Shalguev V.I., Kaboev O.K., Sizova I.A., Hegemann P., Lanzov V.A.

PARALOGS OF Rad51 PROTEIN FAMILY FROM Chlamydomonas reinhardtii:
RECOMBINATIONAL CHARACTERISTICS
V.I. Shalguev
1
, O.K. Kaboev
1
, I.A. Sizova
2
, P. Hegemann
3
and V.A. Lanzov
1
1
Petersburg Nuclear Physics Institute, Russian Academy of Sciences, Gatchina/ Sankt-
Petersburg, 188300, Russia;
2
St.Petersburg State University, Sankt-Petersburg, 198904,
Russia;
3 Institute für Biochemie, Genetik, and Microbiologie, Universität Regensburg, 93040,
Germany
Unicellular green microalga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii is a promissing model for basic and applied research. However, little is known about its system of homologous recombination underlying recombination repair of double-strand DNA break. Sequencing of
C. reinhardtii nuclear genome has revealed many repeats which account for a low level of nuclear homologous recombination compared to that of nonhomologous recombination.
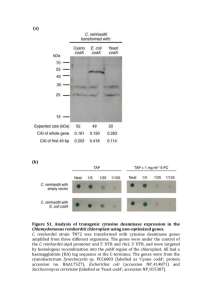
Analyses of the C. reinhardtii EST ( e xpressed s equence t ag)- and genome libraries made it possible to reconstruct and clone cDNA of the RAD51, RAD51B and RAD51C genes. In this work, these cDNAs were expressed, their slightly modified products
(CrRad51, CrRad51B and CrRad51C, respectively) with 6His-tag at their C-terminal ends were purified and the main biochemical activities were studied.
The recombination strand exchange reaction measured in a realtime fluorescent format as exchange between a short oligonucleotide and a short double-stranded DNA molecule showed the following order in the DNA-transferase activity: CrRad51 >CrRad51B> CrRad51C. Interestingly that activity of the mixture of these three proteins was a two-fold higher than a total activity of all three proteins alone. The data suggest a possibility of complex formation between some proteins in this mixture that results in activation of the strand transfer reaction.
The results show that Rad51 paralogs from lower eukaryote C. reinhardtii are identified as typical representatives of the Rad51-like proteins of higher eukaryotes.
The research was supported by Intas (grant 2001-0069) and Program of the Presidium of
RAS “Dynamics of Plant, Animal, and Human Gene Pools”(2004-2005).