Lecture 6
advertisement

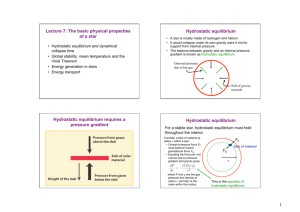
Lecture 5: As Long as the Sun Shines Temperature of the Sun Spectrum of the Sun Sunspots Sodium Hydrogen Magnesium Chromosphere In astronomy, we often see gas glowing in red because of H emission lines. This happens when the gas is ionized. As the electrons jump down to lower energy levels, emission lines are created. Why do stars shine? Corona Stars shine because they are hot. • Emit light with a roughly thermal (blackbody) spectrum • Internal heat “leaks” out of their surfaces. Luminosity = rate of energy loss (energy /second) To stay hot, stars must make up for the lost energy, otherwise they would cool and eventually fade out. Case Study: The Sun Sources of Energy Question: In the 19th Century, two energy sources were known: Chemical Energy How long can the Sun shine? Need two numbers: How much internal energy there is in the Sun. How fast this energy is lost (Luminosity). • Burning of oil or wood by oxidation • Chemical Explosives Gravitational Energy: Internal Energy Lifetime Luminosity The Age Crisis: Part I The most powerful chemical reactions could work for only a few thousand years. But, • Geologists estimated that the Earth was at least a few Million years old. Logical Inconsistency: How can the Earth be older than the Sun? • Water running downhill to power a mill Laws of Stellar Structure I: The Gas Law Most stars obey the Perfect Gas Law: Pressure = Density x Temperature x constant In words: Compressing a gas results in higher P & T Expanding a gas results in lower P & T Laws of Stellar Structure II: The Law of Gravity Stars are very massive & bound together by their Self-Gravity. Gravitational binding changes as 1/R2 R= radius of the star In words: Compress a star, more gravitational binding. Expand a star, less gravitational binding. Hydrostatic Equilibrium Gravity Hydrostatic Equilibrium • Gravity wants to make a star contract. • Pressure wants to make a star expand. Counteract each other: • Gravity confines the gas against Pressure. • Pressure supports the star against Gravity. Gas Pressure Exact Balance = Hydrostatic Equilibrium The star neither expands nor contracts. Core-Envelope Structure Hot, Compact Core Cooler, Extended Envelope Core-Envelope Structure Outer layers press down on the inner layers. The deeper you go into a star, the greater the pressure. The Gas Law says: Greater pressure = hotter, denser gas Consequences: • hot, dense, compact CORE • cooler, lower density, extended ENVELOPE The Essential Tension Core-Envelop Structure Example: The Sun Core: Radius = 0.25 Rsun T = 15 Million K Density = 150 g/cc Envelope: Radius = Rsun = 700,000 km T = 5800 K Density = 10-7 g/cc Gravity & Pressure in Equilibrium The Life of a star is a constant tug-of-war between Gravity & Pressure. G P Tip the internal balance either way, and it will change the star’s outward appearance. Luminosity radiates away heat & Pressure Drops G P Balance tips in favor of gravity, Sun shrinks. G P Contraction makes core heat up, increasing the internal Pressure. G P Balance restored, but with higher gravity, pressure & temperature than before... G P Starts the cycle all over again... Kelvin-Helmholtz Mechanism The Age Crisis: Part II Luminosity radiates away internal heat Late 1800s: • This causes the Sun to cool a little, lowering its internal pressure. • Lower Pressure means Gravity gets the upper hand and the Sun contracts a little. • Gravitational Contraction compresses the Sun, increasing its internal heat & raising the Pressure • The Sun, slightly smaller, starts the cycle again. The Sun can shine by tapping gravitational energy for ~30 Million years. Q. When the principle of hydrostatic equilibrium is applied to the Sun, it implies: A) The center of the Sun is extremely hot B) The surface temperature of the Sun is ~6000K C) The Sun should collapse in a matter of thousands of years D) The lifetime of the Sun is 10 billion years • Geologists estimated that the Earth is at least 300 Million years old. • Kelvin estimated the Sun could shine for only about 30 Million years. Kelvin Says: The Geologists are wrong. Nature Says: Kelvin is wrong... There is new physics.