (a) 21 N (b) 23 N (c) 44 N (d) 110 N 19. An 840 N painter stands on a 7.0 m board of negligible weight. The board is supported by two step-ladders as shown. What is the force exerted on the board by the left step-ladder? (a) 360 N (b) 420 N (c) 630 N (d) 840 N Jun 04 23. A 25 kg mass is suspended from the end of a 5.0 m long uniform boom. If the mass of the boom is 12 kg, what is the tension in the supporting rope? (a) 300 N (b) 380 N (c) 470 N (d) 560 N 24. A uniform 16 m long plank weighing 350 N rests on supports 8.0 m apart. An 850 N man walks along the plank to the right. 20. A 5.0 kg mass suspended by a rope is pulled to the left by a horizontal force of 18 N. What is angle θ? (a) 16º (c) 70 º How far past point B can the man walk before the plank tips? (a) 0.82 m (b) 1.6 m (c) 2.5 m (d) 3.3 m (b) 20 º (d) 74 º Aug 03 21. A uniform 2.0 m long beam is to be kept horizontal by a cord. In which of the four situations shown below will the tension in the cord be onehalf of the beam’s weight? Jan 04 22. Which of these is an acceptable definition of rotational equilibrium? (a) 0 (b) v0 (c) F (d) F F x y 25. A physics exam booklet lying on a table in front of you is in translational equilibrium because (a) there are no forces acting on it. (b) the forces acting on it are balanced. (c) the force due to gravity is holding it down. (d) surface friction is preventing it from sliding. 26. Determine the sum of the torques about the point P for the two forces shown below acting on a very light wooden beam. (Ignore its weight). (a) 10 N·m (c) 35 N·m 29. Two forces are acting at a single point on an object. Force 1 has a magnitude of 8000 N and is directed due W. Force 2 has a magnitude of 6000 N and is directed at 40º N of E. Determine the magnitude of the third force which must act at the same point so that the object will be in translational equilibrium. (a) 2000 N (b) 3400 N (c) 5100 N (d) 6200 N (b) 17 N·m (d) 85 N·m 27. The 0.10 kg metre stick shown below is held up by the perpendicular force F. The bottom of the metre stick is on the verge of sliding to the right. 30. A 40 kg non-uniform beam (centre of mass CM) is supported by two cables. Determine the size of the friction force being provided by the floor. (a) 0.12 N (b) 0.21 N (c) 0.25 N (d) 0.49 N What is the tension in the left hand cable? (a) 170 N (b) 260 N (c) 370 N (d) 560 N Jun 03 28. The diagram below shows a force F applied in several different directions at the point P on a hinged beam. In which direction will the force produce the smallest torque about the hinge? (a) 1 (c) 3 (b) 2 (d) 4 Jan 03 31. Which of the following are correct units for torque? (a) N/m (b) N/kg (c) N·s (d) N·m Written 32. An 80 kg, 12 m uniform diving board in static equilibrium is shown below. Support A is providing a 3000 N force directed downward on the board. (release 06/07) (5 marks). 35. A 4.0 long uniform pole with a mass of 15 kg is pivoted at one end and held in position by a horizontal cable at the other end. If a 25 kg mass is suspended from the end of the pole, what is the tension in the horizontal cable? (Aug 04) (7 marks) Determine the force provided by support B and the distance, l. 33. A 4.0 m long steel beam is supported 3.0 m from a hinge by a cable attached as shown. (release 05/06) (5 marks). 36. A sign is suspended from the end of a 6.0 m long uniform pole of mass 25 kg as shown. If the mass of the sign is 36 kg, what is the tension in the horizontal restraining cable? (Jun 04) (7 marks) If the tension in the cable is 150 N what is the mass of the steel beam? 34. A 65 kg man is 3.0 m up a 5.0 m, 16 kg ladder leaning against a smooth wall at an angle of 72º as shown below. What minimum force of friction between the ladder and floor is required to keep the ladder from sliding? (release 04/05) (5 marks) 37. A student uses a wrench to apply a constant force to turn a nut. He applies the force at various angles and measures the amount of torque produced at each of the angles. 38. A uniform 4.0 m long beam with a mass of 15 kg rests on a pivot at one end and is kept horizontal by a cable at the other end. The beam is supporting a 25 kg mass as shown. What is the tension in the cable? (Jan 04) (7 marks) The torque data collected by the student along with the sine of the angles is shown below. (Jun 04) 39. A 15 kg store sign is hung using two ropes as shown below. Determine the tension in each rope. (Aug 03) (7 marks) (a) Plot a graph of Torque versus Sinθ on the grid (2 marks). 40. A wrecking ball is suspended by two cables as shown below. If the tension in cable 2 is 12 000 N, what is the weight of the wrecking ball? (Jun 03) (7marks) (b) Calculate the slope of the line including units (1 mark) (c) Use the slope of your graph to determine the amount of constant force the student used throughout his experiment (2 marks). 41. The 8.0 kg uniform beam shown below, suspended horizontally by two ropes, has a mass of 75 kg. Determine the tension in rope 1 and the tension in rope 2. (Jan 03) (7 marks) 42. A mass suspended by two ropes is shown below. It is noticed that for any angle used for rope 2, the tension in rope 2 is always greater than the tension in rope 1. Using principles of physics, explain why this is the case. (Jan 03) (4 marks) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. B B D A D B C C D D C A C B C C A B A C 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. D A C B B C B A C A D 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. 38. 39. 40. 41. 9.11 m 16 kg 150 N 270 N 680 N 25 N·m; 42 N 280 N 51 N; 140 N 8 900 N 280 N; 510 N