Opportunity Cost and Production Possibilities
advertisement

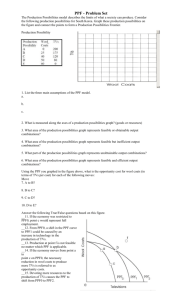
Opportunity Cost and Production Possibilities Production possibilities curve: a curve showing the different combinations of goods and services that can be produced in a fully employed economy, assuming the available supplies of resources and technology are fixed. Law of increasing opportunity costs: a principle stating that as the production of a good increases, the opportunity cost of producing an additional unit rises. If the economy represented by PPC1 produces 12 units of Good B and 0 units of Good A, what is true for the following examples? 1) The opportunity cost of increasing production of Good A from 0 units to 1 unit is the loss of ________ unit(s) of Good B. 2) The opportunity cost of increasing production of Good A from 1 unit to 2 units is the loss of ________ unit(s) of Good B. 3) The opportunity cost of increasing production of Good A from 2 units to 3 units is the loss of ________ unit(s) of Good B. This illustrates CONSTANT opportunity cost per unit for Good A. If the economy represented by PPC2 produces 12 units of Good B and 0 units of Good A, what is true for the following examples? 1) The opportunity cost of increasing production of Good A from 0 units to 1 unit is the loss of ________ unit(s) of Good B. 2) The opportunity cost of increasing production of Good A from 1 unit to 2 units is the loss of ________ unit(s) of Good B. 3) The opportunity cost of increasing production of Good A from 2 units to 3 units is the loss of ________ unit(s) of Good B. This illustrates INCREASING opportunity cost per unit for Good A. Analyzing Tradeoffs In the Production Possibilities Curve above, curve BB' is a country's original production possibilities curve. Assuming that, answer the following: 1) If there is a technological breakthrough in the consumer-goods industry and the new technology is widely adopted, which line would represent the new production possibilities curve? ________ 2) If a new governmental regime comes into power and forbids the use of automated machinery in all industries, which line would represent the new production possibilities curve? ________ 3) If new oil and coal sources were discovered within the nation's natural reserves, sparking massive technological innovation across industries, which line would represent the production possibilities curve? ________ 4) If BB' represents the country's production possibilities curve, what is true about point X? 5) If BB' represents the country's production possibilities curve, what is true about point Y? Analyzing More Tradeoffs Use the Production Possibilities Curve above to answer the following: 1) What societal change could cause the production possibilities curve to shift from XX' to YY'? 2) Under what kinds of conditions might the economy be operating at point Z? 3) Why might a government implement a policy to move the economy from point B to point A? 4) Why might a government implement a policy to move the economy from point A to point B?