AG530K - University of Idaho
advertisement

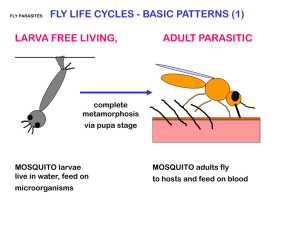
530K - 1 LIVESTOCK DISEASES AND PARASITES AG 530 - K UNIT OBJECTIVE After completion of this unit, students should be able to describe ways to control and treat various diseases and parasites. Students should also be able to diagnose some of the more basic livestock health problems. This knowledge will be demonstrated by the completion of assignment sheets and unit test with a minimum of 85 percent accuracy. SPECIFIC OBJECTIVES AND COMPETENCIES After completion of this unit, the student should be able to: 1. Match terms associated with livestock diseases and parasites to their definitions. 2. Name three ways diseases are diagnosed. 3. List five ways diseases and parasites are spread. 4. Match livestock diseases caused by poisoning to their characteristics, the animals they affect and the symptoms they cause. 5. Describe general measures for controlling internal and external parasites. 6. Distinguish between external and internal parasites. 7. Identify selected internal and external parasites when given a description of their life cycles. 8. Identify external parasites when given a drawing. 9. Complete a chart containing diseases, species affected, symptoms and treatment and control. 10. Complete a chart containing parasites, symptoms and treatment and control. 11. Diagnose various disease and parasite problems when given a description. 530K - 2 LIVESTOCK DISEASES AND PARASITES AG 530 - K SUGGESTED ACTIVITIES I. II. Suggested activities for the instructor A. Make transparencies and necessary copies of materials. B. Provide students with objectives and discuss. C. Provide students with information and discuss. D. Give students assignment sheets. E. Have students prepare a panel discussion about various disease and parasite problems. F. Have students choose one or two disease or parasite problems and write or give a report on them. G. Arrange for students to view a necropsy. H. Arrange a display of pictures of animals with various disease symptoms. I. Have students develop skits representing various disease symptoms. J. Develop a chart of the life cycles of parasites common to the area. K. Write up an assignment sheet containing symptoms of diseases common to the local area. L. Review and give test. M. Reteach and retest if necessary. Instructional materials A. Objective sheet B. Sugggested activities C. Information sheet D. Transparency masters 1. TM 1--Horse Bot Fly 2. TM 2--Cattle Grub or Heel Fly 3. TM 3--Swine Intestinal Roundworm 530K - 3 E. III. 4. TM 4--Liver Fluke 5. TM 5--Stomach Worm 6. TM 6--External Parasites Assignment sheets 1. AS 1--Complete a Chart Containing Diseases, Species Affected, Symptoms and treatment and Control 2. AS 2--Complete a Chart Containing Parasites, Symptoms and Treatment and Control 3. AS 3--Diagnose Various Disease and Parasite Problems When Given a Description of the Problem F. Answers to assignment sheets G. Test H. Answers to test Unit references A. Baker, James K. and Greer, William J., Animal Health. The Interstate Printers and Publishers, Inc., Danville, Illinois, 1980. B. Barrick, R. Kirby, Harmon, Hobart L., Animal Production and Management. McGraw-Hill Book Company, 1988. C. Berrier, Harry H., Animal Sanitation and Disease Prevention. Kendall/Hunt Publishing Co., Dubuque, Iowa, 1977. D. Campbell, John R. and Lasley, John F., The Science of Animals That Serve Mankind. McGraw-Hill Book Company, New York, 1975. E. Cow-Calf Management Guide, Cattleman's Library. University of Idaho Cooperative Extension Service, 1980. F. Haynes, N. Bruce., Keeping Livestock Healthy. Garden Way Publishing, Charlotte, Vermont, 1978. G. Instructional Materials for Vocational Agriculture II. Teaching Materials Center, Agricultural Education Department, Texas A & M University, College Station, Texas. 530K - 4 LIVESTOCK DISEASES AND PARASITES AG 530 - K INFORMATION SHEET I. Terms and definitions A. Parasite--Organism living off another organism B. Diagnosis--What someone has determined a disease to be C. Life cycle--A complete pattern of normal changes an organism goes through D. Necropsy--Examination of a dead animal to determine cause of death (Note: This most often involves dissecting.) E. Aborted fetus--Unborn young of a species that has been expelled or removed from the mother before full term F. Fungus--Plant that lives only off of other dead or living organic matter G. Convulsions--Violent, uncontrollable contractions of the muscles H. Gangrene--Tissue decay caused by loss of blood to the tissue I. Hemorrhage--Excessive bleeding J. Drought--Lack of water K. Bolus--Large pill L. Mucous membrane--Lining of body openings and digestive tract that secretes a watery substance M. Larva--Immature form of insects N. Symptom--Outward expression of a disease O. Placenta--Thin structure in the uterus from which a fetus gets its nourishment; it is expelled soon after birth P. Conception--Uniting of the egg and sperm Q. Infertility--Inability to reproduce R. Inflammation--Condition of body tissue causing it to be hot, red and swollen S. Dehydration--Loss of body fluids T. Glucose--Type of simple sugar U. Diarrhea--Condition of a runny, wet feces 530K - 5 II. III. V. Reactor animals--Animals that have a "positive" reaction to a test used to indicate the presence of a certain disease W. Tumor--Abnormal growth of tissue X. Cornea--Covering of the eyeball Y. Constipation--Inability to expel feces Z. Intravenously--By way of the veins Ways diseases are diagnosed A. Observation of symptoms B. Laboratory tests of blood, animal wastes and animal tissue C. Necropsy Ways diseases and parasites are spread A. Direct contact with infected animals or animal products B. Contact with humans (Note: This usually happens when humans have been working with infected animals and carry the infection on boots or clothing. Some diseases can be spread from humans that actually have the infection to livestock.) IV. C. Contact with livestock facilities and equipment that have contacted infected animals D. Contact with dead livestock or an aborted fetus E. Carried through the air or water F. Insects G. Infected wild animals Livestock poisoning A. Ergot Poisoning 1. Fungus disease that attacks grain 2. Affects cattle, swine, sheep and poultry 3. Symptoms--Lameness in hind legs; nervousness; trembling and painfully contracting muscles; convulsions; gangrene in ears, tail and feet 4. Control--Avoid ergot infested grain; keep affected animals warm 530K - 6 B. C. D. E. Alfatoxin Poisoning 1. Product of fungus growing on stored grain 2. Affects cattle, swine and poultry 3. Symptoms--Reduced growth; decreased appetite; hemorrhaging 4. Control--Keep grains dry Prussic Acid Poisoning (cyanide) 1. Formed on frost or drought-damaged Johnson grass or Sudan grass 2. Affects cattle 3. Symptoms--Staggered walking; difficult respiration; animals go down quickly 4. Treatment--Use nitrate boluses Pine Needle Abortion 1. Affects cattle that eat Ponderosa Pine needles 2. Symptoms--Abortion or premature and weak calves 3. Control--Keep pregnant cattle away from Ponderosa Pine needles Urea Poisoning 1. Caused by overfeeding urea in ration or by putting too much on pastures as fertilizer; also caused by resumption of feeding urea after a short interruption (Note: Cattle can digest up to 400 grams of urea a day, but must first become slowly adjusted to it. They can lose their tolerance in as little as 48 hours.) 2. Affects cattle, sheep 3. Symptoms--Staggering; trembling muscles; rapid pulse 4. Control--Introduce urea slowly into the ration; mix it in well with grain; use caution when introducing cattle to pastures fertilized with urea 530K - 7 F. V. 1. Used as insecticides and are very toxic; can be absorbed through skin or taken in from eating sprayed plants; sometimes animals drink dip or spray 2. Affects cattle, sheep, swine, horses 3. Symptoms--Difficult breathing; excessive drooling; staggering; impaired vision 4. Control--Avoid pastures recently sprayed with organophosphates; use care when spraying or dipping cattle Measures for controlling internal and external parasites A. B. VI. Organophosphate Poisoning Internal 1. Practice pasture rotation 2. Check animals regularly 3. Treat animals showing signs of parasites 4. Practice proper lot sanitation 5. Drain wet pasture sites 6. Graze young animals on clean pastures External 1. Keep manure cleaned from barnyards to prevent fly breeding 2. Spray livestock regularly 3. Spray livestock housing 4. Control grubs before they damage the hide 5. Spray new animals arriving on the farm 6. Check livestock frequently Internal and external parasites A. Internal 1. Coccidia 2. Intestinal worm 3. Lungworm 530K - 8 B. 4. Ascarid 5. Liver fluke 6. Stomach worm 7. Tapeworm External 1. Blowfly 2. Horn fly 3. Screwworm fly (Note: This fly has been nearly eradicated from the United States.) 4. Grub (heel fly) (Note: Although the grub does migrate through the host, it is still considered an external parasite.) VII. 5. Horsefly 6. Tick 7. Lice 8. Ringworm 9. Mite 10. Ked Life cycle of selected parasites (Transparencies 1, 2, 3, 4, 5) A. B. Horse bot fly (Transparency 1) 1. Adult fly lays eggs on horse's hair 2. Larva enters mouth and attaches to stomach wall 3. Larva matures and is carried out with the feces 4. Adult fly emerges and lives only a few days Cattle grub or heel fly (Transparency 2) 1. Adult fly lays eggs on heel 2. Larva enters body and migrates through connective tissue to the back of the animal 530K - 9 C. D. 3. Larva drops to ground 4. Adult fly emerges Swine intestinal roundworm (Transparency 3) 1. Egg eaten by swine 2. Egg hatches to worm 3. Adult worm in small intestine 4. Eggs are passed in feces Liver fluke (Transparency 4) (Note: This affects sheep and cattle.) E. 1. Adult lays eggs in bile ducts 2. Eggs pass in feces and must land in water 3. Larva finds a host snail and matures 4. Larva leaves snail and attaches to plant 5. Larva is eaten by animal 6. Young flukes then burrow into the liver Stomach worms (Transparency 5) (Note: These mainly affect cattle, sheep and horses.) VIII. 1. Adult lays eggs which pass in the feces 2. Larva hatches and is eaten 3. Adult attaches to stomach wall External parasite identification (Transparency 6) A. Mite B. Lice C. Tick D. Horn fly E. Barn fly F. Heel fly 530K - 10 IX. G. Screwworm fly H. Ked Livestock diseases (Note: The symptoms mentioned in the chart on pages 11-19 often vary with each individual situation. Contact a veterinarian when in doubt about a diagnosis.) (Caution: The following treatments and controls are for general information only. They are deliberately vague when dealing with medicines and vaccines. Consult veterinarian before giving animals any kind of treatment.) 530K - 11 530K - 12 530K - 13 530K - 14 530K - 15 530K - 16 530K - 17 530K - 18 530K - 19 530K - 20 TM 1 530K - 21 TM 2 530K - 22 TM 3 530K - 23 TM 4 530K - 24 TM 5 530K - 25 TM 6 530K - 26 LIVESTOCK DISEASES AND PARASITES AG 530 - K ASSIGNMENT SHEET #1--COMPLETE A CHART CONTAINING PARASITES, SYMPTOMS AND TREATMENT AND CONTROL Name _____________________________________ Score __________________________________ Choose diseases most common in the local area and use them to fill in the chart below. Use information in the unit plus more specific information from a local veterinarian, extension agent, agriculture instructor and/or rancher. Parasite and Species Affected Symptoms Prevention and Control ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ 530K - 27 Parasite and Species Affected Symptoms Prevention and Control ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ 530K - 28 LIVESTOCK DISEASES AND PARASITES AG 530 - K ASSIGNMENT SHEET #2--COMPLETE A CHART CONTAINING PARASITES, SYMPTOMS AND TREATMENT AND CONTROL Name _____________________________________ Score __________________________________ Choose parasites most common in the local area and use them to fill in the chart below. Use information in the unit plus more specific information from a local veterinarian, extension agent, agriculture instructor and/or rancher. Parasite and Species Affected Symptoms Prevention and Control ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ 530K - 29 Parasite and Species Affected Symptoms Prevention and Control ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ 530K - 30 LIVESTOCK DISEASES AND PARASITES AG 530 - K ASSIGNMENT SHEET #3--DIAGNOSE VARIOUS DISEASE AND PARASITE PROBLEMS WHEN GIVEN A DESCRIPTION OF THE PROBLEM Name _____________________________________ Score __________________________________ Make a diagnosis of the problems described below. 1. Two of your beef animals have become very lame. You notice they have a high fever. After a while you also notice there is swelling over the hips and shoulder. The skin of the animal feels rather cold and crackles when you touch it. Diagnosis ______________________________________________________________________ 2. You moved your cattle to a new range that has a few swampy areas. A few days later you notice an animal standing with an arched back and a pulled in abdomen. The animal is having a hard time breathing and appears very weak when it tries to move. It has a dark red, foamy urine. Diagnosis ______________________________________________________________________ 3. You have just moved your cattle onto lush pastures. Soon you notice a couple of animals standing with an extended neck and making grunting sounds as they breath out. Diagnosis ______________________________________________________________________ 4. One of your cows has just given birth and is not interested in eating. She is somewhat nervous and has her head turned back into her side. Diagnosis ______________________________________________________________________ 5. Several of your newborn calves are having trouble breathing and act very stiff, especially in their hind quarters. Diagnosis ____________________________________________________________________ 6. In the spring and summer you notice your cattle putting their tails in the air and running for the shade. A few months later you notice bumps start to form on their backs. Diagnosis ______________________________________________________________________ 7. Your sheep have developed diarrhea. Some even have dark bloody feces. You have ruled out any disease. Diagnosis ______________________________________________________________________ 530K - 31 LIVESTOCK DISEASES AND PARASITES AG 530 - K ANSWERS TO ASSIGNMENT SHEETS Assignment Sheet #1 Answered to the satisfaction of the instructor. Assignment Sheet #2 Answered to the satisfaction of the instructor. Assignment Sheet #3 1. Blackleg 2. Red water 3. Emphysema 4. Milk fever 5. White muscle 6. Heel fly 7. Coccidia 530K - 32 LIVESTOCK DISEASES AND PARASITES AG 530 - K UNIT TEST Name _____________________________________ 1. Score __________________________________ Match the terms on the right to their correct definitions. _____a. Abnormal growth of tissue 1. Fungus _____b. Immature form of insects 2. Parasite _____c. Loss of body fluids 3. Cornea _____d. Condition of body tissue causing it to be hot, red and swollen 4. Tumor Examination of a dead animal to determine cause of death 5. Hemorrhage A complete pattern of normal changes an organism goes through 6. Convulsions _____g. Outward expression of a disease 7. Intravenously _____h. Lack of water 8. Constipation _____i. Type of simple sugar 9. Diagnosis _____j. Thin structure in the uterus from which a fetus gets its nourishment; it is expelled soon after birth 10. Mucous membrane _____k. By way of the veins 11. Infertility _____l. Inability to expel feces 12. Drought _____e. _____f. _____m. Plant that lives only off of other dead or living organic matter _____n. 13. Reactor animals Lining of body openings and digestive tract that secretes a watery substance 14. Aborted fetus _____o. Uniting of the egg and sperm 15. Diarrhea _____p. Violent, uncontrollable contractions of the muscles 16. Bolus _____q. Large pill 17. Placenta _____r. Condition of a runny, wet feces 18. Gangrene 530K - 33 _____s. 2. Unborn young of a species that has been expelled or removed from the mother before full term 19. Dehydration _____t. Inability to reproduce 20. Larva _____u. Tissue decay caused by loss of blood to the tissue 21. Necropsy _____v. Covering of the eyeball 22. Conception _____w. What someone has determined a disease to be 23. Life cycle _____x. Organism living off another organism 24. Symptom _____y. Excessive bleeding 25. Inflammation _____z. Animals that have a "positive" reaction to a test used to indicate the presence of a certain disease 26. Glucose Name three ways diseases are diagnosed. a. ____________________________________________________________________________ b. ____________________________________________________________________________ c. ____________________________________________________________________________ 3. List five ways diseases and parasites are spread. a. ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ b. ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ c. ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ d. ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ e. ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ 530K - 34 4. Match the livestock diseases on the right to their characteristics and symptoms. _____a. Found on Ponderosa Pine ranges 1. Urea Poisoning _____b. Fungus disease causing lameness, nervousness and convulsions 2. Pine Needle Abortion _____c. Staggering; rapid pulse; trembling muscles; affects cattle and sheep 3. Prussic Acid Poisoning _____d. Fungus disease causing decreased appetite and hemorrhaging 4. Organophosphate Poisoning _____e. Staggering; difficult respiration; can be treated with nitrate boluses Poisoning 5. Alfatoxin 6. Ergot Poisoning _____f. 5. Can be eaten or absorbed; causes difficult breathing; excessive drooling; impaired vision; caused when spraying or dipping cattle Describe general measures for controlling internal and external parasites. Describe three under each category. External a. ____________________________________________________________________________ b. ____________________________________________________________________________ c. ____________________________________________________________________________ Internal a. ____________________________________________________________________________ b. ____________________________________________________________________________ c. ____________________________________________________________________________ 6. Distinguish between the internal and external parasites listed by placing an "In" by the internal parasites and an "Ex" by the external parasites. _____a. Lice _____g. Horsefly _____m. Intestinal worm _____b. Mite _____h. Blowfly _____n. Grub (Heel fly) _____c. Ascarid _____i. Ked _____o. Ringworm _____d. Tick _____j. Coccidia _____p. Stomach worm _____e. Tapeworm _____k. Lungworm _____q. Screwworm fly _____f. Liver fluke _____l. Horn fly 530K - 35 7. Identify the correct internal and external parasites to the life cycles described below. Write the answer in the blank provided. a. _________________________________________________ Life cycle: Adult fly lays eggs on heel; Larva enters body and migrates through connective tissue to the back of the animal; Larva drops to ground; Adult fly emerges b. _________________________________________________ Life cycle: Egg eaten by swine; Egg hatches to worm; Adult worm in small intestine; Eggs are passed in feces c. _________________________________________________ Life cycle: Adult lays eggs which pass in the feces; Larva hatches and is eaten; Adult attaches to stomach wall d. _________________________________________________ Life cycle: Adult fly lays eggs on horse's hair; Larva enters mouth and attaches to stomach wall; Larva matures and is carried out with the feces; Adult fly emerges and lives only a few days e. ________________________________________________ Life cycle: Adult lays eggs in bile ducts; Eggs pass in feces and must land in water; Larva finds a host snail and matures; Larva leaves snail and attaches to plant; Larva is eaten by animal; Young burrow into the liver 8. Identify the external parasites pictured below. Write the correct name in the blank provided. 530K - 36 530K - 37 LIVESTOCK DISEASES AND PARASITES AG 530 - K ANSWERS TO TEST 1. 2. a. b. c. d. e. f. g. 4 20 19 25 21 23 24 h. i. j. k. l. m. n. 12 26 17 7 8 1 10 o. p. q. r. s. t. u. 22 6 16 15 14 11 18 v. w. x. y. z. 3 9 2 5 13 Observation of symptoms; Laboratory tests of blood, animal wastes and animal tissue; Necropsy 3. Answer should include five of the following: Direct contact with infected animals or animal products; Contact with humans; Contact with livestock facilities and equipment that have contacted infected animals; Contact with dead livestock or an aborted fetus; Carried through the air or water; Insects; Infected wild animals 4. a. b. c. 5. Answer should include three of the following measures under each category: 2 6 1 d. e. f. 5 3 4 External: Keep manure cleaned from barnyards to prevent fly breeding; Spray livestock regularly; Spray livestock housing; Control grubs before they damage the hide; Spray new animals arriving on the farm; Check livestock frequently Internal: Practice pasture rotations; Check animals regularly; Treat animals showing signs of parasites; Practice proper lot sanitation; Drain wet pasture sites; Graze young animals on clean pastures 6. a. b. c. d. e. 7. a. b. c. d. e. 8. a. b. c. Ex Ex In Ex In g. h. i. j. f. Ex Ex Ex In In l. m. n. o. k. Ex In Ex Ex In p. In q. Ex Cattle grub or heel fly Swine intestinal roundworm Stomach worms Horse bot fly Live fluke Barn fly Tick Mite d. e. f. Screwworm fly Lice Horn fly g. h. Heel fly Ked