From Cells to Organisms
advertisement

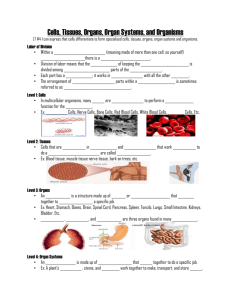
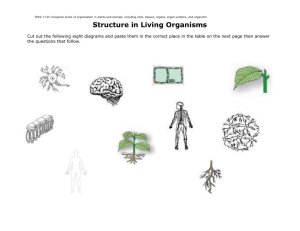
Name LESSON Date Outline From Cells to Organisms Use your textbook to help you fill in the blanks. What are living things? cells 1. All living things are made of . five 2. Living things carry out functions. basic life reproduce 3. Living things must be able to more of their own kind. respond 4. Organisms can react, or environment. or make , to their How do cells work together? tissue 5. A group of similar cells called a(n) work together to do the same job in an organism. 6. Different kinds of tissues can perform different jobs in an organism. 7. The flesh of fruits is an example of tissue that can be found in plants many . 8. Different tissues working together form a(n) © McGraw-Hill Education organ . 9. When different organs work together they form a(n) organ system Unit 4 • Cells to Living Organisms Unit Resources . Use with Lesson 2 From Cells to Organisms 4-19 LESSON Outline Name Date What are some plant and animal organ systems? root system 10. The roots are the main organ in the plants. 11. Stems and leaves make up the in plants. shoot of system 12. In the salamander, the organ system that breaks down food for energy is the digestive system. brain 13. The bones, the muscles, and the are parts of the organ systems that control movement and responses. circulatory 14. The heart is part of the transports blood and other materials. system, which Critical Thinking 15. Do all organisms have cells, tissues, organs, and organ systems? Give examples to support your answer. No, all organisms have cells, but only some multicellular organisms have tissues, organs and organ systems. Even a unicellular organism such as a bacterium is made of a cell. It is does not have tissues, organs, or organ systems. More complex, multicellular organisms like humans have cells, tissues, organs, and organ systems. © McGraw-Hill Education 4-20 Unit 4 • Cells to Living Organisms Unit Resources Use with Lesson 2 From Cells to Organisms