yic_gravity - YES I Can! Science
advertisement

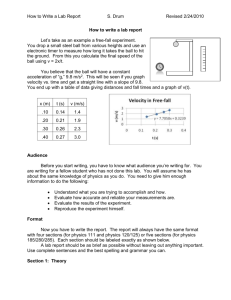
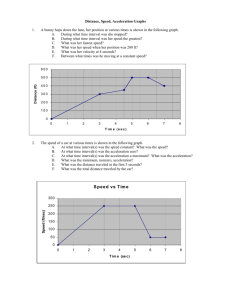
The Mass of the Earth Overview By using a small steel ball as a “test particle” in the Earth’s gravitational field, it is possible to determine the mass of the Earth. The main objective is to make accurate time and distance measurements of a free falling object, (the test particle), in the Earth’s gravitational field and to use this information to calculate the local acceleration, (of the test particle), near the Earth’s surface. Concept If we assume that Galileo was correct, that is, all objects will undergo the same acceleration when allowed to free-fall along identical (or adjacent) paths, then by dropping any small dense object over a moderate distance, we can calculate the acceleration experienced by any object placed in the same gravitational field. If we assume that the acceleration is constant over the distance that we allow our test particle to fall, (within the limits of our measurements), then simple mechanical arguments show that for a given acceleration g, the distance fallen s, during a time interval t, is given by the equation s=1/2at^2 Equipment If your equipment is not already unpacked you will need to open three boxes containing the PASCO equipment. Carefully open the packages and neatly save the packing material so that the equipment can be repacked for storage after you have completed your experiment. The equipment needed is: The ME-8930 Smart Timer with instruction sheets. The Free Fall Adapter with instruction sheets. The support stand. A clamp to attach the ball release mechanism to the support stand. -1- Set-up 1. Open the large box containing the support stand. Attach the leveling screws into the base, insert the aluminum pole, and level the stand on a flat stable surface. 2. Open the Smart Time box. Set up the timer in a location close to the support stand. Carefully open the box containing the 9V AC adapter and unwind the power cord. 3. Do not plug in the AC adapter yet. 4. Open the last box which contains the Free Fall Adapter. Set the steel balls aside for the moment. Attach the Free Fall Adapter near the top of the support stand as shown (using the support clamp). 5. Centre the receptor pad directly below the ball release mechanism. 6. Select one of the steel balls and insert into the ball release mechanism. -2- TIP: Place the ball between the spring, (with the drilled hole centred on the ball), and the brass contact, then holding the release mechanism as shown in the photo, depress the sliding rod until the ball is securely “trapped” in place. Using the small screw at the side, lock the sliding rod. Procedure Step 1 Connect the Free Fall Adapter to the Smart Timer. Step 2 Plug the 9v AC adapter into a 115v outlet and connect the 9v cord to the Smart Timer. -3- Step 3 Turn on the power switch. Note: The display may be hard to see when viewed from directly above the LCD window. It is best viewed at an angle of about 45 degrees. Step 4 If you have not already done so, install the steel ball securely in the Free Fall Adapter and align it so that it will drop onto centre of the receptor pad. Step 5 When you are ready to make your free fall measurement you will need to “arm” the Smart Timer. Press the RED (Select Measurement) button and select TIME. The display “scrolls”, so if you miss your configuration, just keep pressing the selection button until the word “Time” reappears in the display window. Step 6 Next press the BLUE (Select Gate) button and select STOPWATCH mode. The display “scrolls” so if you miss your configuration, just keep pressing the selection button the word “Stopwatch” reappears in the display window. -4- Step 7 Finally, “arm the Smart Timer by pressing the Start/Stop button once Step 8 Release the ball by carefully unscrewing the spring lock. Step 9 Step 10 Accurately measure the height that the ball has fallen (in metres). Record the descent time and the distance fallen (in seconds). (Use the chart provided). Step 11 Repeat the experiment. Set up the steel ball in the Free Fall Adapter. You may begin at Step 7 to repeat the experiment. Try different decent paths (heights). Try using balls of various sizes. -5- Analysis Make several independent determinations of the free-fall time. Record the distance fallen during each of the measured time intervals. (Use the accompanying chart in which to record your data). Trial Number Descent time (s) Height (m) 1 2 3 4 Mean value -6- Acceleration 2/t^2 (m/s/s) Mass of the Earth gr^2/G (kg) Curriculum Expectations apply Newton’s laws of motion to explain inertia, the relationship between force, mass, and acceleration, and the interaction of forces between two objects; identify and explain sources of error and uncertainty in measurement and express results in a form that acknowledges the degree of uncertainty; carry out procedures controlling the major variables and adapting or extending procedures where required; select and use appropriate numeric, symbolic, graphical, and linguistic modes of representation to communicate ideas, plans, and results; work cooperatively with team members to develop and carry out a plan, and troubleshoot problems as they arise. Assessment Rubric R significantly below the standard (below 50%) produces insufficient evidence to demonstrate learning demonstrates significant misconceptions requires additional learning activities and remediation Level 1 Level 2 approaches the standard Level 3 the standard (50-59%) (60-69%) (70-79%) Understanding of Basic Concepts demonstrates limited demonstrates some demonstrates general understanding of understanding of understanding of relationships relationships relationships between force, mass, between force, mass, between force, mass, and acceleration, and and acceleration, and and acceleration, and the interaction of the interaction of the interaction of forces between forces between forces between objects objects objects by providing partial explanations of the concepts involved in the free-fall experiment by providing partial explanations of the concepts involved in the free-fall experiment by providing complete explanations of the concepts involved in the free-fall experiment with significant with minor with no significant misconceptions / misconceptions / misconceptions / inaccuracies inaccuracies inaccuracies Application of Critical and Creative Thinking Skills and/or Processes produces insufficient applies appropriate applies appropriate applies appropriate evidence to skills/strategies of skills/strategies of skills/strategies of demonstrate learning scientific inquiry scientific inquiry scientific inquiry with limited with some with considerable requires additional effectiveness effectiveness effectiveness learning activities and remediation Communication of Required Knowledge produces insufficient communicates communicates with communicates with evidence to unclearly or some clarity and general clarity and demonstrate learning imprecisely precision precision rarely using sometimes using usually using requires additional appropriate scientific appropriate scientific appropriate scientific learning activities conventions conventions conventions and remediation -7- Level 4 exceeds the standard (80-100%) demonstrates thorough understanding of relationships between force, mass, and acceleration, and the interaction of forces between objects by providing complete explanations of the concepts involved in the free-fall experiment with no misconceptions / inaccuracies applies appropriate skills/strategies of scientific inquiry with a high degree of effectiveness communicates clearly and precisely always using appropriate scientific conventions