Cells Organisms can either be unicellular or multicellular. All cells
advertisement

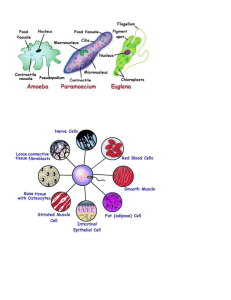
Cells Organisms can either be unicellular or multicellular. All cells work in specific ways and have different functions. Some animals or plants have few cells while others have trillions. Cells: All living things have cells. A cell is the smallest unit of life, anything below that is nonliving. A cell has a membrane around it that separates its interior from the environment. Unicellular: A unicellular organism is the one that has only one cell and grows as the cell grows. They are always going to be microscopic or extremely small. One example is bacteria. Multicellular: A multicellular organism is the one that has more than one cell. It can either be big or small in size and it increase size as more cells are created. In these organisms cells are grouped and each group has a different function. An example is humans. This is an animal cell. This is a unicellular organism. This is a multicellular organism. Sense and Respond to Change All living things feel the change in the environment or inside their body and react to it. These can be internal or external. An internal is when you feel hungry, you eat. The external is when the environment is cold, you try to get hot to stay the same. Stimulus: A change that causes and organism to react. Stimuli can either be internal or external. Homeostasis: This is when your body tries to maintain the same when something in the environment changes. It is the organism’s ability to maintain the same internal conditions. This hamster is hungry so he is eating to keep the same. He sensed the change inside his body and responded to it by eating. Reproduce As the organisms grow and develop they should be able to reproduce. Organisms can reproduce in different ways. Some need a mate, others divide, and others have special cells. Organisms need to reproduce so that they can exist. Organisms reproduce by either sexual or asexual reproduction. Asexual: A reproduction that does not involve the union of two sex cells. One parent has an offspring without a partner. This baby is exactly the same as his parent. Most unicellular organisms are reproduced this way. For example, sea anemones reproduce asexually. Sexual: A reproduction in which two sex cells meet. This reproduction is where a mate is needed. The baby will have characteristics of both parents. For example, humans reproduce sexually. This is an asexual reproduction. First, the baby is formed in the parent. Then, it grows. Third, it starts to separate from the parent. Last, it totally separates and is a new organism. In this picture the sex cells of these two bugs are meeting so that they can have a baby. This is a sexual reproduction. DNA DNA stands for deoxyribonucleic acid. DNA determines many characteristics in the living thing. They provide instructions for creating molecules called proteins. DNA: DNA is genetic information that is passed from parents to offspring. DNA is found in cells. This is an example of DNA. This is another example of DNA that shows you a pattern of DNA. Energy Use The cells of organisms use energy to do things that living things must do; such as repair injured parts and grow. Many living things eat energy (food) and plants go through a process called photosynthesis. Everything you do requires energy. For most organisms energy comes from the sun directly or indirectly. For example, running requires energy. Metabolism: The sum of all the chemical activities that an organism performs. When your body metabolizes food it separates it, sometimes rearranges it and sends it to different parts of the body. This baby is eating so that he gets Growth and Development energy and grows up. Then he becomes like this and eats more to get more energy and grow more. All living things grow and develop during their life. Unicellular organisms develop as the cell increases size, while the multicellular gets bigger as more cells are produced. Living things don’t just change in size, they also change in their appearance and internally. Growth: The process of becoming larger. For example, babies become taller. Development: The process of change that occurs during an organism’s life to produce a more complex one. For example, a seed becomes a tree. In here it shows the development of a tadpole to a frog. It comes from an egg, becomes a tadpole, and slowly becomes a frog. This panda will grow to be the size of the other panda beside it. Water Almost all the body of all living things is made up of water. About 70% of each cell is made up of water. Water is needed for almost all the chemical reactions involved in metabolism. Humans can’t live more than three days without water. Some animals such as the desert-dwelling kangaroo rat don’t drink water. They get all their water from the food they eats. These people are drinking water and showing that everyone and every living thing needs water. This picture shows that the human body is mostly made of water. Air All living things need air to live. Most living things need oxygen to go through the process in which energy is taken from the food. Living things that need oxygen to live are called aerobic. The ones that don’t need oxygen to live are called anaerobic. This an anaerobic organism Underwater volcano animals are anaerobic because they live of what comes out from the volcano and don’t have access to oxygen.. Both of these living things are aerobic. This is a picture of air. A Place to Live All living things need a place to live. This place must have all the things the living thing needs to survive. Large animals like elephants need a large space to live, while bacteria need a small place to live. Living things fight for food and territory. Plants fight for water and sunlight and animals don’t allow other animals to get close to their territory. All these pictures show living things in their habitats. These are their homes, their places to live and where they should always be. This will allow them to survive because they will have all they need to live in this place. These animals all have a place to live so that they can survive. Food All living things need food because it gives organisms energy and the raw materials that it needs to carry out life processes. Producers are living things that create their own food. One example is plants. Consumers are the living things that get food from other living this. An example is a salamander. Decomposers are consumers that get their food by breaking down the nutrients of dead living things or organisms. An example is a mushroom. This bear gets its food from other living things, like fish. This is why it is a consumer. It eats food. Mushrooms are decomposers. They also eat. This tree gets its food from the sun. It produces it. (Producer) It eats food. Proteins Carbohydrates Lipids Nucleic Acids ATP Are the most abundant in the body and cells after water. It is a molecule made up of amino acids and that is needed to build and repair body structures and to regulate processes in the body. Some examples are meat and muscle. Is a class of molecule that includes sugars, starches, and fiber. Cells use it as a kind of energy and energy storage. When an organism needs energy the cell breaks to release it. There are simple and complex carbohydrates. An example of simple carbohydrate is a fruit. Some examples of carbohydrates are bread, rice, pasta, potatoes, and fruit. A fat molecule that cannot mix with water. Lipids have many important functions in cells. Some form membranes and others store energy. Some examples are oils, fat, and butter. Have all the information required for cells to make proteins. They are compounds formed of subunits called nucleotides. A nucleic acid can have thousands of nucleotides. DNA is a nucleic acid. Stands for adenosine triphosphate. It is a molecule that acts as the main energy source for cell processes. Everything that we eat is ATP because it gives us energy.