Chapter 1 Practice Test - New Providence School District
advertisement

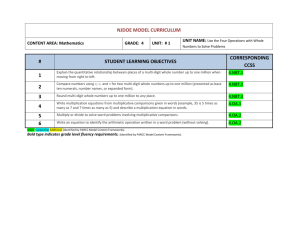
Name: ________________________ Class: ___________________ Date: __________ ID: A Chapter 1 Practice Test ____ 1. Darla copies her uncle’s address and phone number into her contact list. His area code is 775. His ZIP code is 89507. Which statement about the value of the 5 in 775 and 89,507 is true? A. It is the same in both numbers. B. It is 10 times as great in the ZIP code than it is in the area code. C. It is 100 times as great in the ZIP code than it is in the area code. D. It is 10 times as great in the area code than it is in the ZIP code. ____ 2. On Monday, a music site sold 96,527 downloads of the new song by a popular band. What is the value of the digit 6 in 96,527? A. 60,000 B. 6,000 C. 600 D. 60 ____ 3. Mario fills out an information card. His ZIP code is 83628. His area code is 208. Which statement about the value of the 2 in 83,628 and 208 is true? A. It is 10 times as great in the area code than it is in the ZIP code. B. It is 10 times as great in the ZIP code than it is in the area code. C. It is 100 times as great in the area code than it is in the ZIP code. D. It is the same in both numbers. ____ 4. The attendance at a rock concert was 79,408 people. What is the value of the digit 4 in 79,408? A. B. C. D. 40 400 4,000 40,000 10 Name: ________________________ ID: A 5. Compare the values of the underlined digits in 4,312 and 1,432. Explain how you know. ____ 6. What is a way to rename 1 thousand 2 hundreds? A. B. C. D. ____ 7. Which renaming matches the number shown in the model? A. B. C. D. ____ 12 thousands 23 hundreds 12 hundreds 12 tens 123 thousands 123 tens 123 ones 1,203 ones 8. The computer lab provides blank CDs for students to use. The CDs come on spindles of 100. The lab ordered 25 spindles. How many CDs were ordered in all? A. 2,500 B. 250 C. 125 D. 25 ____ 9. Pencils come in boxes of 100. The Zoller School ordered 30,000 pencils to start the school year. How many boxes were ordered? A. 30,000 B. 3,000 C. 300 D. 20 10. Margo wrote 1,000. She renamed 1,000 as 10 hundreds. How can she rename 1,000 as tens? Explain how Margo could use a model to help. 2 Name: ________________________ ID: A ____ 11. Members of a stamp-collecting club have 213,094 stamps altogether. What is 213,094 written in word form? A. B. C. D. two hundred thirteen, ninety-four two hundred thirteen thousand, ninety-four two hundred thirteen thousand, nine hundred four two hundred thirteen thousand, four ____ 12. Two hundred three thousand, one hundred ten people watched the fireworks display in town. What is that number written in standard form? A. B. C. D. 200,010 203,101 203,110 230,110 ____ 13. In 2010, an animal shelter found new homes for one hundred thirty thousand, six hundred nine dogs and cats. What is that number written in standard form? A. B. C. D. 136,309 130,690 130,609 130,069 ____ 14. The tollbooth records show that 105,076 cars passed through the toll plaza on Saturday. What is the expanded form of 105,076? A. B. C. D. 10,000 + 5,000 + 70 + 6 100,000 + 5,000 + 60 + 7 100,000 + 50,000 + 7 + 6 100,000 + 5,000 + 70 + 6 15. The expanded form of a number is 50,000 + 2,000 + 800 + 6. Write this number in standard form. Then explain how you know if any of the digits in standard form are zero. 3 Name: ________________________ ID: A ____ 16. A theme park had 674,989 visitors in June and 812,383 visitors in July. In August, the park had more visitors than in June, but fewer visitors than in July. Which of the following could be the number of visitors in August? A. B. C. D. 544,989 646,844 765,124 820,486 ____ 17. Brenda used number tiles to make the number 735,512. Frank used number tiles to make the number 734,512. Which statement about these numbers is correct? A. B. C. D. 735,512 < 734,512 735,512 > 734,512 735,512 = 734,512 734,512 > 735,512 ____ 18. During summer vacation, a state park had 248,368 visitors and a water park had 214,626 visitors. The zoo had more visitors than the water park, but fewer than the state park. Which of the following could be the number of visitors at the zoo? A. B. C. D. 201,369 212,729 244,321 263,023 ____ 19. The typical number of travelers who use the airport in a month is 250,000. There were 221,829 travelers in October, 283,459 in November, and 282,999 in December. Which number is less than the typical number of travelers? A. B. C. D. 283,459 282,999 250,000 221,829 20. Mr. Lee got 11,302 votes. Ms. Miller got 11,298 votes. Jana said that Ms. Miller won the election. Is Jana correct? Explain how you know. 4 Name: ________________________ ID: A ____ 21. The population of Miguel’s hometown is 23,718. What is 23,718 rounded to the nearest ten thousand? A. B. C. D. 20,000 23,700 24,000 30,000 ____ 22. A DVD rental business has 12,468 different movies. What is 12,468 rounded to the nearest thousand? A. B. C. D. 10,000 12,000 12,500 13,000 ____ 23. Last week, about 456,900 viewers watched a television show on the Egyptian pyramids. What is the greatest whole number that rounds to 456,900? A. B. C. D. 456,850 456,949 460,000 466,000 ____ 24. An office mailroom sorted 182,617 pieces of mail last year. What is 182,617 rounded to the nearest hundred thousand? A. B. C. D. 100,000 180,000 183,000 200,000 25. Flora says that she can round 72,586 at least four different ways, and all of them will be correct. Felix says that Flora’s idea is impossible. What do you think? Use examples to support your thinking. 5 Name: ________________________ ID: A ____ 26. The surface area of Lake Superior is 31,700 square miles. The surface area of Lake Michigan is 22,278 square miles. What is the total surface area of both lakes? A. B. C. D. 9,422 square miles 22,595 square miles 53,278 square miles 53,978 square miles ____ 27. Last season, 57,690 fans went to football games at Oneida High School. This season 54,083 fans went to the games. What is the total number of fans who went to Oneida High School football games in both seasons? A. B. C. D. 59,852 110,673 111,773 112,673 ____ 28. A car wash cleaned 97,612 cars last year and 121,048 cars this year. What is the total number of cars washed in the two years? A. B. C. D. 218,660 118,650 109,760 109,716 ____ 29. Mrs. Torres paid $139,000 for her house. Eight years later, she built an addition for $67,500. How much did Mrs. Torres pay for her house and the addition? A. B. C. D. $296,500 $206,500 $196,500 $81,400 6 Name: ________________________ ID: A 30. The table shows the number of visitors to a cave over four years. In which two years did the cave have a total of about 90,000 visitors? Explain how you found the solution. ____ 31. A total of 3,718 tickets were sold for a skating show. Of that total, 1,279 were adult tickets. The remaining tickets were child tickets. How many child tickets were sold? A. B. C. D. 2,439 2,561 3,439 4,997 ____ 32. The number of people who took the subway to work in Sean’s city one day was 31,426. The number of people who took the bus was 8,317. How many more people took the subway? A. B. C. D. 39,743 33,109 23,119 23,109 ____ 33. Michigan State and Wayne State are two large colleges in Michigan. Michigan State has 45,166 students enrolled. Wayne State has 32,160 students enrolled. How many fewer students are enrolled in Wayne State? A. B. C. D. 3,006 13,000 13,006 13,326 7 Name: ________________________ ID: A ____ 34. A desktop computer that Ryan likes costs $1,275. A laptop model of the same computer costs $1,648. How much more does the laptop cost? A. B. C. D. $473 $433 $373 $333 35. The table shows heights in meters of some mountains in Peru. Roger has climbed Huascaran and another mountain 1,347 meters shorter. Which other mountain has Roger climbed? Explain your solution. ____ 36. The number of inner tubes rented at the river this year increased by 1,009 over last year. The number of inner tubes rented last year was 4,286. How many inner tubes were rented this year? A. B. C. D. 3,277 4,395 5,285 5,295 8 Name: ________________________ ID: A ____ 37. Mr. Rey and Ms. Klein both took long car trips. Mr. Rey drove 2,178 miles. Ms. Klein drove 1,830 miles. How much farther did Mr. Rey drive on his trip? A. B. C. D. 348 miles 748 miles 1,348 miles 4,008 miles ____ 38. A science museum has collected a total of 8,536 plant fossils. They have also collected 3,855 animal fossils. Use the bar model to find the total number of fossils the museum has. A. B. C. D. 12,481 12,391 11,381 4,681 9 Name: ________________________ ID: A ____ 39. Volunteers worked for a total of 10,479 hours at the science center this year. Last year, they worked 8,231 hours. How many hours did the volunteers work in both years combined? A. B. C. D. 18,710 hours 18,600 hours 2,648 hours 2,248 hours 40. Mr. Dimka drove his truck 9,438 miles last year. This year he drove his truck 3,479 fewer miles. How many miles did Mr. Dimka drive this year? 10 ID: A Chapter 1 Practice Test Answer Section 1. ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: average REF: Lesson 15: Model Place Value Relationships OBJ: Model the 10-to-1 relationship among place-value positions in the base-ten number system. NAT: CC.4.NBT.1 Recognize that in a multi-digit whole number, a digit in one place represents ten times what it represents in the place to its right. For example, recognize that 700 ÷ 70 = 10 by applying concepts of place value and division. TOP: Generalize place value understanding for multi-digit whole numbers. NOT: Number and Operations in Base Ten 2. ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: average REF: Lesson 15: Model Place Value Relationships OBJ: Model the 10-to-1 relationship among place-value positions in the base-ten number system. NAT: CC.4.NBT.1 Recognize that in a multi-digit whole number, a digit in one place represents ten times what it represents in the place to its right. For example, recognize that 700 ÷ 70 = 10 by applying concepts of place value and division. TOP: Generalize place value understanding for multi-digit whole numbers. NOT: Number and Operations in Base Ten 3. ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: average REF: Lesson 15: Model Place Value Relationships OBJ: Model the 10-to-1 relationship among place-value positions in the base-ten number system. NAT: CC.4.NBT.1 Recognize that in a multi-digit whole number, a digit in one place represents ten times what it represents in the place to its right. For example, recognize that 700 ÷ 70 = 10 by applying concepts of place value and division. TOP: Generalize place value understanding for multi-digit whole numbers. NOT: Number and Operations in Base Ten 1 ID: A 4. ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: average REF: Lesson 15: Model Place Value Relationships OBJ: Model the 10-to-1 relationship among place-value positions in the base-ten number system. NAT: CC.4.NBT.1 Recognize that in a multi-digit whole number, a digit in one place represents ten times what it represents in the place to its right. For example, recognize that 700 ÷ 70 = 10 by applying concepts of place value and division. TOP: Generalize place value understanding for multi-digit whole numbers. NOT: Number and Operations in Base Ten 5. ANS: Possible answer: the value of 3 in 4,312 is 10 times the value of 3 in 1,432. In 4,312 the 3 is worth 300, but in 1,432 it is worth 30. 300 is ten times the value of 30. PTS: 1 DIF: average REF: Lesson 15: Model Place Value Relationships OBJ: Model the 10-to-1 relationship among place-value positions in the base-ten number system. NAT: CC.4.NBT.1 Recognize that in a multi-digit whole number, a digit in one place represents ten times what it represents in the place to its right. For example, recognize that 700 ÷ 70 = 10 by applying concepts of place value and division. TOP: Generalize place value understanding for multi-digit whole numbers. NOT: Number and Operations in Base Ten 6. ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: average REF: Lesson 16: Investigate • Rename Numbers OBJ: Rename whole numbers by regrouping. NAT: CC.4.NBT.1 Recognize that in a multi-digit whole number, a digit in one place represents ten times what it represents in the place to its right. For example, recognize that 700 ÷ 70 = 10 by applying concepts of place value and division. TOP: Generalize place value understanding for multi-digit whole numbers. NOT: Number and Operations in Base Ten 2 ID: A 7. ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: average REF: Lesson 16: Investigate • Rename Numbers OBJ: Rename whole numbers by regrouping. NAT: CC.4.NBT.1 Recognize that in a multi-digit whole number, a digit in one place represents ten times what it represents in the place to its right. For example, recognize that 700 ÷ 70 = 10 by applying concepts of place value and division. TOP: Generalize place value understanding for multi-digit whole numbers. NOT: Number and Operations in Base Ten 8. ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: average REF: Lesson 16: Investigate • Rename Numbers OBJ: Rename whole numbers by regrouping. NAT: CC.4.NBT.1 Recognize that in a multi-digit whole number, a digit in one place represents ten times what it represents in the place to its right. For example, recognize that 700 ÷ 70 = 10 by applying concepts of place value and division. TOP: Generalize place value understanding for multi-digit whole numbers. NOT: Number and Operations in Base Ten 9. ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: average REF: Lesson 16: Investigate • Rename Numbers OBJ: Rename whole numbers by regrouping. NAT: CC.4.NBT.1 Recognize that in a multi-digit whole number, a digit in one place represents ten times what it represents in the place to its right. For example, recognize that 700 ÷ 70 = 10 by applying concepts of place value and division. TOP: Generalize place value understanding for multi-digit whole numbers. NOT: Number and Operations in Base Ten 3 ID: A 10. ANS: 100 tens; Possible answer: to model 1,000 using only tens, Margo would have to show 10 × 10 or 100 longs. 100 tens = 1 thousand. PTS: 1 DIF: average REF: Lesson 16: Investigate • Rename Numbers OBJ: Rename whole numbers by regrouping. NAT: CC.4.NBT.1 Recognize that in a multi-digit whole number, a digit in one place represents ten times what it represents in the place to its right. For example, recognize that 700 ÷ 70 = 10 by applying concepts of place value and division. TOP: Generalize place value understanding for multi-digit whole numbers. NOT: Number and Operations in Base Ten 11. ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: average REF: Lesson 17: Read and Write Numbers OBJ: Read and write whole numbers in standard form, word form, and expanded form. NAT: CC.4.NBT.2 Read and write multi-digit whole numbers using base-ten numerals, number names, and expanded form. Compare two multi-digit numbers based on meanings of the digits in each place, using <, =, and > symbols to record the results of comparisons. TOP: Generalize place value understanding for multi-digit whole numbers. KEY: word form | standard form | expanded form | period NOT: Number and Operations in Base Ten 12. ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: average REF: Lesson 17: Read and Write Numbers OBJ: Read and write whole numbers in standard form, word form, and expanded form. NAT: CC.4.NBT.2 Read and write multi-digit whole numbers using base-ten numerals, number names, and expanded form. Compare two multi-digit numbers based on meanings of the digits in each place, using <, =, and > symbols to record the results of comparisons. TOP: Generalize place value understanding for multi-digit whole numbers. KEY: word form | standard form | expanded form | period NOT: Number and Operations in Base Ten 4 ID: A 13. ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: average REF: Lesson 17: Read and Write Numbers OBJ: Read and write whole numbers in standard form, word form, and expanded form. NAT: CC.4.NBT.2 Read and write multi-digit whole numbers using base-ten numerals, number names, and expanded form. Compare two multi-digit numbers based on meanings of the digits in each place, using <, =, and > symbols to record the results of comparisons. TOP: Generalize place value understanding for multi-digit whole numbers. KEY: word form | standard form | expanded form | period NOT: Number and Operations in Base Ten 14. ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: average REF: Lesson 17: Read and Write Numbers OBJ: Read and write whole numbers in standard form, word form, and expanded form. NAT: CC.4.NBT.2 Read and write multi-digit whole numbers using base-ten numerals, number names, and expanded form. Compare two multi-digit numbers based on meanings of the digits in each place, using <, =, and > symbols to record the results of comparisons. TOP: Generalize place value understanding for multi-digit whole numbers. KEY: word form | standard form | expanded form | period NOT: Number and Operations in Base Ten 15. ANS: 52,806; Possible answer: this number goes up to ten thousands. Even though there are no tens in this number, it must have a zero for the tens place. PTS: 1 DIF: average REF: Lesson 17: Read and Write Numbers OBJ: Read and write whole numbers in standard form, word form, and expanded form. NAT: CC.4.NBT.2 Read and write multi-digit whole numbers using base-ten numerals, number names, and expanded form. Compare two multi-digit numbers based on meanings of the digits in each place, using <, =, and > symbols to record the results of comparisons. TOP: Generalize place value understanding for multi-digit whole numbers. KEY: word form | standard form | expanded form | period NOT: Number and Operations in Base Ten 5 ID: A 16. ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: average REF: Lesson 18: Compare and Order Numbers OBJ: Compare and order whole numbers based on the values of the digits in each number. NAT: CC.4.NBT.2 Read and write multi-digit whole numbers using base-ten numerals, number names, and expanded form. Compare two multi-digit numbers based on meanings of the digits in each place, using <, =, and > symbols to record the results of comparisons. TOP: Generalize place value understanding for multi-digit whole numbers. NOT: Number and Operations in Base Ten 17. ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: average REF: Lesson 18: Compare and Order Numbers OBJ: Compare and order whole numbers based on the values of the digits in each number. NAT: CC.4.NBT.2 Read and write multi-digit whole numbers using base-ten numerals, number names, and expanded form. Compare two multi-digit numbers based on meanings of the digits in each place, using <, =, and > symbols to record the results of comparisons. TOP: Generalize place value understanding for multi-digit whole numbers. NOT: Number and Operations in Base Ten 18. ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: average REF: Lesson 18: Compare and Order Numbers OBJ: Compare and order whole numbers based on the values of the digits in each number. NAT: CC.4.NBT.2 Read and write multi-digit whole numbers using base-ten numerals, number names, and expanded form. Compare two multi-digit numbers based on meanings of the digits in each place, using <, =, and > symbols to record the results of comparisons. TOP: Generalize place value understanding for multi-digit whole numbers. NOT: Number and Operations in Base Ten 19. ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: average REF: Lesson 18: Compare and Order Numbers OBJ: Compare and order whole numbers based on the values of the digits in each number. NAT: CC.4.NBT.2 Read and write multi-digit whole numbers using base-ten numerals, number names, and expanded form. Compare two multi-digit numbers based on meanings of the digits in each place, using <, =, and > symbols to record the results of comparisons. TOP: Generalize place value understanding for multi-digit whole numbers. NOT: Number and Operations in Base Ten 6 ID: A 20. ANS: No; Possible explanation: Mr. Lee received more votes than Ms. Miller. 11,302 is greater than 11,298 because 3 hundreds are greater than 2 hundreds. 11,302 > 11,298. PTS: 1 DIF: average REF: Lesson 18: Compare and Order Numbers OBJ: Compare and order whole numbers based on the values of the digits in each number. NAT: CC.4.NBT.2 Read and write multi-digit whole numbers using base-ten numerals, number names, and expanded form. Compare two multi-digit numbers based on meanings of the digits in each place, using <, =, and > symbols to record the results of comparisons. TOP: Generalize place value understanding for multi-digit whole numbers. NOT: Number and Operations in Base Ten 21. ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: average REF: Lesson 19: Round Numbers OBJ: Round a whole number to any place. NAT: CC.4.NBT.3 Use place value understanding to round multi-digit whole numbers to any place. TOP: Generalize place value understanding for multi-digit whole numbers. KEY: round NOT: Number and Operations in Base Ten 22. ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: average REF: Lesson 19: Round Numbers OBJ: Round a whole number to any place. NAT: CC.4.NBT.3 Use place value understanding to round multi-digit whole numbers to any place. TOP: Generalize place value understanding for multi-digit whole numbers. KEY: round NOT: Number and Operations in Base Ten 23. ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: average REF: Lesson 19: Round Numbers OBJ: Round a whole number to any place. NAT: CC.4.NBT.3 Use place value understanding to round multi-digit whole numbers to any place. TOP: Generalize place value understanding for multi-digit whole numbers. KEY: round NOT: Number and Operations in Base Ten 7 ID: A 24. ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: average REF: Lesson 19: Round Numbers OBJ: Round a whole number to any place. NAT: CC.4.NBT.3 Use place value understanding to round multi-digit whole numbers to any place. TOP: Generalize place value understanding for multi-digit whole numbers. KEY: round NOT: Number and Operations in Base Ten 25. ANS: Possible answer: Flora is right, because she could round 72,586 to the nearest ten thousand, thousand, hundred, or ten. So, she could correctly round to 70,000, 73,000, 72,600, or 72,590. PTS: 1 DIF: average REF: Lesson 19: Round Numbers OBJ: Round a whole number to any place. NAT: CC.4.NBT.3 Use place value understanding to round multi-digit whole numbers to any place. TOP: Generalize place value understanding for multi-digit whole numbers. KEY: round NOT: Number and Operations in Base Ten 26. ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: average REF: Lesson 20: Add Whole Numbers OBJ: Add whole numbers and determine whether solutions to addition problems are reasonable. NAT: CC.4.NBT.4 Fluently add and subtract multi-digit whole numbers using the standard algorithm. TOP: Use place value understanding and properties of operations to perform multi-digit arithmetic. NOT: Number and Operations in Base Ten 27. ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: average REF: Lesson 20: Add Whole Numbers OBJ: Add whole numbers and determine whether solutions to addition problems are reasonable. NAT: CC.4.NBT.4 Fluently add and subtract multi-digit whole numbers using the standard algorithm. TOP: Use place value understanding and properties of operations to perform multi-digit arithmetic. NOT: Number and Operations in Base Ten 8 ID: A 28. ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: average REF: Lesson 20: Add Whole Numbers OBJ: Add whole numbers and determine whether solutions to addition problems are reasonable. NAT: CC.4.NBT.4 Fluently add and subtract multi-digit whole numbers using the standard algorithm. TOP: Use place value understanding and properties of operations to perform multi-digit arithmetic. NOT: Number and Operations in Base Ten 29. ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: average REF: Lesson 20: Add Whole Numbers OBJ: Add whole numbers and determine whether solutions to addition problems are reasonable. NAT: CC.4.NBT.4 Fluently add and subtract multi-digit whole numbers using the standard algorithm. TOP: Use place value understanding and properties of operations to perform multi-digit arithmetic. NOT: Number and Operations in Base Ten 30. ANS: Year 1 and Year 3; Possible answer: I rounded all the numbers to the nearest ten thousand. 52,753 is about 50,000; 55,168 is about 60,000; 37,047 is about 40,000; and 61,590 is about 60,000. 50,000 + 40,000 = 90,000. PTS: 1 DIF: average REF: Lesson 20: Add Whole Numbers OBJ: Add whole numbers and determine whether solutions to addition problems are reasonable. NAT: CC.4.NBT.4 Fluently add and subtract multi-digit whole numbers using the standard algorithm. TOP: Use place value understanding and properties of operations to perform multi-digit arithmetic. NOT: Number and Operations in Base Ten 9 ID: A 31. ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: average REF: Lesson 21: Subtract Whole Numbers OBJ: Subtract whole numbers and determine whether solutions to subtraction problems are reasonable. NAT: CC.4.NBT.4 Fluently add and subtract multi-digit whole numbers using the standard algorithm. TOP: Use place value understanding and properties of operations to perform multi-digit arithmetic. NOT: Number and Operations in Base Ten 32. ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: average REF: Lesson 21: Subtract Whole Numbers OBJ: Subtract whole numbers and determine whether solutions to subtraction problems are reasonable. NAT: CC.4.NBT.4 Fluently add and subtract multi-digit whole numbers using the standard algorithm. TOP: Use place value understanding and properties of operations to perform multi-digit arithmetic. NOT: Number and Operations in Base Ten 33. ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: average REF: Lesson 21: Subtract Whole Numbers OBJ: Subtract whole numbers and determine whether solutions to subtraction problems are reasonable. NAT: CC.4.NBT.4 Fluently add and subtract multi-digit whole numbers using the standard algorithm. TOP: Use place value understanding and properties of operations to perform multi-digit arithmetic. NOT: Number and Operations in Base Ten 34. ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: average REF: Lesson 21: Subtract Whole Numbers OBJ: Subtract whole numbers and determine whether solutions to subtraction problems are reasonable. NAT: CC.4.NBT.4 Fluently add and subtract multi-digit whole numbers using the standard algorithm. TOP: Use place value understanding and properties of operations to perform multi-digit arithmetic. NOT: Number and Operations in Base Ten 10 ID: A 35. ANS: Huapi; Possible explanation: I rounded the height of Huascaran to 6,800, and then subtracted 1,300, which is 5,500. The closest mountain to that height is Huapi, at 5,421 meters. So I did the subtraction: 6,768 – 5,421 = 1,347. PTS: 1 DIF: average REF: Lesson 21: Subtract Whole Numbers OBJ: Subtract whole numbers and determine whether solutions to subtraction problems are reasonable. NAT: CC.4.NBT.4 Fluently add and subtract multi-digit whole numbers using the standard algorithm. TOP: Use place value understanding and properties of operations to perform multi-digit arithmetic. NOT: Number and Operations in Base Ten 36. ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: average REF: Lesson 22: Problem Solving • Comparison Problems with Addition and Subtraction OBJ: Use the strategy draw a diagram to solve comparison problems with addition and subtraction. NAT: CC.4.NBT.4 Fluently add and subtract multi-digit whole numbers using the standard algorithm. TOP: Use place value understanding and properties of operations to perform multi-digit arithmetic. NOT: Number and Operations in Base Ten 37. ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: average REF: Lesson 22: Problem Solving • Comparison Problems with Addition and Subtraction OBJ: Use the strategy draw a diagram to solve comparison problems with addition and subtraction. NAT: CC.4.NBT.4 Fluently add and subtract multi-digit whole numbers using the standard algorithm. TOP: Use place value understanding and properties of operations to perform multi-digit arithmetic. NOT: Number and Operations in Base Ten 11 ID: A 38. ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: average REF: Lesson 22: Problem Solving • Comparison Problems with Addition and Subtraction OBJ: Use the strategy draw a diagram to solve comparison problems with addition and subtraction. NAT: CC.4.NBT.4 Fluently add and subtract multi-digit whole numbers using the standard algorithm. TOP: Use place value understanding and properties of operations to perform multi-digit arithmetic. NOT: Number and Operations in Base Ten 39. ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: average REF: Lesson 22: Problem Solving • Comparison Problems with Addition and Subtraction OBJ: Use the strategy draw a diagram to solve comparison problems with addition and subtraction. NAT: CC.4.NBT.4 Fluently add and subtract multi-digit whole numbers using the standard algorithm. TOP: Use place value understanding and properties of operations to perform multi-digit arithmetic. NOT: Number and Operations in Base Ten 40. ANS: 5,959 miles PTS: 1 DIF: average REF: Lesson 22: Problem Solving • Comparison Problems with Addition and Subtraction OBJ: Use the strategy draw a diagram to solve comparison problems with addition and subtraction. NAT: CC.4.NBT.4 Fluently add and subtract multi-digit whole numbers using the standard algorithm. TOP: Use place value understanding and properties of operations to perform multi-digit arithmetic. NOT: Number and Operations in Base Ten 12