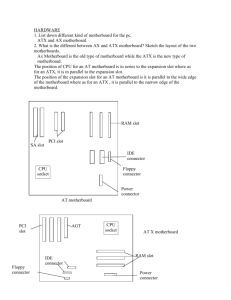
Now…
advertisement

Mother Boards Objectives • • • • • • • Explain the types of memory. Explain the types of RAM. Explain the working of the RAM. List the different memory packages. Install the memory module. Upgrade the memory module. Troubleshoot the memory problems. Objectives - II • • • • • Explain the use of chipsets. List the types of chipsets. Configure the motherboard. Install the motherboard. Troubleshoot the motherboard. Types of Motherboards • Integrated motherboards – Have all peripheral device slots, input output ports, serial and parallel ports mounted on the board. • Non-Integrated motherboards – Have RAM slots integrated on the board. • Desktop Motherboards – Used in personal computers and desktops. • Server Motherboards– Designed to offer high-end services. • Laptop Motherboards– Have very advanced features, as compared to the desktop motherboards. Form Factors of Motherboards • Refers to motherboards physical shape, layout and positioning of components on it. • Determines the type of system case it will fit into. Obsolete Form Factor • Types of obsolete form factors: Baby AT – Similar to original IBM XT motherboard structure. Advanced Technology (AT) – Matches the original IBM AT motherboard in structure and layout. Low Profile Extended (LPX) – Advantages are low cost and small size. Modern Form Factor • Types of modern form factors: ATX – Popular and has best features of LPX and AT form factors. Micro ATX – Limited expandability and capacity. Flex ATX – Provides benefits of ATX and micro ATX form factors. Mini ITX – Similar to ATX, micro ATX, Flex ATX, and BTX form factors. NLX form factors – New addition to motherboard form factors, easier assembly, reduced cost, space efficiency and flexibility. Proprietary Form Factor • Compaq and HP both use different form factors such as ATX and Micro ATX. • Products sold by these companies are of different form factors. Components of a Mother Board • Motherboard contains slots, sockets and connectors for connecting various devices. • Contains super I/O chip, bus slots for connecting various peripheral devices. • Configure the motherboard using jumpers. Connectors - I • • • • • • • System panel connector. USB headers. Digital audio connector. MDC connector. Internal audio connectors. GAME/MIDI connector. System Management Bus (SMBus) connector. Connectors - II ATX 12V connector. ATX Power Connector. CPU and chassis fan connectors. Serial Advanced Technology Attachment (SATA) connectors. • IDE connectors. • Serial port connector. • Floppy disk drive connector. • • • • On Board Disk Drive Connectors • Hard drive, floppy drive and CD-ROM drive is connected to motherboard using on-board disk drive connectors. • Primary connector used to connect storage devices is the Integrated Development Environment (IDE) port. Keyboard and Mouse Connectors • Keyboard and mouse device are connected to (Personal System) PS/2 port of computer. • Ports are located at the back side of the system. • PS/2 port contains 6 holes and a notch in the middle. Expansion Slot • Enable to connect expansion cards to motherboard. • Different PCI cards include LAN card, SCSI card and USB card. • Extend the capacity of the existing motherboard. Audio/Modem Riser • Card with capabilities of modem and audio. • AMR slot is smaller than the standard PCI slot. • Now used only for modems. Peripheral Component Interconnect (PCI) Slot • Bus standard developed by Intel Corporation. • Used for attaching peripheral devices to motherboard. • Slots work at 33 MHz. PCI Express (PCI-E) • Newest Peripheral Component Interconnect Special Interest Group’s specification for the I/O bus. • Extends the capabilities of PCI bus. • Having point-to-point, hot-pluggable and hot-swappable system bus. AGP Slot • Accelerated Graphics Port (AGP) is used to display graphics and 3D images in efficient manner. • Offers high data transfer speed between the video chipset and the CPU. • AGP cards are available at different speeds, AGP 1x, 2x, 4x, 8x. Front Side Bus • Data Bus which carries two-way signal information between the processor and other peripheral. • CPU frequency is set as a multiple of FSB. Jumpers • Small pins that enable you to configure motherboard settings. • Jumpers vary on all motherboards. • You need to perform some jumper settings to make motherboard ready for installation. • Location of jumpers and connectors are different for different motherboards. Onboard Components - I • • • • • • • • • CPU socket Northbridge Southbridge DDR DIMM sockets Super I/O controller Flash ROM Standby Power LED Audio CODEC LAN controller Onboard Components - II • • • • • • • • • • Mouse port Parallel port LAN port Line In jack Line Out jack Microphone jack USB ports Video port Serial port Keyboard port Memory Slots • Provide interface for attaching RAM on motherboard. • Maximum number of slots depend on the motherboard. • Memory slots are either Single Inline Memory Module (SIMM) or Double Inline Memory Module (DIMM). CPU Socket • Interface that connects CPU with motherboard. • Consists of holes in which the pins of the processor are installed. • Sockets are used with particular type of processor. • Sockets already installed on board. CMOS Battery • Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor (CMOS) batteries power CMOS chip of motherboard. • Saves settings and time when computer is switched off. BIOS • Contains necessary code required to operate basic system utilities. • Built into Read Only Memory (ROM) of computer. • Provides the basic input output functionality of the system. DIP Switches • Used to configure circuit board. • Two states namely on or off. • Now all devices are plug and play (PnP) and no setting to be made on circuit board. • DIP switches in XT motherboard. Super I/O Chip • • • • Single chip similar to system chipset. Controls I/O functions of motherboard. Located below PCI slots on motherboard. Supports Enhanced Parallel Port (EPP) and the Extended Capabilities Port (ECP) technology. Chipsets • Group of integrated circuits (IC). • Provide interface for various devices such as the I/O devices, CPU, memory, etc. • Control all functionalities of the computer. CPU Voltage Regulator • Regulates voltage supplied over a line. • Protects devices from power surges and spikes. • Installed on motherboard and regulates voltage that is needed by CPU. • Senses voltage needed by processors from the processor itself. Bus Architecture • Paths through which data is transferred between devices and components • Classified into two main categories: System bus I/O buses Bus Standards • Different types of I/O buses that transfer data across components of the system. • Common bus standards are: Video Electronics Standards Association (VESA) Local Bus. Peripheral Component Interconnect (PCI) Local Bus. Accelerated Graphics Port (AGP) bus. Industrial Standard Architecture (ISA) bus. Extended Industrial Standard Architecture (EISA) bus. Micro Channel Architecture (MCA) bus. Chipsets • • • Leading manufacturers are. Intel, AMD, VIA, and SiS. Type of CPU you use determines the chipset you can use. Modern chipset consists of the Northbridge and the Southbridge. Manufacturers of Motherboard • Manufacturers of motherboards are: Asus Intel AMI Gigabyte Factors for selecting a Motherboard – I • • • • • Form Factor – Defines size and shape of board. CPU Support – Supports different types of microprocessor and sockets. Memory slots – Supports different types of memory and number of slots. Expansion Slots – Supports different types of card and number of slots. SATA support – Allows higher transfer rates of data between hard disk and motherboard. Factors for selecting a Motherboard – II • Number of Ports – Supports how many number of ports to connect different devices to the system. • Hard Drive transfer speed and RAID support – Ultra Direct Memory Access (UDMA) 133 fastest bus for transferring data. • Bus Speed – Allows faster transfer rate of data in and out of the processor. • Chipset – Backbone of system and important part. Configuring the Motherboard • Configure motherboard before it is installed in the system. • Configuration done with the help of jumpers. • Set clock frequency, CPU voltage and other settings. Installing a Motherboard • It’s a complicated task. • Read and understand motherboard manual before attempting to install or configure motherboard. • Incorrect step cause permanent damage. • Before installing motherboard, install CPU, fan and heat sink on the motherboard. Upgrade a Motherboard • Involves replacing the motherboard and also some components of the system. • Factors that need to be considered before upgrading the motherboard. Power Connector Memory Support Hard Disk Support System Case Keyboard Troubleshooting Motherboard • Various problems with the motherboard: Instability in a New System Motherboard has a Crack System does not work properly after recent repair System does not start though fans are working When switched on, the system only beeps or shows POST error Intermittent crashing/stopping of system System fails displaying Parity Error Summary - I • Motherboard is a printed circuit board that is the most important part of a system. • Every component of the system connects to the motherboard directly or indirectly. • There are different types of motherboard. • There are different motherboard form factors. • There are different components on the motherboard. • Jumpers on motherboard enable you to configure the motherboard. Summary - II • You can connect different parts of the system to the motherboard using the connectors and expansion slots. • Northbridge and Southbridge which constitute a modern chipset are the most important components on the motherboard. • Buses on a system are paths or wires through which every device on the system sends and receives information. • Buses on a system can be classified into two main categories. Summary - III • There are different bus architecture. • Chipset on a motherboard is a group of integrated circuits and microprocessors. • You must configure motherboard using the jumpers, before you perform motherboard installation in the system case. • You must install CPU, fan and heat sink on motherboard before you install motherboard. • Follow instructions in motherboard manual when performing configuration or installation.