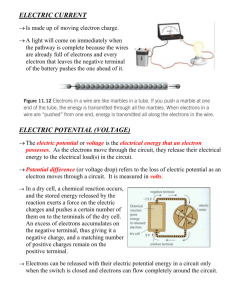
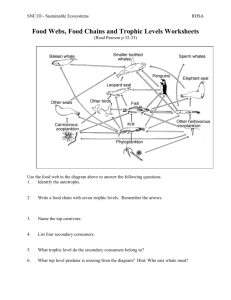
EXAM REVIEW: CHEMISTRY
advertisement

SNC1D Exam Review Chemistry EXAM REVIEW: CHEMISTRY Topics to be Covered What is matter Properties of Matter (malleability, lustre, etc.) Density Particle Theory of Matter Classification of matter (mixtures, compounds, solutions, etc.) Chemical Symbols and Formulas Names and Formulas for Compounds Counting Atoms Bohr; Bohr-Rutherford; Lewis Dot Diagrams Standard Atomic Notation (atomic number, mass number, proper notation, etc.) Charged Atoms (Ions) Organization of the periodic table (metals, non-metals, metalloids, etc.) groups of elements and their properties YOU MUST MEMORIZE THE SYMBOLS/NAMES FOR THE FIRST 20 ELEMENTS (with proper spelling) Additional Practice Questions 1) For the following experiment prepare a materials list and write a step-by-step procedure in the past passive as if you had done the experiment. Also identify the independent, the dependent variables, and the controlled variables. The grade 9 class is doing an experiment to see if pH level (level of acidity) affects plant growth. Students tested three different solutions: pH 4 (acidic), pH 7 (neutral), and pH 10 (alkaline or basic). Each pair of students did only one pH level. The students measured 100 g of potting soil using an electronic balance. Then they put the potting soil into a small pot (all the same size). They placed a pea seed that was starting to grow (already germinated) on top of the soil. They measured 15 mL of their pH solution in a 25 mL graduated cylinder and poured this onto the pea seed. Every day the students watered their plant with an additional 5 mL of their pH solution measured in a 10 mL graduated cylinder. Every day the students measured the height of their pea plants using a ruler. a) What is the independent variable? b) What is the dependent variable? c) What are the controlled variables? d) What variables were not controlled in this experiment, but should have been? 2a. What is matter? 2b. What are the 3 states of matter? 3a. What is a physical change? 3b. What are the 3 ‘clues’ that a physical change has taken place? 4a. What is a chemical change? 4b. What are the 5 ‘clues’ that a chemical change has taken place? 5. Decide whether the descriptions below are examples of a physical change (P) or chemical change (C). ____ ____ ____ ____ ice melting baking a cake cutting carrots a fire burning ____ ____ ____ ____ a firecracker exploding breaking glass a car rusting mixing salt and pepper 6a. Complete the table below of physical properties: PROPERTY Hardness Malleability Solubility Ductility Melting/Boiling Point Conductivity PHYSICAL PROPERTIES MEANING EXAMPLE SNC1D Exam Review Chemistry 6b. Complete the table below of the chemical properties: CHEMICAL PROPERTIES MEANING PROPERTY Combustibility EXAMPLE Reaction with Acid Corrosion 7. List the 5 Points of the Particle Theory of Matter. i) ii) iii) iv) v) 8. Complete the following chart with respect to the Particle Theory of Matter: Space Between Particles Attraction Between Particles Motion of Particles SOLID LIQUID GAS 9a. Match the term on the left with the description on the right. ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ Pure Substance Compound Homogeneous Mixture Matter Heterogeneous Element a. can only see 1 phase b. the same properties and composition throughout c. anything that has mass and takes up space d. particle with 1 type of atom e. can see 2 or more phases f. 2 or more elements put together g. different properties and composition throughout 9b. Use the words below to fill in the Classification of Matter table. element, matter, heterogeneous, homogeneous, compound, pure substance, Mixture 10. Complete the following classification of matter table. Type of Matter CLASSIFICATION OF MATTER Explain what this is Heterogeneous or Homogeneous? or N/A Element Compound Solution Mechanical Mixture 11. Write the symbol for the following elements: _____ _____ _____ _____ carbon potassium nitrogen calcium _____ _____ _____ _____ boron helium sodium beryllium Example SNC1D Exam Review Chemistry 12. Write the name of the element for the following symbols: Li _________________ K _________________ Al _________________ S __________________ Ne _________________ Si __________________ H __________________ O __________________ 13. Draw Bohr diagrams for the following elements. Nitrogen Sodium Chlorine 14. Draw Bohr Rutherford diagrams for the following elements. Carbon Fluorine Aluminum Sodium ion Chlorine ion 15. Draw Lewis dot diagrams for the following ions. Nitrogen ion 16. Complete the following chart. Isotope Standard Atomic Notation Beryllium-9 9 Atomic Number Mass Number # protons # electrons # neutrons 10 16 2+ 4Be Silicon-30 14 Selenium-79 79 34 36 Phosphorus-31 15 18 17a. Protons have a _____________ charge. 17b. Electrons have a ________________ charge. 17c. Neutrons have a charge of __________. For the following question, describe the location of the 3 subatomic particles 18a. Protons are found __________________________________________ 18b. Electrons are found ________________________________________ 18c. Neutrons are found _________________________________________ 19. Complete the following charts on counting atoms. a) Na2CrO4 Element b) 2K2S # of Atoms Element c) 4Mg(NO3)2 # of Atoms Questions 20 and 21 refer to the Periodic Table of Elements. 20a. Vertical columns are called ____________________ 20b. Horizontal rows are called _____________________ 20c. Metals are found on the ____________________ side 20d. Non-metals are found on the _________________ side 20e. Elements which are metalloids are ________________________________ 20e. Transition metals are found in groups ______________ Element # of Atoms SNC1D Exam Review 21a. Elements found in group 1 (IA) are called __________________________ 21b. Elements found in group 2 (IIA) are called _________________________ 21c. Elements found in group 17 are called _____________________________ 21d. Elements found in group 18 are called _____________________________ 22. What does the term ‘stable octet’ mean? 23. What group of elements on the periodic table have a stable octet? 24. A piece of lead is placed in a graduated cylinder that initially reads 10.0 mL. After a piece of lead is added to the graduated cylinder, it has a new reading of 45.6 mL. What is the mass of the lead? (density of lead = 11.3 g/cm 3) 25. A cylindrical object has a diameter of 0.06 m and a height of 12 m. The mass of the object is 3.6 kg. What is the density of the object? What is the object made of? (refer to table 1 on page 24 of your text). 26) Use the values for combining capacities shown in the tables to write chemical formulas for: a) b) c) d) e) f) g) sodium fluoride magnesium fluoride potassium bromide zinc oxide silver oxide (note: the symbol for silver does not need to be memorized) aluminum fluoride aluminum sulphide Table 1: Combining Capacity of Some Metals Element Combining Capacity METALS silver 1 sodium 1 potassium 1 zinc 2 calcium 2 aluminum 3 NON-METALS chlorine 1 bromine 1 hydrogen 1 iodine 1 sulfur 2 oxygen 2 nitrogen 3 carbon 4 SNC1D Exam Review 27. Determine the density of the following samples using the graph provided Sample 1 4 3 4 5 Volume (mL) 5 15 20 25 35 Mass (g) 3.7 10.0 13.1 18.0 23.8 SNC1D Exam Review EXAM REVIEW: CHEMISTRY (SOLUTIONS) Additional Practice Questions 1) For the following experiment prepare a materials list and write a step-by-step procedure in the past passive as if you had done the experiment. Also identify the independent, the dependent variables, and the controlled variables. The grade 9 class is doing an experiment to see if pH level (level of acidity) affects plant growth. Students tested three different solutions: pH 4 (acidic), pH 7 (neutral), and pH 10 (alkaline or basic). Each pair of students did only one pH level. The students measured 100 g of potting soil using an electronic balance. Then they put the potting soil into a small pot (all the same size). They placed a pea seed that was starting to grow (already germinated) on top of the soil. They measured 15 mL of their pH solution in a 25 mL graduated cylinder and poured this onto the pea seed. Every day the students watered their plant with an additional 5 mL of their pH solution measured in a 10 mL graduated cylinder. Every day the students measured the height of their pea plants using a ruler. a) What is the independent variable? pH (acidity) level b) What is the dependent variable? plant growth c) What are the controlled variables? soil, balance, pot size, age of seed, volume of solution poured onto pea seed, watering, how growth was measured d) What variables were not controlled in this experiment, but should have been? other environmental conditions (i.e. temp, light), type of potting soil, how deep seed was planted, how compact soil was in pot, procedure for measuring height of plant (i.e. was plant stretched prior to measuring), etc. 2a. What is matter? Anything that takes up space and has a volume 2b. What are the 3 states of matter? Solid, liquid, gas 3a. What is a physical change? A change where no new substance is formed 3b. What are the 3 ‘clues’ that a physical change has taken place? Change in form, change in state, or a substance has dissolved 4a. What is a chemical change? A change that produced a new substance with different properties 4b. What are the 5 ‘clues’ that a chemical change has taken place? New colour, heat or light given off, bubbles of gas form, a solid material (called a precipitate) forms in a liquid, the change is difficult to reverse 5. Decide whether the descriptions below are examples of a physical change (P) or chemical change (C). __P__ ___C_ ___P_ __C__ ice melting baking a cake cutting carrots a fire burning ___C_ _P___ __C__ __P__ a firecracker exploding breaking glass a car rusting mixing salt and pepper 6a. Complete the table below of physical properties: PROPERTY Hardness PHYSICAL PROPERTIES MEANING The resistance of a solid to scratching Malleability Solubility EXAMPLE Diamond is very hard A paper clip is malleable Ability to be hammered or bent into different shapes. Ability to dissolve in a solvent such as water Salt is soluble in water Ductility Ability to be stretched out into a wire. Copper is ductile. Melting/Boiling Point Temperature at which a substance changes state. Water boils at 100 degrees Celsius. Conductivity A conductor is a substance in which electrons or heat can move freely throughout. Copper is a good conductor of heat and electricity. 6b. Complete the table below of the chemical properties: PROPERTY Combustibility CHEMICAL PROPERTIES MEANING EXAMPLE Ability to react with oxygen and produce carbon dioxide (burn). Propane is combustible. Reaction with Acid Ability of a substance to react with acid. Limestone reacts with acid. Corrosion Reaction with oxygen to form an oxide. Iron reacts with oxygen to form iron oxide (rust). 7. List the 5 Points of the Particle Theory of Matter. SNC1D Exam Review i) All matter is made of tiny particles. ii) All particles of one substance are the same. Different substances are made of different particles. iii) Particles are always moving. iv) Particles are attracted to each other. v) As temperature increases, particle motion increases and visa versa. 8. Complete the following chart with respect to the Particle Theory of Matter: Space Between Particles SOLID LIQUID GAS Attraction Between Particles Motion of Particles Small Medium Large Medium Small Medium Large Small large 9a. Match the term on the left with the description on the right. _B___ __F__ __A__ __G__ __C__ __E__ __D__ Pure Substance Compound Homogeneous Mixture Matter Heterogeneous Element a. can only see 1 phase b. the same properties and composition throughout c. anything that has mass and takes up space d. particle with 1 type of atom e. can see 2 or more phases f. 2 or more elements put together g. different properties and composition throughout 9b. Use the words below to fill in the Classification of Matter table. element, matter, heterogeneous, homogeneous, compound, pure substance, matter Pure substance element Mixture compound heterogeneous homogenous 10. Complete the following classification of matter table. Element CLASSIFICATION OF MATTER Explain what this is Heterogeneous or Homogeneous? or N/A NA Made up of one type of atom Made up of two types of atoms chemically linked together NA Water Compound Mixture with only one phase Homogenous Apple juice Mixture with more than one phase Heterogeneous Pop (with bubbles) Type of Matter Example Copper Solution Mechanical Mixture 11. Write the symbol for the following elements: __C___ ___K__ __N___ __Ca___ carbon potassium nitrogen calcium ___B__ ___He__ ___Na__ ___Be__ boron helium sodium beryllium 12. Write the name of the element for the following symbols: Li __________lithium_______ K __________potassium_______ Al _________aluminum________ S ____________sulfur______ Ne ________neon_________ Si _________silicon_________ H ________hydrogen__________ O ________oxygen__________ 13. Draw Bohr diagrams for the following elements. Nitrogen N Sodium Na Chlorine Cl SNC1D Exam Review 14. Draw Bohr Rutherford diagrams for the following elements. Carbon Fluorine Aluminum 13P 14N 9P 10N 6P 6N 15. Draw Lewis dot diagrams for the following ions. Nitrogen ion Sodium ion Chlorine ion Cl [Na]+ N3- 16. Complete the following chart. Isotope Standard Atomic Notation Beryllium-9 9 Atomic Number Mass Number # protons # electrons # neutrons 4 9 4 2 5 10 16 2+ 4Be Silicon-30 30 30 4+ 14Si 14 14 Selenium-79 79 2- 34Se 34 31 15 79 34 45 36 Phosphorus-31 15P 3- 15 31 16 18 17a. Protons have a _____+________ charge. 17b. Electrons have a ____-____________ charge. 17c. Neutrons have a charge of ______zero____. For the following question, describe the location of the 3 subatomic particles 18a. Protons are found ____________in the nucleus______________________________ 18b. Electrons are found __________orbiting around the nucleus______________________________ 18c. Neutrons are found __________in the nucleus_______________________________ 19. Complete the following charts on counting atoms. a) Na2CrO4 b) 2K2S Element Sodium Chromium Oxygen # of Atoms 2 1 c) 4Mg(NO3)2 Element # of Atoms Element # of Atoms Potassium 4 Magnesium 4 Sulphur 2 Nitrogen 8 Oxygen 24 4 Questions 20 and 21 refer to the Periodic Table of Elements. 20a. Vertical columns are called ______groups/families______________ 20b. Horizontal rows are called ______periods_______________ 20c. Metals are found on the _______left_____________ side 20d. Non-metals are found on the ______right___________ side 20e. Elements which are metalloids are ________B, Si, Ge, As, Sb, Te________________________ 20f. Transition metals are found in groups ___3-12___________ 21a. Elements found in group 1 (IA) are called _______alkali metals___________________ 21b. Elements found in group 2 (IIA) are called ______alkaline earth metals or rare earth metals___________________ 21c. Elements found in group 17 are called ___________halogens__________________ 21d. Elements found in group 18 are called __________noble gases___________________ 22. What does the term ‘stable octet’ mean? Refers to the valence electrons (outermost electrons) of an atom. If an atom has 8 valence electrons, then it has a stable octet 23. What group of elements on the periodic table have a stable octet? Noble gases 24. A piece of lead is placed in a graduated cylinder that initially reads 10.0 mL. After a piece of lead is added to the graduated cylinder, it has a new reading of 45.6 mL. What is the mass of the lead? (density of lead = 11.3 g/cm 3) SNC1D Exam Review Given D = 11.3 g/cm3 Vi = 10.0 mL Vf = 45.6 mL Required M=? Analyse V= Vf-Vi M = DV Solve: V = 45.6 mL – 10.0 mL V = 35.6 mL (1 mL = 1 cm3) V = 35.6 cm3 M = DV M = (11.3 g/cm3)(35.6 cm3) M = 402.28 g Therefore the mass of the lead sample is 402.28 g. 25. A cylindrical object has a diameter of 0.06 m and a height of 12 m. The mass of the object is 3.6 kg. What is the density of the object? What is the object made of? (refer to table 1 on page 24 of your text). Given M = 3.6 kg diam = 0.06 m h = 12m Required D=? Analyse V = πr2h R = D/2 D = M/V Solve: V = π(0.06m/2)2(12m) V = 0.03392m3 D = M/V D = (3.6 kg)/(0.03392m3) D = 106.1 kg/m3 Therefore the density of the object is 106.1 kg/m3. The table of densities does not list this substance. 26 a) NaF b) MgF2 c) KBr d) ZnO e) Ag2O f) AlF3 g) Al2S3 27 Volume (mL) vs Mass (g) 30 Mass (g) 25 20 15 10 5 0 0 5 10 15 20 Volume (mL) Density = slope = 0.68 g/mL 25 30 35 40 SNC1D Exam Review Grade 9 Science Earth and Space Review Textbook Questions: Planetary Motion (p. 283-290) Effects of planetary motion (rotation/revolution) Direction of Revolution of Earth Explanation of the seasons Explanation of how much light North/South receives on any day of the year (equal amounts, 24 hours of light/dark, etc.) Distances in space (p.291-296) Know the differences in using different units to measure distances in space (ie. kilometers, astronomical units, light years) Model of the solar system (pg. 291-296) Know how to convert units and construct a model of the solar system with appropriate units. Formation of solar systems, stars and galaxies (pg. 333-340, pg. 361-366) Describe the steps involved in the formation of solar systems, stars, and galaxies.. 1. Put each term in the box in the correct space of the Venn diagram. • turning around axis • one object orbiting another • an object is turning • takes Earth 24 h • takes Earth one year 2. Label the diagram using the terms in the box. Sun December June rotation revolution 3. Circle the best answer to complete the sentence. SNC1D Exam Review In the northern hemisphere, summer is warmer than winter because __________________. A. Earth’s northern hemisphere is tilted toward the Sun in summer and away from it in winter. B. Earth’s northern hemisphere is tilted away from the Sun in summer and toward it in winter. C. Earth is closer to the Sun in summer than in winter. D. Earth turns upside down in the winter. 4. Which unit would you use to measure each distance? You may use each unit more than once. centimetre (cm) (AU) a. b. c. d. e. metre (m) kilometre (km) astronomical unit the length of your classroom ________ the distance between the Sun and Neptune ________ the length of a textbook ________ the distance between Toronto and Ottawa ________ the distance between the Earth and Uranus 5. In the winter, sun light rays are more: _________________ (direct, indirect). In the summer, sun light rays are more: _______________ (direct, indirect). Seasons do occur at the equator but they’re not as noticeable as at higher latitudes 6. The longest daylight period in the northern hemisphere is on ___________________ . 7. The longest daylight period in the southern hemisphere is on ___________________ . 8. In the northern hemisphere on: June 21st we will receive more hours of daylight or darkness? _________. March 21st daylight = ____ hours and darkness = ____ hours. December 21st we will receive more or less hours of daylight? _______. September 21st, more, less or the same # of hours of daylight & darkness? _______. 9. On certain dates, all places on Earth experience equal hours of day and night. When do we experience this? Explain why. 10. In the winter how is the Earth tilted relative to the Sun in the (a) northern hemisphere and the (b) southern hemisphere? SNC1D Exam Review 11. What causes seasons? 12. Explain what unit do we use to measure distances to stars? To our Sun? Mercury Venus Earth Mars Jupiter Saturn Uranus Neptune diameter (km) 4,878 12,104 12,756 6,787 142,800 120,000 51,118 49,528 mass (Earth=1) 0.055 0.815 1 0.107 318 95 15 17 mean distance from Sun(km) 57,910,000 108,200,000 149,600,000 227,940,000 778,330,000 1,424,600,000 2,873,550,000 4,501,000,000 orbital period (Earth years) 0.24 0.62 1 1.88 11.86 29.46 84.01 164.8 gravity (Earth=1) 0.38 0.9 1 0.38 2.64 0.93 0.89 1.12 mean density 5.43 5.25 5.52 3.93 1.33 0.71 1.24 1.67 13. Using the table above, If we made a map of the solar system, where 20 cm represented 1 astronomical unit (a.u.), how many centimetres would there be between the Sun and Jupiter? SNC1D Exam Review 14. Does a star’s apparent brightness depend on just its distance from Earth? Explain your answer. 15. List four properties of stars 16. Place the following in order from youngest to oldest: A. star; B. nebula; C. red giant; D. white dwarf 17. What is a neutron Star? 18. What is the fate of our Sun? 19. Can a star less massive than the Sun become a supernova? Explain 20. Why are the more massive stars the only important contributors in enriching the universe with heavy elements? 21. The Canadian songwriter Joni Mitchell wrote, “We are stardust” in her song called “Woodstock”. She was being factual as well as poetic. Explain why. SNC1D Exam Review Grade 9 Science Earth and Space Review ANSWERS Textbook Questions: Planetary Motion (p. 283-290) Effects of planetary motion (rotation/revolution) Direction of Revolution of Earth Explanation of the seasons Explanation of how much light North/South receives on any day of the year (equal amounts, 24 hours of light/dark, etc.) Distances in Space (p. 291-296) Know the differences in using different units to measure distances in space (ie. kilometers, astronomical units, light years) Model of the solar system (pg. 291-296) Know how to convert units and construct a model of the solar system with appropriate units. Formation of solar systems, stars, galaxies ( pg. 333-340, 361-366) Describe the steps involved in the formation of solar systems, stars, and galaxies. 1. Put each term in the box in the correct space of the Venn diagram. turning around axis takes Earth 24 h an object is turning • turning around axis • one object orbiting another • an object is turning • takes Earth 24 h • takes Earth one year one object orbiting another takes Earth one year 2. Label the diagram using the terms in the box. revolution June Sun December June rotation revolution Sun December rotation 3. Circle the best answer to complete the sentence. SNC1D Exam Review In the northern hemisphere, summer is warmer than winter because __________________. a. Earth’s northern hemisphere is tilted toward the Sun in summer and away from it in winter. b. Earth’s northern hemisphere is tilted away from the Sun in summer and toward it in winter. c. Earth is closer to the Sun in summer than in winter. d. Earth turns upside down in the winter. 4. Which unit would you use to measure each distance? You may use each unit more than once. centimetre (cm) (AU) a. b. c. d. e. metre (m) kilometre (km) astronomical unit the length of your classroom ___m_____ the distance between the Sun and Neptune ___AU_____ the length of a textbook ____cm____ the distance between Toronto and Ottawa ___km_____ the distance between the Earth and Uranus ____AU_____ 5. In the northern hemisphere, during winter, sun light rays are more: (direct, indirect). In the northern hemisphere, during summer, sun light rays are more: (direct, indirect). Seasons do occur at the equator but they’re not as noticeable as at higher latitudes 13. The longest daylight period in the northern hemisphere is on JUNE 21. 14. The longest daylight period in the southern hemisphere is on DECEMBER 21. 15. In the northern hemisphere on: June 21st we will receive more hours of daylight or darkness? _daylight. March 21st daylight = _12_ hours and darkness = _12_ hours. December 21st we will receive more or less hours of daylight? _less__. September 21st, more, less or the same # of hours of daylight & darkness? _same__. 16. On certain dates, all places on Earth experience equal hours of day and night. When do we experience this? Explain why. On the equinoxes, September 23 and March 21. Equal day and night because the Earth is the part of its revolution where it does not tilt towards or away from the Sun. 17. In the winter how is the Earth tilted relative to the Sun in the (a) northern hemisphere and the (b) southern hemisphere? SNC1D Exam Review a) away from Sun b) towards the Sun 18. What causes seasons? a. The Earth’s tilt and its revolution. Depending where the Earth is on it’s orbit, its tilt will cause different places on the Earth to receive differentiate amounts of energy. 19. Explain what unit do we use to measure distances to stars? To our Sun? We measure distances to stars with light years. We measure distances in our solar system with A.U. Mercury Venus Earth Mars Jupiter Saturn Uranus Neptune diameter (km) 4,878 12,104 12,756 6,787 142,800 120,000 51,118 49,528 mass (Earth=1) 0.055 0.815 1 0.107 318 95 15 17 mean distance from Sun(km) 57,910,000 108,200,000 149,600,000 227,940,000 778,330,000 1,424,600,000 2,873,550,000 4,501,000,000 orbital period (Earth years) 0.24 0.62 1 1.88 11.86 29.46 84.01 164.8 gravity (Earth=1) 0.38 0.9 1 0.38 2.64 0.93 0.89 1.12 mean density 5.43 5.25 5.52 3.93 1.33 0.71 1.24 1.67 13. Using the table above, If we made a map of the solar system, where 20 cm represented 1 astronomical unit (a.u.), how many centimetres would there be between the Sun and Jupiter? # of A.U. to Jupiter = 778 330 000 km/ 150 000 000 km = 5.1888 A.U. 1 A.U. = 20 cm. therefore, 5.1888 A.U. x 20 cm = 103.77 cm 22. Does a star’s apparent brightness depend on just its distance from Earth? Exaplin your answer. No, a star’s brightness also depends on its luminosity. A bright star is not necessarily closer to Earth; it could just be large and more luminous 23. List four properties of stars Four properties of stars are brightness, colour, temperature, and composition 24. Place the following in order from youngest to oldest: A. star; B. nebula; C. red giant; D. white dwarf B. nebula; A. star; C. red giant; D. white dwarf 25. What is a neutron Star? A neutron star is an extremely dense star that is made only of neutrons SNC1D Exam Review 26. What is the fate of our Sun. In about 5 billion years, the Sun will become a red giant, then collapse to become a white dwarf 27. Can a star less massive than the Sun become a supernova? Explain No, stars have to be more than 12 times the mass of the Sun before they can become a supernova 28. Why are the more massive stars the only important contributors in enriching the universe with heavy elements? The heavy elements come from supernovae; only more massive stars become supernovae 29. The Canadian songwriter Joni Mitchell wrote, “We are stardust” in her song called “Woodstock”. She was being factual as well as poetic. Explain why. Possible answer: I am made of stardust. Heavier elements released through supernova explosions are ejected throughout the universe, eventually showing up in stars, planets, and other bodies, including humans SNC1D Exam Review EXAM REVIEW: PHYSICS Topics to Be Covered Electrical nature of matter charging by friction (electrostatic series), contact, induction insulators, conductors parts of an electric circuit direction electrons travel in a circuit how a circuit works schematic circuit diagrams (including proper use of Ammeter and Voltmeter) definition, symbols, units of measurement, and calculations for charge, electrical energy, current, voltage, and resistance Ohm’s Law Properties and calculations involving of parallel and series circuits Practice Questions 1a. What is the charge of a proton? 1b. What is the charge of an electron? 1c. What is the charge of a neutron? 2a. What is static electricity? 2b. What is current electricity? 3. Complete the following table. INSULATOR CONDUCTOR Definition Type of Electricity (Static or Current) Examples 4. List the 3 parts of the Law of Electric Charges. i. ii. iii. 5. Complete the following table. Object A positive neutral negative positive negative Object B Attract or Repel positive positive neutral negative negative 6. Use the table of the electrostatic series to draw a diagram and explain what happens when the following objects are rubbed together Electrostatic Series WEAK a. Glass rubbed with plastic Acetate Before rubbing After rubbing Glass Fur, Hair Calcium Silk Aluminum Cotton Wax b. Calcium rubbed with platinum Ebonite Before rubbing After rubbing Plastic Rubber Carbon Sulfur Platinum Gold STRONG c. If acetate has a weak hold on electrons it will __________________(lose/gain) electrons when rubbed with rubber, which has a strong hold on electrons. 7. What are the three methods of charging an object? i. ii. 8. Complete the following table of circuit diagrams. iii. SNC1D Exam Review TERM DEFINITION SYMBOL Cell A combination of cells Conductor/Wire Path that carries electric current Load Resists flow of electrons Switch Light Bulb Device within a circuit Ammeter ` 9a. In an electric circuit, where do electrons leave from and return to? 9b. In an electric circuit, what do electrons move through? 10a. If the switch in a circuit is open, what does it mean? 10b. If the switch in a circuit is closed, what does it mean? 11a. What is a series circuit? 11b. What is a parallel circuit? 12a) Sketch a circuit that has: three cells wired in series two light bulbs wired in series that are parallel to a third bulb an open switch controlling the entire circuit arrows showing electron flow b) Sketch a circuit that has three cells wired in series two light bulbs wired in series, in parallel with the third bulb a fourth bulb placed in such a way that if it is unscrewed nothing in the circuit works an open switch controlling the entire circuit a second open switch controlling each of the parallel branches only 13. Complete the following table. VARIABLE Charge SYMBOL UNIT Current Potential Difference/Voltage Resistance 14a. What does an ammeter measure? 14b. What does a voltmeter measure? 15. What is the formula for Ohm’s Law? 16. A heater has a resistance of 8.0Ω when it is plugged into a 110V outlet. What is the current? (Answer using GRASP) SNC1D Exam Review 17) A battery delivers 5.0 C or charge in 20 s. What is the current from the battery in amperes and milliamperes?(Answer using GRASP) 18) 14 A or current flows through a load that draws 4.2 C of charge. How long, in seconds, is the load drawing current? (Answer using GRASP) 19) Find the current that will blow a fuse if the fuse burns out when 60 C of charge passes through it in 8.0 s. (Answer using GRASP) 20) Find the charge drawn from a battery if a calculator draws 20 mA of current in 26 s. (Answer using GRASP) 21) Find the drop in potential difference across a light bulb if 60 C of charge provides 7200 J of energy to the bulb. (Answer using GRASP) 22) A hair dryer draws 14 A of current for 10 minutes. a) How much charge flows through the dryer? (Answer using GRASP) b) If the hair dryer is connected to a 120 V supply, how much energy does the dryer use? (Answer using GRASP) . 23. Identify the following circuits as series or parallel. SNC1D Exam Review 24. Complete the following Formula Table. COMPONENT SERIES CIRCUIT FORMULA PARALLEL CIRCUIT FORMULA Current (I) Potential Difference (V) Resistance 25. Solve for each of the following circuits using Ohm’s Law and the formulae for series and parallel circuits: a. b. c. d. 26. Solve for equivalent (total) resistance (RT) when a 4Ω bulb and 6Ω bulb are connect in: a) Series b) Parallel SNC1D Exam Review 27. Dr. Volta conducted an electricity experiment involving Ohm’s Law. During the experiment, he measured both the potential difference (V) and noted the current (I). In the table below are Dr. Volta’s experimental results. Current (A) Voltage (V) 0.5 1.4 1.0 2.2 a) Plot the information on the graph below 1.5 3.7 b) Draw the line of best fit 2.0 4.9 c) Find the resistance using slope. 2.5 6.1 d) What is the voltage when current is 0.18A? _________ 3.0 7.3 e) What is the current when voltage is 6.0V? _________ REMEMBER TO TITLE YOUR GRAPH AND AXES!!! SNC1D Exam Review PHYSICS EXAM REVIEW (SOLUTIONS) Practice Questions 1a. What is the charge of a proton? Positive (+1) 1b. What is the charge of an electron? Negative (-1) 1c. What is the charge of a neutron? Neutral (0) 2a. What is static electricity? A charge that does not move 2b. What is current electricity? Electric charges that move from a source through a controlled path in an electric circuit. 3. Complete the following table. Definition INSULATOR CONDUCTOR Does not allow electrons to flow freely from atom to atom Does allow electrons to flow freely from atom to atom Static Current Type of Electricity (Static or Current) Examples Rubber, wood Wire, water 4. List the 3 parts of the Law of Electric Charges. i. like charges repel ii. unlike charges attract iii. charged objects attract uncharged (neutral) objects 5. Complete the following table. Object A Object B positive neutral negative positive negative + - + - positive positive neutral negative negative Attract or Repel R A A A R 6. Use the table of the electrostatic series to draw a diagram and explain what happens when the following objects are rubbed together Electrostatic Series WEAK a. Glass rubbed with plastic Acetate Before rubbing After rubbing Plastic Glass Glass Fur, Hair + + Calcium - + + + + + + + Silk Aluminum + + Cotton Wax b. Calcium rubbed with platinum Ebonite Before rubbing After rubbing Plastic Platinum Rubber + Calcium - Carbon + + + + + Sulfur + + + Platinum + Gold + STRONG e. If acetate has a weak hold on electrons it will __________________(lose/gain) electrons when rubbed with rubber, which has a strong hold on electrons. 7. What are the three methods of charging an object? i. friction ii. contact iii. induction 8. Complete the following table of circuit diagrams. TERM Battery DEFINITION Two electrodes and an electrolyte that provide an electric current A combination of cells Conductor/Wire Path that carries electric current Cell SYMBOL SNC1D Exam Review Load Resists flow of electrons Results can vary, e.g., Switch Device that controls flow of electrons Light Bulb Device within a circuit Ammeter Device to measure current in amperes 9b. In an electric circuit, what do electrons move through? Conductor/wire 10a. If the switch in a circuit is open, what does it mean? No current flows, the switch is “off” 10b. If the switch in a circuit is closed, what does it mean? Current flows, the switch is “on” 11a. What is a series circuit? A circuit where all loads are connected one after each other, each electron flows through each load. 11b. What is a parallel circuit? A circuit where some loads are connected in parallel, each electron flows only through some loads 12a) Sketch a circuit that has: three cells wired in series two light bulbs wired in series that are parallel to a third bulb an open switch controlling the entire circuit arrows showing electron flow b) Sketch a circuit that has three cells wired in series two light bulbs wired in series, in parallel with the third bulb a fourth bulb placed in such a way that if it is unscrewed nothing in the circuit works an open switch controlling the entire circuit a second open switch controlling each of the parallel branches only 13. Complete the following table. VARIABLE Charge SYMBOL Q UNIT C Current I A Potential Difference/Voltage V V Resistance R ohm or Ω 14a. What does an ammeter measure? current 14b. What does a voltmeter measure? voltage (potential difference) 15a. What is the formula for Ohm’s Law? V=IR 16. A heater has a resistance of 8.0Ω when it is plugged into a 110V outlet. What is the current? (Answer using GRASP) Given: R = 8.0 Ω, V = 110 V SNC1D Exam Review Required: I = ? Analysis: I = V/R Solution: I = 110 V/8.0 Ω = 110/8 A = 13.75 A Paraphrase: The heater’s current is 13.8 A 17) A battery delivers 5.0 C or charge in 20 s. What is the current from the battery in amperes and milliamperes?(Answer using GRASP) Given: C = 5.0 C, T = 20s Required: I = ? Analysis: I = C/T Solution: 0.25A and 250 mA Paraphrase: The current is 0.25 A or 250 mA 18) 0.3 s 19) 7.5 A 20) 0.52 C 21) 120 V 22a) 8400 C b) 1.008 x 10 6 J . 23. Identify the following circuits as series or parallel. Mixed parallel & series Series Parallel Parallel 24. Complete the following Formula Table. COMPONENT SERIES CIRCUIT FORMULA PARALLEL CIRCUIT FORMULA Current (I) IT = I1 = I2 = … IT = I1 + I2 + … Potential Difference (V) VT = V1 + V2 + … VT = V1 = V2 = … Resistance RT = R1 + R2 + … 1/RT = 1/R1 + 1/R2 + … SNC1D Exam Review 25. Solve for each of the following circuits using Ohm’s Law and the formulae for series and parallel circuits: V1 = V2 = 6.0 V I2 = 0.25 A R1 = R2 = 24 Ω Rt = 12 Ω a) (c) V1 = 6.0 V; V3 = 12 V I1 = I2 = 1.0 A R1 = R2 = 6.0 Ω R3 = 12 Ω Rt = 6.0 Ω b) c) d) 26. Solve for equivalent (total) resistance (RT) when a 4Ω bulb and 6Ω bulb are connect in: c) Series G: R1 = 4 Ω, R2 = 6 Ω R: RT A: RT = R1 + R2 S: RT = 4 Ω + 6 Ω = 10 Ω P: equivalent resistance is 10 Ω d) Parallel G: R1 = 4 Ω, R2 = 6 Ω R: RT A: 1/RT = 1/R1 + 1/R2 S: 1/RT = 1/4 Ω + 1/6 Ω = 3/12 Ω + 2/12 Ω = 5/12 Ω RT = 12/5 Ω = 2.4 Ω P: equivalent resistance is 2.4 Ω 27. Dr. Tram conducted an electricity experiment involving Ohm’s Law. During the experiment, she measured both the potential difference (V) and noted the current (I). In the table below are Dr. Tram’s experimental results. Current (A) 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0 REMEMBER TO TITLE YOUR GRAPH AND AXES!!! a) Plot the information on the graph below b) Draw the line of best fit c) Find the resistance using slope. d) What is the voltage when current is 0.18A? _________ e) What is the current when voltage is 6.0V? _________ R = V/I = 2.8 V/1.2 A = 2.3 d) What is the voltage when current is 0.18A? _________ V = IR = (0.18 A)(2.3 ) = 0.4 V e) What is the current when voltage is 6.0V? _________ I = V/R = 6.0 V/2.3 = 2.6 A Voltage (V) 1.4 2.2 3.7 4.9 6.1 7.3 SNC1D Exam Review Current vs. Voltage 8 7 6 Voltage (V) 5 4 rise = y2 - y1 = 4.8 V - 2.0 V = 2.8 V 3 2 1 run = x2 - x1 = 2.0 A - 0.8 A = 1.2 A 0 0 1 2 Current (A) 3 4 SNC1D Exam Review Ecology Exam Review 1. What is an ecosystem . Give 2 examples. 2. What is an abiotic factor? Give 2 examples. 3. What is a biotic factor. Give 2 examples. 4. What is a producer? Give an example. 5. What is a decomposer ? Give an example? 6. What type of organism is in the: 1st trophic level = 2nd trophic level = 3rd trophic level = 4th trophic level = 7. A consumer is... 8. What is the primary source of energy for all living things? 9. Show the differences & similarities between photosynthesis & respiration. You may use a Venn diagram to show this. SNC1D Exam Review Ecology Exam Review - ANSWERS 1. What is an ecosystem . Give 2 examples. The interaction of a community of organisms with their environment. e.g. forest, farmer's field, pond 2. What is an abiotic factor? Give 2 examples. The non-living components of an environment, not produced through the action of living things. e.g. wind, water, tornadoes, sand Note: a bird's nest is a BIOTIC factor, not an ABIOTIC factor! 3. What is a biotic factor. Give 2 examples. Something that affects living things that is living itself or a product of a living organism. e.g. bird's nest, viral disease, predation, competition, humans, grizzly bears 4. What is a producer? Give an example. An organism that produces its own food (in the form of sugar) from sunlight and inorganic molecules through the process of photosynthesis. e.g. plants (all types) 5. What is a decomposer ? Give an example? Is an organism that breaks down dead or decaying organisms. e.g. worms, bacteria, fungi 6. What type of organism is in the: 1st trophic level = producer, e.g. plants 2nd trophic level = herbivore, e.g. rabbit 3rd trophic level = carnivore, e.g. fox 4th trophic level = top carnivore, e.g. wolf 7. A consumer is... An organism that eats another organism. e.g. rabbit, fox, wolf. 8. What is the primary source of energy for all living things? The Sun and the visible light that the Sun emits. 9. Show the differences & similarities between photosynthesis & respiration. You may use a Venn diagram to show this. Photosynthesis only: H2O + CO2 + visible light => C6H12O6 + O2 Captures energy from sunlight and stores it in glucose for LATER use by the organism Occurs only in light Occurs only in plants Occurs only in chloroplasts Common: Both involve H2O, CO2, C6H12O6 and O2. Both involve energy stored in glucose Photosynthesis is the reverse of cellular respiration Cellular respiration only: C6H12O6 + O2 => CO2 + H2O + release of energy Energy stored in glucose is used by organism to do things (e.g. human running). SNC1D Exam Review Occurs any time, day or night Occurs in plants, animals and fungi Occurs in mitochonria