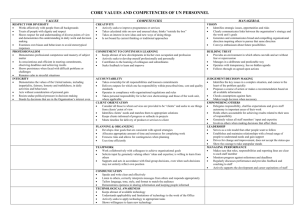
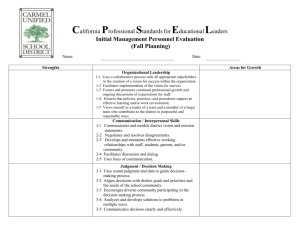
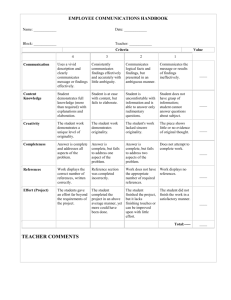
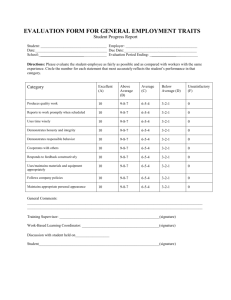
Leadership Excellence: The Exceptional Leader Self
advertisement

Leadership Excellence: The Exceptional Leader Self-Assessment System Assessment Scales Scale 1 Living Mission and Values ................................................................2 Scale 2 Modeling Effective Leadership ..........................................................5 Scale 3 Modeling Supervisory Skills ...............................................................8 Scale 4 Ensuring Optimum Care Standards ..................................................11 Scale 5 Attracting and Retaining Staff...........................................................14 Scale 6 Developing Staff ..............................................................................17 Scale 7 Championing Quality Improvement .................................................20 Scale 8 Integrating Risk Management ..........................................................23 Scale 9 Exhibiting Regulatory Expertise ......................................................26 Scale 10 Managing Resources .....................................................................29 Scale 11 Communicating Effectively .............................................................32 Scale 12 Facilitating Change ..........................................................................36 Scale 13 Managing Conflict............................................................................40 Scale 14 Advocating Customer Satisfaction ...................................................43 1|Page Scale 1 LIVING MISSION AND VALUES Performance Descriptions The Leader in Long Term Care: A Is seen as the leader in collaboratively creating systems, setting and achieving goals; embracing the position with passion for service to others and demonstrates this commitment at all times; and assures alignment with the organization's vision/mission of all collaborative efforts. B Consistently demonstrates knowledge of the organization's vision/mission; applies those values in his/her daily work; and seeks to collaborate with other disciplines in creating systems and implementing and achieving goals. C Understands the organization's vision/mission; applies its values in daily work and relationship with others; and participates in the collaborative efforts of other disciplines to set and achieve facility goals. D Shows some knowledge and interest in the organization's mission/vision; applies some of the organizational values; and participates in the interdisciplinary collaboration of goal setting and agrees to system changes. E Demonstrates limited knowledge and application of the organization's mission/vision; participates in collaboration with other departments only when assigned; and accepts assigned responsibilities in the implementation of systems, processes, and programs. OPTIMAL PERFORMANCE CHARACTERISTICS The mission and values of a company are the basis upon which it is built and the motivation for its continued growth. A leader leads in setting and achieving goals, which apply to the company's mission and values. The leader is a model for others and exhibits those values through daily interactions involving personal excellence, integrity, enthusiasm, leadership, and collaboratively working relationships. leads in creating systems, processes, and programs that further attain the organization's vision, mission and goals. He/she advocates innovative and creative approaches to meeting the organization's needs and furthering mission/goals and reinvents his/her role as necessary to assist the organization in achieving its mission/vision. 2|Page models excellence through daily interaction with others. With these interactions he/she is sensitive to staff needs (at all levels) to be involved and to feel part of the facility culture; demonstrates customer focus in all interactions by embracing the position with passion for service to all customers and caregivers and communicates the organization's vision/mission effectively to others. works collaboratively with other managers to implement and achieve facility goals; develops departmental long- and short-range goals, all of which are aligned with the organization's vision/mission to promotes and enable interdisciplinary collaboration and cooperation. SUPPORTIVE DATA (current or past activities) may include, but are not limited to: Demonstrating support for others and enthusiasm toward the work by coordinating meetings on a regular basis (department specific or team centered) that keep people informed and vested in the Mission and Vision of the organization. Sharing his/her vision with others and seeks and encourages fresh ideas via formal or informal communication systems, e.g. “Mission Control Idea of the Month” rewards incentive programs; o Examples: Maintenance creates an “Ambiance Team” to address how to change the environmental culture of the facility o Social Services conducts “Mission Control” meetings with staff to promote the facility mission and foster person centered care o Nursing launches a “Simple Pleasures” campaign to identify a daily simple pleasure that can be coordinated for all residents in the facility o Dietary works on the “Mission Control” team to identify positive changes in the food/dining experience o Activities works with nursing to help implement designated “Daily Pleasures” within their activities Translating customer wants and needs into action using formal and informal customer service feedback systems such as “My Inner view” Utilizes innovative strategies such as visual tools, (graphs, storyboards), newsletters, quality fairs, etc. to tell the story of process improvements Blending high expectations into daily routine and job descriptions 3|Page Stating values and explaining how he/she exhibits and applies them in daily work Integrates values education into staff meetings, daily standup meetings, theme days, etc. Encouraging individuals to use their ideas, knowledge, and creativity Demonstrating special commitment to understand those we serve COMPETENCY CROSS REFERENCE 1.1, 1.2, 1.3, 1.4, 1.4.2, 1.5 , 1.7 , 1.9 , 1.10.2 , 1.11.2 , 2.11.1, 7.7: 1.1 Models the organization’s values and mission/vision in his/her daily work and interactions with others. 1.2 Works collaboratively with other managers to implement and achieve facility short and long term goals which are aligned with organizational vision/mission. 1.3 Collaboratively develops department's long and short range goals which are aligned with organization's vision/mission. 1.3.1 Develops implementation strategies to achieve those goals. 1.4 Leads in creating systems, processes, and programs that further attain organization's vision, mission and goals. 1.4.2 Reinvents his/her role as necessary to assist the organization in achieving its vision/mission. 1.5 Communicates the organization's vision /mission effectively to others. 1.7 Advocates for innovative and creative approaches to meeting organizational needs and furthering the mission/vision. 1.9 Embraces position with passion for service to all customers. 1.10.2 Is sensitive to staff needs (at all levels) to be involved and to feel part of the organizational/facility culture. 1.11.2 Models excellence and a commitment to quality. 2.11.1 Promotes and enables interdisciplinary collaboration and cooperation. 7.7 Models customer focus in all interactions. 4|Page Scale 2 MODELING EFFECTIVE LEADERSHIP Performance Descriptions The Leader in Long Term Care: A Inspires confidence through visionary leadership that reflects credibility, integrity, and respect for others; enthusiastically reinforces positive outcomes and a positive facility image through community involvement; and actively seeks professional development opportunities, including professional credentialing. B Models commitment to quality and a clear vision of the organization's goals; seeks new ideas and understands the importance of an effective public relations program; and participates in a variety of professional development opportunities. C Demonstrates a desire for quality and is perceived as trustworthy; shows awareness of the importance of community perceptions and is open to new ideas; and develops leadership skills through readily available sources, collaborating at times with other organizations. D Performs daily work with little awareness of the effect of personal behavior on others; makes changes only as needed, demonstrating limited understanding of public relations issues; and participates in professional development opportunities as directed. E Demonstrates a disregard for integrity and respect for others; encourages the status quo, unreceptive to most new ideas and disregarding feedback from the community; and lacks awareness of need for continuing professional growth and development. OPTIMAL PERFORMANCE CHARACTERISTICS Visionary leadership is central to the effectiveness of long term care leader. This strong, effective leadership is demonstrated through personal behavior that reflects integrity and credibility in all relationships, openness to new ideas, and a commitment to lifelong learning and development. demonstrates integrity, credibility, and trustworthiness in the execution of his/her responsibilities. He/she inspires trust and confidence through modeling excellence, a commitment to quality, and a respect for the beliefs, values, and customs of individuals. He/she maintains a clear vision of the organization's mission and is able to communicate this vision in a way that inspires others. 5|Page reinforces positive thinking and positive outcomes by actively generating new ideas and changes as appropriate, encouraging others to take calculated risks in decisionmaking, and demonstrating flexibility and openness to new ideas and paradigms. He/she functions as facility liaison with community professionals and leaders, improving the community perception of the facility's image through an effective public relations program while providing coordinated client care. champions lifelong personal and professional learning by systematically assessing his/her own need for personal and professional education, availing him/herself of a variety of growth and self-improvement opportunities. He/she uses various strategies to improve, such as continuing education, professional credentialing, collaboration with other community organizations, public speaking, research, marketing, networking, etc. SUPPORTIVE DATA (current or past activities) may include, but are not limited to: Department and facility examples of actions taken in response to positive and negative outcomes Departmental Examples o Maintenance participates in the facility safety program o Maintenance works with the Falls team to identify environmental deficits and opportunities to promote safety through lighting, grab bars, elevated toilet seats, innovative call systems, monitoring of call response times, and identification of new products for evaluation o Social Services works on the Falls Team and provides feedback/data on at risk residents, behavioral strategies and interventions, use of psycho actives and the current reduction plan, pain management goals, and resident and family education related to fall management o Therapy participates in the falls team and provides data and updates on therapy referrals/screenings related to those at risk; therapy coordinates a seating clinic with nursing and maintenance to look at seating options, restraint alternatives and least restrictive means, etc. o Dining is working with the Falls team on dining schedules and the coordination of a “Walk to Dine” program o Dining is working with nursing and therapy to coordinate more person centered dining times 6|Page Departments work collaboratively and independently as an initiator/leader of process improvements and innovation in the workplace Examples of motivating and inspiring others (team building activities, employee recognition, performance appraisal process, etc.) Ways they have evaluated facility care services against current industry trends; Examples include ways in which the department has embraced the concepts of culture change Maintenance has assisted in writing an article on F323 and environmental safety Activities ands are involved in a professional association Participation in continuing education seminars or participation as a presenter at an educational event on topics such as Disaster preparedness, Safety, etc. Evidence of innovative projects that have been piloted by the LTC leaders Examples of how they encourage individuals to use their ideas, knowledge, and creativity COMPETENCY CROSS REFERENCE Primary 1.7.1, 1.8, 1.11, 1.11.1, 1.11.2, 1.11.4, 1.11.5, 1.14, 1.16, 1.16.1, 1.16.2, 1.16.3, 2.13 Secondary 1.5, 1.7.2, 1.7.3, 1.8.1, 1.14.1, 1.14.2, 1.14.3 Primary: 1.7.1 Models and reinforces positive thinking and positive outcomes. 1.8 Is flexible, adapting to new ideas and paradigms. 1.11 Consistently models effective leadership through personal behavior. 1.11.1 Executes tasks and responsibilities with utmost integrity, credibility, and trustworthiness. 1.11.2 Models excellence and a commitment to quality. 1.11.4 Respects the beliefs, values, and customs of individuals. 1.11.5 Inspires mutual trust and confidence. 1.14 Champions lifelong personal and professional learning. 1.16 Functions as facility liaison with community professionals and leaders for: 1.16.1 Providing coordinated client care. 1.16.2 Maintaining public relations. 1.16.3 Improving community perception of the facility's image. 2.13 Seeks feedback on own performance from supervisors, peers, and staff. 7|Page Scale 3 MODELING SUPERVISORY SKILLS Performance Descriptions The Leader in Long Term Care: A Constantly conveys performance expectations persuasively, utilizing well-established systems and processes to provide effective and timely feedback that help staff understand what is expected; empowers subordinates through effective delegation, providing excellent mentoring, coaching, and follow up to ensure clear understanding and successful completion; and masterfully promotes staff goal-setting, actively reinforcing successes through recognition and celebration. B Communicates performance expectations, providing constructive and timely feedback, counseling, and disciplinary action and overseeing an effective performance appraisal system; delegates effectively to subordinates, providing strong mentoring, coaching, and follow up to ensure clear understanding and successful completion; and encourages individual and team goal-setting, reinforcing progress by celebrating their successes. C Communicates performance expectations sufficiently, using performance appraisals, constructive feedback, counseling and disciplinary action, as appropriate; delegates responsibilities adequately, using feedback to ensure mutual understanding of the expectations; assists individuals and teams in goal-setting as needed. D Utilizes performance appraisals and sporadically feedback to convey performance expectations; delegates’ responsibilities with some regard for the subordinate's ability to succeed; and assists individuals and teams in goal-setting when requested. E Relies on disciplining actions to communicate performance expectations; delegates with apparent disregard for the employee's understanding or ability to succeed; and lacks awareness of how to support individuals and teams in goal-setting efforts. OPTIMAL PERFORMANCE CHARACTERISTICS Excellent supervision is a cornerstone of an organization's efforts to ensure quality care and exceptional delivery of services. As a leader and mentor, the leader’s behavior is key to staff development of supervisory skills. By conveying and clarifying expectations, empowering staff through appropriate delegation, and encouraging staff in goal setting, he/she promotes the development of supervisory skills throughout the organization. 8|Page conveys performance expectations clearly through well established systems and processes that are consistent with the organization's vision and mission. By providing constructive and timely feedback, including counseling and disciplinary action as appropriate, he/she helps staff understand what is expected. The leader oversees an effective performance appraisal system, supporting the timely completion and delivery of performance appraisals for all nursing employees. delegates responsibilities appropriately, including the establishment of a clear understanding of the expectations and the level of authority granted. He/she recognizes delegation as an opportunity to assist in the professional growth and development of subordinates, utilizing delegation to empower them to participate in decision-making, and encouraging them to develop new ideas and standards that exceed customer expectations. To ensure successful completion of the delegated task, the leader provides excellent mentoring and coaching and appropriate follow-up with the employee. encourages staff to set individual and team goals that are both measurable and attainable. By conveying expectations, promoting cooperative behaviors, and seeking feedback to promote mutual understanding, the leader supports appropriate communication for small groups and teams, enhancing their effectiveness. He/she helps the individuals/teams remain focused on the organization's vision and mission and reinforces their progress by acknowledging and celebrating successes. SUPPORTIVE DATA (current or past activities) may include, but are not limited to: Clarity of written and verbal communication outlining expectations, e.g., individual and departmental memos, newsletter articles, teaching/coaching notes, and methods to illicit staff feedback, etc. Frequency and quality of performance appraisals; participation in employee goal setting; Example: Safety Board with a listing of injury free days Quality and timeliness of performance counseling documentation Successful completion of delegated tasks Involvement of subordinates in decision-making and facility Mission and Vision Evidence of effective mentoring and coaching: Regularly scheduled meetings with staff, defined methods to solicit feedback and promote team work Evidence of appropriate staff goals having been supported and progress celebrated Staff satisfaction surveys and examples of how feedback was used to remedy or enhance satisfaction 9|Page COMPETENCY CROSS REFERENCE Primary 1.5.1, 1.12.1, 2.2, 2.11, 2.12.1, 2.14, 3.8, 3.9.1, 4.7, 4.7.3, 4.7.4, 4.8, 4.14 Secondary 1.12.2, 3.8.1, 3.8.2, 3.8.3, 7.4 Primary: 1.5.1 Helps teams and individuals maintain their focus on the organization's mission/vision. 1.12.1 Delegates as appropriate. 2.2 Communicates performance expectations clearly. 2.11 Empowers staff to participate in decision-making. 2.12.1 Encourages staff to set individual and team goals. 2.14 Acknowledges and celebrates successes to reinforce progress and achievement. 3.8 Supports appropriate communication for small groups and teams. 3.9.1 Presents feedback constructively. 4.7 Oversees an effective staff performance appraisal system. 4.7.3 Supports timely completion and delivery of performance appraisals by staff. 4.7.4 Ensures follow-up with coaching/counseling and mentoring/training. 4.8 Implements the organization's progressive disciplinary policy in a fair and consistent manner. 4.14 Models expert coaching and mentoring 10 | P a g e Scale 4 ENSURING OPTIMUM CARE STANDARDS Performance Descriptions The Leader in Long Term Care: A Establishes optimum care standards that exceed compliance requirements; develops dynamic systems and protocols; and uses a wide variety of methods to ensure that the optimum standards of health services are maintained. B Establishes optimum care standards that meet or exceed compliance; improves current systems and protocols; and ensures that high level health care systems are maintained. C Maintains care standards which meet compliance requirements; establishes systems and protocols that promote compliance; and ensures that minimum standards of health services are maintained. D Maintains health care standard systems and protocols that meet minimum requirements; and displays limited ability to ensure that health services are maintained. E Fails to maintain care standards that meet compliance requirements; makes minimal effort to establish systems and protocol that meet minimum requirements; and displays limited ability to ensure that health services are maintained. OPTIMAL PERFORMANCE CHARACTERISTICS The exceptional leader ensures that optimum standards of health services are established, operationalized, and maintained in the facility’s daily operations. The leader does this successfully by achieving mastery of standards set by regulatory and accrediting bodies and professional organizations and by developing facility systems and protocols that promote meeting or exceeding these standards. He/she educates customers and staff on standards and ensures ongoing compliance through pro-active risk management and implementation of corrective action whenever areas of non-compliance are identified. establishes optimum care standards which meet or exceed compliance requirements. He/she maintains current knowledge and mastery of federal, state, and local regulations, and accreditation and industry standards. The exceptional leader is able to apply this knowledge and work collaboratively with other staff in the development of dynamic systems that promote survey preparedness at all times, placing the facility in the forefront of the profession. establishes systems and protocols that promote meeting or exceeding regulatory standards. He/she interprets these standards to residents, families, and professional 11 | P a g e representatives. The staff’s knowledge of and adherence to the regulatory standards result in the high quality of care provided in the facility. ensures maintenance of high standards of health services in daily operations. He/she achieves this by educating his/her staff and other departments on regulations and standards, instituting pro-active risk management strategies, and implementing necessary corrective action based on accurate analysis of non-compliance areas. SUPPORTIVE DATA (current or past activities) may include but are not be limited to: Policy and procedures are current and reflect interdisciplinary oversight and collaboration; examples include the interdisciplinary Disaster Preparedness plan Current resources are available to include SOM, State regulations, Life Safety Codes, Building Codes, MSDS information, etc. Guidelines or protocols are current and are reviewed on a regular basis as part of the QA process Current clinical reference materials are available to clinical staff; Examples include SOM, Current PDR, periodicals, clinical guidelines, current P&P, etc. In-service programs covering a wide variety of current regulatory and standards information are offered and attended by staff Upon interview, staff can answer (or refer to the correct person) questions regarding resident's care and services in accordance with regulatory and clinical standards Upon observation, clinical staff performs their duties and job functions in accordance with regulatory and clinical standards. Survey preparation paperwork is complete, accurate, and available at the time of survey Compliance rounds and audits are conducted on a routine basis and the findings are addressed collaboratively Describing the survey process and proactive strategies necessary to achieve compliance. Attendance or participation, during the last year, in a program or seminar on regulatory and other professional standards COMPETENCY CROSS REFERENCE Primary 6.1, 6.2, 6.3, 6.4, 6.5, 6.6, 6.7, 6.7.1, 6.9, 6.10 Secondary 1.11.3, 1.15, 1.15.1, 1.15.2, 4.5, 4.5.1, 4.5.2, 4.5.3, 4.5.4, 4.6.2, 5.8, 6.8, 7.4 12 | P a g e Primary: 6.1 Maintains current knowledge of Federal, State, and local standards and regulations for long term care, such as those for certification, licensure, and accreditation, Medicare, state Medicaid and, if applicable, JCAHO. 6.2 Educates his/her staff and other departments on regulations and standards. 6.3 Interprets regulatory standards to residents and external customers such as families, discharge planners, referral sources, insurance companies, etc. 6.4 Establishes optimum care standards which meet or exceed compliance requirements. 6.5 Establishes systems and protocols that promote meeting and exceeding regulatory standards. 6.6 Ensures maintenance of high standards in all daily operations. 6.7 Promotes survey preparedness at all times. 6.7.1 Maintains survey readiness via current accurate reports and department records. 6.9 Implements necessary corrective action based on accurate analysis of non- compliance areas. 6.10 Institutes pro-active risk management strategies. 13 | P a g e Scale 5 ATTRACTING AND RETAINING STAFF Performance Descriptions The Leader in Long Term Care: A Applies innovative strategies to craft an optimal work environment; pro-actively assesses staffing roles to ensure congruence with hiring criteria and resulting decisions; and utilizes rigorous measurements of staff satisfaction and implement improvement meaningful to staff. B Employs multiple methods to sustain a positive work environment; periodically assesses staff roles to update hiring criteria; and utilizes proven measures of staff satisfaction with consistent effort to make improvement. C Demonstrates use of accepted strategies to assess staff satisfaction and attract and retain staff; and applies hiring criteria when selecting new staff. D Displays some knowledge and effort in utilizing strategies for attracting and retaining staff; uses hiring criteria that are inconsistently linked with skill sets of new staff; and sporadically makes an effort to assess staff satisfaction. E Makes hiring decisions that are poorly supported, and new staff come to positions lacking critical skills; lacks demonstrated understanding of staff needs; and makes little effort to assess or respond to staff requests. OPTIMAL PERFORMANCE CHARACTERISTICS The role of the Long Term Care Leader in attracting and retaining staff is paramount to sustaining the delivery of quality care and exceeding customer expectations. Vigilance in hiring the best staff and fostering a dynamic and vital work environment results in increased job satisfaction and stability. employs a wide variety of methods and strategies to foster an optimal work environment that promotes staff self-governance, independent thinking, empowerment, safety, and flexibility. pro-actively reassesses the roles of staff to guarantee that job descriptions reflect roles required and that hiring criteria clearly reflect the necessary knowledge, skills, and competencies. Hiring decisions are made based upon these criteria plus the individual’s ability to contribute successfully to the organization. fosters high levels of job/staff satisfaction. This occurs through the clear articulation of the functions and values of each person’s position and the interdependence of positions 14 | P a g e required to achieve quality care. This is supported by fair and competitive compensation and the inclusion and celebration of unique employee characteristics. SUPPORTIVE DATA (current or past activities) may include, but is not limited to: Examples of flexible staff assignments and creative, flexible staffing patterns and schedules to include weekends and off shifts Examples of hiring and employment incentives; Examples include Mentoring Programs Department specific employee recognition programs and strategies to promote job satisfaction; Example: Maintenance participates in facility Safety Programs, coordinates interdisciplinary “Do You See What I See? Environmental Rounds, and provides a monthly prize for the “Going Green” tip of the month. Demonstrated opportunities for staff participation in decision-making, e.g. councils, task or project management teams Demonstrated review of job descriptions, and hiring criteria Periodic formal and informal satisfaction surveys with staff Stated satisfaction of staff with job descriptions, role responsibilities, and modification Stated satisfaction with level of compensation and related employee perks and incentive programs: give examples Absence of/ or minimal grievances regarding work environment issues Evidence of safety needs being heard and addressed Use of storyboards and/or visual data to demonstrate safety initiatives and progress towards safety goals Demonstrated use of bench marking Shows documentation of adherence to hiring criteria in selection of new staff Demonstrated performance evaluations of recently hired staff that show competencies Feedback forms from staff and residents that show satisfaction with coworkers, managers and staff. COMPETENCY CROSS REFERENCE 1.1, 1.10.2, 1.10.3, 2.11, 2.11.1, 2.11.2, 4.1, 4.2, 4.3, 4.3.1, 4.3.2, 4.3.3, 4.4, 4.7, 4.7.1, 4.7.2, 4.7.3, 4.7.4, 5.4 15 | P a g e 1.1 Models the organization's values and mission/vision in his/her daily work and interactions with others. 1.10.2 Is sensitive to staff needs (at all levels) to be involved and to feel part of the organizational/facility culture. 1.10.3 Values and incorporates staff opinions in decision making. 2.11 Empowers staff to participate in decision-making. 2.11.1 Promotes and enables interdisciplinary collaboration and cooperation. 2.11.2 Utilizes collective wisdom and decision making capabilities of staff. 4.1 Works collaboratively to recruit and select exceptional staff. 4.2 Exhibits skillful interview techniques. 4.3 Implements effective strategies to retain quality staff. 4.3.1 Participates in developing, reviewing, and revising job descriptions. 4.3.2 Reviews retention policies and procedures and modifies them as needed. 4.3.3 Makes jobs meaningful, challenging, and contributory to the department and the organization. 4.4 Ensures staffing patterns and processes which maximize resident care and deployment of staff. 4.7 Oversees an effective staff performance appraisal system. 4.7.1 Bases system on clear and meaningful, job-based criteria 4.7.2 Collects objective data as basis for feedback. 4.7.3 Supports timely completion and delivery of performance appraisals by staff. 4.7.4 Ensures follow-up with coaching/counseling and mentoring/training. 5.4 Creatively manages flexible staffing patterns that meet changing client service level/needs. 16 | P a g e Scale 6 DEVELOPING STAFF Performance Descriptions The Leader in Long Term Care: A Ensures a complete, thorough orientation to health services and facility; uses new hire selfassessment for effective orientation and provides ongoing documented feedback throughout orientation, also actively provides and promotes that all staff receive/attend regular education/training programs; and seeks and empowers staff to participate in decision making along with encouraging staff to seek advancement opportunities. B Provides a complete orientation to health services and the facility; gives feedback to new hire at mid-point and 90-day introductory period performance evaluations, and has consistent and regular ongoing education and training for all shifts; and involves staff in most decision-making, encouraging utilization of staff in leadership positions and advancement opportunities. C Provides consistent basic orientation to health services and the facility; provides feedback to new hire at 90-day introductory period performance evaluation, and education/training programs are available to all shifts; and involves staff in some decision-making. Posts position advancement opportunities. D Provides basic orientation to health services and inconsistently to the facility; inconsistently makes feedback or presents only if new hire requests; and makes occasional education/ training available on multiple shifts. Allows minimum staff participation. E Provides minimal orientation to health services and the facility; offers feedback to new hire only in failure to perform; and offers sporadic training only on one shift. Disallows staff participation. OPTIMAL PERFORMANCE CHARACTERISTICS The Long Term Care Leader recognizes that orientation, education/training, and staff participation and advancement opportunities are key to successful operations and to enriching and developing highly exceptional staff. works collaboratively with administrative and interdisciplinary team members to provide orientation. He/she provides a complete and thorough orientation to health services and to the facility. The leader seeks staff self-assessment and provides feedback to staff throughout the orientation process. actively promotes and provides education and training for all health services staff. He/she utilizes staff as trainers and mentors; ensures staff attendance at trainings via 17 | P a g e flexible scheduling; and maintains a current, readily available reference library to include a current employee handbook, policy and procedure manual, and regulatory guidelines. Also channels information about accessing outside educational opportunities. supports, encourages, and advocates participation and advancement opportunities for all health services staff. He/she strives to make jobs meaningful, challenging, and contributory by being sensitive to the staff’s need to be involved and included, empowering and enabling them to participate in decision-making opportunities. The leader mentors and develops subordinates in their professional growth. He/she encourages all staff to set individual goals and to seek and attain position advancement and/or leadership opportunities. SUPPORTIVE DATA (current or past activities) may include, but are not limited to: Orientation checklist and calendar, completed, dated, and initialed within company orientation time line for facility and company operations for all new hires Education and Training binder is current with dates and synopsis of programs provided, and sign in logs of staff who attended Annual educational calendar reflects both facility provided and community available education/training programs Educational calendar reflects participation by all staff departments and is reflective of staff and federal regulations, community standards, and the facility strategic plan; Examples follow: o Social Services provides Advance Directives, End of Life Resident Rights, Grievance Policies, Coordination of Ancillary Services education, (etc) o Dietary provides education on therapeutic diets, substitutes, the ambiance of dining, food and sanitation, etc. o Maintenance provides education on Disaster Preparedness, Safety, Water temperatures, creating a culture of safety, and related regulations such as F323, etc. o The facility involves residents, volunteers, and families in the educational plan o Educational planning is done in conjunction with Risk and Quality Committee initiatives; the facility uses data to evaluate the effectiveness of the current plan and to make adaptations as needed Resource library is in a readily available location for all staff and houses updated policy/regulatory manuals and resource materials Staff Mentor list reflects current staff leaders with the tasks assigned and completed Staff bulletin board exhibits current position change/leadership opportunities and both internal and external education and training programs, via postings and current educational calendar 18 | P a g e Staff suggestion box is a user-friendly location, and a log of ideas/comments is maintained and complete with follow-up/response log Staff meeting’s agenda/ minutes reflect staff participation in decision-making process COMPETENCY CROSS REFERENCE Primary 1.10, 1.10.2, 2.11, 2.11.1, 2.12, 2.12.1, 3.9.1, 4.5, 4.5.1, 4.5.2, 4.5.3, 4.5.4, 4.10, 4.11, 4.11.1, 4.11.3, 4.12, 4.13, 4.13.2, 7.4, 7.8 Secondary 1.7.1, 1.11.3, 1.12.1, 2.12, 3.6, 4.6, 4.9, 4.11, 4.13.1, 6.2, 6.8, 7.1, 7.8 Primary: 1.10 Actively seeks ongoing feedback to make necessary changes/adjustments from current to desired state. 1.10.2 Is sensitive to staff needs (at all levels) to be involved and to feel part of the organizational/facility culture. 2.11 Empowers staff to participate in decision-making. 2.11.1 Promotes and enables interdisciplinary collaboration and cooperation. 2.12 Promotes staff self-evaluation and learning targeted toward performance improvement. 2.12.1 Encourages staff to set individual and team goals. 3.9.1 Presents feedback constructively. 4.5 Enforces regulatory and employee law compliance. These may include: 4.5.1 OSHA requirements. 4.5.2 Physical, TB, or drug testing. 4.5.3 Worker compensation. 4.5.4 Child/adult abuse reporting. 4.10 Provides staff with outside resources and other services as appropriate. 4.11 Provides effective clinical orientation and on-going training. 4.11.1 Uses adult learning principles. 4.11.3 Utilizes staff as trainers and mentors. 4.12 Collaboratively ensures that employee handbook, policy and procedure manuals, and other materials are current, readily available, and used in orientation and training. 4.13 Actively promotes training and education for staff, residents, and community. 4.13.2 Promotes flexible scheduling so staff on all shifts can attend. 7.4 Empowers staff to develop new ideas and standards to exceed customer expectations. 7.8 Supports staff orientation and ongoing training on positive customer service by all staff to all customers. 19 | P a g e Scale 7 CHAMPIONING QUALITY IMPROVEMENT Performance Descriptions The Leader in Long Term Care: A Pro-actively evaluates situations to identify performance improvement opportunities; performs ongoing systematic objective data collection and then uses the objective data to analyze problems and measure outcomes; and employs a wide range of planned interventions that promote performance improvement. B Consistently evaluates situations to identify performance improvement opportunities and routinely reviews clinical practice standards; collects and effectively uses objective data; and is able to implement planned interventions that improve performance. C Evaluates most situations to identify performance improvement opportunities and routinely examines clinical practice standards; uses objective data collection; and is able to implement planned interventions that contribute to performance improvement. D Demonstrates limited ability to evaluate situations when they arise as means to identify performance improvement opportunities; minimally collects and analyzes objective data; and has difficulty identifying underlying root causes or implementing planned interventions that contribute to performance improvement. E Performs daily work with minimal attention to evaluating situations to identify performance improvement opportunities or examine clinical practice; lacks ability to analyze problems; and rarely identifies underlying root causes or implements planned interventions for quality improvement. OPTIMAL PERFORMANCE CHARACTERISTICS The Long Term Care Leader embraces and pro-actively fosters the principles and processes of quality improvement, integrating them into the daily operations of the nursing department on an ongoing basis. He/she does this successfully by evaluating situations to identify performance improvement opportunities, ensuring implementation of planned interventions that promote performance improvement, and using objective data to analyze problems and measure outcomes to enhance continuous improvement. ensures implementation of planned interventions that promote performance. He/she empowers and encourages other staff members to fully participate in quality improvement efforts by promoting and enabling interdisciplinary 20 | P a g e collaboration/cooperation; utilizing collective wisdom and decision-making capabilities of staff; and integrating the processes and programs across departments. He/she models continuous quality performance improvement philosophy and techniques in daily behavior. The leader uses each specific improvement opportunity to further develop and enhance the facility’s overall quality improvement systems and processes and communicates performance expectations clearly. evaluates situations to identify performance improvement opportunities. He/she continuously examines clinical practice, identifying underlying dynamics or the root cause of the problem. demonstrates knowledge of quality improvement principles by collecting and using objective data to analyze problems and measure outcomes that enhance continuous improvement. He/She uses analysis strategies, including both quantitative and qualitative measures and implements, monitors, and updates plans to improve quality indicators. Based on this data, the leader determines the effect of the changes and identifies activities to sustain or enhance improvements. SUPPORTIVE DATA (current or past activities) may include, but are not limited to: Conducting data (current or past activities) collection, analysis, and presentation from possible data (current or past activities) sources: Notes/audits from clinical and environmental rounds, results of satisfaction surveys, etc. Environmental rounds are scheduled on a regular basis, at diverse times and include diverse staff representatives 24-hour nursing report is reviewed as part of a formal meeting with processes in place to address action steps and ensure follow up Departmental logs: Infection control, Incident/Accident, Grievance/complaint; durable medical equipment and safety checks, Advance Directives/DNRO, and logs and data tools that reflect department specific indicators for tracking and trending Medical record audits Satisfaction surveys: Resident, Staff, and Family Ongoing reviews of new interpretive guidelines and regulatory updates Resident Council minutes and related grievance reports such as Consultant reports (pharmacy, registered dietitian) and use of Quality Measure/Quality Indicator reports; CMS Nursing Home Compare, Advancing Excellence data, etc. Participation in Quality Assurance and Assessment (Quality Management) activities and Risk meetings. Demonstrating and applying Continuous Quality Improvement Tools: o o o o o idea generating tools (i.e. brainstorming) consensus generating tools (i.e. multi-voting, rank ordering) team meeting skills Run charts, flow charts, control charts, etc. action plans 21 | P a g e Examples of assistance provided to integrate Quality Management into daily work; daily standup meetings, rounds, etc. Providing opportunities for interdepartmental quality fairs and venues that emphasize facility initiatives such as safety, infection control, etc. Examples of motivating and inspiring others COMPETENCY CROSS REFERENCE Primary 2.1, 2.2, 2.3.1, 2.3.2, 2.4, 2.5, 2.6, 2.7, 2.8, 2.9, 2.10, 2.11, 2.11.1, 2.11.2, 2.11.3 Secondary 1.10, 1.11, 1.12, 1.12.1, 1.13, 1.14, 6.5, 6.6, 6.9, 7.2, 7.3, 7.5 Primary: 2.1 Models continuous quality performance improvement philosophy and techniques in daily behavior. 2.2 Communicates performance expectations clearly. 2.3.1 Identifies underlying dynamics or root cause of problems. 2.3.2 Examines practice in all departments. 2.4 Maintains objective focus on needed changes in operational process rather than on people involved. 2.5 Collects objective data. 2.6 Uses objective data to analyze problems and measure outcomes to enhance continuous improvement. 2.7 Uses analysis strategies, including both quantitative and qualitative measures. 2.8 Ensures implementation of planned interventions that promote performance improvement. 2.9 Implements, monitors, and updates plans to improve facility/department quality indicators. 2.10 Develops and uses a variety of instruments to evaluate outcomes regarding customer satisfaction, employee turnover/retention, quality of care, etc. 2.11 Empowers staff to participate in decision-making. 2.11.1 Promotes and enables interdisciplinary collaboration and cooperation. 2.11.2 Utilizes collective wisdom and decision making capabilities of staff. 2.11.3 Integrates processes and programs across departments. 22 | P a g e Scale 8 INTEGRATING RISK MANAGEMENT Performance Descriptions The Leader in Long Term Care: A Pro-actively seeks opportunities for early identification of risk factors through analysis of supportive data; models surveillance techniques; and demonstrates an exceptional ability to lead in the integration of quality improvement strategies and collaboration with all disciplines. B Consistently investigates accidents and incidents and ensures appropriate follow up to mitigate risk factors; assures ongoing surveillance; and promotes quality improvement initiatives. C Adequately identifies risk factors; demonstrates acceptable surveillance techniques by tracking accidents and incidents; and supports quality improvement initiatives. D Exhibits limited participation in quality improvement initiatives and the identification of risk factors; and demonstrates some understanding of necessary surveillance techniques. E Demonstrates poor understanding of risk factors; lacks follow through on surveillance outcomes; and poorly participates in quality improvement initiatives. OPTIMAL PERFORMANCE CHARACTERISTICS Risk management is an integral component of the Long Term Care Leader’s role. The most important aspects of risk management are identifying and preventing potential loss based on systems failures, as well as guarding against loss. assists others in recognizing major risk factors within the organization through careful analysis of objective data, such as incident/accident reports, Workers' Compensation claims, and Quality Indicator reports (where applicable). Such analysis includes tracking/trending of issues, in addition to carefully scrutinizing the identifiable risk factors associated with each specific event. He/she effectively manages the integration of risk identification, evaluation, and loss prevention, which are critical to the organization's risk management success. conveys the value of ongoing surveillance by all departments, with the goal of promptly identifying potential systems failures and recognizing areas needing improvement. Beginning with new employee orientation and continuing with ongoing staff collaboration to reinforce risk management concepts, the leader encourages others to identify risk factors in order to pro-actively prevent losses. 23 | P a g e promotes the total integration of quality improvement throughout the organization by modeling risk management strategies, including monitoring safety-related activities (such as ergonomics issues and needle-stick precautions). He/she enhances staff buy-in to the quality improvement process by effectively demonstrating the relationship between early identification and prevention of problems. SUPPORTIVE DATA (current or past activities) may include, but are not limited to: Ways the facility was assisted in the development of new systems; Examples include: a new wireless call light system, fall reduction strategies, “Going Green” strategies, introduction of technology into existing documentation systems, etc. Supporting interdisciplinary problem solving and creating a blame free environment when reviewing Safety Committee reports, maintenance logs, and OSHA logs Examples of assistance provided to integrate quality improvement into daily work Prompt analysis of objective data (current or past activities) such as insurance claims history, incident reports, and survey results Effective and efficient methods used to assure ongoing surveillance Careful tracking and trending of quality indicator reports, falls tracking system, and other areas with high risk potential Facility remains proactive in identification of new products and technology that can promote work efficiency, safety, and financial stewardship COMPETENCY CROSS REFERENCE Primary 1.11.2, 1.12.2, 2.1, 2.5, 2.6, 2.8, 2.11.1, 4.6.1, 6.10 Secondary 1.7.1, 1.8.1, 2.3, 7.5 Primary: 1.11.2 Models excellence and a commitment to quality. 1.12.2 Mentors and develops staff in their professional growth. 2.1 Models continuous quality performance improvement philosophy and techniques in daily behavior. 2.5 Collects objective data. 2.6 Uses objective data to analyze problems and measure outcomes to enhance continuous improvement. 24 | P a g e 2.8 Ensures implementation of planned interventions that promote performance improvement. 2.11.1 Promotes and enables interdisciplinary collaboration and cooperation. 4.6.1 Initiates, maintains, and follows up on each work related injury/illness with complete and accurate worker compensation reports and records, adhering to company policy. 6.10 Institutes pro-active risk management strategies. 25 | P a g e Scale 9 EXHIBITING REGULATORY EXPERTISE Performance Descriptions The Leader in Long Term Care: A Possesses mastery of regulatory standards; establishes systems and resources, which enable performance that exceeds regulations; and takes an assertive, pro-active position, serving as a strong client advocate and seeking an opportunity to influence the profession’s direction. B Models thorough knowledge of regulatory standards; applies knowledge in developing systems to meet standards; and exhibits a pro-active position and client advocacy skills involving input to influence the profession’s direction. C Demonstrates sufficient knowledge of regulatory standards; collaboratively develops systems to meet regulations; and exhibits some pro-active and client advocacy skills. D Exhibits some knowledge of regulatory standards; assists in developing systems to meet regulations; and sometimes serves as a client advocate. E Shows some knowledge of regulatory standards; and lacks expertise to promote facility regulatory compliance. OPTIMAL PERFORMANCE CHARACTERISTICS The Long Term Care Leader has a current mastery of all Federal, State and local regulatory standards. It is critical that he/she ensures that the operational system and staff training and resources meet or exceed compliance. He/she actively participates in professional/educational organizations. He/she seeks political opportunities that influence the regulatory process and the profession’s direction. masters and maintains updated knowledge of federal, state, and local regulatory standards. He/she continuously expands his/her knowledge base and maintenance of his/her expertise. ensures continuous compliance with regulatory standards. He/she develops, implements and maintains systems, which exceed these regulatory standards. He/she effectively empowers and ensures staffs exceed compliance standards through education and use of available resources. 26 | P a g e actively participates in continued development of regulatory guidelines. He/she takes pro-active positions and seeks opportunities to influence the regulatory process and profession’s direction. SUPPORTIVE DATA (current or past activities) may include, but are not limited to: Past survey reports and implementation of any necessary plan of corrections with demonstrated processes in place to sustain the gains Examples of survey readiness; Examples: Generator run time logs, Durable Medical Equipment checks, disaster drills, daily, weekly, and monthly safety checks; participation in education, etc. Examples of recently attended/completed professional regulations updates, and resources Participation in facility education and regulatory updates and readiness Reviewing staff training and available resources Examples of pro-active or client advocacy positions COMPETENCY CROSS REFERENCE 1.4, 1.6, 1.12, 1.13, 1.15, 1.15.1, 1.15.2, 2.2, 2.3, 2.8, 2.9, 2.11, 3.5, 3.6, 4.5, 4.5.1, 4.5.2, 4.5.3, 4.5.4, 4.10, 4.12, 4.13, 6.1, 6.9, 7.1, 7.4 1.4 Leads in creating systems, processes, and programs that further attain organization's vision, mission and goals. 1.6 Serves as an expert resource, involving other disciplines to achieve quality care and service. 1.12 Carries out supervisory responsibilities in accordance with organizational policies and applicable laws. 1.13 Efficiently uses time management principles to ensure timely accomplishment of all duties. 1.15 Actively participates in the profession's efforts to implement and improve standards of: 1.15.1 Professional practice and 1.15.2 Long term care. 2.2 Communicates performance expectations clearly. 2.3 Evaluates situations to identify performance improvement opportunities. 2.11 Empowers staff to participate in decision-making. 27 | P a g e 3.5 Communicates effectively with all levels of the organization (senior management, peers, and employees.) 3.6 Communicates effectively through writing, speaking and listening channels. 4.5 Enforces regulatory and employee law compliance. These may include: 4.5.1 OSHA requirements. 4.5.2 Physical, TB, or drug testing. 4.5.3 Worker compensation. 4.5.4 Child/adult abuse reporting. 4.10 Provides staff with outside resources and other services as appropriate. 4.12 Collaboratively ensures that employee handbook, policy and procedure manuals, and other materials are current, readily available, and used in orientation and training. 4.13 Actively promotes training and education for staff, residents, and community. 6.1 Maintains current knowledge of Federal, State, and local standards and regulations for long term care, such as those for certification, licensure, and accreditation, Medicare, state Medicaid and, if applicable, JCAHO. 6.9 Implements necessary corrective action based on accurate analysis of non-compliance areas. 7.1 Builds and maintains trust relationships with customers. 7.4 Empowers staff to develop new ideas and standards to exceed customer expectations. 28 | P a g e Scale 10 MANAGING RESOURCES Performance Descriptions The Leader in Long Term Care: A Pro-actively is involved in budget development; consistently monitors and modifies budget variances; integrates creative staffing patterns, optimizes non-personnel resources; and seeks opportunities for positive financial outcomes. B Is involved in budget development; routinely monitors budget variances; and analyzes and implements modifications through flexible staffing patterns and non-personnel resources management. C Understands the budget process; manages personnel and non-personnel resources to established budget; and reviews budget reports and assists with developing modifications as directed. D Exhibits limited ability to understand budget process; requires assistance with analyzing and modifying budget variances; and displays minimal capability to manage resources. E Lacks knowledge and ability to contribute to the budget process; and displays inability to adjust resources relating to fluctuations in census and/or acuity. OPTIMAL PERFORMANCE CHARACTERISTICS The Long Term Care Leader is integral in creating a positive financial outcome. He/she has an in-depth knowledge of the budget process and is able to analyze budget variances. Utilizing creativity and sound judgment the is able to manage resources effectively. integrates methods for monitoring and modifying budget priorities based on the department’s performance throughout the year. He/she tracks the financial performance through regular reports. The leader maintains current knowledge of reimbursement programs and methodology. maintains staffing within budgeted hours. He/she continually creates flexible staffing patterns to meet the needs of the changing resident population. He/she is knowledgeable about any state imposed or company standards. manages non-personnel resources to minimize negative impact on financial operations. He/she empowers the staff then holds them accountable for efficient use of resources. The leader is involved with product selection to define the facility/client needs and assure best cost-in-use. 29 | P a g e SUPPORTIVE DATA (current or past activities) may include, but are not limited to: Ways the department leader positively impacts the budget such as inventorying wheelchairs/seating plans to establish a realistic budget and determine new purchases; Helps identify and evaluate new products and provides feedback on pricing comparisons Refocusing budget variances; Example: review of PAR levels such as linen and incontinent products, current usage, programs and services, and methods to reduce loss Involvement in the budget process; Approaches for selecting and managing nonpersonnel resources; Example: how staff is accountable for resource utilization: Participation in a “Going Green Team” Examples of state and or company staff standards Examples of modifications to census and acuity fluctuation; Situational examples of leader initiated modifications COMPETENCY CROSS REFERENCE Primary 4.4, 5.1, 5.1.1, 5.1.2, 5.3, 5.3.1, 5.3.2, 5.5, 5.5.1, 5.5.2, 5.5.3, 5.6, 5.7, 5.8 4.4 Ensures staffing patterns and processes which maximize resident care and deployment of staff. 5.1 Continually collects and assesses staffing, equipment, and supply data to note budget implications. 5.1.1 Makes realistic budget projections. 5.1.2 Considers clinical profit and loss information. 5.2 Develops a realistic budget for nursing and other departments which meets objectives and financial parameters. 5.3 Monitors revenues and expenses throughout the year. 5.3.1 Uses regular reports (daily, weekly, monthly, and quarterly) to track expenditures. 5.3.2 Modifies budget priorities, based on budget variances. 5.5 Manages non-personnel resources to minimize negative impact on financial operations. 5.5.1 Develops creative and efficient use of budget resources. 5.5.2 Monitors adequate inventory of supplies and equipment. 5.5.3 Engages staff in exploring best use of budget resources. 5.6 Delegates and then holds staff accountable for efficient use of resources. 30 | P a g e 5.7 Establishes and nurtures vendor relationships to obtain facility/client supplies at best prices. 5.8 Keeps current on reimbursement program regulations and methodology. 31 | P a g e Scale 11 COMMUNICATING EFFECTIVELY Performance Descriptions The Leader in Long Term Care: A Pro-actively demonstrates that he/she values the diversity of others; models effective communication through varied and appropriate use of all communication skills and styles, including appropriate use of humor, and is clear and concise in all communications, also actively solicits feedback; and maintains safe trusting relationships, honoring noncompromising confidences. B Acknowledges respectfully the diversity of others; demonstrates clear communication skills using multiple techniques including active listening and regularly requests feedback; and maintains a safe, approachable, and trustworthy environment for communication, honoring appropriate confidences. C Recognizes the diversity of others; demonstrates adequate communication utilizing written, spoken, and listening methods as well as non-verbal skills, also seeks feedback; and can establish a safe, trustworthy environment for communication. D Demonstrates limited understanding of diversity; displays inappropriate use of humor, and uses written and spoken methods of communication with minimal listening and nonverbal skills; and often betrays confidences. E Exhibits disregard for the diversity of others; has poor communication skills, interacting primarily via written memos/letters; and lacks professional discretion. OPTIMAL PERFORMANCE CHARACTERISTICS Positive, effective communication is essential in the professional workplace and is achieved by the Long Term Care Leader through maximizing interpersonal skills. By understanding and respecting the diversity of all with whom information is shared, utilizing varied appropriate communication styles and skills, and being a trusted leader who honors confidences, the leader can effectively communicate. understands the diversity among the persons with whom he/she communicates, the leader maintains effective communication. He/she serves as a liaison between staff, residents/patients, and their family members, with community professionals and leaders. The leader respects the beliefs, values, and customs of individuals, which enables him/her to communicate effectively and interact sensitively with various populations, based on their needs, interests, and desired results. Diversity extends beyond ethnicity to include perspective distinction by persons of differing ages, gender, spirituality, socioeconomic status, educational level, and geographical homeland etc. The leader might demonstrate 32 | P a g e this awareness by supporting various special events/holidays celebrations in the facility and soliciting personal preferences for type and timing of communication. He/she adapts his/her communication style by such means as modifying vocabulary or using large-print lettering. He/she maintains a nonjudgmental decorum as evidenced by neutral and clearly value-free communications and actively seeks to understand the all viewpoints. uses various communication styles and skills in order to achieve positive and effective communication. He/she is adept in selecting the proper style for different situations. The leader exhibits a mastery of writing, listening, and speaking skills; utilizes appropriate humor; actively solicits feedback, and understands the importance of nonverbal communication. He/she is able to intently focus on the conversation, actively listening to the participant(s). He/she is clear and concise in all communications, including performance expectations, making decisions, and managing conflict as well as to newly admitted residents and family members. building, maintaining, and inspiring mutual trust and confidence is a vital component of all communication. The leader is able to create and secure a safe, comfortable environment which is open to the exchange of information, including complaints. Via qualities of honesty, sincerity, and consistency, he/she models professional behavior and discretion in all interactions. The leader honors confidentiality when it does not compromise laws, regulations, company business policies, or personal values. SUPPORTIVE DATA (current or past activities) may include, but are not limited to: Demonstrating knowledge of diversity of customers served by describing similarities and differences among them, and situations/events when they were honored Giving examples of times when he/she was both successful and challenged as a liaison Providing examples of multiple techniques of communication, reporting on effectiveness of each style and why it was chosen for each particular situation Describing actual situations in which humor was used either appropriately or inappropriately Demonstrating active listening skills by paraphrasing or rephrasing a participant’s communication Clear concise spoken communication skills by verbally rephrasing a written memo for a staff meeting Clear written skills by showing evidence of a delicate message sent in a letter to a family member Displaying a clear understanding of honoring confidences by defining when they can and cannot be maintained and giving an example of actual situation Describing behaviors or methods used to build a trusting relationship with challenging person(s) 33 | P a g e COMPETENCY CROSS REFERENCE Primary 1.10, 1.11.4, 1.11.5, 1.16, 1.16.1, 1.16.2, 1.16.3, 2.2, 3.1, 3.2, 3.3, 3.3.1, 3.3.4, 3.4, 3.4.1, 3.5, 3.6, 3.6.1, 3.7, 3.8, 3.8.1, 3.8.3, 3.9., 3.10, 7.1, 7.9.1, 7.9.3, 7.10.2 Secondary 1.4.1, 1.10.2, 3.3.4, 7.9.2, 7.9, 7.9.4, 7.11 Primary: 1.10 Actively seeks ongoing feedback to make necessary changes/adjustments from current to desired state. 1.11.4 Respects the beliefs, values, and customs of individuals. 1.11.5 Inspires mutual trust and confidence. 1.16 Functions as facility liaison with community professionals and leaders for: 1.16.1 Providing coordinated client care. 1.16.2 Maintaining public relations. 1.16.3 Improving community perception of the facility's image. 2.2 Communicates performance expectations clearly. 3.1 Communicates organizational values in daily work. 3.2 Communicates effectively with various populations based on their needs, interests, and desired results. Populations include nursing members, physicians, and other clinical practitioners, internal and external customers, families and visitors, and staff at all levels. 3.3 Models healthy communication. 3.3.1 Builds trust through honest interactions. 3.3.2 Extends courtesy to every person. 3.3.3 Exhibits empathy toward individuals in all situations. 3.3.4 Is sensitive to the impact of his/her communication on others. 3.4 Interacts sensitively with diverse populations. 3.4.1 Respects beliefs, values, and customs of all individuals. 3.5 Communicates effectively with all levels of the organization (senior management, peers, and employees.) 3.6 Communicates effectively through writing, speaking and listening channels. 3.6.1 Uses active listening skills. 3.8 Supports appropriate communication for small groups and teams. 3.8.1 Communicates expectations. 3.8.2 Promotes cooperative behaviors. 34 | P a g e 3.8.3 Seeks feedback in order to improve communications. 3.9 Uses effective communications in managing conflict and making decisions. 3.9.1 Presents feedback constructively. 3.10 Displays and encourages appropriate humor. 7.1 Builds and maintains trust relationships with customers. 7.9.1 Creates safe and comfortable opportunities for customers to complain. 7.9.3 Maintains confidentiality regarding resident and employee information. 7.10.2 Communicates effectively with newly admitted residents and family members to ensure that their expectations are heard and that the facility's capabilities are clear. 35 | P a g e Scale 12 FACILITATING CHANGE Performance Descriptions The Leader in Long Term Care: A Actively keeps abreast of new professional trends and innovatively seeks opportunities to improve upon current operational processes or programs; regularly involves staff in both the designing and implementation of all changes, encouraging their leaders to make calculated risk decisions in thinking out of the box for opportunities to improve; and models positive thinking/outcomes of “it can be done.” B Seeks to update operations with new professional trends, as long as they can be easily assimilated into daily structure; encourages staff to make suggestions for improvement and solicits input into the new operational design; and delegates implementation of most new programs to appropriate staff and establishes an ongoing feedback process. C Recognizes that new standards/regulations must be incorporated into operations; will occasionally consider restructuring operational systems, and will involve a select few staff in the revision of policy and/or procedures; and dictatorially implements the new processes or systems without seeking appropriate feedback. D Is open to new ideas when presented to him/her; seeks staff input into the redesigning of operations; involves the staff in the implementation; while feedback is welcomed, once established, new processes are seldom reviewed or changed. E Resists integrating new ideas/concepts into operations, preferring to stay with the “tried and true”; and when new directives are received, develops and implements change under the direct guidance of his/her immediate supervisor without staff input or involvement. OPTIMAL PERFORMANCE CHARACTERISTICS In the ever evolving and expanding world of long term care, change is constant: a way of life. The Long Term Care Leader serves as a guide and integrator of all new developed or revised policies or procedures implemented to enable the organization to keep current with growth/change in the LTC profession. He/she assures all change remains in alignment with the organization’s vision/mission. guides and integrates change in the long term care (LTC) profession, exploring the relationship of organizational strategic priorities with cues from the external environment and global trends in LTC. Maintaining current knowledge of all standards and regulations, he/she actively seeks to generate new ideas and change as appropriate. A 36 | P a g e leader uses independent judgment and discretion and integrates standards of professional practice. He/she must be flexible, adapting to new ideas and paradigms. works collaboratively with professionals, organizational managers, and staff in developing health services’ long and short range goals. He/she leads in creating systems, processes, and programs that further attain these goals. He/she advocates innovative approaches; accepts and encourages appropriate, calculated risk-taking decisions; and utilizes the collective wisdom of staff, empowering them to participate in decisions. designs implementation strategies. He/she continues to work collaboratively with other managers to execute the changes, and achieves both short- and long-term goals. The leader incorporates planning and implementation elements in every change. He/she recognizes the need for all staff to be involved, and promotes and enables interdisciplinary collaboration and cooperation. The leader seeks ongoing feedback while ensuring timely accomplishment of duties. SUPPORTIVE DATA (current or past activities) may include, but are not limited to: Providing documentation of seeking staff input into decision making and program/process changes such as: Committee meeting attendees, minutes Informal notes from rounds/stand up meetings Providing evidence of frequent communications with staff, residents, and families via staff meetings, resident councils, resident care/service plan meetings, family meetings/events, etc. Describing/displaying evidence of seeking input from peers at professional and networking meetings Giving evidence of actively seeking and receiving ongoing updates on regulatory, accreditation, and professionals standards Resident and Family Annual and Exit Satisfaction Surveys are reviewed, with complaints/ suggestions received as constructive feedback and evaluated for potential changes needed Employee Annual Satisfaction Surveys and Discharge/Resignation Exit Interviews and/or surveys are reviewed with complaints/suggestions received as constructive feedback and evaluated for potential changes needed COMPETENCY CROSS REFERENCE Primary 1.2, 1.3, 1.3.1, 1.4, 1.4.2, 1.4.3, 1.5.1, 1.7, 1.7.1, 1.7.2, 1.7.3, 1.8, 1.8.1, 1.10, 1.10.1, 1.10.2, 1.10.3, 1.11.3, 1.12, 1.13, 2.11, 2.11.1, 2.11.2, 6.1 37 | P a g e Secondary 1.11, 1.12, 1.5 Primary: 1.2 Works collaboratively with other managers to implement and achieve facility short and long term goals which are aligned with organizational vision/mission. 1.3 Collaboratively develops department's long and short range goals which are aligned with organization's vision/mission. 1.3.1 Develops implementation strategies to achieve those goals. 1.4 Leads in creating systems, processes, and programs that further attain organization's vision, mission and goals. 1.4.1 Communicates needs to upper management. 1.4.2 Reinvents his/her role as necessary to assist the organization in achieving its vision/mission. 1.4.3 Explores relationship of organization strategic priorities with cues from the external environment and global trends. 1.5.1 Helps teams and individuals maintain their focus on the organization's mission/vision. 1.7 Advocates for innovative and creative approaches to meeting organizational needs and furthering the mission/vision. 1.7.1 Models and reinforces positive thinking and positive outcomes. 1.7.2 Willingly accepts appropriate risk taking. 1.7.3 Encourages taking calculated risks in decision-making. 1.8 Is flexible, adapting to new ideas and paradigms. 1.8.1 Actively seeks new ideas and change as appropriate. 1.10 Actively seeks ongoing feedback to make necessary changes/adjustments from current to desired state. 1.10.1 Incorporates planning and implementation elements in every change. 1.10.2 Is sensitive to staff needs (at all levels) to be involved and to feel part of the organizational/facility culture. 1.10.3 Values and incorporates staff opinions in decision making. 1.11.3 Integrates standards of professional practice. 1.12 Carries out supervisory responsibilities in accordance with organizational policies and applicable laws. 1.13 Efficiently uses time management principles to ensure timely accomplishment of all duties. 2.11 Empowers staff to participate in decision-making. 2.11.1 Promotes and enables interdisciplinary collaboration and cooperation. 2.11.2 Utilizes collective wisdom and decision making capabilities of staff. 38 | P a g e 6.1 Maintains current knowledge of Federal, State, and local standards and regulations for long term care, such as those for certification, licensure, and accreditation, Medicare, state Medicaid and, if applicable, JCAHO. 39 | P a g e Scale 13 MANAGING CONFLICT Performance Descriptions The Leader in Long Term Care: A Demonstrates an in-depth understanding of skills that effectively identify and manage conflict; models effective listening skills; and applies a variety of methods to consistently manage conflict in a mutually satisfactory way. B Identifies the need for managing conflict; uses employee-appropriate methods to manage conflict; and adequately manages conflict and promotes cooperative behaviors. C Is able to identify and assist with managing conflict; and is an effective communicator using active listening skills. D Exhibits limited ability to identify and manage conflict; behaves in ways that often exacerbate conflict; and shows limited communication skills. E Lacks ability and understanding of skills necessary to identify, manage, or resolve conflict; and demonstrates poor communication skills. OPTIMAL PERFORMANCE CHARACTERISTICS The Long Term Care Leader demonstrates an in-depth understanding of skills that effectively identify and manage conflict. He/she accepts the role as mediator of conflict. The Leader is able to apply a variety of methods to consistently resolve conflict in a mutually satisfactory way. conflict can be a catalyst for positive change. The leader identifies conflict as a normal aspect of interpersonal relationships and views it as an opportunity to promote cooperative behavior. The leader ensures a complaint friendly culture; and uses active listening skills. and the leader facilitates conversations to identify underlying situational dynamics to identify conflict. employs a variety of methods to manage conflict. He/she collects objective data to determine root causes. The leader uses effective communication in managing conflict and making decisions. The leader is sensitive to his/her communication with others, presents constructive feedback, and promotes constructive behaviors. 40 | P a g e effectively manages conflict and attempts to negotiate a win/win situation. He/she models expert coaching and mentoring skills and is able to communicate expectations. The Leader promotes and enables interdisciplinary collaboration and cooperation. He/she promotes and respects the beliefs, values, and customs of individuals. These methods result in a conflict-reducing alternative that is mutually beneficial, agreeable, and acceptable. SUPPORTIVE DATA (current or past activities) may include, but are not limited to: Employee satisfaction surveys that demonstrate areas of potential conflict and/or resolution of conflict Educational programs related to conflict management, communication, and team work Team meeting techniques used to resolve or confront conflict Use of consensus generating tools Modeling of assertive behavior Modeling of effective communication skills; Examples of past conflict situations and ways resolved COMPETENCY CROSS REFERENCE Primary 2.3.1, 2.5, 2.11.1, 3.3.4, 3.6.1, 3.8.1, 3.8.2, 3.9, 3.9.1, 4.14, 7.9, 7.9.2 Secondary 1.8, 1.8.1, 1.12.2, 2.6, 2.14 Primary: 2.3.1 Identifies underlying dynamics or root cause of problems. 2.5 Collects objective data. 2.11.1 Promotes and enables interdisciplinary collaboration and cooperation. 3.3.4 Is sensitive to the impact of his/her communication on others. 3.6.1 Uses active listening skills. 3.8.1 Communicates expectations. 3.8.2 Promotes cooperative behaviors. 3.9 Uses effective communications in managing conflict and making decisions. 3.9.1 Presents feedback constructively. 41 | P a g e 4.14 Models expert coaching and mentoring. 7.9 Ensures a complaint-friendly culture. 7.9.2 Patiently facilitates conversations to uncover underlying situation dynamics. 42 | P a g e Scale 14 ADVOCATING CUSTOMER SATISFACTION Performance Descriptions The Leader in Long Term Care: A Pro-actively assesses the customer needs and actively solicits feedback from the customer; makes immediate adjustments to services in order to exceed customer expectations, and collaborates with staff to create an environment that promotes continuous quality improvement and customer service. B Actively assesses customer needs; solicits feedback from customer in order to make adjustments to services; and anticipates customer needs and collaborates with staff to enhance the quality of service. C Assesses customer needs and expectations; requests customer input in order to make adjustments to services; and communicates information to staff and seeks to meet the needs and expectations of the customer. D Shows some awareness of customer needs and expectations; makes limited adjustments to accommodate customer needs and lacks enthusiasm in pursing objective data; and is unable to collaborate with staff. E Lacks awareness of customer needs and expectations; makes adjustments in an attempt to accommodate customer needs only as directed; and lacks understanding of the continuous quality improvement process. OPTIMAL PERFORMANCE CHARACTERISTICS Standards of care are driven by customer satisfaction and regulations. The customers we refer to in this scale are our residents, family members and staff. The Long Term Care Leader must be able to assess the customer needs, meet the customer needs, and evaluate the standards of care to deliver high value service to the customer. establishes a strong trust relationship with the customer by recognizing the individual needs, values and priorities. The leader uses a variety of methods to pro-actively assess the customer needs on a consistent and on-going basis; such as with pre-admission questionnaires or customer satisfaction surveys. The leader assures a timely response to customers by developing new systems and upgrading existing ones to accommodate changing customer needs and expectations. 43 | P a g e The leader actively initiates contact with customers in order to be pro-active in his/her approach to meet the customer needs. The leader communicates effectively with newly admitted residents and family members to ensure that their expectations are heard and that the facility’s capabilities are clear so as to assure a smooth transition at admission. The Leader seeks ways to obtain feedback and makes immediate adjustments to services and programs being provided. Some examples might include minutes from resident council meetings or customer complaints/ grievances. elevates the standard of care through an organized process directed at improving programs or service delivery systems. He/she uses objective data to analyze problems and measure outcomes to enhance continuous improvement. The leader assures followthrough on customer issues. By example and in collaboration with staff, he/she creates an environment that promotes continuous quality improvement and customer satisfaction. Examples might include QI/PI programs that demonstrate the positive effect of the standards and satisfied our customer. SUPPORTIVE DATA (current or past activities) may include, but are not be limited to: Methods used to obtain feedback such as formal and informal satisfaction surveys; Employee of the Month Programs, Going Green Tip of the Month, etc. Methods used to assess customer needs such as customer satisfaction surveys Examples of any adjustments to services or programs to meet the customer needs Examples of a situation when the has collaborated with staff to create a new program that increased customer satisfaction Examples of a program that exceeded your customer’s expectation COMPETENCY CROSS REFERENCE Primary 1.1, 1.10, 2.5, 7.1, 7.2, 7.3, 7.5, 7.6, 7.10, 7.10.1, 7.10.2, 7.11 Secondary 1.4 Primary: 1.1 Models the organization's values and mission/vision in his/her daily work and interactions with others. 1.10 Actively seeks ongoing feedback to make necessary changes/adjustments from current to desired state. 2.5 Collects objective data. 7.1 Builds and maintains trust relationships with customers. 44 | P a g e 7.2 Initiates customer feedback to determine satisfaction. 7.3 Conducts ongoing customer service monitoring in order to assess customer needs, expectations, and priorities. 7.5 Makes adjustments to current services to accommodate changing customer needs and expectations. 7.6 Ensures timely response to customers, by both developing new systems and upgrading existing ones. 7.10 Assures smooth transition of new admissions. 7.10.1 Reviews new and potential admissions to ensure needs can be met. 7.10.2 Communicates effectively with newly admitted residents and family members to ensure that their expectations are heard and that the facility's capabilities are clear. 7.11 Assures follow-through on customer issues. 45 | P a g e