Ohm's Law :- Ohm's law states that the voltages ( V ) across a

Dr. Sameir Abd Alkhalik Aziez
University of Technology (Lecture (2))
Ohm's Law :- Ohm's law states that the voltages ( V ) across a resistor ( R ) is directly proportional to the current ( I ) flowing through the resistor .
Slop =
I
1
V R
V
I
= constant = R
R
V
I
Ω ; V = I . R ; I
V
R
The resistance of short circuit element is approaching to zero.
The resistance of open circuit is approaching to infinity.
O.C.
R
G
1
R
0
Hence G
1
R
I
V
Siemens ( S ) or mhos ( ) .
R
0
S.C.
G
1
R
-
١٢
-
Dr. Sameir Abd Alkhalik Aziez
University of Technology (Lecture (2))
Electrical Energy ( W ) :-
P
W t
W
.
I
P .
t
.
t
I
2
.
R
.
t
V
R
2
.
t
W
P .
t KWh
Energy in KWh ( W ) =
Power
time
1000
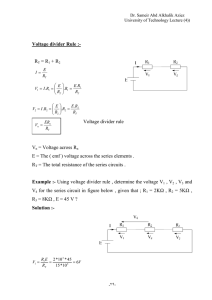
Example : For the following circuit diagram , calculate the conductance and the power ?
Solution :
I
V
R
30
5
10
3
6 mA
1 1
G
0 .
2 m
R 5
10
3
P or
P
I .
V
I
2
.
R
6
10
3
30
180 mW
6
10
3
5
10
3
180 mW or P
V
2
.
G
2
0 .
2
10
3
180 mW or P
V
2
R
0 .
2
2
10
3
180 mW
-
١٣
-
Dr. Sameir Abd Alkhalik Aziez
University of Technology (Lecture (2))
Efficiency ( η ) : -
W i/p
= W o/p
+ W loss
W i / p t
W o / p t
W loss t
P i/p
= P o/p
+ P loss
Efficiency ( η ) = Output power
100 %
Input power
P o
100 %
P i
W o
W i
100 %
T
1
2
3
......
n
Example: A 2 hp motor operates at an efficiency of 75 %, what is the power input in Watt, if the input current is (9.05) A, calculate also the input voltage?
Solution:
1 hours power (hp) = 746 Watt
-
١٤
-
Dr. Sameir Abd Alkhalik Aziez
University of Technology (Lecture (2))
P o
100 %
P i
0 .
75
2
746
P i
P i
1492
0 .
75
1989 .
33 W
P
E .
I
E
P
I
1989 .
33
9 .
05
219 .
82
220 V
Example: What is the energy in KWh of using the following loads:a) 1200 W toaster for 30 min.
b) Six 50 W bulbs for 4 h.
c) 400 W washing machines for 45 min.
d) 4800 W electric clothes dryer for 20 min.
Solution :
P
W
1000
W
1200
30
60
6
50
4
400
45
60
1000
4800
20
60
600
1200
300
1600
1000
3700
1000
3 .
7 KWh
D.C. Sources:-
The d.c. sources can be classified to:-
1- Batteries .
Voltage
Amper - hours
2- generators .
3- Photo cells .
4- Rectifiers .
-
١٥
-
Dr. Sameir Abd Alkhalik Aziez
University of Technology (Lecture (2))
V = E = constant voltage element
I = I o
= constant current element
.
ﺔﺗﺑﺎﺛ نوﻛﺗ ﺔﯾﺗﻟوﻔﻟا نﻛﻟ و ﺔﯾﺗﻟوﻓ و رﺎﯾﺗ دﻟوﯾ ﺔﯾﺗﻟوﻔﻟا ردﺻﻣ
.
تﺑﺎﺛ نوﻛﯾ رﺎﯾﺗﻟا نﻛﻟ و ﺔﯾﺗﻟوﻓ و رﺎﯾﺗ دﻟوﯾ رﺎﯾﺗﻟا ردﺻﻣ
Series Circuit :-
V
1
= I.R
1
V
2
= I.R
2
-
١٦
-
Dr. Sameir Abd Alkhalik Aziez
University of Technology (Lecture (2))
V
3
= I.R
3
E
–
V
1
–
V
2
–
V
3
= 0 E = V
1
+ V
2
+ V
3
E = I.R
1
+ I.R
2
+ I.R
3
E = I.[R
1
+ R
2
+ R
3
] = I.R
T
The current in the series circuit is the same through each series element &
R
T
= R
1
+ R
2
+ R
3
+ -------- + R
N
I
E
R
T
V
1
R
1
V
2
R
2
V
3
R
3
P t
= P
1
+ P
2
+ P
3
= E.I
Voltage Source in Series:-
-
١٧
-
Dr. Sameir Abd Alkhalik Aziez
University of Technology (Lecture (2))
Example: Find the current for the following circuit diagram?
2Ω
7V
10V 3Ω
6V
3V
Solution:
E
T
= 10 + 7 + 6
–
3 = 20 V
R
T
= 2 + 3 = 5
Ω
I
I
T
E
R
T
T
20
5
4 A
Kirchoff's voltage law ( K.V.L. ):-
The algebraic sum of all voltages around any closed path is zero.
m m
1
V m
0
Where m is the number of voltages in the path ( loop ) , and V m is the m th voltage .
-
١٨
-
Dr. Sameir Abd Alkhalik Aziez
University of Technology (Lecture (2))
E
–
V = 0
E = V
I
V
R
E
R
E
–
V
1
–
V
2
= 0
E = V
1
+ V
2
I
E
R
T
V
1
V
2
R
T
; R
T
= R
1
+ R
2
Example: Use K.V.L. to find the current in the following circuit diagram?
I R
1
V
1
E
1
E
2
V
2
R
2
Solution: From K.V.L.
V
0
E
1
–
V
1
–
E
2
–
V
2
= 0
E
1
–
E
2
= V
1
+ V
2
E
1
–
E
2
= IR
1
+ IR
2
E
1
–
E
2
= I ( R
1
+ R
2
)
I
E
1
R
1
E
2
R
2
-
١٩
-
Dr. Sameir Abd Alkhalik Aziez
University of Technology (Lecture (2))
Example: For the following circuit diagram, Find I using:a) Ohm's law.
b) K.V.L.
Solution: a ) By applying ohm's law :-
I
E
R
T
20
10
40
7
10
6
10
17
40
40
1 A b ) By applying K.V.L. :-
10 + 6I + 7I - 40 + 10I
–
20 + 10 + 17I = 0
10
–
40
–
20 + 10 + I ( 6 + 7 + 10 + 17 ) = 0
-40 = -I ( 40 )
I
40
40
1 A
-
٢٠
-