PSYC 182 Illusions
advertisement
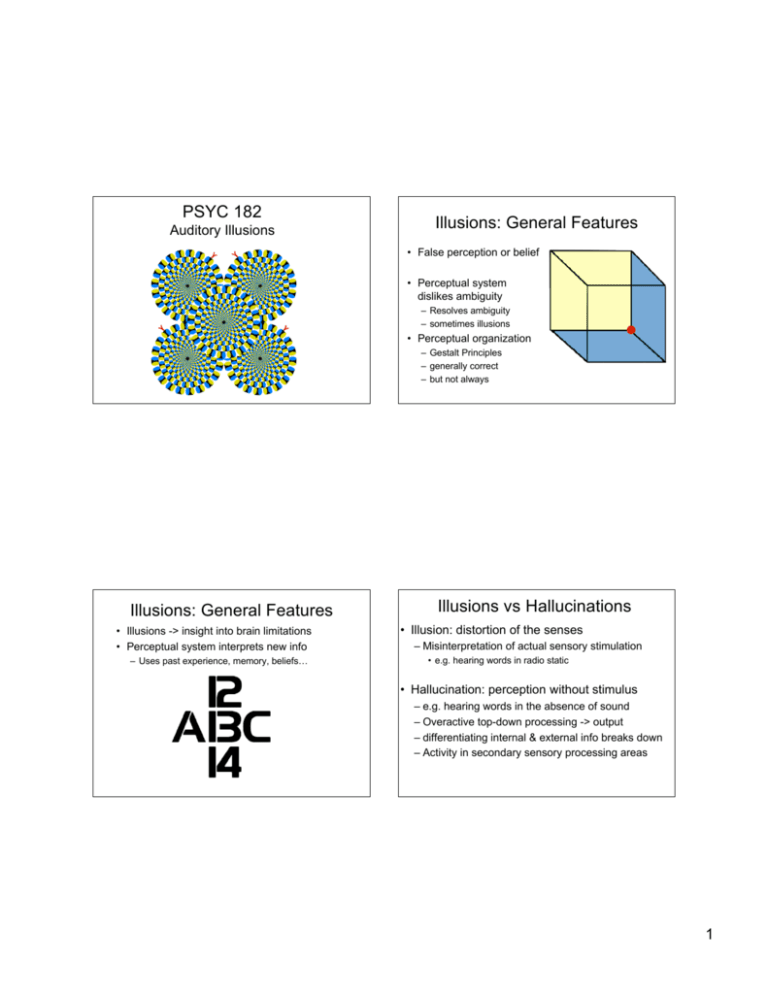
PSYC 182 Auditory Illusions Illusions: General Features • False perception or belief • Perceptual system dislikes ambiguity – Resolves ambiguity – sometimes illusions • Perceptual organization – Gestalt Principles – generally correct – but not always Illusions: General Features • Illusions -> insight into brain limitations • Perceptual system interprets new info – Uses past experience, memory, beliefs… Illusions vs Hallucinations • Illusion: distortion of the senses – Misinterpretation of actual sensory stimulation • e.g. hearing words in radio static • Hallucination: perception without stimulus – e.g. hearing words in the absence of sound – Overactive top-down processing -> output – differentiating internal & external info breaks down – Activity in secondary sensory processing areas 1 Grouping Mechanisms • Gestalt Concepts – Proximity Picket fence effect • Gliding tone ‘continues’ through noise bursts – Similarity – Continuity – Common fate – Familiarity Continuity • Continuity in noise burst Applied streaming segregation • Two interleaved melodies blend into one. 2 Grouping demo: proximity • Slow: 1 melody • Fast: 2 melodies • Grouped by proximity Scale illusion • Spatial reorganization • Proximity & Continuity • Handedness Scale illusion • Musical Implications: • Orchestral seating – High stage-right, low-left • Rules of voice leading – Too many leaps – Avoid crossover • Tchaikovsky’s 6th Symphony – Melody split up – between 1st, 2nd violins 3 Chromatic illusion Cambiata Illusion Glissando Illusion Octave Illusion • Oboe tone alternating with sine wave glissando • Different percepts – Typically, oboe alternates – Glissando: low-left to high-right • High pitch->location • Dominant ear-> pitch • Implications: – – – – Handedness What vs. Where Binding problem Echo suppression? 4 Phantom Words • Ambiguous • Percepts include: SPECTRAL (FOURIER) ANALYSIS – what’s on one’s mind – other languages – Knowledge about the word Harmonic Fusing and Common Fate Brain combines frequency components into one pitch -Gestalt law of common fate -Harmonics begin, shift, and end at the same time - Calculated based on common denominator of partials Harmonic Fusing and Common Fate Missing fundamental a.k.a. Virtual Pitch -Fundamental frequency (f0) = perceived pitch -even if fundamental is missing! e.g. 100 Hz, 200 Hz, 300 Hz, 400 Hz, 500 Hz = 100 Hz 200 Hz, 300 Hz, 400 Hz, 500 Hz = 100 Hz! 5 Pitch – Perceptual Phenomena Proximity: Shepard tones • Octave-related complexes • Follow by proximity – pitch class circle – smaller intervals Octave equivalence – a note doubled in frequency sounds similar to the original • cross-cultural (cross-species?) • perceptual quality is “chroma” • pitch = “chroma” + “height” “SHEPARD’S ILLUSION” 6