partial solutions
advertisement

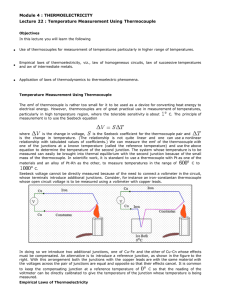
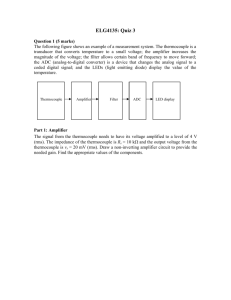
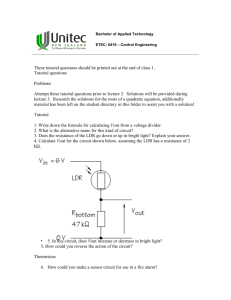
1. THEORY (10) Answer each of the following question with one or two sentences (phrases): (Yes/NO answer require justification) a) Mention what three laws govern the thermocouples. Sol: Law of Homogeneous Materials.A thermoelectric current cannot be sustained in a circuit of a single homogeneous material by the application of heat alone, regardless of how it might vary in cross section. Law of Intermediate Materials.The algebraic sum of the thermoelectric forces in a circuit composed of any number of dissimilar materials is zero if all of the circuit is at a uniform temperature. Law of Successive or Intermediate Temperatures.If two dissimilar homogeneous materials produce thermal emf1 when the junctions are at T1 and T2 and produce thermal emf2 when the junctions are at T2 and T3 ,the emf generated when the junctions are at T1 and T3 will be emf1 + emf2. b) Why the reference junction is important in the measurement with thermocouples? The output of a thermocouple circuit is a voltage, and there is a definite relationship between this voltage, and temperatures of the junctions that make up the thermocouple circuit. To demonstrate the errors introduced in this procedure, introduced the junction of a type T thermocouple in boiling water (known to be at 100ºC) and read the voltage across the leads. The reading was 3.634 mV, which corresponds to 86.1ºC. This temperature error arises because the connection of the thermocouple leads to the voltimeter constitutes two additional thermoelectric junctions that substract voltage from the signal being measured. One thermocouple junction is held in an ice bath at 0ºC. This called THE REFERENCE JUNCTION. c) What is the reason of using a Weatsstone bridge in the calibration of a thermistor? Conventional Ohmmeters cause small current to flow during resistance measurements, creating self-heating in the Thermistor. An appreciable temperature change of the sensor may be caused by this current, in effect a loading error. Bridge circuits are used to measure the resistance of thermistor. d) What is the main difference between an RTD and a thermocouple when they are measuring temperature? RTD’s functions as a result of increasing resistance in proportion to increasing temperature. The resistivity of the metal used in a RTD is dependent upon the temperature. A thermocouple is a device based upon the findings of SEEBECK (1821) who showed that a small electric will flow in a circuit composed of two dissimilar conductors when their junctions are kept at different temperatures. The electromotive force (emf) produced under these conditions is known as the “Seebeck emf”. e) Explain the difference between Seebeck, Peltier and Thomson effect. The Seebeck effect refers to the generation of avoltage potential, or emf, in an open thermocouple circuit caused by a difference intemperature between junctions in the circuit. The difference in I2R and the amount of energy generated by the current flowing through the junction is due to the Peltier effect. f) The measurement system of an oven uses a thermocouple type K (max 1372oC) as a sensor which had a irreparable damage. Here is only a thermistor in the warehouse. Is it possible to replace the thermocouple with the last one? Justify your answer. No max range for thermistor is 200oC. g) What is the physical meaning of RC for a capacitive circuit? Explain. RC is the time constant for discharge or charge of the capacitor. Problem page 293 to 295. Problem page 298.