Imperialism Militarism
advertisement
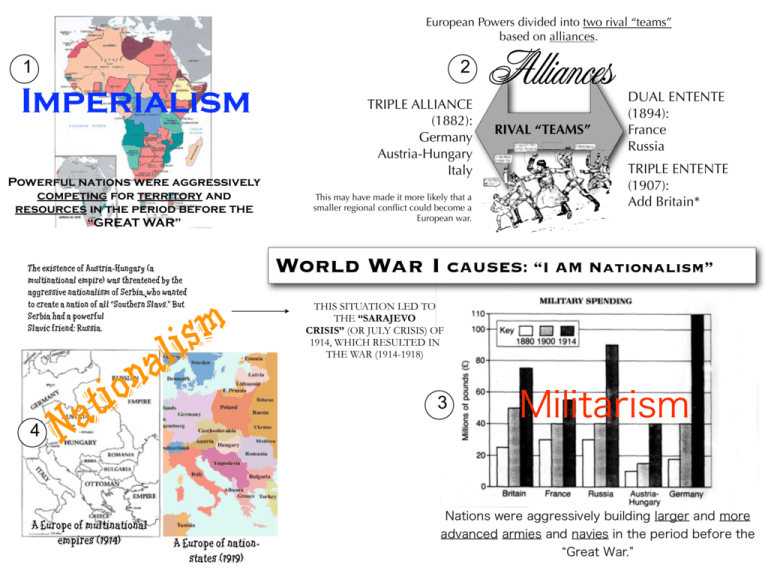
European Powers divided into two rival “teams” based on alliances. 1 2 Imperialism Powerful nations were aggressively competing for territory and resources in the period before THE “GREAT WAR” The existence of Austria-Hungary (a multinational empire) was threatened by the aggressive nationalism of Serbia, who wanted to create a nation of all “Southern Slavs.” But Serbia had a powerful Slavic friend: Russia. l a n o 4 i t a N A Europe of multinational empires (1914) m is A Europe of nationstates (1919) TRIPLE ALLIANCE (1882): Germany Austria-Hungary Italy This may have made it more likely that a smaller regional conflict could become a European war. Alliances RIVAL “TEAMS” DUAL ENTENTE (1894): France Russia TRIPLE ENTENTE (1907): Add Britain* World War I CAUSES: “I AM Nationalism” THIS SITUATION LED TO THE “SARAJEVO CRISIS” (OR JULY CRISIS) OF 1914, WHICH RESULTED IN THE WAR (1914-1918) 3 Militarism Nations were aggressively building larger and more advanced armies and navies in the period before the Great War. IMPERIALISM Desire for empire caused increased competition KEY IMPERIAL RIVALRIES: Britain vs. France in Africa Britain vs. Russia in Asia France vs. Italy in Africa * * * Increased competition over territory caused increased tensions SUEZ CRISIS (1882) & FASHODA CRISIS (1898) - Britain and France nearly went to war TWO MOROCCAN CRISES (1905, 1911) - France vs. Germany Militarism Belief that a military is a crucial factor in a nation’s strength and, therefore, support for bigger, more advanced militaries (even in peacetime). Glorification of war (often in official propaganda). Infrastructure (railways, stations, roads, warehouses) is built to aid the movement of armies. Tangled Alliances Triple Alliance 1882; BINDING ALLIANCE IF DEFENSIVE TERMS MET Austria-Hungary 1870s-1880s: Germany (under Chancellor Bismarck) created defensive alliances to isolate France from other nations (which worked) Triple Entente N G D IN IN D G IN -B AL N LI AN CE Russia O N 1900s: Britain makes friendship agreements, but not alliances, with France & Russia to counter Germany Italy BI 1890s: Germany (under Emperor Wilhelm II), in pursuit of Britain, cut Russia loose; FrancoRussian alliance resulted (rival alliances now exist) Germany France NON-BINDING Britain Tangled Alliances The alliance system meant that a local conflict could become a much larger regional or world conflict. Nationalism Belief in the great worth, even superiority, of a nation by its people. Belief that a nation should be ruled by its own people and not a foreign nation or empire. Desire to demonstrate a nation’s greatness to the world. “THE STRONG ARMS OF CANADA”: National pride was often displayed in propaganda posters using symbolic “ideal” images. The Balkan Nationalism Threat (1912-1914) Serbia THE BALKAN LEAGUE (1912; flags at right) was formed by new Balkan states determined to drive the Ottoman Turks from the region forever. THE BALKAN WARS (1912-13) led to the enlargement of Serbia, Greece and Rumania, at the expense of the Turks. SERBIAN AMBITION threatened the multinational Austro-Hungarian empire, whose leaders wanted a war to put Serbia in its place in 1914. Bulgaria Greece Montenegro AustriaHungary Ottoman Empire The Balkans Serbia = Slavic Russia = Slavic Russia protects Serbia (Panslavism) Austria-Hungary has a Slavic minority – they do not want to be a part of AustriaHungary Serbian nationalists wanted to create a new nation (Yugoslavia) with all Slavic peoples of the Balkans living under one government Bosnia-Herzegovina = Slavic Austria-Hungary annexed BosniaHerzegovina, creating the Bosnian Crisis (1908-09) = The oft-stated “Powder Keg of Europe” 2 AUSTRIA- HUNGARY “Black Hand” RESPONDS 1 Assassinates Archduke Franz Ferdinand on June 28, 1914 (Franz Ferdinand was going to be the next Emperor of Austria-Hungary) 3 1. Blames Serbian government. 2. Seeks (and receives) promise of backup support from ally Germany. 3. Issues an ultimatum to Serbia. 4. Declares war July 28 when Serbia rejects 1 of 10 conditions. Russia MOBILIZES ON AUSTRIAN & GERMAN BORDERS It is preparing to defend Serbia. It has not declared war, but German generals believed Mobilization IS war. B.A.R.G.E: five “july crisis” steps to war 5 d n a l g s n E ter n r E Wa e th The British Expeditionary Force (BEF) landed in Belgium in late August 1914. ENGLAND (Britain) DECIDED TO PROTECT BELGIUM AND FRANCE (and look out for its interests in Europe). IT DECLARED WAR ON AUGUST 4, 1914. 4 Germany 1. Ultimatum to Russia to cease mobilization. 2. Asks Belgium for passage of troops to France German Emperor Kaiser Wilhelm II attempted to convince his cousin, Russian Tsar Nicholas II, to stop mobilization, but failed. Instead, the cousins went to war. 3. When Belgium refuses, they launch the SCHLIEFFEN PLAN invasion of Belgium and France.











