Wrist and Hand Unit
advertisement

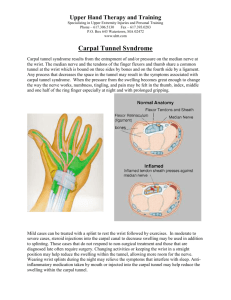
Wrist and Hand Unit Anatomy, Injuries, Evaluations, Treatments, and Rehabilitation Anatomy of wrist Bones: carpals and metacarpals Joints: radiocarpal, carpal, metacarpal, and phalangeal joints Ligaments: “many at each joint in the hand” Musculature: “many intrinsic and extrinsic muscles” Blood and Nerve Supply: ulnar, median, radial nerve and radial and ulnar superficial and deep palmar arch arteries Wrist and hand joints Radiocarpal joints:condyloid jt. Permits flex/ext, abd/add, circum. Carpal joints:gliding jts. Stabilized by ant/post interosseous lig. Metacarpal joints: 5 bones forming the MCP jt Condyloid jt. But the thumb is a saddle jt. Phalangeal joints: interphalangeal is a hinge jt. Ext/flex only Wrist ligaments: Radius=radial collateral lig attaches the radial styloid to the scaphoid Ulna=ulnar collateral lig. Attaches the ulnar styloid to thepisiform and triquetral bone Transverse carpal lig. = roof of the carpal tunnel Phalangeal ligaments: PIP/DIP joint same ligaments as the wrist. Volar plate on the palmar surface of the phalange Extensor expansion= sheath that expands over the dorsal surface of the phalange. Assessment of Wrist, Hand, and Finger Injuries History Observation Palpation Special Tests: Finklestein’s test, Tinel’s Sign, Phalen’s test, valgus and varus stress test, Glide test, Lunotriquetral Ballotment test Circulatory and Neurological Evaluation Allen test Functional Evaluation Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Carpal tunnel syndrome Etiology: transverse carpal lig. Is the roof of the tunnel, 8 long flexor tendons and median N pass through this. Over use of wrist flexion and sometimes a direct blow can cause this. Signs and symptoms: tingling, numbness over the thumb, 2-3 phalanges, and palm of the hand. Also thumb weakness Management: rest, immobilization, NSAID’s then surgery to relieve the compression by cutting the transverse carpal lig. Carpal Tunnel Carpal Tunnel Injuries of the wrist Wrist Sprain Etiology: Falling on hyperextended wrist most common but you can fall on a flexed wrist Signs and Symptoms: pain, swelling, limited ROM Management: Severe sprain go for x-ray. For mod/minor injury RICE and start exercise ASAP Triangular Fibrocartilage Complex Injury (TFCC) Etiology: fall on an outstretched hand in hyperextension that compresses the TFCC between radioulnar jt and carpals. UCL involved Signs and Symptoms: pain along the ulnar side of the wrist, swelling and pain in wrist extension Management: referred to physician. If not properly managed, permanent loss of motion and disability can occur. Tenosynovitis Etiology: occurs to extensor carpi rad. Longus/brevis mainly in wt. Lifters and rowers chronic injury of repetitive use Signs and Symptoms: pain in passive stretching and swelling and tenderness Management: RICE and NSAID’s, along with increase ROM exercises in contrast baths. US Tendinitis Etiology: common flexor carpi rad./ulnaris= overuse Signs and Symptoms:pain in active/passive stretching Management: Same as above Nerve Compression, Entrapment, Palsy Etiology:direct blow- median/ulnar nerve is involved. Median N is compressed in the carpal tunnel. Unlar N is compressed in the tunnel of Guyon (pisiform and hook of the hamate Signs and Symptoms: sharp, burning pain with possibility of numbness. Ulanr N= Bishops/Benediction hand 4/5th finger is flexed Ulnar/median n= claw hand distal phalanx flexed, median N= drop wrist or ape hand 2-5 distal phalanx flexed and thumb extended Management: RICE, NSAID’s or surgery for decompression Fractured wrist Dislocation of the Lunate Bone Etiology: Most common of the carpals. Fall on an outstretched hand. Dislocated anteriorly (palmar side) Signs and Symptoms: pain, swelling, difficult to flex fingers/wrist Management: send to Dr. to reduce dislocation, 1-2 months recovery. Scaphoid Fracture Etiology: most frequent fx. Force on the outstretched hand. Signs and Symptoms: swelling, pt. Tender over anatomical snuffbox. Pain in radial flexion. Management: Ice, splint, and early immobilization. If not aseptic necrosis might occur because of very poor blood supply. Scaphoid Fracture Hamate Fracture Etiology: direct contact to the wrist while holding a a sports implement: tennis racket, bat, golf club. Signs and Symptoms: wrist pain, weakness, pt. Tender over hamate. Management: cast. Wrist Ganglion Etiology: synovial cyst, most commonly on the back of the wrist Signs and Symptoms: occasional pain, lump, Management: direct pressure, US, or surgery Mallet Finger Etiology: blow to the tip of the finger rupturing the extensor tendon. Signs and Symptoms: pain about the DIP jt. Unable to extend the finger. Management: RICE splinted in extension. Mallet finger Boutonnière Deformity Boutonniere deformity Etiology:rupture of the extensor tendon dorsal to the middle phalanx. Direct blow to an ext. DIP/ flexed PIP joint Signs and Symptoms: inability to to extend PIP joint. Management: splint the PIP in extension. Ice applied Boutonnière Gamekeeper’s thumb Etiology: sprain of the ulnar collateral lig. MCP jt. Forceful abduction Signs and Symptoms: pain over the MCP, unable to pinch Management: refer to orthopedist, splint, ice, possible surgery. Gamekeeper’s thumb Collateral Lig. Sprain, volar plate rupture, central slip tear Etiology: PIP/DIP sprains, volar plate rupture, central slip tear Signs and Symptoms: pain, loss of function, swelling, deformity Management: RICE, x-ray, splinting, taping later PIP Dorsal dislocation Etiology: Hyperext. With volar plate rupture direct blow to finger Signs and Symptoms: deformity, pain, swelling Management: Rice, Dr for reduction, splinting of 20-30 degrees of flexion for three weeks. Then buddy taping MCP dislocation Etiology: twisting or shear force Signs and Symptoms: pain, swelling, and stiffness of the MCP joint and prox. Phalanx is dorsally angulated 60-90 degrees Management: Rice, splinting, Dr. reduced, buddy taped and given early ROM Metacarpal fracture Etiology: axial loading, fifth MC from boxing Signs and Symptoms: pain deformity, angular/rotational deformity Management: RICE splinting, Dr. splint for 4 weeks Bennett’s Fracture Etiology: Carpometacarpal CMC jt. Of the thumb. Signs and Symptoms: pain swelling over the base of the thumb Management: referred to orthopedic surgeon, ice, splint De Quervain’s Disease( Hoffman’s disease) Etiology: stenosing tenosynovitis in the thumb. First tunnel of the wrist narrows and inflamed synovial lining. Muscle involved would be the extensor pollicis brevis and abductor pollicis longus. Constant wrist movement can be a source of irritation Signs and Symptoms: aching pain that radiates into the hand or forearm. Movement of the wrist causes pain. (+)Finklestein test. Muscle weakness of the thumb extensors and abduction. Possible snapping/catching of the tendons during movement Management: immobilization,rest, cryotherapy, and NSAID’s. US and Ice massage Dupuytren’s Contracture Etiology: Unknown how it happens. Nodules develop over the palmar aponeurosis that limit finger extension and cause a flexion deformity Signs and Symptoms: 4th/5th finger stays in flexion Management: nodules removed surgically Trigger finger or thumb Etiology:repeated movement of tendons causes tenosynovitis. Common areas involve the flexor tendons of the phalanges. Signs and Symptoms: pain while flexing thumb or finger. Inability to extend finger or thumb produces a snapping sensation. Management: same as Dequervain’s disease, steroid injection or splinting last resort. Trigger finger Swan neck deformity Etiology: The volar plate of the PIP jt. Is most commonly injured from a severe hyperextension force. Signs and Symptoms: pain, swelling at PIP jt and volar plate. More movement of hyperextension of the PIP jt compared to others Management: Rice, splinting at 20-30 degrees of flexion for 3 weeks Swan neck deformity Jersey finger Etiology: rupture of flexor digitorum profundus. From grabbing a jersey. 4th phalange most commonly injured Signs and Symptoms: pain, pt tenderness, unable to flex distal phalanx Management: splint and surgery. Fingernail deformity Scaling or ridging= psoriasis Ridging and poor development= hyperthyroidism Clubbing and cyanosis= congenital heart disorders or chronic respiratory disease Spooning or depression= chronic alcoholism or vitamin deficiencies