Jigsaw: Roman Entertainment
advertisement

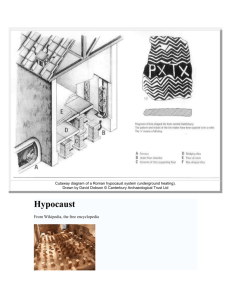
Jigsaw: Roman Entertainment Objectives: Students will be able to identify Roman entertainment buildings. Students will learn vocabulary associated with Roman entertainment. Context: Introducing a unit on Roman entertainment and the vocabulary associated with the buildings and activities Teacher’s Instructions: Break up your class into groups of four. Assign each group member a letter: A, B, C, or D. Then, pass out the worksheet and the readings as follows: A’s- Circuses B’s- Amphitheaters C’s- Theatres D’s- Public Baths Instruct your students to read their passage. When this is complete, have the student’s get together in “expert groups”- all of the As together, Bs together etc. Instruct the students that they are to become experts on their topic. Once the students have had time to discuss, send them back to their original A,B,C,D and have each student teach their section of the readings. After a few minutes discussion, make sure the students are working on their worksheets. Remind the students that although they are an expert on one of the forms of entertainment, they are still responsible for all of the information. Time needed: 30-50 minutes Circuses: Chariot racing was Rome's oldest and most popular pastime, dating back to at least the Roman monarchy. Greek chariot races were held in hippodromes in the east, but in the west they were held in circuses. Other events eventually infiltrated the circus games (ludi circenses), such as Greek athletics and wrestling, but chariot racing remained the popular favorite. As a sport, it was highly expensive, but organized into a highly profitable business. There were four chariot facing factions, the blues, greens, whites, and reds, the colors of which were worn by respective charioteers during races. If successful, a charioteer could become rich and famous throughout Rome. Images of charioteers survive in sculpture, mosaic, and molded glassware, sometimes even with inscribed names. The factions rivaled greatly, sometimes leading to violence among supporters. In general, however, the greens and blues were the favorites. The circus itself consisted of tiers of seats build around a U-shaped arena with an elaborately ornamented barrier, the spina, running down the middle. Metae, or turning posts, adorned each end of the course. At the open end of the U waited up to twelve four horse chariots (quadrigae), which began the race from starting gates (carceres), drove to the right of the spina, and then continued counter-clockwise for seven laps. At each end of the spina were seven lap markers, one of which was removed after each lap run by the charioteers. Circuses were also used for two horse chariot racing (bigae), and by the late republic other events, such as foot and horse racing, athletics, and gladiatorial shows/mock battles were commonplace in the circus. The 1st circus was the Circus Maximus, supposedly built during the monarchy. Later circuses were often confused with Greek stadia, which were later adapted to the Roman world by their own right, but were only approximately one-half the size of the typical circus (180-200 meters in length, 30 meters wide, with only two turning posts and QuickTime™ and a decompressor no spina). Circuses remained are needed to see this picture. common in the west and stadia common in the Hellenistic east in the tradition of the Greek games. http://library.thinkquest.org/26602/entertainment.htm Amphitheatres: Several different types of shows all took place in the arena of an Amphitheater. The word arena comes from the Latin for "sand," which was placed on the Amphitheater floor to soak up spilled blood. Amphitheaters were most commonly used for gladiatorial matches which had been adapted from Etruscan funeral rites (munera). By the last 1st century BC, however, the games had lost their ritualistic significance. Gladiators came from various lots of life. Originally, there were gladiatorial schools, but these came under state control in the 1st century BC to avoid them becoming private armies. The majority of gladiators were either condemned criminals (damnati), slaves, prisoners of war, or volunteers who signed up to do shows for a fee. There were four main types of gladiator: Murmillo: Fought with a helmet adorned by a fish crest, an oblong shield, and a sword. He usually fought a retiaritus. Retiaritus: A lightly armed gladiator with a net, brandishing either a trident or a dagger. Samnite: Utilized a sword, visor and helmet, and an oblong shield. Thracian: Combated with a curved scimitar and round shield. Special types of "wild animal matches" (venationes) were introduced in the 2nd Century BC and became very popular. Such bouts included men on foot and on horseback, known as beastiarii, who were usually either criminals, prisoners of war, or trained and paid fighters. Beastiarii fought exotic animals, which eventually led to an extensive trade market. Other spectacles included mock naval battles (naumachiae), known to take place on artificial lakes, as well as animal performances, accompanied by music.velum or velarium) provided protection from the elements for spectators, and in larger amphitheaters, service corridors and chambers beneath the floor held animals until they were to go out onto the arena, which was done by facility of trapped doors. Due to their massive size, they were usually constructed on QuickTime™ and a the edge of a city or directly outside its decompressor walls. Military amphitheaters (ludi) are needed to see this picture. built near forts and fortresses served as training grounds for soldiers. http://library.thinkquest.org/26602/entertainment.htm Theatres: In Ancient Rome, plays were presented at the time of the games on contemporary wooded stages. The first such permanent Roman theater was ordered to be built by Pompey in 55 BC, eventually erected on the Campus Martius at Rome. Built of stone, it had a seating capacity of 27,000. Essentially patterned after the Greek theater, it differed in the respect that it was built on level ground. Excavated out of the sides of hills, the circular space located in front of the stage in a Greek theater was called the orchestra, where choruses and actors performed. Since Roman plays usually lacked a true chorus, the area in front of the stage which might have been an orchestra simply became a semicircular area. All actors in Roman plays were male slaves. Men played the parts of women. The typical stock characters included the rich man, the king, the soldier, the slave, the young man, and the young woman. If necessary, an actor would play two or more roles in a single performance. The most notable part of an actor's regalia was probably his mask. While different masks and wigs were used for comedies than tragedies, certain characteristics remained constant. All masks had both cheek supports and special chambers which acted as amplifiers. Gray wigs represented old men, black for young men, and red for slaves. Young men donned brightly colored clothing, while old men wore white. In this manner the characters could be easily identified by the audience. Admission to the Roman plays was free for citizens. Originally, women were barred from viewing comedies and were only admitted to tragedies, but later, no such restrictions were imposed. Pantomimes, popular during the 1st century BC, involved miming roles to accompaniment of singers, dancers, and musicians, in addition to visual effects, similar to a ballet. In mimes of antiquity actors spoke. Women were allowed in mimes and pantomimes, which were more popular than typical plays but eventually degenerated into vulgar and disgusting tastelessness. QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. http://library.thinkquest.org/26602/entertainment.htm Public Baths: In the time of the Roman empire, the baths were a place of leisure time during many Romans daily routine. People from nearly every class - men, women, and children - could attend the thermae, or public baths, similar to modern day fitness clubs and community centers. The two most well preserved baths of ancient Rome are the baths of Diocletian and Caracalla. Diocletian's baths cover an enormous 32 acres, and now, the ruins include two Roman churches, St. Mary of the Angels and the Oratory of St. Bernard. The baths of Caracalla cover 27 acres. Towards the center of the Roman baths, adjoining the dressing room, could be found the tepidarium, an exceedingly large, vaulted and mildly heated hall. This could be found surrounded on one side by the frigidarium, a large, chilled swimming pool about 200 feet by 100 feet, and on the other side by the calidarium, an area for hot bathing warmed by subterranean steam. Hot air and steam baths had been known to the Greeks as early as the 5th century BC, and have been found in Italy dating back to the 3rd century BC. The original thermae were small, hand activated individual sweets called balinae. By the 1st century BC, hypocaust heating allowed for the creation of hot/cold rooms and plunge baths. Bathing quickly became a communal activity. The term thermae was first applied to the baths built by Aggripa in the last 1st century BC. Emperors later built gradually grander baths, and the thermae became an Ancient Roman tradition. Not only were the baths meant for leisure, but also, for social gathering. In addition to the bathing areas could be found portico shops, marketing everything from food, to ointments, to clothing. There were also sheltered gardens and promenades, gymnasiums, rooms for massage, libraries, and museums. Complimenting these scholarly havens were slightly more aesthetic marble statues and other artistic masterpieces. h QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. http://library.thinkquest.org/26602/entertainment.htm Nomen:__________________ Roman Entertainment Directions: Assemble in your groups of A, B, C & D. Read your assigned section. When you are finished, meet with your Expert Group (all of the students that have the same letter as you.) As experts, you should discuss the important parts of your section and what the members of the other groups should know. When time is up, return to your original group. Each expert will teach their section. When you all feel confident, answer the questions below: 1. What was the most popular pass time in ancient Rome? Where does it take place? 2. Where would you go if you wanted to see art in the Roman Empire? 3. Were woman allowed to act in the theatre? Who were the actors mainly? 4. Why was sand used on the bottom of the amphitheatre? 5. In our society today, do we use circuses, amphitheatres, and theatres the same way as the Romans? What buildings do we have that function as our “baths”? Define: 1. Damnati: 2. Thermae: 3. Spina: 4. Tepidarium: Complete the Venn Diagram for 2 of the buildings (your choice): QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. Answer Key: 1. The chariot races. They are in the circuses. 2. Roman art was displayed in the baths. 3. No, the actors were mainly slaves. 4. The sand was used to absorb the blood. 5. Our circuses are more about entertainment than sport, amphitheatres generally have concerts or sporting events, and theatres still have plays. Baths are now art museums, spas, social gatherings. Damnati: condemned criminals Thermae: public baths Spina: the barrier running down the middle of the circus Tepidarium: exceedingly large mildly heated hall Venn diagram: -Multiple answers