Create a Food Web - Marine Conservation Society
advertisement

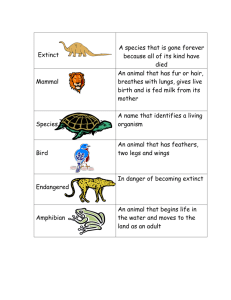
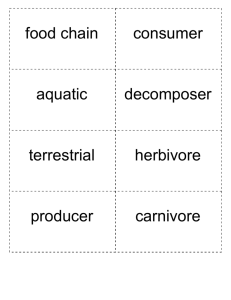
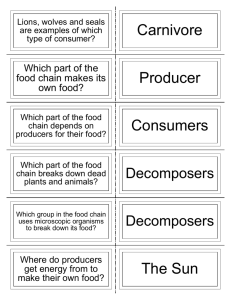
Create a Food Web 1 Background d All plants and animals nee to live. energy from their food e Plants (producers) produc sun. e their own energy from th by Animals get their energy ey Th . eating other organisms chain are consumers. A food rgy, or who eats who. ene of shows this transfer rts with the sun, as the A food chain always sta t producers. Consumers ea source of energy for the o have few e top are predators wh the producers and at th many food an ecosystem, there are natural threats. Within s the e a food web, which show at cre to ed ink erl int ins cha particular ce between species in a interconnections and relian m ecosystem to recover fro habitat. The ability of an . ed erv ns co vital and must be threats, its resilience, is 6 Reflect Subject/Topic: 2 Set the Sc ene Write the following on the board: sun, grass, cow, human. Ask child ren to explain the connection. Add this wi th arrows to show who eats who. Introd uce/revise the terms producer and consum er. Ask children to identify examples of each in the given food chain. 5 Extend b Elements Children to use Food We of the food sheet to draw a diagram web created. cause the being removed. Consider what could Discuss the impact of the shellfish hing, damage a particular species (pollution, overfis of s ber num in n ctio redu or on ncti exti problems. think of ways we can prevent these to habitats) In pairs, ask children to food web s) as one approach to protecting the Introduce Marine Protected Areas (MPA uss the MPAs visit www.mcsuk.org/mpa Disc in certain areas. For information on nct?’, pen if one of the animals became exti following questions: ‘What would hap als?’ ‘What can we do to ‘How would this impact the other anim to identify actions we can all reduce this risk?’ Encourage children take to make a difference. A project made possible by Food chains and webs, biodiversity, UK marine life Suitable for: Older years 3 Resources ments Worksheet: Food Web Ele 4 Investigate Move to an open spac e - a school hall or classroom with table s moved is ideal. Ask children what they th ink a food web is (a connection of food ch ains) Display the Food Web Elements sheet on the whiteboard. Identify any unknown animals. Allocate each child an element of th e food web. These sh ould be printed and attach ed with tape to each child. Draw attention to th e smaller text showing where the organism gets its energy. Remind children this is really important for the ga me. Start with the ‘sun’ st anding at the front. As k who gets their energy from the sun (plankt on and seaweed) Connec t these to the sun us ing string. Now ask who gets their energy fro m seaweed, link with st ring. Ask who gets en er gy from plankton and lin k. Continue until all ch ild ren are linked together us ing string, then remo ve ‘Shellfish from the we b. Children to identify impacts (animals feed ing on shellfish would have less food, possibly im pacting their number s. Creatures that shell fish feed on would be come more popular. Each ele ment affects the othe rs. They are all reliant on one another. seaweed sun Provides all energy. n. Eats plankto worms Eats plankton. Eats porpoises, dolphins, cod, seal and otter. Orca d shellfish. Eats fish an cod Eats sand eels. herring Eats fish. seal Eats fish. dolphin Eats sand eels. puffin sand eel Gets energy from the sun. Food Web Elements ark basking sh n. Eats plankto plankton Gets energy from the sun . haddock . and shellfish Eats worms porpoise Eats fish and octopus. otter s., sea urchin Eats octopu and crab. Food Web Elements (continued) edible crab Eats shellfish. shellfish n. Eats plankto starfish Eats shellfish. whelk . Eats shellfish eider duck Eats shellfish. jellyfish flatfish Eats shellfish. turtle sea eagle Eats fish. gull s, fish and Eats octopu seaweed. human Eat plankton. Eats jellyfish. Eats seaweed. sea urchin Eats shellfish. hermit crab birds. Eats fish and octopus Eats crab and shellfish. tuna Eats fish.