Software Engineering Course Outline (CE-202)
advertisement

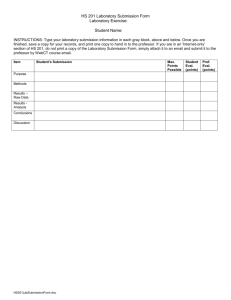
Course Plan Form SSUET/QR/110 REV# 00. Rev Date 01-11-07 COURSE OUTLINE 2011 (Version. 3) SOFTWARE ENGINEERING (CE-202) TEXT BOOK: Software Engineering (A Practitioners Approach) By Roger S. Pressman 7th Edition and 6th Edition. ** Please Purchase your own copy of Book it is not available in library. Pre-requisites: Complete command on software development projects as studied in CPPS. For Lab work you should have knowledge of HTML tags and MSACCESS database. For theory try to explore and understand the definition of Software Engineering and What is SDLC. Grade Weighting: Assignments Quizzes, Tests Lab Work (Labs, Project) Midterm : : : : 05% 05% 15% 15% Final Exams : 60% Course Philosophy 1. Weekly Assignment Scheme: 2. Research based Class Activities: 3. Workshop Style Labs Philosophy, Software Development Activities Scheme and Group Discussions as teaching methodology: 4. Career Counseling and guideline: (SEMINAR) Note: Lab demonstration of above Software Engineering Tools is very necessary for building their Software Engineering concepts in reality. Rule: 1. Only Hand written Theory assignments and will be submitted in every week’s first Class else half marks will be deducted and considered as Late work and will then be submitted along with next submission on submission time. Every assignment will comprise of staples pages of class lectures and the given questions for that assignment. Write down your Roll number on every page of your assignment. 2. Work Format Lab File will be submitted in next Lab else half marks will be deducted and considered as Late work and will then be submitted along with next submission on submission time. By: Syeda Umema Hani, Course Coordinator, Software Engineering (CE 202) Assistant Professor, CED, SSUET. First Version: 11/June/2011, 22/July/2011, 25/July/2011, 3/Aug/2011 Topics (Tools): Note: For Theory Section only follow Yellow highlighted part Week W1 25-31 July Theory Topics L1 CH 1) Software and SE: The Nature of Software -1.1 Software Application Domain - 1.1.2 Characteristic of Software in comparison with Hardware, 3 new challenges -1.1.1 Legacy Software - 1.1.3 The Unique Nature of WebApp -1.2 Lab Work /Project Assignments (10 mark each lab task, 1 mark each lab File checked in time, 10 marks for each Project task submitted in time) Web Development: Web Application Architecture and HTML Frame based Layout with link, banner and content panels using Dreamweaver. Assignments (To be Assigned on last class of each week) /Test /Quiz Collect CVz and Form Project Groups each comprising of 5 individuals [CH included in Lab Theory] 11.5.2. Interface Design Workflow L2 Building Software realities and definition of Software Engineering Layered Technology (Process, Methods & Tools)-1.3 CH 1) Introduction to Software Engineering its Applications & Characteristics The Software Characteristics Software Application Domain Defining Software and Failure curve Legacy Software W2 1-7 Aug L3 Software Process-1.4 Generic process Framework for software engineering-1.4 Project level differences which causes selection of Different Process -1.4 L4 Software Engineering Practices (Definition, its Essence and general principles)-1.5. Myths-1.6 How all Starts-1.7 Web Development: Client Side, “HTML” Coding for (Login Scenario) Form objects and its Validation “Java Scripting” for (Login Scenario) and CSS using Dreamweaver. CH 2) A Generic View of Process Group Wise Project Selection Announced Software Engineering and its Layered Technology (Process, Methods & Tools) Software Process Framework Capability Maturity Model [CH included in Lab Theory] 17.6.3. Validation Testing Assignment 1 Re-draw Architecture diagram discussed in Lab 1 for your Web Project in more details W3 8-14 Aug W4 15-21 Aug Personal and Team Process Model L5 CH 2) Process Models: Definition – 1.4 Generic Process Model - 2.1 Defining a Framework Activity -2.1.1 L6 Identifying task set - 2.1.2 Process Assessment and improvement (SCAMPI, CBA IPI, SPICE, ISO/IEC 15504, ISO 9001:2000) -2.2 CH 3) Process Models: Prescriptive Process Models: o Waterfall/The Linear Sequential Model o The Incremental Model o The RAD Model Evolutionary Software Process Models: o The Prototyping Model o The Spiral Model L7 Discuss Water Fall in detail and cover other models in comparison to it in terms of phases, flow direction, change adaptability and Iterations. Prescriptive Process Models: – 2.3 o Waterfall/The Linear Sequential Model -2.3.1 o The Incremental Model -2.3.2 L8 o The RAD Model (from 6th ed.) Evolutionary Software Process Models: 2.3.3 o The Prototyping Model o The Spiral Model W5 22-28 Aug o The Concurrent Development Model Specialized Process Models: o Component Based Development o Formal Methods Model o Agile Process Model o XP o Scrum L9 The Concurrent Development Model – 2.3.4 Specialized Process Models: 2.4 o Component Based Development 2.4.1 o Formal Methods Model-2.4.2 o Aspect Oriented Software Development - 2.4.3 Unified Process Model - 2.5 L10 Personal and Team Process Model-2.6 o PSP- 2.6.1, o TSP- 2.6.2 Process Technology -2.7 o Web Development: RDBMS Tool “mySQL” in XAMP. Assignment 1 (Submission) [CH included in Lab Theory] 6.4. Data Modeling ERD Web Development: Server Side Scripting “PHP” in XAMP (Authentication through mySQL using PHP code) [CH included in Lab Theory] 10.5. Designing Traditional Components - Flow Chart or pseudo code Group Wise Project Selection, FORM Submission Assignment 2 Make comparison chart for possible differences in between different “Process Models”. And select one suitable process Model for your own project. Web Development: Server Side Scripting “PHP” in XAMP (after Authentication List Employee Information Report) Quiz 1: Group Wise: SDLC selection for Project and Poster Assignment Brainstorming Comparison of candidate SDLC for a given scenario Product and Process relationship –2.8 Ch 4) Software Process and Project Metrics Process & Project Metrics Measures,Metrics & Indicators Software Measurements Metrics for Software Quality W6 29Aug-4 Sep W7 5-11 Sep W8 12-18 Sep Ramdan and Eid Ul Fitar Vocations L11 CH 3) Agile Development: What is it ? Agility and the cost of change -3.2 What is an Agile Process (when to use it) and its principals -3.3.1,3.3.2 Agile Process Models o XP- 3.4 L12 o SCRUM-3.5.2 Agile UPM 3.5.8 Ch 5) Software Project & Planning -Observation & Estimating -Project & Planning Objectives -Software Scope -Software Project Estimation Web Development: Server Side Scripting “PHP” in XAMP (after Authentication Execute Update Query) L13 CH 5) Understanding Requirements: Requirement Engineering Tasks –5.1 SRS, Multiple View Point – 5.2 L14 First Questions, QFD, Usage Scenario and modeling – 5.2 to 5.7 Web Development: Server Side Scripting “PHP” in XAMP (after Authentication Execute Delete, Insert Query) Project Poster draft copy review Assignment 2 (Submission) Group Wise: Final Project Poster Submission Ch5) Decomposition Techniques -Problem Based Estimation(LOC based & FP Based Estimation -Function & Object Point & its Examples W9 19-25 Sep L15 CH 6) Requirement Modeling: (Scenarios, Information and Analysis Class): Req Modeling Approaches –6.1.4 Scenario BM usecases – 6.2, 6.3 Data Modeling Concepts (Flow Oriented Models) – 6.4 Class BM – 6.5 L16 CH 7) Requirement Modeling (Flow, Behavior, Patters and Web Application): System Requirement Specification (SRS) IEEE Standard Document - 5.1 Assignment 3 [CH included in Lab Theory] SRS -5.1, Req modeling approaches – 6.2 DFD SSAD – 7.2.4 Analysis modeling – 7.5 First/Formulation Questions (CH5) Developing Scenario and Flow Oriented Model for Selected projects. (Assignment) Flow oriented DFD- 7.2.1 Creating a behavioral Model (Use case, Sequence and State diagram) – 7.3 Requirement Modeling for Web App-7.5 Requirement Modeling 7.2) Test 1: Whole Course CH 5) Cost Estimation Model -The Basic COCOMO Model -COCOMO II Application Model(Object Point its Example) W 10 MID TERM 26 Sep - 2 Oct W 11 3 Oct -9 Oct L17 CH 8) Design Concepts Software Quality Guideline and Attributes FURPS - 8.2.1 Evaluation of Software Design and Generic Task Set for Design - 8.2.2 L18 Design Concepts (Abstraction, Architecture, patters, separation of concern, modularity, information hiding, functional independence, refinement, Aspects, refactoring) - 8.3 The Design Model (Data, Architecture, Interface and Component Level Design) - 8.4 System Requirement Specification (SRS) II: Case Study [CH included in Lab Theory] Architectural Mapping using DFD diagram (9.1, 9.6) Components 8.2.1 Assignment 3 (Submission) Class Activity 3: On MDA Methodology Assignment 4 Equivalence Mapping of SSAD diagrams and UML diagrams Ch 6) Risk Analysis & Management: -Reactive vs Proactive Risk Strategies -Software Risks -Risk Identification -Risk Mitigation Monitoring & Management plan -Safety Risk & Hazard W 12 10-16 Oct L19 CH 9) Architectural Design: Architectural Styles- 9.3.1 Architectural Mapping using Data Flow Diagram - 9.6 L20 CH 10) Component Design: What is component? The traditional View10.1.2 Designing Traditional Components (flow chart Code) -10.5 Component Based Development and Domain Engineering-10.6, 10.6.1 Ch 7) Project Scheduling & tracking -Defining task Network -Scheduling -Earned Value Analysis with Examples Software Project Management Planning I: Documentation, Software Project Management Plan (SPMP) Assignment 4 (Submission) [CH included in Lab Theory] 26.2, 26.3 and 24.3.1, 26.4, 26.5, 24.3.2, 24.4, 24.4.1, 24.4.2, 25.5, 25.7, 24.7 Draw Architecture Diagram for your selected project and also design traditional components i.e. Flow charts for your application’s main Functions (discussed in SRS lab 9 and 10) for your selected Group Wise: SRS Submission Assignment 5 W13 17-23 Oct L21 CH 11) User Interface Design: Interface Analysis 11.3 Interface Design Workflow - 11.5.2 Software Project Management Planning II: Documentation, Software Project Management Plan (SPMP) L22 CH 13) WebApp Design A design pyramid for WebApp -13.3 Interface Design: Interaction Mechanism 13.4 Aesthetic Design (layout and graphics design issues) -13.5 WebApp. Architecture MVC -13.7.2 Navigation Design - 13.8 Component Level Design –13.9 [CH included in Lab Theory] 26.2, 26.3 and 24.3.1, 26.4, 26.5, 24.3.2, 24.4, 24.4.1, 24.4.2, 25.5, 25.7, 24.7 Group Wise: SRS Submission Chapter 8) Software Quality Assurance -Quality Concepts -Quality Control -Quality Assurance Cost of Quality SQA Activities -Software Reviews Formal Technical Reviews W14 24-30 Oct L22 CH 28) Risk Management: Reactive Vs Proactive Risk Strategies Software Risks Risk Identification Risk Projection Risk Refinement Risk Mitigation, Monitoring & Management RMMM Plan L23 CH 22) Software Configuration Management-22.1 Configuration Management for web App -22.4 Scheduling: Gantt Chart and PERT Chart using “MS Project 2003” tool. [CH included in Lab Theory] 25, 27.2, 27.2.1, 27.2.3, 27.3, 27.4, 27.5, 27.5.1, 27.5.4, 27.5.2 Group Wise: Plan Doc Submission Ch 29) Web Engineering -The Attributes of Web –Based Application -The WebE Process -Formulation & Analyzing Web –Based System modules. Assignment 5 (Submission) Assignment 6 Draw Professional Interface design by adopting interface design workflow and considering aesthetic as well as graphics design issues for Your Selected project and show all interface screens elaborated during Requirement Engineering Assignment 6 (Submission) Assignment 7 Revise Risk Identification, mitigation and Monitoring list from SPMP document you did in Lab 11 for your Project. Quiz 2: Design for Web-based Application -Architectural Design -Navigation Design -Interface Design W 15 31Oct-6 L24 Ch 30) SPI What is SPI - 30.1 Analysis and Designing: UML Diagrams “Visual Paradigm” tool Assignment 7 (Submission) Nov CMMI - 30.3 Other SPI Frameworks – 30.5 SPI ROI - 30.6 L25 Ch 31) Emerging Trends Just a Quick Review Ch 11) Analysis Concepts & Principles Introduction -Requirement Overview -Introduction to Requirement Engg -Reasons for success pf Project -System Requirement -Developing Use case -Negotiating Requirement -Validating Requirement W16 7 -13 Nov L26 CH 14) Quality concepts Quality of conformance - 14.1 ISO 9126 quality factors - 14.2.3 Cost of Quality - 14.3.2 Achieving Software quality - 14.4 L 27 CH 15) Review Techniques: Cost impact of software defect - 15.1 Defect Amplification and Removal - 15.2 Review Metrics - 15.3 Informal and formal Reviews - 15.5 and 15.6 W17 14-20 Nov Ch 17) Software Testing -White Box Testing -Blackbox Testing -Testing Tools & techniques Revision Should be covered in Lab theory otherwise take extra class to cover CH 16) SQA Definition, Elements - 16.2 Tasks, goals and metrics - 16.3 Statistical SQA and 6 SIGMA - 16.5 Reliability and availability - 16.6 ISO 9000 quality standard - 16.7 SQA Plan - 16.8 CH 20) Testing Web App 20.1.1. Dimensions of Quality 20.1.3. Testing Strategy 20.3. Content Testing 20.1. Testing Interface Mechanism 20.4.2 [CH included in Lab Theory] 6.1.4, 5.2, 6.2, 6.2.1, 6.2.2, 6.4 Research Topic: Model Driven Architecture (10 min discussion) Platform Independent Model Platform Specific Model Code Generation Assignment 8 Make possible Software Configuration Item list and revise SCM which you did in SPMP document for your project. Grosup Wise: GANTT Chart Submission Metrics: Cost Estimation: Automated Costing using “COSTAR” Software for cocomo and FP based estimations [CH included in Lab Theory] 26.5, 23.1.1, 23.1.4, 23.2, 23.2.1, 14.1, 5.1, 23.1.4, 14.2.2, 14.2.3, 26.6.7, 26.6.2, 26.7.2, 26.5, 26.6, 26.7, 26.6.9 Assignment 8 (Submission) Assignment 9 Make report on how you have planned to Control Quality of your Project. Group Wise: UML A&D Submission Group Wise: Estimation Reports Assignment SQA: Automated Testing: Test Case generation using “Quick Test Pro” Software. [CH included in Lab Theory] 14.1, 16.2, 17.1.1, .3, .2,16.6, 16.7, 20.1.4, 18.6, .3, 17.3, 16.8, 17.6.3, 20.4.2, 20.9 Test Cases for your project to be submitted in Final Report Assignment 9 (Submission) W18 21-27 Nov Student’s Web Application Demonstrations All Lab Notes Submission Complete Typed, Report Submission and Presentation Complete Assignment Class Activities Tests (Submission, Rechecking) Test 2: Post Mid W 19 28 Nov – 4 Dec Preparation Week (Dated: 3/Aug/2011)