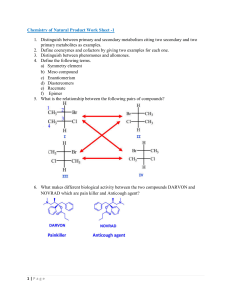
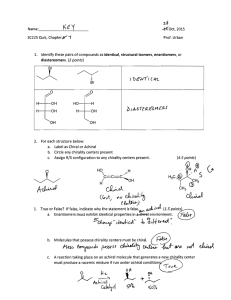
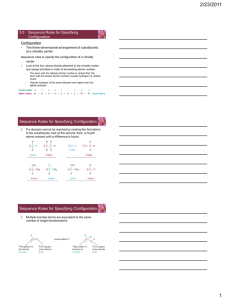
Chapter 5—Stereochemistry At Tetrahedral Centers
advertisement

Chapter 5—Stereochemistry At Tetrahedral Centers SHORT ANSWER Section 5-1 For the following question(s) MATCH each definition to a term from the list below. Place the letter of the term in the blank to the left of the definition. a. b. c. d. e. racemates chirality center chirality diastereomers enantiomers f. g. h. i. j. meso compounds optically active prochirality center optically inactive achiral 1. ____ describes organic molecules which rotate plane-polarized light. 2. _____ is the property of "handedness"; the property of an object that causes it to be nonsuperimposable on its mirror image. 3. _____ are stereoisomers that are not mirror images. 4_____ is an atom in a molecule that is bonded to four different atoms or groups of atoms. 5. _____ are molecules which contain chirality centers and a plane of symmetry. 6. _____ describes an sp3-hybridized atom that can become a chirality center by changing one of its attached groups. 7. a. b. c. d. The specific rotation of a compound is denoted by the symbol: R S α Section 5-2 Place asterisks at all the chirality centers in each molecule below. 8. 1 Stereochemistry At Tetrahedral Centers 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. Section 5-3 Assign R, S configurations to each indicated chirality center in the molecules below. 2 Chapter 5 14. Refer to Section 5-3. The configuration of this carbon atom (A) is _____. 15. Refer to Section 5-3. The configuration of this carbon atom (B) is _____. 16. Refer to Section 5-3. The configuration of this carbon atom (C) is _____. 17. Refer to Section 5-3. The configuration of this carbon atom (D) is _____. 18. Refer to Section 5-3. The configuration of this carbon atom (E) is _____. Section 5-4 Consider the structure of streptimidone to answer the following question(s). 19. Refer to Section 5-4. Assign R or S configuration to each chirality center indicated in streptimidone. 20. Refer to Section 5-4. Based on the number of chirality centers, how many stereoisomers of streptimidone are possible? 21. Refer to Section 5-4. Will streptimidone have a meso stereoisomer? Explain your answer. Section 5-5 Label each pair of stereoisomers below as: 3 Stereochemistry At Tetrahedral Centers a. b. c. enantiomers diastereomers identical Place the letter of the correct answer in the blank to the left of the pair of stereoisomers. 22. _____ 23. _____ 24. _____ 25. _____ 26. Draw a wedge-dash projection of (2R,3S)-dibromobutane. ANS: 30. Draw a Newman projection of the most stable conformation of (2R,3S)-dibromobutane sighting down the C2−C3 bond. 31. (2R,3S)-Dibromobutane is: a. b. c. d. 34. 4 optically active. racemic. dextrorotatory. a meso compound. Refer to Section 5-6. Draw the enantiomer of (S)-(−)-serine in a wedge-dash projection.