Constitutional Law I_Kelley_2012 Fall
advertisement
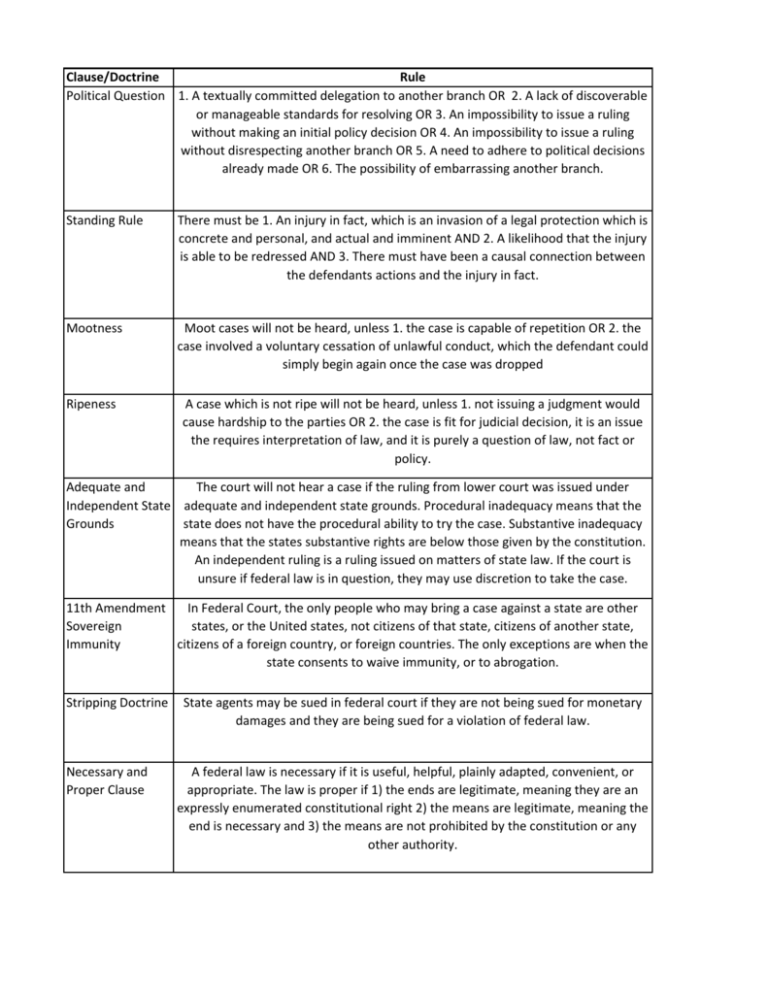
Clause/Doctrine Rule Political Question 1. A textually committed delegation to another branch OR 2. A lack of discoverable or manageable standards for resolving OR 3. An impossibility to issue a ruling without making an initial policy decision OR 4. An impossibility to issue a ruling without disrespecting another branch OR 5. A need to adhere to political decisions already made OR 6. The possibility of embarrassing another branch. Standing Rule There must be 1. An injury in fact, which is an invasion of a legal protection which is concrete and personal, and actual and imminent AND 2. A likelihood that the injury is able to be redressed AND 3. There must have been a causal connection between the defendants actions and the injury in fact. Mootness Moot cases will not be heard, unless 1. the case is capable of repetition OR 2. the case involved a voluntary cessation of unlawful conduct, which the defendant could simply begin again once the case was dropped Ripeness A case which is not ripe will not be heard, unless 1. not issuing a judgment would cause hardship to the parties OR 2. the case is fit for judicial decision, it is an issue the requires interpretation of law, and it is purely a question of law, not fact or policy. Adequate and The court will not hear a case if the ruling from lower court was issued under Independent State adequate and independent state grounds. Procedural inadequacy means that the Grounds state does not have the procedural ability to try the case. Substantive inadequacy means that the states substantive rights are below those given by the constitution. An independent ruling is a ruling issued on matters of state law. If the court is unsure if federal law is in question, they may use discretion to take the case. 11th Amendment In Federal Court, the only people who may bring a case against a state are other Sovereign states, or the United states, not citizens of that state, citizens of another state, Immunity citizens of a foreign country, or foreign countries. The only exceptions are when the state consents to waive immunity, or to abrogation. Stripping Doctrine Necessary and Proper Clause State agents may be sued in federal court if they are not being sued for monetary damages and they are being sued for a violation of federal law. A federal law is necessary if it is useful, helpful, plainly adapted, convenient, or appropriate. The law is proper if 1) the ends are legitimate, meaning they are an expressly enumerated constitutional right 2) the means are legitimate, meaning the end is necessary and 3) the means are not prohibited by the constitution or any other authority. Commerce Clause Commerce is buying, selling, trading, exchanging, or transporting good. Commerce Rule 1 is not manufacturing or production. Interstate commerce is commerce which occurs between the states. Congress may regulate interstate commerce. Events which took place in the stream of commerce may be regulated Commerce Clause Rule 2 Congress may regulate instrumentalities of commerce (people and things in the stream of commerce), channels of interstate commerce (transportation), and anything which substantially effects economic interstate commerce. Congress may regulate anything which, directly or indirectly, in aggregate or singularly, substantially effects interstate commerce, which is an enumerated power and a legitimate end. Commerce Clause Rule 3/ Substantial Effects Congress may regulate instrumentalities of commerce (people and things in the stream of commerce), channels of interstate commerce (transportation), and economic activities which substantially effects economic interstate commerce. Congress may regulate economic activities, which in aggregate or singularly, effect interstate commerce, which is an enumerated power and a legitimate end; the effects must not be too attenuated. 10th Amendment Because of the sovereign immunity of the states, laws which specifically address the commandeering states may not force the states to enact legislation or force the states to govern in a laws certain way. Congress may pass laws that bribe or urge state governments to act, but never force or coerce the states. Laws of General Applicability Laws of general applicability do not violate the 10th amendment and are always allowed to be passed by Congress. Spending Clause Congress may levy any taxes so long as: 1) the revenue is spent on the general welfare 2) If there are conditions, they are clear and related to the general welfare 3) there is a legitimate federal interest which is related to the conditions AND 4) there are no constitutional provisions preventing the grant Treaty Power Property Clause Treaties are the supreme law of the land. Only congress has the power to pass treaties. Congress has the right to control federal lands, including the disposal or the right to make any rules and regulations over them. Congress has police power over federal lands. Proportional and Congruent Test When applying abrogation under the 14th amendment Congress must make it clear that there is an unequivical intention to prevnt or remedy an action based on the 14th amendment. There must be congruency, which means 1) the wrong addressed in consitutionally based, the wrong is persistent and widespread, and there is congressional evidence to the effect. There must be proportionality, which means congress is not over reaching in their correction of the wrong; the correction is the best fit for the wrong. Preemption Doctrine Any valid federal law preempts conflicting state law. Preemption may be express or implied. Implied preemption may be field or conflict. Field conflict consists of Dominant and Pervasive. Conflict preemption may be "Physically Impossible" or "Frustrated". The Market Participation Doctrine If a state is a market participant (buyer or seller), the Dormant Commerce Clause does not apply. However, the state may not act as a regulator of the market. The Delegation (non-delegation) Doctrine Executive Immunity One branch may not delegate duties constitutionally, textually delegated to their branch. However, where congress's duty is to delegate duties it may be permissible. The president is immune from civil suits for damages if the he acted in his official capacity, while in office. Plaintiff's Burden Discriminatory The law discriminated either laws- Dormant 1) facially 2) in its effects OR Commerce Clause 3) in it's intent Ends There was a legitimate state purpose for the discrimination, a legitimate purpose for the state is a use of police powers (public welfare, health, safety, etc.), which may not be economic protectionism. There was a substantial Privileges and A non-citizen of the state was reason for the Immunities Clause discriminated against. discrimination. Means There was no less restrictive alternative means or nondiscriminatory means There is a substantial relationship between the means and the reason for discrimination There is a reasonable relationship between the means and the legitimate purpose: Either 1) the impairment of the contract must be There was a significant and reasonable OR 2) the There was a substantial legitimate public purpose, degree of fit is more The Contracts burden to a currently existing which is real. Society must than a rational Clause contract. have something at stake. relationship. The state must use The Contract other means of Clause (where the There was a substantial The law must further an addressing this purpose state is a party to burden to a currently existing important and legitimate if they are reasonably the contract) contract. public purpose. available. "True" Rational Basis Test (Carolene Products) Any possible, conceivable Any rational relationship A violation of Substantive Due or hypothetical legitimate between the ends and Process government interest the means Any rational relationship Rational Basis Test A violation of Substantive Due A real and actual legitimate between the ends and (Lochner) Process government interest the means Tiers of Scrutiy Compelling Narrowly Tailored/Best Fit Tiers of ScrutinyMiddle Important and Substantial Substantially Related Legitimate With This Rationally Related And This… Tiers of ScrutinyLow Balance This Evan Handed Laws - Dormant The effects on interstate Commerce Clause commerce Executive Privileges The benefits to the state/locality: 1) the nature of the government interest 2) less burdensome AND alternatives The nature of the need for The method of The reason for the privileges disclosure disclosure