Node Voltage Analysis
advertisement

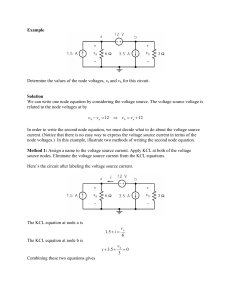
Revised 12 October 2004 Node Voltage Analysis Nodal Analysis ENGI 241 Node Voltage Procedure • Use Node Voltage Analysis when: – We are solving for node voltages – The number of independent nodes is less than the number of independent loops • We begin by – Assume all branch currents enter the node – Write a KCL equation for each node • If the node is driven by a source current, IS is negative if it enters the node and positive if it leaves the node – It is usually more convenient to use conductance's instead of resistances – Collect the terms for each node – Solve for the unknown node voltage using Ohm’s Law, KVL, and KCL as appropriate. • Use Simultaneous Linear Equations for multiple unknown node voltages Andrew H. Andersen ENGI 241 - Node Voltage Analysis ENGI 241 - Node Voltage Analysis 2 1 Revised 12 October 2004 Node Voltage Analysis Node Voltage Example A Find VA Andrew H. Andersen ENGI 241 - Node Voltage Analysis 3 Node Voltage Example 1A Write KCL for all currents entering the node Andrew H. Andersen ENGI 241 - Node Voltage Analysis ENGI 241 - Node Voltage Analysis 4 2 Revised 12 October 2004 Node Voltage Analysis Node Voltage Example 1B Same Circuit as 1A, but with VS2 reversed Andrew H. Andersen ENGI 241 - Node Voltage Analysis 5 Node Voltage Example 2 A B Write KCL for all currents entering nodes A and B Andrew H. Andersen ENGI 241 - Node Voltage Analysis ENGI 241 - Node Voltage Analysis 6 3 Revised 12 October 2004 Node Voltage Analysis Node Voltage Example 2 Andrew H. Andersen ENGI 241 - Node Voltage Analysis 7 Node Voltage Example 3 B A Andrew H. Andersen ENGI 241 - Node Voltage Analysis ENGI 241 - Node Voltage Analysis 8 4 Revised 12 October 2004 Node Voltage Analysis Node Voltage Example 3 Andrew H. Andersen ENGI 241 - Node Voltage Analysis 9 Node Voltage Example 4 Andrew H. Andersen ENGI 241 - Node Voltage Analysis ENGI 241 - Node Voltage Analysis 10 5 Revised 12 October 2004 Node Voltage Analysis Nodal Analysis with a Supernode • A Supernode exists when a voltage source (may be either dependent or independent) is present between two essential nodes – These two nodes connected only by the source can be combined to form a supernode (.2VD between nodes B and C in previous graphic) • Account for the currents that flow through the supernode (from node C to node B in the previous graphic) – In the KCL equation for Node B, the branch currents entering node C flow though the supernode to node B • To solve a circuit with a supernode – Write the KCL equations for the two nodes of the supernode not adjacent to the reference or adjacent to a voltage source – Write the KVL equation for the supernode – Solve for one node of the supernode voltages in terms of the other node • Solve for VC in terms of VB in the previous graphic – Collect all terms in the equation – Solve the Simultaneous Liner Equation Andrew H. Andersen ENGI 241 - Node Voltage Analysis 11 Node Voltage Example with Supernode VD = VS1 - VB 0.2VD = VB - VC VC = VB - 0.2VD VC = VB - 0.2(VS1 – VB) VC = 1.2VB - 0.2VS1 Andrew H. Andersen ENGI 241 - Node Voltage Analysis ENGI 241 - Node Voltage Analysis 12 6 Revised 12 October 2004 Node Voltage Analysis Node Voltage Example 5 Andrew H. Andersen ENGI 241 - Node Voltage Analysis 13 Node Voltage Example 6 with Supernode Andrew H. Andersen ENGI 241 - Node Voltage Analysis ENGI 241 - Node Voltage Analysis 14 7 Revised 12 October 2004 Node Voltage Analysis Node Voltage Example 6 with Supernode VC = VB + 10ID Andrew H. Andersen ENGI 241 - Node Voltage Analysis 15 Example 7 R1 14 rs1 R3 A rs2 R2 B C 4.5 7.7 .1 .1 VS1 RL 120Vdc VS2 .1 120Vdc Andrew H. Andersen ENGI 241 - Node Voltage Analysis ENGI 241 - Node Voltage Analysis 16 8 Revised 12 October 2004 Node Voltage Analysis Bridge Using Node Voltage Analysis Calculate VA and VB as if RM is not present VAB = VA – VB Andrew H. Andersen ENGI 241 - Node Voltage Analysis ENGI 241 - Node Voltage Analysis 17 9