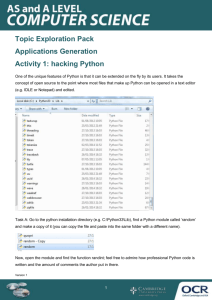
Flowcharts to Python: Activity Workbook
advertisement

From Flowcharts to Python Activity Workbook LLiissaa M M.. O Olliivviieerrii,, S SS SJJ,, P PhhD D From Flowcharts to Python This Activity Workbook introduces students who already know flowchart fundamentals to the Python Programming language. The materials in this booklet were developed to help students collaborate with each other in the learning process and to become self-learners in an active learning environment. Students learn programming concepts by doing programming and reflecting on the results of the activities that they engage in. Author: Lisa M. Olivieri, SSJ, Ph.D. 2 Name: _______________________________________ Partners: ________________________________ Python Activity 1: Flowcharts and Python “What is the relationship between a flowchart and a Python program?” Learning Objectives Students will be able to: Content: Explain how to display data in Python Explain how to create a comment in Python Determine the difference between a string literal and a number Process: Create print statements in Python Create Python code that displays results to calculated addition facts Discuss problems and programs with all group members Prior Knowledge Understanding of flowchart output symbols Further Reading Transitioning from Visual Logic to Python: Chapter 1 Critical Thinking Questions: Python Program Flowchart 1. What does the line of Python code in the Python program do? _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ 2. Circle equivalent representation of the Python code in the flowchart. 3. Execute following code. What output is produced? a. print(“Hello, my name is Pat!”) ________________________________ b. print(Hello, my name is Pat) ________________________________ c. print(“Hello.\nMy name is Pat”) ________________________________ Python Activity 1: Flowcharts and Python 4. Was there a problem with any of the sample code in question 3? If so, what caused the problem? ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 5. What caused the different output format for samples “a” and “c” in question 3? ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 6. What do you think the following Python statements output? a. print(2+5) _________________________ b. print(2*5) _________________________ c. print(“2+5”) _________________________ d. print(“Age:”,20) _________________________ Enter the statements in the Python interpreter to verify your answers. 7. Examine the output for each statement in question 6. a. What is the difference in the output for the statements in “a” and “c” of question 6? ______________________________________________________________________________ b. What caused the difference? ____________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ c. Which statements contain a string literal? ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ d. What does the comma (,) do in the print statement in part “d” of question 6? How does it affect the spacing of the output? ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 8. Examine the following code and its output. What do the first three lines of the program do? Output ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 4 Python Activity 1: Flowcharts and Python 9. What would happen if you placed a “#” in front of the code: in the previous program? ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ Application Questions: Use the Python interpreter to design and check your work 1. Create a Python program containing three statements to implement the flowchart on the first page of this activity. Write the statements below. 2. Create one Python statement to produce the output expected from the flowchart. Be sure the output is printed on three lines. 3. Create a Python program containing two statements that prints the output to the right. Have the program calculate the answers to the two arithmetic problems. 5 Python Activity 1: Flowcharts and Python Notes and Questions Make note of any questions you have about Activity 1 on this page. 6 Name: _______________________________________ Partners: ________________________________ Python Activity 2: Input and Variables in Python “How do you input and store data in a Python program?” Learning Objectives Students will be able to: Content: Explain how to input data in Python Explain the meaning and purpose of a variable Determine if a variable name is valid Explain concatenation and the use of “+” Process: Create input statements in Python Create Python code that prompts the user for data and stores it in a variable Create valid and good variable names Prior Knowledge Understanding of flowchart input symbols Further Reading Transitioning from Visual Logic to Python: Chapter 2 Critical Thinking Questions: Python Program Flowchart Program 1. Enter and execute the Python program. What is printed on the screen when the Python program is executed? _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ FYI: input() and print() are functions in Python. 2. Draw a line between each flowchart symbol and its corresponding Python code. Python Activity 2: Input and Variables in Python 3. Examine the first line of Python program: name = input(“What is your name? ”) a. What happens when this line of code is executed? ______________________________________________________________________________ b. What appears on the screen when this line of code is executed? ______________________________________________________________________________ FYI: The words that appear on the screen to tell the user what to enter are known as a prompt. c. What happens to the data when the user enters their name and presses the Enter button? That is, where is their name stored? ______________________________________________________________________________ FYI: The word name in the Python code is a variable – name given to a memory location used to store data. 4. What happens when you execute each of the following lines of Python code? a. name? = input(“What is your name?”) ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ b. your name = input(“What is your name?”) ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ c. 1st_name = input(“What is your name?”) ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ d. from = input(“Where were you born?”) ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 5. Examine the errors that occurred when executing the lines of code in question 5. Then examine the following lines of valid code. name2 = input(“What is your name?”) your_name = input(“What is your name?”) yourName = input(“What is your name?”) List the rules that need to be followed to create a valid variable name. ________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________ 8 Python Activity 2: Input and Variables in Python 6. Are the following variable names valid? Are they good names? Why or why not? Variable name price costoffirstitem Ic firstName 7. Comments about variable name Execute the following lines of code. Is the output what you would expect? Why or why not? _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ 8. Use the following set of Python statements to answer the questions below. a. State the output for each of line of code. _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ b. Examine the first two print statements. How are they different? Does the difference affect the output? _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ c. Notice that some statements include a comma (,) between the two literals being printed and some statements use a “+”. Do they produce the same output? ____________________ d. Explain the purpose of the comma. _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ e. Why does the last print statement crash the program? What would you do to correct it? _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ FYI: “+” concatenates two strings. The strings can be string literals or a variable containing string literals. 9 Python Activity 2: Input and Variables in Python 9. State what is displayed on the screen when the following program is executed: _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ Application Questions: Use the Python Interpreter to input your code and check your work 1. State a good variable name for an employee’s ID number. ________________________________ 2. Write a line of Python code that prompts the user for the name of their favorite ice cream and stores it in a valid variable name. __________________________________________________________ 3. Crazy Sentence Program. Create a program that prompts the user for the name of an animal, a color, the name of a vehicle, and the name of a city. Then print a sentence that contains the user input in the following order. Include the additional words in the sample output as part of your output. Example: Assume the user enters the words: tiger, green, motorcycle, and Wildwood. The output would be: The green tiger drove the motorcycle to Wildwood. _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ Notes and Questions Make note of any questions you have about Activity 2 on this page. 10 Python Activity 3 Part A: Arithmetic Operations and Assignment Statements Name: _______________________________________ Partners: ________________________________ Python Activity 3 Part A: Arithmetic Operations and Assignment Statements “Get the program to compute that!” “How do I assignment values to variables?” Learning Objectives Students will be able to: Content: Explain each Python arithmetic operator Explain the meaning and use of an assignment statement Review string literals and print statements Explain the use of “+” and “*” with strings and numbers Use the int() and float() functions to convert string input to numbers for computation Incorporate numeric formatting into print statements Recognize the four main operations of a computer within a simple Python program Process: Create input statements in Python Create Python code that performs mathematical and string operations Create Python code that uses assignment statements Create Python code that formats numeric output Prior Knowledge Understanding of Python print and input statements Understanding of mathematical operations Understanding of flowchart input symbols Further Reading Transitioning from Visual Logic to Python: Chapter 3 Critical Thinking Questions: Python Program Flowchart Program 11 Python Activity 3 Part A: Arithmetic Operations and Assignment Statements 1. Execute the print statements in the Python program. What is the output for each statement? _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ 2. Draw a line between each flowchart symbol and its corresponding line of Python code. 3. Explain the purpose of each arithmetic operation: a. + ________________________________________________________________________ b. - ________________________________________________________________________ c. * ________________________________________________________________________ d. ** ________________________________________________________________________ e. / _______________________________________________________________________ f. // _______________________________________________________________________ g. % _______________________________________________________________________ FYI: An assignment statement is a line of code that uses a “=” sign. The statement stores the result of an operation performed on the right-hand side of the sign into the variable memory location on the lef0hand side. 4. Enter and execute the following two lines of Python code: age = 15 print(“Your age is”, age) a. What does the assignment statement: age = 15 do? ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ b. What happens if you replace the comma (,) in the print statement with a plus sign (+) and execute the code again? Why does this happen? ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 5. What is stored in memory after each assignment statement is executed? Assignment Statement answer = 6 ** 2 + 3 * 4 // 2 final = answer % 4 Computer Memory Answer Final 12 Python Activity 3 Part A: Arithmetic Operations and Assignment Statements 6. What happens if you try to use the “+” with strings instead of numbers? Test the following program: The third line of code contains an assignment statement. What is stored in fullName when the line is executed? ______________________________________________________________________________ a. b. How can you fix the output so that the words are separated? ______________________________________________________________________________ FYI: The “+” concatenates the two strings stored in the variables into one string. The assignment statement stored the results in the variable fullName. “+” can only be used when both operators are strings. c. What happens when you execute the following code? Why? ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 7. Before entering the following code into the Python interpreter, try to figure out what you think the statement should print. Now execute it. What does it do? Is this what you thought it would do? ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 8. Let’s take a look at a program that prompts the user for two numbers and subtracts them. Execute the following code. a. What output do you expect? _____________________________________________ b. What is the actual output? _____________________________________________ c. Revise the program in the following manner: Between lines 2 and 3 add the following lines of code: num1 = int(firstNumber) num2 = int(secondNumber) 13 Python Activity 3 Part A: Arithmetic Operations and Assignment Statements Next, replace the statement: difference = firstNumber – secondNumber with the statement: difference = num1 – num2 Execute the program again. What output did you get? ________________________ d. Explain the purpose of the function int(). ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ e. Explain how the changes in the program produced the desired output. ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ Application Questions: Use the Python Interpreter to check your work 1. Write the line of Python code that calculates and prints the answer to the following arithmetic expressions: a. 8 to the 4th power ___________________________________________________ b. The sum of 5 and 6 multiplied by the quotient of 34 and 7 using floating point arithmetic _______________________________________________________________________ 2. Write an assignment statement that stores the remainder obtained from dividing 87 and 8 in the variable leftover ______________________________________________________________________________ 3. Assume: courseLabel = “CMSC” courseNumber = “190” Write a line of Python code that concatenates the label with the number and stores the result in the variable courseName. Be sure that there is a space between the course label and the course number when they are concatenated. _________________________________________________________________ 4. Create a program the outputs the total cost of a lunch order. Users should be prompted to input the number of hamburgers, fries, and drinks they want and the program should print the total cost of the order. The hamburgers cost 2.00, fries cost 1.50, and drinks cost 1.00. Be creative and professional in prompting the user for the information and in displaying the output. ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 14 Name: _______________________________________ Partners: ________________________________ Python Activity 3 Part B: Arithmetic Operations and Assignment Statements “Get the program to compute that!” Learning Objectives Students will be able to: Content: Incorporate numeric formatting into print statements Recognize the four main operations of a computer within a simple Python program Process: Create Python code that uses assignment statements Create Python code that formats numeric output Prior Knowledge Understanding of Python print and input statements Understanding of mathematical operations Understanding of flowchart input symbols Further Reading Transitioning from Visual Logic to Python: Chapter 3 Critical Thinking Questions: 1. So far you have not been concerned about formatting output on the screen. Now you will discover how Python allows a programmer to precisely format output. Some of the differences are very subtle, so take notice of the differences in outputs. Start by entering and executing the following code. a. What is the problem with the manner in which the output is displayed? _____________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ b. Replace the last line of code with the following: print("Total cost of laptops: %.2f" % price) Discuss the change in the output. _____________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ c. Replace the last line of code with the following: print("Total cost of laptops: $%.2f" % price) Discuss the change in the output. ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ Python Activity 3 Part B: Arithmetic Operations and Assignment Statements d. Experiment with the number “.2” in the print statement by substituting the following numbers and explain the results. .4 ________________________________________________________________________ .0 ________________________________________________________________________ .1 ________________________________________________________________________ .8 ________________________________________________________________________ e. Now try the following numbers in the same print statement. These numbers contain a whole number and a decimal. Explain the output for each number. 2.5 _______________________________________________________________________ 8.2 _______________________________________________________________________ 3.1 _______________________________________________________________________ f. Explain what the formatting code: “%n.nf % variable” does in a print statement where n.n represents a number. _____________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ g. Revise the print statement by changing the “f” to “d” and the decimal number to a whole number. Explain the sample formatting statements: print("Total cost of laptops: %2d" % price) print("Total cost of laptops: %10d" % price) ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ h. Explain how “%nd % variable” formats numeric data. “n” represents a whole number. ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ FYI: Computers perform four main operations on data: Input data into a computer Output data to a screen or file Process data using arithmetic, logical, searching or sorting operations Store data 2. Use the following program to answer the questions below. 16 Python Activity 3 Part B: Arithmetic Operations and Assignment Statements a. Using the code and comments in the program listed above, explain how the four main operations are implemented in the program. ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ b. There is one new concept exemplified in this sample program. What is it? From the corresponding output, determine what it does. ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ Application Questions: Use the Python Interpreter to check your work 1. Write one line of Python code that will print the word “Happy!” one hundred times. ______________________________________________________________________________ 2. 3. Assume: itemCost = input(“Enter cost of item: “) a. Write one line of code that calculates the cost of 15 items and stores the result in the variable totalCost ________________________________________________________________________ b. Write one line of code that prints the total cost with a label, a dollar sign, and exactly two decimal places. Sample output: Total cost: $22.50 ________________________________________________________________________ height1 = 67850 height2 = 456 Use Python formatting to write two print statements that will produce the following output exactly at it appears below: Assume: ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 4. You have already completed the following program in a previous activity. Format the output. Create a program the outputs the total cost of a lunch order. Users should be prompted to input the number of hamburgers, fries, and drinks they want and the program should print the total cost of the order. The price of hamburgers is 2.00, fries is 1.50, and drinks is 1.00. Be creative and professional in prompting the user for the information and in displaying the output. _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ 17 Python Activity 3 Part B: Arithmetic Operations and Assignment Statements Notes and Questions Make note of any questions you have about Activity 3 on this page. 18 Name: _______________________________________ Partners: ________________________________ Python Activity 4: Predefined Functions “How can I use the built-in code that is already part of Python?” Learning Objectives Students will be able to: Content: Explain the purpose of a predefined function Explain the functions: abs(), pow(), int() round(), random Explain the math library functions: floor() and ceil() Explain the use of the import statement Explain the purpose of a function argument Process: Write code that uses predefined functions Prior Knowledge Python concepts from Activities 1-3 Understanding of flowchart input symbols Further Reading Transitioning from Visual Logic to Python: Chapter 4 Model 1: Predefined functions in Python print(), round(), abs(), pow(), int(), etc. are known as predefined functions. Information that a function needs to do its work is sent to the function between the parentheses (). This information is known as an argument. To use a function, call the function. input(“Enter your name”) is a call to the input function sending the string “Enter your name” as an argument Critical Thinking Questions: 10. Circle the predefined functions in the following program. 11. Draw a line between each statement in the Python program and its corresponding statement in the flowchart. Python Activity 4: Predefined Functions 12. Enter and execute the Python program on the previous page. a. What is the output for each statement ? print(abs(-4.67)) _________________________ print(pow(5,3)) _________________________ print(pow(49,.5)) _________________________ print(int(34.8)) _________________________ print(round(6.9)) _________________________ import random print(random.randint(1,100)) ___________________ b. What is the difference between the round() function and the int() function? ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 4. What is the output for each line of code? Verify your answers by executing the code and explain the answer given by the interpreter. a. abs(4.5) _________________________________________________ b. int(“678”) _________________________________________________ c. round(-5.6) _________________________________________________ d. import random random.randint(4,10) ___________________________________________ What is the purpose of “import random”? What happens if you omit that line of code? ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 5. Write a definition of a predefined function. ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 6. Circle the argument in the following predefined function: number = 45.78 answer = round(number) 7. How many arguments can a function have? 8. answer = pow(4,3). What is/are the argument(s) in this code? ______________________ 9. If a function contains more than one argument, do you think the order of the arguments makes a difference? Explain your answer. ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________ 20 Python Activity 4: Predefined Functions 10. Execute the following code: import math x = 4.7 y = 5.3 z = -4.8 a = -3.2 print(math.ceil(x)) print(math.ceil(y)) print(math.ceil(z)) print(math.ceil(a)) print(math.floor(x)) print(math.floor(y)) print(math.floor(z)) print(math.floor(a)) a. Explain what the ceil() function does. ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ b. Explain the purpose of the floor() function. ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ c. Why are the calls to the math() and ceil() functions preceded by “math.”? ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ Application Questions: Use the Python Interpreter to check your work 1. Write a line of code that prints the integer portion of the number 21.45. ______________________________________________________________________________ 2. Write code that prompts the user for a floating point number and prints the smallest integer that is larger than the number the user entered. ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 3. Write a line of code that prints a random number between one and 6. ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 4. Assume that a user enters any number and that the number is stored in the variable userNumber. Write a line of code that converts the input to a float. Then write a line of code that prints the positive value of the user’s input. ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 5. Write a line of code that calculates the square root of 900 and stores the result in the variable answer. ______________________________________________________________________________ 21 Python Activity 4: Predefined Functions Notes and Questions Make note of any questions you have about Activity 4 on this page 22 Name: _______________________________________ Partners: ________________________________ Python Activity 5: Boolean Expressions and Selection Statements “True or False and making choices” Learning Objectives Students will be able to: Content: Explain the three types of programming structures Explain how conditional operators and logical operators are used in programming Use conditional operators with strings and numeric values Implement the Python syntax of an if/else statement Determine good test data for programs that include if/else statements Process: Write code that includes if statements and if/else statements Write correct Boolean expressions and compound expressions Prior Knowledge Python concepts from Activities 1-4 Understanding of flowchart input symbols Further Reading Transitioning from Visual Logic to Python: Chapter 5 Model 1: Programming Structures Sequence Structure Decision or Branching Structure Looping Structure Critical Thinking Questions: 1. Each of the flowchart symbols in the chart above represents lines or segments of code. After examining the chart, write a description of: a. sequence structure ________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ b. decision or branching structure _____________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ c. looping structure ____________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ Python Activity 5: Boolean Expressions and Selection Statements 2. Which structure best describes the types of Python programs you have written so far? Do you think this structure is the best structure to use for all programs? Why or why not? ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 3. Which structure allows the programmer to create code that decides what code is executed? _____________________________________________________________________________ Model 2: Conditional Operators Conditional operators, also known as relational operators, are used to compare the relationship between two operands. Expressions that can only result in one of two answers are known as Boolean expression. 4. Determine the meaning of each of the following conditional operators. If you are not sure of the meaning of any symbol, create some example expressions, type them into the Python interpreter (see figure to the right) and examine the results. a. < ___________ b. > ____________ c. <= ___________ d. >= ____________ e. != ___________ f. == ____________ 5. What is the result of each of the following expressions? Assume x = 4, y = 5, z = 4 a. x>y ______________________________________ b. x<y ______________________________________ c. x == y ______________________________________ d. x != y ______________________________________ e. x >= z ______________________________________ f. x <= z ______________________________________ g. x+y>2*x ______________________________________ h. y * x – z != 4 % 4 + 16 ______________________________________ i. pow(x,2) == abs(-16) ______________________________________ 6. What is the result of the following expressions? Assume word1 = “hello”, word2 = “good-bye” a. word1 == word2 ______________________________________ b. word1 != word2 ______________________________________ c. word1 < word2 ______________________________________ d. word1 >= word2 ______________________________________ 24 Python Activity 5: Boolean Expressions and Selection Statements 7. Explain how the conditional operators are used when the operands are strings. ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 8. There are only two possible answers to the expressions in questions 5 and 6. What are they? _______________________________________________________________________________ Model 3: IF/ELSE Statement Flow chart Python Program 9. What is the Python code equivalent of the diamond flowchart symbol in the program above? ________________________________________________________________________ 10. Enter and execute the following code. Use various values for the original cost and the sale price. Explain what the following lines of code do. Each line appears in the program above. a. originalPrice = int(originalPriceString) ________________________________________________________________________ b. percentOff =(originalPrice - salePrice)/originalPrice * 100 ________________________________________________________________________ c. print("Sale price: $%.2f" %salePrice) ________________________________________________________________________ d. print("Percent off: %2d" % percentOff + "%") ________________________________________________________________________ e. if percentOff >= 50: print("You got a great sale!") ________________________________________________________________________ 25 Python Activity 5: Boolean Expressions and Selection Statements 11. Revise the program in #10. If the percent off is 50% or more print “Congratulations!” in addition to what is already printed. Use a second print statement to do this. Write the code for this part of the program. ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 12. Revise the program in #12 so that it prints “Done!” when the program is complete – no matter what the percent off is. How does the placement of this line of code differ from the placement of the code created for #12? ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ Python Program Flowchart 13. Compare the flowchart above with the corresponding Python Program. Carefully compare if/else statement in the two programs. Enter and execute the Python program above. a. Test the program at least three times. List the three test data you used and the corresponding output. Explain why they were the best data to use as a test for the program. ___________________ __________________ ___________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 26 Python Activity 5: Boolean Expressions and Selection Statements b. Now you want to add another print statement to the Python program above so that it printed “That’s really hot!” when the water is 212 degrees or hotter. Rewrite the code below with this statement included. ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ FYI: We can use logical operators to determine logic between conditions (relational expressions). 14. Sometimes you want to test more than one condition to determine which code segment should be executed. You can use the following logical operators to create compound conditions. Examine each operator and a sample of its use. Provide an explanation of how each operator works. Operator 15. Example Explanation and (age >= 17) and (hasLicense = = true) or (cost < 20.00) or (shipping = = 0.00) not not (credits> 120) Assume the value of the variable numBooks is 40. State the values of each of the Boolean expression. Expression (numBooks > 5) and (numBooks < 100) Value (numBooks < 5) or (numBooks > 100) not(numBooks * 10 == 100) 16. Suppose you want to determine if a student is ready to graduate. The 3 criteria for graduation are that the student has earned at least 120 credits, their major GPA is at least 2.0 and their general GPA is also at least 2.0. Missing Boolean expression 27 Python Activity 5: Boolean Expressions and Selection Statements Which Boolean expression would be the correct test for Python code? a. numCredits >= 120 or majorGPA >= 2.0 or overallGPA >= 2.0 b. numCredits > 120 and majorGPA > 2.0 or overallGPA > 2.0 c. numCredits > 119 and majorGPA >= 2.0 and overallGPA >= 2.0 d. numCredits >= 120 and majorGPA >= 2.0 and overallGPA >= 2.0 17. Enter and execute the program in #16. Include your choice for the correct Boolean expression. Create several data sets to test all possibilities for the Boolean expression. List the data you used to test all possibilities for the expression. Data Set 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 numCredits majorGPA overallGPA Expression Result (True or False) Application Questions: Use the Python Interpreter to check your work 1. Write a Boolean expression that tests if the value stored in the variable num1 is equal to the value stored in the variable num2. ______________________________________________________________________________ 2. Write a Boolean expression that tests if the value stored in the variable time is less than the value stored in the variable maxTime or if the value stored in the variable cost is less than the value stored in the variable maxCost ______________________________________________________________________________ 3. Write the code for an if statement that adds 5 to the variable num1 if the value stored in the variable testA equals 25. Otherwise subtract 5 from num1. ______________________________________________________________________________ 4. Write the code for an if statement that prints a random number between one and 6 if the value stored in the variable isValid equals the Boolean value true. ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 28 Python Activity 5: Boolean Expressions and Selection Statements 5. Write a Python program that prompts the user for the cost of two items to be purchased. Then prompt the user for their payment. If they enter an amount that is less than the total cost of the two items, print a message that tells them how much they still owe. Otherwise, print a message that thanks them for their payment and tells them how much change they will receive. Thoroughly test your code for all possible input. ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 6. Write a Python program that prompts the user for a word. If the word comes between the words apple and pear alphabetically, print a message that tells the user that the word is valid, otherwise, tell the user the word is out or range. ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 7. Write a Python program that prompts the user for a multiple of 5 between 1 and 100. Print a message telling the user whether the number they entered is valid. ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 29 Python Activity 5: Boolean Expressions and Selection Statements Notes and Questions Make note of any questions you have about Activity 5 on this page. 30 Name: _______________________________________ Partners: Python Activity 6: Functions ________________________________ “Modularizing your code” Learning Objectives Students will be able to: Content: Explain the meaning and purpose of a function Recognize a function definition, function header, and function call in a program Combine the use of functions with if/else statements Explain programs that use the same function multiple times Use good test data for programs that include functions Process: Write code that includes function definitions and function calls Write programs that incorporate functions and if/else statements Prior Knowledge Python concepts from Activities 1-5 Understanding of flowchart input symbols Further Reading Transitioning from Visual Logic to Python: Chapter 6 Critical Thinking Questions: Python Program Flowchart Python Activity 6: Functions FYI: A function is a segment of code that performs a single task. 1. Closely examine the flowchart and Python program above. a. Draw arrows between each flowchart symbol and the equivalent Python code. FYI: A function definition is the segment of code that tells the program what to do when the function is executed. The first line of a function definition is known as the function header b. 2. What Python keyword is used to indicate that a code segment is a function definition? ________________________________________________________________________ c. What is the function header in the Python code above? ________________________________________________________________________ d. The name of the function is in the function header. What is the name of the function? ________________________________________________________________________ e. Examine the Python function. Explain the syntax required for a function: indentation, etc. ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ f. Enter and execute the Python program. What is the output? ________________________________________________________________________ g. What line of code would you add to the program to print the last two lines twice? Where would you add the code? ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ Examine the following program a. Label the function definition and the function call. b. The function call and the function definition each include a variable within the parentheses. The variable in this role is known as an argument. What is the argument in the function definition? What is its purpose? ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 32 Python Activity 6: Functions c. In this example the argument in the function definition and the argument in the function call have the same name. Is this required? _______________________________ d. Enter and execute the program. Verify your answer to question ‘c’ by changing the variable name in the main program from radius to number. Do not change the variable name in the function definition. Does the program still work? __________________ e. Write a line of code that calls the calculateArea function and sends the value “6” as the argument. Add the line of code to the main program and execute it to be sure it works properly. _______________________________________________________________ f. Add a second function to the program that calculates and prints the diameter of a circle, given the radius as an argument (parameter). Place the function definition above the main part of the program. Write the function below. ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ g. Add another line of code to the main part of the program that calls the function that was created in part ‘f’. Send the radius entered by the user as the argument to the function. ________________________________________________________________________ 3. What is the purpose of a function? Why do programmers use them? ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 4. Carefully examine the following program. a. What is the first line of code executed by the Python interpreter? ________________________________________________________________________ 33 Python Activity 6: Functions b. Enter and execute the program. Use the following test data and indicate what the output is for each set of data. Data Set 1 2 3 4 Operand 1 2 3 34 4 Operand 2 6 8 23 5 Operator Result + + / c. What problems did you notice when you entered Data Sets 3 and 4? ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ d. Add code to the program that would warn the user about the problems that could occur when data similar to that in Data Sets 3 and 4 are entered. See sample output below. List the lines of code below the sample output. ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 34 Python Activity 6: Functions FYI: So far, the functions you have printed any results within the function. They did not send back any information to the original calling code. Functions that do not send back information to where they are called are known as void functions. Functions often send back or return the result and are known as value returning functions. 5. 6. Enter and execute the code below. Carefully examine the code. a. What is the new keyword used in the function definition? What do you think the keyword tells the program to do? ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ b. Write the line of code from the program that includes the function call to getSmaller. ________________________________________________________________________ c. In a void function, the function call is on a line by itself. Why is this function call placed on the right-hand-side of an assignment statement? ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ d. What are the arguments used for the function call? _______________________________ Examine the following Python program. a. b. What does the program do? ________________________________________________________________________ Circle the function call. What is different about the placement of the function call? ________________________________________________________________________ 35 Python Activity 6: Functions 7. c. Is the function a void function or a value returning function? ____________________ d. Why is the import statement needed in this program? _______________________________________________________________________ The following Python program performs the same operations and produces the same output as the previous program. Describe the major differences between the two programs. Edit the previous program so that it looks like this one and execute it. ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ Application Questions: Use the Python Interpreter to check your work 1. Write a function that draws a frog. Call the function to be sure it works. Sample frog: ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 36 Python Activity 6: Functions 2. Expand the program in #1 to produce the following output. ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ 3. Write a Python program that prompts the user for three words and prints the word that comes last alphabetically. Use a function to create the program. ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ 37 Python Activity 6: Functions Notes and Questions Make note of any questions you have about Activity 6 on this page. 38 Name: _______________________________________ Partners: ________________________________ Python Activity 7: Nested IF/ELSE Statements “Decisions, decisions – decisions within decisions!” Learning Objectives Students will be able to: Content: Explain the purpose of a nested if-else statement Explain how to use Python if-elif structure Explain how to test code using Python if-elif structure Process: Write code that includes if-elif statements Write code that uses if-elif statements and functions Prior Knowledge Python concepts from Activities 1-6 Understanding of flowchart input symbols Further Reading Transitioning from Visual Logic to Python: Chapter 7 Critical Thinking Questions: 1. Closely examine the flowchart and Python program above. Python Program Flowchart Python Activity 7: Nested IF/ELSE Statements a. Draw arrows between each flowchart symbol and the equivalent Python code. b. In the Python code, circle the if/else statement that is nested within another if/else statement. c. Enter and test the code. List five numbers that you would use to test this program. Indicate why you chose the numbers. Number 2. Why chosen Enter and execute the following Python program using the same data as you used for #1c. a. How does the output for this program compare with the output for the previous program? ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ b. What new keyword is used in this program? _______________________________________ c. Notice the syntax of this program compared to the previous program. Which program contains simpler indentation? _____________________________________________ FYI: elif is the Python keyword that represents else if and allows you to test for one of several options. As soon as one of the tests is true, the rest are ignored. d. You can use elif as many times as you need to. Suppose you wanted to add the comment “Good!” for grades that are between 80 and 89. Where would you add it? Write the code for this additional choice. ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ e. Does the placement of an additional elif clause matter? ______________________________ f. When is the code associated with the else statement executed? ___________________________________________________________________________ 40 Python Activity 7: Nested IF/ELSE Statements g. Describe how an if/elif/else statement works. ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ h. Change the program in #2 so that it prints the following messages. Write the code below. Greater than 90 Between 80 and 89 Between 70 and 79 Between 60 and 69” Less than 60 “Very Good!” “Good!” “Satisfactory” “Fair” “Poor” ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ i. 3. Make a final change to the program so that it prints an error message if the grade entered is greater than 100 or less than 0. ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ Is the use of the else statement mandatory when creating an if/elif statement? Explain your answer. ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ 41 Python Activity 7: Nested IF/ELSE Statements Application Questions: Use the Python Interpreter to check your work 1. Write an if/elif statement that assigns a value to the variable bonus depending on the amount of sales. Assume the amount of the sales is stored in a variable called sales. Sales Bonus >= 100,000 10,000 >= 75,000 5,000 >= 50,000 2,500 >= 25,000 1,000 _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ 2. Carefully examine and then complete the following Python program. The program prompts the user to enter a number between 1 and 5 and also generates a random number between 1 and 5. The program prints the number the user enters and prints the random number. The program then compares the two numbers. If the numbers are the same, it prints the message “You picked the same number as the computer!”. If the number the user entered is higher than the random number, the program should print “Your number is higher than the computer’s number.” Otherwise, it should print: “Your number is smaller than the computer’s number”. Explain what the if/else statement does in the Main Program. 42 Python Activity 7: Nested IF/ELSE Statements . 43 Python Activity 7: Nested IF/ELSE Statements Notes and Questions Make note of any questions you have about Activity 7 on this page. 44 Name: _______________________________________ Partners: ________________________________ Python Activity 8: Looping Structures – WHILE Loops “Repeating code” Learning Objectives Students will be able to: Content: Explain the three parts of a loop Explain the syntax of a while loop Explain sentinel-controlled and counter controlled loops Explain short-cut operators Process: Write code that includes sentinel-controlled and counter controlled loops Write code that uses short-cut operators Prior Knowledge Python concepts from Activities 1-7 Understanding of flowchart input symbols Further Reading Transitioning from Visual Logic to Python: Chapter 8 Critical Thinking Questions 1. Closely examine the flowchart and Python program below. FYI: A looping structure allows a block of code to be repeated one or more times. A while loop is one of the two looping structures available in Python. Python Program Flowchart a. Draw arrows between each flowchart symbol and the equivalent Python code. b. In the Python code, circle all the code associated with the WHILE loop. Python Activity 8: Looping Structures – WHILE Loops c. Enter and test the code. What does the line of code: x=x+1 do? ___________________________________________________________________________ d. How does the Python interpreter know what lines of code belong to the loop body? ___________________________________________________________________________ e. Every loop structure requires three actions. Identify the line of code in the Python program that corresponds to each of the three actions. Initialize a variable used in the test condition: ________________________________________________________________________ Include a test condition that causes the loop to end when the condition is false: ________________________________________________________________________ Within the loop body, update the variable used in the test condition: ________________________________________________________________________ 2. Enter and execute the following code. _______________________________ _______________________________ __________________________________________________ _______________________________ __________________________________________________ __________________________________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ __________________________________________________ _______________________________ __________________________________________________ _______________________________ __________________________________________________ _______________________ __________________________________________________ 3. a. Beside each line of code below explain what the code does. b. Explain the difference between the two print statements. ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ The following code should print the numbers from 1 to 10, but it does not print anything. Correct the problem. number = 12 while number <= 10: print(number) number = number + 1 4. Enter and execute the following code: number = 0 while number <= 10: print(number) number = number - 1 a. Describe the output. ____________________________________________________ 46 Python Activity 8: Looping Structures – WHILE Loops 6. 7. b. What caused the output to be what it was? ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ c. Does the program end? Why or why not? ________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ Enter and execute the following code: number = 1 while number <= 10: if number % 2 == 0: print(number, end= " number = number + 1 ") a. State the output. ________________________________________________________________________ b. What caused the output to display on one line? ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ c. What control structures are used in this code? ________________________________________________________________________ We want to create a program that prompts the user to enter a number between 1 and 10. As long as the number is out of range the program re-prompts the user for a valid number. Complete the following steps to write this code. a. Write a line of code the prompts the user for number between 1 and 10. ________________________________________________________________________ b. Write a Boolean expression that tests the number the user entered by the code in step “a.” to determine if it is not in range. ________________________________________________________________________ c. Use the Boolean expression created in step “b.” to write a while loop that executes when the user input is out of range. The body of the loop should tell the user that they entered an invalid number and prompt them for a valid number again. ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ d. Write a line of code that prints a message telling the user that they entered a valid number. ________________________________________________________________________ e. Put the segments of code from steps “a-d” together. Enter and execute the code. Does it work properly? If not, correct it and test it again. _________________________ 47 Python Activity 8: Looping Structures – WHILE Loops f. How many times does the loop execute? ______________________________________ FYI: A looping structure for which you know the number of times it will execute is known as a count-controlled loop. 8. Sometimes a programmer does not know how many times data is to be entered. For example, suppose you want to create a program that adds an unspecified amount of positive numbers entered by the user. The program stops adding numbers when the user enters a zero or a negative number. Then the program prints the total. Before creating this program, review the three actions required for all loops: a. Initialize a variable that will be used in the test condition: What will be tested to determine if the loop is executed or not? Write a line of code that initializes a variable to be used in the test condition of the loop for this program. The variable should contain a value entered by the user. ________________________________________________________________________ b. Include a test condition that causes the loop to end when the condition is false: What is the test condition for the while loop used in this program? ________________________________________________________________________ c. Within the loop body, update the variable used in the test condition: Write the code for the loop body. Include the code to update the variable in the test condition. ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ d. Is this a count-controlled loop? Why or why not? ________________________________________________________________________ e. Complete the program. Enter and execute the code. Does it work properly? __________ FYI: Short-cut operators provide a concise way of creating assignment statements when the variable on the left-hand side of the assignment statement is also on the right-hand side. The addition short-cut operator (+=) is usually used for incrementing a variable. 9. Enter and execute the following code: number = 1 number += 3 print(number) a. What does the “+=” shortcut operator do? ________________________________________________________________________ b. The code: x += 5 is equivalent to which of the following lines of code? x=5 x=x+5 x=y+5 y=x+5 48 Python Activity 8: Looping Structures – WHILE Loops c. Replace the operator ‘+=’ with the following shortcut operators and execute the code. Explain what each operator does. -= _________________________________________________________ *= 10. _________________________________________________________ Enter and execute the following code: bonus = 25 salary += bonus print(“Total salary:”, salary) a. What is the output of the preceding code? Is it what you expected? ________________________________________________________________________ b. Edit the code so that it produces valid output. ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ c. As a result of correcting this code segment, what is needed in order for the shortcut operators to work properly? _______________________________________________________________________ d. Is the following line of code valid: 23 += total? Why or why not? ________________________________________________________________________ 11. The following code should print the numbers beginning at 100 and ending with 0. However it is missing a line of code. Add the missing code, using the shortcut operator. Indicate where the code belongs. countdown = 100 while countdown > 0: print(countdown) print(“Done!”) ________________________________________________________________________ 12. Enter and execute the following code: doAgain = "y" while doAgain == "y": word = input("Enter a word:") print("First letter of " + word + " is " + word[0]) doAgain = input("Type ‘y’ to enter another word and anything else to quit.") print("Done!") a. What does the program do? ________________________________________________________________________ b. What is the name of the variable used to store the user’s input? ____________________ c. In the print statement, what does word[0]represent? ___________________________ 49 Python Activity 8: Looping Structures – WHILE Loops d. If you changed 0 to 1 in word[0]in the print statement above, what is printed? ________________________________________________________________________ e. When does the program end? _____________________________________________ FYI: A sentinel-controlled while loop is a loop that repeats the loop body until the user enters a prespecified value. 13. g. Why is the loop in this program is an example of a sentinel control loop? ________________________________________________________________________ h. Examine the print statement in this program: print("First letter of " + word + " is " + word[0]) What is the purpose of the “+” as part of the argument in the print statement? What happens if you replace the “+” with a “,”? ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ Examine the code below. name = “Simone” cost = 3.56 numApples = 89 What type of data is stored in each variable: (integer, floating point, or string) name – __________________________ cost – __________________________ numApples – __________________________ FYI: A variable that can store only the values True and False is called a Boolean variable. 14. Given the assignment statement: foundCost = False What value is stored in the variable foundCost? ________________________________ What type of data is stored in foundCost? 15. ________________________________ Enter and execute the following code: a. What type of variable is ‘doAgain’? 50 _______________________________________ Python Activity 8: Looping Structures – WHILE Loops b. What does the program do? ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ c. What does the following line of code do? maxNum1 = max(num1, num2, num3, num4) ________________________________________________________________________ d. Experiment with the arguments in the max() function in the program to determine if the function must have four arguments. Demonstrate your answer. ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ e. What does the following code in the program do? if another != 'y': doAgain = False ________________________________________________________________________ Application Questions: Use the Python Interpreter to check your work 1. Write a code segment that prompts the user for an even number. As long as the number is not even, the user should be given a message and prompted again for an even number. ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 2. Write code segment that prompts the user for a letter from ‘a-z’. As long as the character is not between ‘a-z’, the user should be given a message and prompted again for a letter between ‘a-z’. ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 3. Complete the following program: ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 51 Python Activity 8: Looping Structures – WHILE Loops Notes and Questions Make note of any questions you have about Activity 8 on this page. 52 Name: _______________________________________ Partners: ________________________________ Python Activity 9: Looping Structures: FOR Loops “Another form of loops” Learning Objectives Students will be able to: Content: Explain the difference between while loop and a FOR loop Explain the syntax of a FOR loop Explain how to use the range() function in a FOR loop Explain an accumulator in a FOR loop Process: Write code that includes FOR loop Write code that uses use FOR loops within functions Prior Knowledge Python concepts from Activities 1-8 Understanding of flowchart input symbols Further Reading Transitioning from Visual Logic to Python: Chapter 9 Critical Thinking Questions: 4. Enter and execute the following two Python programs. WHILE LOOP -- Python Program FOR LOOP – Python Program a. What is the output for each program? ___________________________________________________________________________ b. Both programs produce the same output. Which code fragment is more concise? ___________________________________________________________________________ FYI: The Python predefined range() function is used to define a series of numbers and can be used in a FOR loop to determine the number of times the loop is executed. . 2. Enter and execute the following code fragments and state the output: a. for x in range(5): print(x, end=” “) ________________________________ b. for x in range(1,5): print(x, end=" ") ________________________________ 53 Python Activity 9: Looping Structures: FOR Loops c. 3. for x in range(3,20,2): print(x, end=” “) ___________________________ d. numIterations = 6 for x in range(numIterations): print(x, end=” “) ___________________________ e. numIterations = 6 for x in range(1, numIterations+1): print(x, end=” “) ___________________________ After examining the five code fragments in #2, explain how the range() function works. Include an explanation of the arguments. _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ FYI: In a FOR loop you can include a list of values in place of the range() function. 4. 5. Enter and execute the following code. for x in [3,6,9,12,15,18]: print(x, end=” “) a. Rewrite this code using the range() function. ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ b. Why would you use the range() function when you could just list the numbers? _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ As you learned in Activity 8, every loop structure requires three actions. Explain how these actions are implemented in the following Python FOR loop. for x in range(1,5): print(x, end=" ") a. Initialize a variable used in the test condition; ________________________________________________________________________ b. Include a test condition that causes the loop to end when the condition is false: ________________________________________________________________________ c. Within the loop body, update the variable used in the test condition: ________________________________________________________________________ 54 Python Activity 9: Looping Structures: FOR Loops 6. Read through the code and determine what it does. favorite = input("Enter your favorite ice cream flavor: ") for x in range(1,5): print(str(x) + “.”, favorite, end="\t") a. Explain what you think the program does. _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ b. Enter and execute the code to determine if you were correct. What does the program actually do? Provide a detailed explanation. _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ c. Explain the use of the str() function in the print statement. Why is it needed? _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ 7. Complete the arguments in the following range function so that the code prints the even numbers between 100 and 200 inclusive. for x in range(_____________________________): print(x) 8. Complete the arguments in the following range function so that the code prints: 5 4 3 2 1 0. for x in range(______________________________): print(x) FYI: An accumulator is a variable that stores the sum of a group of values. 9. Examine the following code segment. total = 0 for x in range(5): number = int(input("Enter a number: ")) total += number print("The total is:",total) a. Why is the variable total initialized to 0 in the first line of code? ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ b. Explain what the following code does: number = int(input("Enter a number: ")) ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 55 Python Activity 9: Looping Structures: FOR Loops 10. c. Explain what the following code does: total += number ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ d. How many numbers does the program prompt for? e. What is the accumulator in the code segment? ________________________________________________________________________ __________________________ Is it better to use a FOR loop when you know the number of times the loop should be executed or when you do not know? Explain your answer. ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ Application Questions: Use the Python Interpreter to check your work 1. Write a code segment using a FOR loop that prints multiples of 5 from 5 to 500. ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 2. Complete the program on the following page. The program should: Display five addition facts, one at a time, and allow the user to answer them. Provide the correct answer if user enters incorrect answer. Print a congratulatory answer, if the answer is correct. Keep track of the number of problems the user answers correctly. Prints a special message, if the user gets all five problems correct. Fill in the missing code; comments (also written below) indicate location of missing code. # include the required import statement ______________________________________________________________________________ # include a FOR loop that prints the numbers from 10 to 0 ______________________________________________________________________________ # Assign a random number between 1 and 10 to num1 and num2 ______________________________________________________________________________ # Write the test condition to determine if the user’s # answer is equal to the sum of the two numbers ______________________________________________________________________________ # Write the line of code to increment the variable # that is keeping track of the number of correct answers. ______________________________________________________________________________ # Print the addition fact and include the correct answer. ______________________________________________________________________________ 56 Python Activity 9: Looping Structures: FOR Loops # Write the test condition to determine if the user answered # all the questions correctly ______________________________________________________________________________ # Write the code to call the function that prints the rocket ______________________________________________________________________________ 57 Python Activity 9: Looping Structures: FOR Loops Notes and Questions Make note of any questions you have about Activity 9 on this page. 58 Name: _______________________________________ Partners: ________________________________ Python Activity 10: Files and Nesting Looping Structures “Alternative input and loops inside loops” Learning Objectives Students will be able to: Content: Explain how to open a text file for reading and for writing Explain the difference between the read() and readline() functions Explain the purpose of the str() function. Explain the effect of the arguments of the range function when reading data from a file. Explain the purpose of the rstrip(), open(), close(), and write() functions Explain the difference between writing and appending to a file Read and write nested FOR loops Identify inner and outer loops Process: Write code that opens, writes to and closes a file Write code that opens, reads from and closes a file Write code that uses a nested FOR loop Prior Knowledge Python concepts from Activities 1-9 Further Reading Transitioning from Visual Logic to Python: Chapter 10 Critical Thinking Questions: FYI: In Python, you can access data from a text file as well as from the keyboard. You can create a text file in any text editing tool. You should only have one data item per line in the file. 5. Create a text file named sports.txt and enter the sports listed below, one word per line. Enter and execute the Python program. Be sure the saved program is in the same folder as the text file. Python Program sports.txt file 59 Python Activity 10: Files and Nesting Looping Structures a. What does the program do? _______________________________________________________________________ b. Explain the purpose and syntax of the first line of code. What does the ‘string argument’ for the function open represent? _______________________________________________________________________ 2. c. Replace the function read() with the function readline(). Execute the program again. What happens? _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ d. Explain the difference between the two functions: read() and readline(). _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ Enter and execute the following code. a. Explain the format and content of the output. ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ b. How does the output from this programs differ from the output of the program that used the “read()” function? What caused the difference? ________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ c. What is the subtle difference in the output if the following print statement replaced the one above? Which is better? ________________________________________________________________________ d. What does str(index) do in the program above? Why is the str () function necessary? ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ e. What happens when you change the arguments in the range() function to 1,10? _______________________________________________________________________ f. What happens when you change the arguments in the range() function to (0, 30)? _______________________________________________________________________ 60 Python Activity 10: Files and Nesting Looping Structures g. What do the results from “f.” and “g.” tell you about the arguments of the range() function when you are using it in a FOR loop to read data from a file? ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ FYI: The purpose of the rstrip() function is rather subtle. rstrip() returns a copy of the string after all characters have been stripped from the end of the string (default whitespace characters, EOL characters, and newline characters). 3. The following program is slightly different from the program in #2. Enter and execute the program. a. Compare the output from this program to the output in the previous program. What is the difference? ________________________________________________________________________ b. What code caused the difference in the output? ________________________________________________________________________ c. In this example the rstrip() function strips the newline character from the string that is read from the file. Why is the newline character attached to the end of the string? ________________________________________________________________________ d. Does the rstrip() function contain any arguments? How does it know what string to act upon? ________________________________________________________________________ e. lstrip() is a similar function. What do you think it does? ____________________________________________________ 4. The following program is slightly different from the program in #3. Enter and execute the program. a. What does the program display? ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ b. How many functions are used in this program? _________________________________ c. Two functions use what is known as dot(.) notation. What are the two functions? ________________________________________________________________________ 61 Python Activity 10: Files and Nesting Looping Structures d. 5. Examine the output and explain what the len() function does. ________________________________________________________________________ Enter and execute the following program: a. What output appears on the screen? ________________________________________________________________________ b. What does the program do? ________________________________________________________________________ c. Locate the file studentInfo.txt on your computer. The file is stored in the same folder as the program. What is stored in the file? ________________________________________________________________________ d. What is the purpose of “w” in the following line of code? ________________________________________________________________________ e. Did you create the file: studentInfo.txt before you included it in the code? ___________ f. Execute the program again using different input. Open the studentInfo.txt file. What is in the file? Is the data from the first program execution still there? ________________________________________________________________________ g. Change the ‘w’ to ‘a’ in the open() function. Execute the program again with different input. Examine the student Info.txt file. What did ‘a’ as an argument in the open() function do? What word do you think ‘a’ represents? ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ h. Notice the new function – write(). How many arguments does the write function have? ________________________________________________________________________ i. How does the write() function know what file to write to? ________________________________________________________________________ j. What line of code closes the file? Where is the line of code positioned in the program? ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 62 Python Activity 10: Files and Nesting Looping Structures k. Revise the program so that the user can enter three names during one execution of the program. You may need to change the order of some of the code. ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ FYI: A loop within another loop is known as a nest loop. Proper indentation is essential for the loops to work properly.. 6. 6. Enter and execute the following code: a. What does the program display? ________________________________________________________________________ b. How many FOR loops are in this code? Is one loop completely executed before the next loop begins? What do you call this type of loop? ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ c. How many times is the following line of code executed in the program? ______________ d. In the program listed at #6, above, label the inner loop and the outer loop. e. What does the inner loop do? ________________________________________________________________________ f. What does the outer loop do? ________________________________________________________________________ If you were asked to created a Python program that displayed the adjacent rectangle, you could easily do it with a set of print statements or a FOR loop and a print statement. We will go through several steps to create a program that will print similar output but allows the user to determine the length and width of the figure when they execute the program. 63 Python Activity 10: Files and Nesting Looping Structures 7. a. Create a code segment that prompts the user for a number between 1 and 10 and then prints that many asterisks (*) on one line. Use a FOR loop. ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ b. You want to create several lines of asterisks. Revise the code in “a.” to also prompt the user for how many lines to print. Use an “outer” loop to print that many lines of asterisks. ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ c. Edit the program so that it prints numbers instead of asterisks. Write the line of code that was changed. ________________________________________________________ Examine the following code and determine the output. Indicate the changes in memory as the program is executed. Assume the user input is 5. Variable height row column Memory Application Questions: Use the Python Interpreter to check your work 1. Create a text file that contains 10 numbers between 50 and 100. Write a program that reads the numbers from the file and totals the numbers. The program should print all the numbers and display the total when all the numbers have been added together. (Warning! The input from the file will be considered a string. Be sure to convert the input to int or float – just as you do when numbers are entered from the keyboard.) ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 64 Python Activity 10: Files and Nesting Looping Structures 2. Revise the following program. Allow the user to enter the name of the file and use the input to open the file. ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 3. Create a Python program that prompts the user for a number and then prints an inverted right triangle containing that many rows similar to the output to the right. ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 65 Python Activity 10: Files and Nesting Looping Structures Notes and Questions Make note of any questions you have about Activity 10 on this page. 66 Name: _______________________________________ Partners: ________________________________ Python Activity 11 Part A: Lists “More versatile than arrays -- lists” Learning Objectives Students will be able to: Content: Define a list Identify elements of a list Explain the purpose of positive and negative indexes in a list. Explain how to access individual elements of a list Explain how the following functions are used with lists: append(), insert(), remove(), count(), index() Explain how to replace an item Process: Write code that prints a list Write code that edits a list – add, remove, and insert items Prior Knowledge Python concepts from Activities 1-10 Further Reading Transitioning from Visual Logic to Python: Chapter 11 pp. 95-101 Critical Thinking Questions: FYI: A sequence is an object that stores multiple data items in a contiguous manner. Two types of sequences are strings and lists. Each value stored in a list is called an element. 6. Examine the sample lists below. Sample Lists in Python a. How many elements does the list named digits contain? ___________________ b. What type of data is stored in each list (String, numeric)? digits list: __________________________________________________________ fruits list: __________________________________________________________ studentData list: c. ___________________________________________________ How would you define a list? _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ 67 Python Activity 11 Part A: Lists 2. The following line of code prints the first element in the digits list. a. What value does fruits[3] represent? _______________________________________ b. Enter and type the fruits list and write a line of code that prints the last value. ________________________________________________________________________ c. Edit your print statement in ‘b’ so that it prints fruits[4]. What is printed? Why? ________________________________________________________________________ d. Edit your print statement so that it prints fruits[-1]. What is printed? _______________________________________________________________________ e. Change -1 to -2 in “d.”. What is printed? _______________________________________________________________________ FYI: The number used to locate an element in the list is called an index. 3. f. Explain how the positive and negative indexes locate the desired elements. _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ g. What is printed with the following print statement: print(fruits)? How is the information displayed? _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ Enter and execute the following code: a. What is the output? _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ b. Explain the first line of code especially the code on the right hand side of the equal sign. ________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ c. Explain why the second line of code produces the same output as the first line above. ________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ ______ 68 Python Activity 11 Part A: Lists d. 4. Add the following line of code to the program: print(len(mult2)) What is the output? What does the len() function do? _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ Enter and execute the following code: a. What is the output for the second line of code: ________________________________________________________________________ b. Examine the following code. It contains a FOR loop but does not use the range() function. In previous FOR loops the values resulting from the range() function were stored in x during each iteration of the loop. i. What is being stored in x for each iteration of the loop in the following code? ________________________________________________________________________ ii. What is the output for this code? ________________________________________________________________________ c. What are the similarities and differences between the output for “a.” and “b.”? _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ d. Add each of the following print statements to the code above. What is the output for each statement? Explain the output. _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ 69 Python Activity 11 Part A: Lists 5. 6. 7. 8. Enter and execute the following code: a. Explain what the following line of code does: flowers.append(‘gardenia’) _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ b. Write a line of code that would add the flower lavender to the list. _______________________________________________________________________ Enter and execute the following code: a. Explain what the following line of code does: flowers.insert(2,‘lily’) _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ b. Write a line of code that would place the flower: sunflower at the beginning of the list. _______________________________________________________________________ Enter and execute the following code: a. Explain what the following line of code does: del flowers[2] _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ b. Write a line of code that would delete the last flower in the list. _______________________________________________________________________ Enter and execute the following code: a. Explain what the following line of code does: flowers.remove(‘tulip’) _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ 70 Python Activity 11 Part A: Lists 9. 10. b. Write a line of code that would delete ‘daffodil’ from the list. ________________________________________________________________________ c. Edit the code to determine what happens if the same flower appears in the list twice and use the remove()function to remove the word. Does it remove both instances of the word? _________________________________________________________________ d. Write a line of code that attempts to remove the flower: sweet pea. What happens when the code is executed? _______________________________________________________________________ Enter and execute the following code: a. Explain what the following line of code does: flowers[1]= ‘freesia’ _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ b. Write a line of code that would replace ‘daffodil’ with ‘gardenia’. _______________________________________________________________________ c. Explain what the following line of code does: flowers[-3]= ‘lily’ _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ d. Explain what happens when the following line of code is added to the program: flowers[8]= ‘lily’ _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ Enter and execute the following code: 71 Python Activity 11 Part A: Lists a. What is the output of this program? _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ b. Explain the line of code: numY = ballot.count(‘y’) What does the count() function do? How many arguments does it have? ________________________________________________________________________ c. Add the following lines of code to the program: What do the lines print? ____________________________________________________ What does the index() function do? _______________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ What happens if you replace ‘y’ or ‘n’ with ‘x’? Why does this happen? _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ Application Questions: Use the Python Interpreter to check your work 1. Create a program that prints a given list, prompts the user for a name and average, adds the new information to the list and prints the new list. It should produce output similar to the following: _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ 7. Revise the previous program so that it allows the user to enter the name of a person in the list whose average needs updating and also prompts the user for the new average. The program should then update the list and print the new list. The program should produce output similar to the output on the following page: 72 Python Activity 11 Part A: Lists _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ 73 Python Activity 11 Part A: Lists Notes and Questions Make note of any questions you have about Activity 11A on this page. 74 Name: _______________________________________ Partners: ________________________________ Python Activity 11 Part B: List Functions “More versatile than arrays -- lists” Learning Objectives Students will be able to: Content: Explain how the following functions are used with lists: reverse(), sort(), max(), min() Explain how to use lists with files Process: Write code that reverses and sorts lists Write code the finds the largest or smallest element of a list Write code that reads from a file into a list Prior Knowledge Python concepts from Activities 1-10 and 11_1 Further Reading Transitioning from Visual Logic to Python: Chapter 11 pp. 101-109 Critical Thinking Questions: 1. Enter and execute the following code: a. What does the code print? ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ b. What does the reverse() function do? ___________________________________________________________________________ 2. Revise the program in #1 to test each of the following functions. a. sort function: <listName>.sort() Write the revised line of code here: ___________________________________________ Does the function make a permanent change to the list? __________________________ Does the function need to be called within an assignment statement? _____________ b. max function: max(<listName>) Write the revised line of code here: _______________________________________ Explain the difference between the call to this function and the call to the sort function. ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 75 Python Activity 12: More about Lists and Strings Does the function need to be called within an assignment statement? c. min function: min(<listName>) Write the revised code here: _____________ _____________________________________________ Is the call to this function similar to the call to the sort function or the max function? _______________________________________________________________________ Does the function need to be called within an assignment statement? ____________ FYI: The member operation determines if a given item is an element of a list. The operation returns True if the item is an element of the list and False otherwise. Syntax: <element> in <list name>. 3. The following program demonstrates the member operation for a list. Enter and execute the program: a. Circle the line of code that uses the member operation. b. Edit the program so that if the number the user entered is not in the list, it is added to the list. Print the list again to be sure the number is added to the list. Here is some sample output: ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ 76 Python Activity 12: More about Lists and Strings c. Suppose the program prompted the user for two numbers and stored them in the variables guess1 and guess2. Write the code segment that would print “Super guess!” if the user entered two numbers in the list. ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ 4. Let’s write a program – step by step -- that generates 100 numbers between 1 and 500 and puts them in a list, prints the numbers, sorts the numbers, reverses the order of the numbers, determines the number of times a given number is in the list and prints the largest and smallest number. a. Create an empty list to store the number __________________________________ b. Create code to generate 100 numbers between 1 & 500 store them in the list __________________________________ __________________________________ __________________________________ c. Create the code to print the list without the brackets. Create a separate function for this since you will be printing the list several times. __________________________________ __________________________________ __________________________________ __________________________________ __________________________________ __________________________________ __________________________________ __________________________________ __________________________________ d. Write the code that sorts and then reverses the numbers. Print the code after it is sorted and after the numbers are reversed. __________________________________ __________________________________ __________________________________ __________________________________ e. Does the order of these two lines of code matter? ________________________ 77 Python Activity 12: More about Lists and Strings f. Write the code that prompts the user for a number between 1 and 500 and prints how many times that number is in the list. If the number is not in the list print the message: “Sorry, your number is not here!” ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ g. Print the largest and smallest number. ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ h. Enter and execute the code from a-e. be sure that it executes properly. List one sample output. ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ i. To make the numbers appear in columns, replace the print statement in the print function with the following line of code: print("%3d" %x, end=" "). What causes the change in output format? ___________________________________________________________________________ 5. Enter and execute the following code. What does the program do? 6. ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ Add the following code to the program above: a. What does the program do once this code is added? ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ b. Explain the following code: ________________________________________________________________________ 78 Python Activity 12: More about Lists and Strings c. Explain what the following line of code does: ________________________________________________________________________ d. Add a final line of code to the program that prints the list. ________________________________________________________________________ Application Question: Use the Python Interpreter to check your work Complete the missing sections of the following program in the Python interpreter. Most of the code is missing. Where there is code, comments are needed. First create a text file with several numbers, one on a line. 79 Python Activity 12: More about Lists and Strings Notes and Questions Make note of any questions you have about Activity 11B on this page. 80 Name: _______________________________________ Partners: ________________________________ Python Activity 12: More about Lists and Strings “Lists and Strings and Functions and more….” Critical Thinking Questions: Learning Objectives Students will be able to: Content: Explain how to send a list as an argument to a function Explain the purpose of the following functions: isalpha(), isdigit(), isspace(), upper(), lower() Explain what is meant by the fact that “Strings are immutable.” Demonstrate the use of slicing with strings and lists. Process: Write code that uses the following functions: isalpha(), isdigit(), isspace(), Write code that uses slicing to access elements of a list Prior Knowledge Python concepts from Activities 1-11_2 Further Reading Transitioning from Visual Logic to Python: Chapter 12 1. 2. At the end of the previous activity you created a function to print a list and passed the list to the function. Here is another program that includes a function that takes a list as an argument. Enter and execute the code. a. What is the name of the function defined in this program? b. What does the function do? ________________________________________________________________________ Enter and execute the following code. 81 ___________________ Python Activity 12: More about Lists and Strings 3. 4. a. Execute the program with at least five different types of input that include just letters, just numbers, letters, numbers and other characters. Examine the output for each input. What does the program do? ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ b. What does the isalpha() function do? ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ Enter and execute the following code. a. Execute the program with at least five different types of input. Examine the output for each input. What does the program do? ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ b. What does the isdigit() function do? ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ Enter and execute the following code. a. What does the program do? ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 82 Python Activity 12: More about Lists and Strings b. 5. What does the isspace() function do? ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ Enter and execute the following code: c. Execute the program with the following input and examine the corresponding output. cmsc190 __________________________________________________________ Cmsc190 __________________________________________________________ CMSC180 __________________________________________________________ CMSC190 __________________________________________________________ d. What does the upper() function do? __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ c. Use the lower() function instead of the upper() function in the program above. Revise the line of code so that it still produces the same output. Execute the program again with the data listed in ‘a’. (Write the revise code below.) ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ 6. Examine the following code: a. b. What do you think the program prints? _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ Enter and execute the code. Does the program do what you thought it did? _______________________________________________________________________ c. What would you think the code word[0] = ‘c’ should do? What does it actually do? _______________________________________________________________________ d. “Strings are immutable.” From the output you saw when you executed this program, what do you think this statement means? _______________________________________________________________________ 83 Python Activity 12: More about Lists and Strings FYI: Slicing is a technique available in Python that allows you to access parts of lists or strings. You can select multiple elements of a list or string. Syntax: <listOrStringName>[indexOfFirstItem : indexAfterLastItem]. 7. In this section we are going to try to access parts of a string using slicing. Enter and execute the following code. Examine the syntax of the code. It uses slicing to access parts of a string. a. What is the output for each print statement in the program? _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ b. The first three print statements should be familiar. What does the fourth print statement do? Explain the meaning of [0:13]. ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ c. What does the following print statement do? Explain the meaning of [16:27]. ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ d. What does the following print statement do? Explain the meaning of [28:]. ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 8. Finally, examine slicing using lists. Enter and execute the following program. 84 Python Activity 12: More about Lists and Strings a. What is the output of each print statement in the program? ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ b. Explain what the following code does. ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ c. Explain what the following code does: ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ d. Are lists immutable? Explain your answer. ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ e. Explain what the following code does: ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ Application Questions: Use the Python Interpreter to check your work 1. Create a list named “Days” that includes all the days of the week. Print the list. ______________________________________________________________________________ 2. Create a line of code that uses slicing to print the last three days in the list “Days” which you created in question 1. ______________________________________________________________________________ 3. Create a list named “Vowels” that includes the vowels ‘a’, ‘e’, ‘i’, ‘o’, ‘u’. ______________________________________________________________________________ 4. Use the code in question 3, and create a program that analyzes a user’s input. Complete the following steps: a. Create code that prompts the user for a vowel. ________________________________________________________________________ b. Create code to determine if the user input is a vowel. If so, congratulate them. _______________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ c. Create code that determines if it is a letter, but not a vowel and prints a message that indicates that. _______________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 85 Python Activity 12: More about Lists and Strings d. Add code that determines if the user input is a digit instead of a letter, print a message that indicates that as well. _______________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ e. Otherwise, tell the user that their input was not a vowel, a letter, or a number. _______________________________________________________________________ f. Prevent the program from crashing by terminating the program if the user enters more than one character. This should actually be tested first. ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ g. Put all the code together and test the program with several sets of data. List a sample output. ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ Notes and Questions Make note of any questions you have about Activity 12 on this page. 86