Mother board elements Computer hardware ICT S6
advertisement

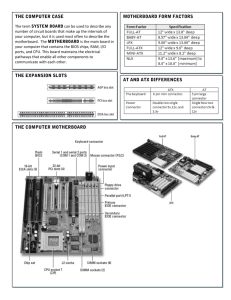
ICT S6 Lesson 3 of 8 Developed by Joseph SSERWANJA Computer hardware 2 x 50 minutes Computer lab Mother board elements Overview This lesson is about identification and role of the following elements: Chipset northern and southern, system bios, CPU, Jumpers, Switches, Connectors, IDE, SIMM, DIMM, Power supply connector and CPU socket (CPU slot). Specific objectives Identify motherboard elements Lesson objectives By the end of this lesson, the learner should be able to: List and explain the roles of the elements found on a specific motherboard. Summary of evaluation Objectives being Evidence Criteria evaluated By whom, when Recording and how and how is the evidence Learners will be evaluated. able to: Identify, name and Answers to a A mark is The teacher marks The marks are give the roles of class test awarded for the test. recorded for the different each correct motherboard answer. assessment. elements References Patrick Regan, IT ESSENTIALS PC HARDWARE AND SOFTWARE Labs and Study Guide, 3rd Edition, 2008 Last updated: 17 January 2011 Other websites PC Guide www.pcguide.com/ref/mbsys/mobo/comp.htm This website identifies the various components that you will find on your motherboard, and provides a brief description of each. Escotal www.escotal.com/motherboarddiagram.html The website provides a well labeled diagram of a computer motherboard. Wordiq www.wordiq.com/definition/CPU_socket The site gives a definition of CPU socket or slot. PC Architecture www.karbosguide.com/books/pcarchitecture/chapter04.htm This website talks about the functions of the different elements of the motherboard. PC Mag www.pcmag.com/encyclopedia_term/0,2542,t=SIMM&i=51369,00.asp This website gives the definitions of SIMM and DIMM memory modules. Key concepts Term / Definition / Concept Meaning BIOS chip(Basic Input/ Output System) Is a chip which stores the program that starts up your computer and communicates between the devices in your computer (such as your hard drive and graphics card) and the system. CPU socket (slot) Is the connector that interfaces between a computer's motherboard and the processor itself. SIMM (Single In-line Memory Module) An earlier printed circuit board that holds memory chips and plugs into a SIMM socket on the motherboard. DIMM (Dual In-Line Memory Module) A printed circuit board that holds memory chips and plugs into a DIMM socket on the motherboard. Connector Any plug and socket that links two devices together. IDE (Integrated Drive Electronics) Is a standard electronic interface used between a computer motherboard's data paths or bus and the computer's disk storage devices. Power supply connector To connect the power supply to the motherboard. Jumper Is a pair of prongs that are electrical contact points set into the computer motherboard. The jumper acts as a switch by closing (or opening) an electrical circuit. Last updated: 17 January 2011 Motherboard chipset A chipset consists of the chips and other components on the motherboard that allow different PC components, including the processor, to communicate with each other. The north bridge chipset The north bridge is a controller which controls the flow of data between the CPU and RAM, and to the AGP port. The south bridge chipset It looks after the transfer of data to and from the hard disk and all the other I/O devices, and passes this data into the link channel which connects to the north bridge. Motherboard Main printed circuit board that connects all the major components of a computer. CPU (Central Processing Unit) Brain of the computer where most calculations take place. Expansion Slots They allow the system to be expanded by the insertion of circuit boards, called expansion cards. Expansion slots consist of connectors and metal traces that carry signals from the expansion card to the rest of the computer, specifically the RAM and processor. Introduction The teacher shows the learners a motherboard. He asks them what it is and name the different components. Link to previous or other relevant topic This lesson links to the lesson about connectors. Activity 1: Identifying the different components of the motherboard 15 minutes Demonstrate the motherboard and the different components. If old motherboards are available, group the learners into small groups and give them old motherboards one group each to touch and look at while explaining the different components. In case the old motherboards are not available, the help the learners to open the CPU casing of the computer and observe the motherboard and its components. The whole computer is built up around a motherboard, and it is the most important component in the PC. It can be considered the nervous system of the computer. The Last updated: 17 January 2011 motherboard is a large printed circuit board, which has lots of chips, connectors and other electronics mounted on it. Inside the PC, data is constantly being exchanged between or via the various devices. Most of the data exchange takes place on the motherboard itself, where all the components are connected to each other. Motherboards are often described by their form factors (physical dimensions, sizes, and layout). Older motherboards are based on the Baby AT. Newer form factors include ATX, NXL, and BTX. Different from the Baby AT form factor, the ATX motherboards have the expansion slots parallel to the short side of the board, which allows more space for other components. When working with a PC, you must be able to identify the different parts of the motherboard, including the processor, expansion slots, drive connectors, and power connectors. You should also be able to look at the layout to determine its form factor. Motherboard Components Give an illustration of the motherboard components. The motherboard is a large printed circuit board, which has lots of chips, connectors and other electronics mounted on it. Last updated: 17 January 2011 Chips These are tiny electronic circuits which are crammed with transistors. The chips have various functions. For example, there are: ROM chips, which store the BIOS and other programs. The ROM BIOS chip contains a small collection of programs (software) which are permanently stored on the motherboard, and which are used, for example, when the PC starts up. CMOS storage, which contains user-defined data used by the setup program. Sockets (slots) These are holders, which have been soldered to the motherboard. The sockets are built to exactly match a card or a chip. For example, there are sockets (slots) to mount: The CPU and memory (SIMM and DIMM). Expansion cards, also called adapters (PCI, AGP and AMR slots, etc.). The idea of a socket is that you can install a component directly on the motherboard without needing special tools. The component has to be pushed carefully and firmly into the socket, and will then hopefully stay there. Here you can see three white PCI (expansion) sockets, in which plug-in cards can be installed. Last updated: 17 January 2011 Plugs, connectors and ports The motherboard also contains a number of inputs and outputs, to which various equipment can be connected. Most ports (also called I/O ports) can be seen where they end in a connector at the back of the PC. These are: Ports for the keyboard and mouse. Serial ports, the parallel port, and USB ports. Sockets for speakers/microphone etc. Often, the various connectors are soldered onto the motherboard, so that the external components, like the keyboard, mouse, printer, speakers, etc., can be connected directly to the motherboard as shown below: In addition, the motherboard contains a number of other contacts. These include: The power connector which supplies the motherboard with power from the power supply. The power supply is connected to the motherboard via a multicoloured cable and a large white plastic connector as shown: Last updated: 17 January 2011 Other connectors for the diskette drive, hard disk, CD-ROM drive, etc. Jumpers which are used on some motherboards to configure voltage and various operating speeds, etc. A number of pins used to connect the reset button, LED for hard disk activity, built-in speaker, etc. The tiny connectors and jumpers that are hidden on any motherboard. The chip set The two chips which make up the chipset are the South Bridge and North Bridge chips. They share the work of managing the flow of data on the motherboard. The north bridge is a controller which controls the flow of data between the CPU and RAM, and to the AGP port. Since a lot of data traffic runs through the north bridge, it is attached to a heat sink as shown below: Last updated: 17 January 2011 The south bridge looks after the transfer of data to and from the hard disk and all the other I/O devices, and passes this data into the link channel which connects to the north bridge. Activity 2: 20 minutes The learners answer the following multiple choice questions about motherboards. The answers are underlined. 1. Which one of the following is NOT found on a motherboard? a. RAM; b. CPU; c. HDD; d. BIOS. 2. Which company invented the ATX form factor? a. Compaq b. Intel c. IBM d. Toshiba Last updated: 17 January 2011 3. What is one of the differences between AT and ATX form factors? a. The processor slot and memory sockets are moved from the back right side of the board to the front. b. 'Soft Power' support was eliminated c. It did not allow 3.3V support anymore d. The expansion slots parallel to the short side of the board, which allows more space for other components. 4. Which of the following parts is not usually integrated into the motherboard? a. Hard drive b. Voltage Regulators c. CPU socket d. Flash BIOS ROM 5. Which of the following chipsets would not be found on a motherboard? a. SCL chipset b. The keyboard controller c. The system chipset d. The 'Super IO' chip 6. What does BIOS stand for? a. Basic Input Output System b. Biography c. Binary Input Output System d. Binary Integrated Operating System 7. What is the general use of the IDE plug in on the motherboard? a. Monitor b. Mouse c. Hard Drive d. Keyboard Last updated: 17 January 2011 8. Which hardware was originally attached to the motherboard? a. RAM b. Hard Drive c. Floppy Drive d. Graphics Card 9. Which of the below are motherboard types? a. TRY b. ATX c. XTY d. ABC 10. Power connectors receive electrical power from the ________ and distribute it to the CPU, chipset, main memory, and expansion cards. a. Motherboard b. Universal Serial Bus c. Power supply unit d. Hard disk drive 11. Additional peripherals such as _______ were provided as expansion cards. a. USB flash drive b. Mouse c. Serial port d. Universal Serial Bus 12. Most modern motherboard designs use a ________, stored in an ROM chip soldered to the motherboard, to boot the motherboard. a. BIOS b. Extensible Firmware Interface c. Operating system d. Macintosh Last updated: 17 January 2011 13. The Motherboard is also called? a. Board b. Component Board c. System Board d. Computer Board 14. The functionality of a motherboard chipset can be divided into two broad regions. What are the two regions of a motherboard chipset? a. Northbridge b. Memory c. Controller d. Southbridge For questions 15-20, answer whether true or false. 15. The function of jumper on the motherboard is to configure voltage. a. True b. False 16. South bridge controls the flow of data between the CPU and RAM, and to the AGP port. a. True b. False 17. The motherboard is the brain of the computer where most calculations take place. a. True b. False 18. The main function of the power supply connector is to connect the power supply unit to the motherboard. a. True b. False Last updated: 17 January 2011 19. IDE in full is International Drive Electronics. a. True b. False 20. The various connectors are soldered onto the motherboard, so that the external components, like the keyboard and speakers can be connected directly to the motherboard. a. True b. False Homework Activity Read more about the North Bridge and South Bridge chipset components of the motherboard and why they are called Bridges. References Text books (Patrick Regan, IT ESSENTIALS PC HARDWARE AND SOFTWARE Labs and Study Guide, 3rd Edition, 2008) Last updated: 17 January 2011