Backtrack 5 Tutorial
advertisement

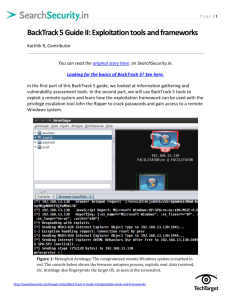
Collaborative Virtual Computer Lab (CVCLAB) Penn State Berks Using Backtrack 5 in CVCLAB Before you start using Backtrack 5 in CVCLAB, please review the following important information: ● The Backtrack distribution available in CVCLAB boots from a virtual machine image and you are sharing computing resources with other students. Please “poweroff” the virtual computers when you are done. ● The IP address of your Backtrack virtual machines (VM) is automatically assigned by a DHCP server. ● Most Backtrack commands and tools are run in the command­line prompt. You must become familiar with using the command­line prompt. ● The default user is “root”, and the default root password is “toor”. A. Login to the CVCLAB 1. First, enter your username and password. The IP Address / Name field should be set to 146.186.225.170 or istvc.bk.psu.edu. In some computers, the DNS name does not work, so please use IP address 146.186.225.170 in such a case. 2. If you are prompted by a security warning, press Ignore. "You can check the Install this 1 of 7 Collaborative Virtual Computer Lab (CVCLAB) Penn State Berks certificate and do not …" box, not to display this message. 3. Once you have logged in, you will be greeted by the vSphere Client interface. Click Hosts and Clusters. This screen may not appear if the VMWare client on your system has been used before. If you do not see the screen below go to the next step. 4. Select the Virtual Machines tab. 2 of 7 Collaborative Virtual Computer Lab (CVCLAB) Penn State Berks 5. In this tab you can see all of the virtual computers that you have access to. To start using a virtual machine, first select it by clicking on the name of it, then click the Launch Virtual Machine Console icon on the toolbar. Your virtual machine may already have been turned on by your instructor. 3 of 7 Collaborative Virtual Computer Lab (CVCLAB) Penn State Berks B. Booting Up BackTrack When booting up the BackTrack virtual computer, there are a few steps you must follow prior to beginning this exercise. To begin, follow the steps below: 1. Click on the Power On button to start the Backtrack virtual machine. From the View menu, you can select various screen sizes. Crtl­Alt is used to escape from the Full Screen mode. Note:Your computer will automatically start and login as root. However, if you are prompted for a login, complete the steps 2 and 3. Otherwise, continue with activity B in the next page. 2. When the virtual machine is ready, use “root” as the login and “toor” as the password. The password will not be appearing as you type. Press Enter to log in. 3. Next, you will have the option to start BackTrack on either a GUI display or continue using BackTrack from the command prompt. To start the GUI environment type startx in the command prompt, then press Enter. 4. When you finish your activity, please type “poweroff” to shutdown the Backtrack virtual machine. 4 of 7 Collaborative Virtual Computer Lab (CVCLAB) Penn State Berks B. Start a Command­line Console (Terminal) You will use a terminal to run many Linux commands. Start a terminal as follows: 1. Click on the icon on the Main Menu Bar in the upper left hand corner of the screen. This will bring up the command­line terminal. 2. You can open as many terminal windows as you wish. For example, two command­line terminals can be used at the same time. Linux commands are typed in the command­line prompt. C. Checking the IP Address in Linux Now that you have the command­line terminal up, the next step is to check the IP address of your VM as follows: 1. Type the command “ifconfig –a”, then press enter (see the figure below). 2. Check the interfaces and their TCP/IP setting. 5 of 7 Collaborative Virtual Computer Lab (CVCLAB) Penn State Berks “ifconfig ­a” lists all network interfaces of the system. The “lo” interface is not a physical adapter but an alias for the system itself. As you can see it has the address 127.0.0.1, which is the IP of the localhost. The system above has one physical interface, eth2 which stands for Ethernet 2. The IP address of eth2 is 192.168.1.6 in this particular Virtual Machine (VM).? Review Questions: Use “ifconfig ­a” to answer the following questions: ● What is the IP address of your VM? ● What is the MAC address of your VM? ● What is the default gateway of your VM? ● What is the subnet mask of your VM? D. Renewing IP Address 6 of 7 Collaborative Virtual Computer Lab (CVCLAB) Penn State Berks By default, your Backtrack VM is setup for DHCP. Command “dhclient” is used to request a new IP address from the DHCP server: 1. Type dhclient to renew the IP address for all network interfaces. 2. Type ifconfig –a in the command­line and press Enter to see the new IP. In the example above, the VM is assigned to the same IP address, 192.168.1.6. In the figure above, the communication between the VM and the DCHP server is also displayed. The IP address of the DCHP server is 192.168.1.1 as indicated by the red box in the example above. Review Questions: ● Did you receive a new IP address? What is it? (you will most likely receive the same IP address). ● What is the IP address of your DHCP server? 7 of 7