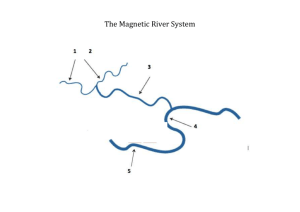
Empirical version of the Rational method to estimate peak discharge
advertisement

A study guide on the Empirical version of the Rational Method to estimate peak discharge runoff Bruce Carey Soil conservationist Brisbane, Queensland, Australia July 2014 bcarey@tpg.com.au 1 This study guide was prepared in 2014 as supplementary material for the publication Soil conservation measures – Design manual for Queensland. The manual was produced in 2004 by the Queensland Department of Natural Resources and Mines and can be downloaded from the Department of Environment and Heritage Protection library catalogue (search for DEHP library catalogue) and from the Landcare Queensland website. The manual contains the following chapters: 1 Introduction 2 Soil conservation planning 3 Runoff processes 4 Designing for risk 5 Peak discharge estimation 6 The Empirical version of the Rational Method 7 Darling Downs Regional Flood Frequency version of the Rational Method 8 Channel design principles 9 Contour banks 10 Diversion banks 11 Waterways 12 Floodplain applications Carey Bruce and Stone Barry (2004). Soil conservation measures – A design manual for Queensland. Queensland Department of Natural Resources and Mines. The manual is currently being revised on a voluntary basis by Bruce Carey and will contain the following additional chapters. 12 Land management on floodplains 13 Stream stability 14 Soil conservation in horticulture 15 Gully control 16 Property infrastructure Soil erosion had become a major problem in Queensland cropping areas by the late 1940s. Visible evidence of this erosion is readily apparent from the aerial photography program that the Queensland government began at that time. There has been considerable progress in the adoption of soil conservation practices in cropping areas since the State government began an extension program to assist farmers to implement soil conservation measures beginning in the late 1940s. However, the task is by no means complete and with the phasing out of the soil conservation extension service in the 1990s, the pool of knowledge required to assist farmers to implement soil conservation measures has rapidly declined. In many ways, we know less about the condition of our land, then we did in the last century, when 50 soil conservation extension officers working in 30 centres throughout Queensland regularly reported on what was happening in their area. Of special concern is the lack of young people with soil conservation skills. Tertiary institutions offer minimal, if any, training in this area and academic staff and scientists generally have a very limited knowledge of this topic – hence the need for the study guides. They are intended for use by soil conservation practitioners, farmers, students, academics and staff from industry, NRM regional bodies, Landcare groups and government. 1955 2003 Soil conservation study guides are available on the following topics (additional topics are planned). • • • • • • • Runoff processes Planning soil conservation layouts Empirical version of the Rational Method to estimate peak discharge runoff The Darling Downs Flood Frequency version of the Rational Method to estimate peak discharge runoff Design of channels for soil conservation Contour banks Grassed waterways for erosion control in cropping lands These study guides can be downloaded from the Landcare Queensland website at http://landcare.org.au/resources-links/achieving-soil-conservation-in-queensland/ (from the homepage click on ‘Resources and links’ and then ‘Achieving soil conservation’. About the author Bruce Carey began his career as a soil conservation extension officer with the Queensland Department of Primary Industries in 1971. He carried out this role in Millmerran, Goondiwindi, Emerald and Toowoomba before moving to Brisbane in 1988. He maintained his links to soil conservation while working in several Queensland government agencies until his retirement in 2012. Like most soil conservationists, he has a keen interest in the relationships between soil, water and vegetation. His special interest is in documenting the knowledge gained about soil conservation in Queensland. He is an author of the publications Soil conservation measures – A design manual for Queensland and the book Managing grazing lands in Queensland. He has written over 50 fact sheets related to sustainable land management. 5 Acknowledgement Thanks to the Queensland Murray Darling Committee(QMDC) for providing assistance to produce these study guides and to Landcare Queensland for hosting them on their website. Thanks also go to the Queensland Department of Science, Information Technology, Innovation and the Arts (DSITIA) for the use of many of the photographs in this study guide which were taken by soil conservation extension officers in the 1970s and 1980s. Google earth Thanks also to Google earth. Introduced in 2005, we now have a tendency to take this incredible tool for granted. In the last century, one of the tools of trade for soil conservationists was aerial photography. This photography was generally taken every 10 years, for most parts of Queensland since the 1940s. It was usually black-and-white photography at a fairly broad scale. But it was always consulted before any property visit. When on the property, it was used as a basis of discussion with the farmer during the property inspection and while planning and designing soil conservation structures. It provided a base for the property plans that were produced. Google Earth is nirvana for anyone interested in soil conservation. For no cost on your home computer, you can take a closer look at any piece of land in the world and get some indications of how it is being used and 6 managed. Tips on using this study guide It is best to view this PDF file in ‘Full screen mode’ (click on ‘View’ and then ‘Full screen mode’) This publication has hyperlinks. From the table of contents you can link to any section in the study guide. From each section heading you can link back to the table of contents. You can go to the next slide by a left click of the mouse or by pressing ‘Page down’ on the keyboard. You can return to the previous slide by pressing ‘page up’ on the keyboard. To exit the publication at any time press the ‘Escape’ button on the keyboard 7 A study guide for the Empirical version of the Rational Method to estimate peak discharge runoff Table of Contents • • • • Introduction Factors affecting the peak runoff rate Designing for risk Applying the Rational method A study guide on the Empirical version of the Rational Method to estimate peak discharge runoff Return to Table of Contents Introduction There are two components to the design of soil conservation structures • How much runoff does the structure need to handle? – use of the Rational Method • How big does it have to be to handle this runoff? – use of the Manning formula ? ? ? This study guide deals with runoff estimation. Other study guides deals with the Manning formula for the design of structures. How many m3/s ??? In soil conservation design, the peak rate of runoff that a structure will have to accommodate (in m3/sec)needs to be estimated. Such estimates are needed for structures like contour banks, waterways, dam spillways and road culverts. For the design of storage structures like dams for water supply and irrigation, the volume of run-off (in megalitres) produced by catchment over a period of time needs to be estimated. This study guide and the soil conservation design manual only deals with estimations of peak rates of run-off. A hydrograph for a single flood event Peak discharge A study guide on the Empirical version of the Rational Method to estimate peak discharge runoff Return to Table of Contents Factors affecting the peak runoff rate The Rational Formula is said to have been conceived by an engineer in the 1850s. If you were that engineer, how would you go about developing a formula to estimate a peak rate of runoff for the design of a structure? The first step might be to think about all of the factors that affect the production of run-off. What are they? Factors affecting the runoff rate • • • • • • • • Rainfall – intensity and amount Soil types Slope Area of the catchment Shape of the catchment Land use and management Storage and detention in the catchment How wet is the catchment likely to be for the design event? The proportion of rainfall that becomes runoff is generally smaller than most people would expect • Freebairn and Silburn (2004) in Southern Qld, runoff occurs at the paddock scale on an average of 5 days per year (and a significant soil movement about once every 2 to 4 years) • Lawrence and Cowie (1992) Brigalow Research Station project, average annual runoff under brigalow forest represented only 3% of the total annual rainfall (6% for pasture) • (from section 3.1 of the manual) Water Balance and Yield (Greenmount 1978-88) Bare fallow Stubble mulch Evap 67% Evap 68% Runoff 12% Soil Water 20% Runoff 8% Soil Water 25% Extra water 5% t/ha 3 Crop Yield extra yield 2.7 Under stubble mulch an average of only 8% of the total annual rainfall became run-off 2.5 2.25 0 1 Bare Fallow 2 3 Stubble Mulch 18 The hydrologic cycle Plant Available Soil Water Courtesy: Department of Atmospheric Sciences at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, Catchment shape These catchments have the same area but they would have different peak rates of run-off. A contour bay is an unusual shape for a catchment. Contour banks act like a dam and they detain a considerable amount of run-off. Run-off along the channel can be very slow especially when the channel is lined with, a crop or stubble. Natural catchments Contour bay catchments During the 16 year period, the largest run-off events consistently occurred on land where the stubble had been burnt This event occurred late in the fallow when the difference in the amount of cover between treatments was not so great So if you were the engineer asked to determine a method of obtaining the peak rate of run-off from a small catchment, how would you go about it? Lets forget about a typical catchment for now and look at a very simple catchment like the roof of a house Let’s suppose a storm occurs where the rate of rainfall is constant for the entire event (not very likely in reality). You measure the rate of flow from the roof as it flows down the downpipe. What would the resulting hydrograph look like? Assuming rain falls at a constant rate Peak discharge A hydrograph At this point, the whole of the roof is contributing What are the 2 factors affecting the runoff rate from the roof? (assuming it is impermeable and has no leaks !) • The rainfall rate (in mm/hr) • The area of the roof (assume it’s a very large roof and we’ll use hectares) These two factors are used in the next equation. Q = I * A * 0.00278 • Q = the peak rate of runoff in (m3/sec) • I = the rainfall rate (mm/hr) • A = the area of the roof (in hectares) 0.00278 balances the units (mm to m3 and hours to seconds) 0.00278 = 1/360. There are 3600 seconds in an hour ThIs formula is the basis of the Rational Method To apply it to a catchment, we simply add a C factor which estimates what proportion of the rainfall becomes runoff during the event. This accounts for “losses” such as infiltration. So the Rational Formula becomes Q = C* I * A * 0.00278 (m3/sec) The basis of the rational method is that it assumes that a 1 in 10 year runoff event occurs when a 1 in 10 year rainfall event occurs on a catchment under ‘average’ conditions So how do we apply this formula to calculate the peak discharge at a design point in a catchment? Q = C* I * A * 0.00278 (m3/sec) • A the catchment area in hectares contributing to the design point • C The C value we get from Table 6.2 of the design manual • I is the rainfall intensity in mm/hr for the design period eg 1 in 10 years Now we’ll have a closer look at how we determine values for C and I Q = Cy* I * A * 0.00278 (m3/sec) Cy The runoff coefficient • Defined as the ratio of the peak runoff rate of a given ARI (Annual Recurrence Interval in years) to the mean rate of rainfall for the design event • In essence this is the ‘black box’ – it attempts to take into account all of the catchment characteristics that affect how much rainfall becomes runoff during the design rainfall event • See Tables 6.1 and 6.2 to determine C values. Note that these are arbitrary values and are not based on hydrological data First step is to determine the ‘runoff potential’ Second step is to select a C value from this table The keyword on TV busy on the panel A roof would have a run-off coefficient of 1, while a deep sand on the beach would have a runoff coefficient of 0.1. Equivalent Impervious Area The Equivalent Impervious Area of a catchment is the area that would produce a design flood of the same size as that estimated for the catchment if that Equivalent Impervious Area has a runoff coefficient of 1; this means that all the rainfall falling on the Equivalent Impervious Area runs off. It is calculated by dividing a catchment into components having similar runoff producing characteristics. The Equivalent Impervious Area for each component is then determined by multiplying its area by its runoff coefficient. The Equivalent Impervious Areas for each component are then added to determine the Equivalent Impervious Area for the total catchment. As Equivalent Impervious Area incorporates both the runoff coefficient and the catchment area, the Rational Method formula then becomes: Qy = Where Qy = Itc,y = equal to Aei,y = 0.00278 Itc,y Aei,y Equation 6.2 design peak runoff rate (m3/s), for an ARI of y years average rainfall intensity (mm/h), for the design ARI and for a duration the tc (minutes) of the catchment, and Equivalent Impervious Area (ha) for the design ARI of y years Example: Determine the Equivalent Impervious Area for a 90 ha catchment which consists of 20 ha of cultivation (Cy = 0.6), 30 ha of forest (Cy = 0.3) and 40 ha of pasture (Cy = 0.4). Q = C* I tc,y * A * 0.00278 (m3/sec) I tc,y The rainfall intensity • I tc,y = average rainfall intensity (mm/h), for the design ARI and for a duration equal to the ‘time of concentration’ tc (minutes) for the design point Time of concentration (Tc) is the time estimated for water to flow from the most hydraulically remote point of the catchment to a design point The time of concentration for the area between two contour banks ( a contour bay) The time of concentration for a catchment The Rational Method assumes that the highest peak rate of runoff from the catchment will be caused by a storm of duration just long enough for runoff from all parts of the catchment to contribute simultaneously to the design point. The ‘time of concentration’ is calculated by summing the travel times of flow in the different hydraulic components. Those components may include one or more of the following. • overland flow • stream flow • flow in structures (contour banks and waterways) Several flow paths may need to be assessed to determine the longest estimated travel time, which is then considered to be the time of concentration. Note that stream flow in this situation generally refers to a drainage line which may only produce runoff on two or three occasions per year. Streamflow rarely occurs in a paddock with contour banks flowing into a constructed waterway. Determining the time of concentration for design point P2 Overland flow (determined from the graph on the next slide Bank flow (interception bank) Waterway flow Flow time in the contour bank channel and waterway is determined by dividing the length of the flow path by the design velocity Compare the flow times for the red and blue pathways. The time of concentration (tc) will be the longest of these times. Poorly grassed surface Land slope of 2% Time of concentration 15 minutes 100 metres of overland flow Rainfall intensity design chart for Capella in the Central Highlands RIFD chart Design rainfall intensity of 90 mm/hour ARI of 10 yrs (1 in 10 rainfall event) Storm duration of 30 minutes The storm duration is the calculated time of concentration for a design point and is used to to determine the design rainfall intensity for the required ARI (annual recurrence interval) This data can be obtained for any location in Australia from the Bureau of Meteorology A study guide on the Empirical version of the Rational Method to estimate peak discharge runoff Return to Table of Contents Designing for risk When designing a structure to carry or store runoff, it is necessary to consider how often it will be acceptable for the structure to fail or to surcharge. The following terms, which refer to both rainfall and runoff, are used when discussing probability or risk: • Average Recurrence Interval (ARI), also referred to as average return period, is the average number of years (denoted as y years) within which an event will be equalled or exceeded. • Frequency is an alternative way of expressing ARI. A frequency of 1 in y years means that the event will be equalled or exceeded once in y years on average. • Probability is the inverse of frequency, that is, 1/y. It is often expressed as percentage probability, this being 100/y %. It is important to understand that whatever terms are used, they all refer to long-term averages and that the periods between events are random. This means, that if an event with an ARI of 10 years occurred last year, the chances of a similar event occurring this year have not lengthened, they remain the same. That is, there is a 10% chance (or odds of 10 to 1) of it happening again. This concept should be fully explained to clients for whom designs are prepared. For the design of soil conservation structures, the estimation of runoff usually relates only to very small areas such as a paddock or a small catchment on a farm. Extremely high rainfall events that are ‘off the scale’ of a district rainfall intensity chart can occur in very localised areas. So it is likely that in any district, at the paddock scale, rare events, such as those with an ARI of 100 years, will occur somewhere in a catchment on a much more frequent basis than 1 in 100 years. Structures should be designed for ‘average’ conditions. Extreme values of the parameters of runoff estimation models are used by some operators to provide safety margins in design. This results in runoff estimates with unknown ARI’s and increased construction costs. If a more conservative design is required, it is better to design for a higher ARI. A study guide on the Empirical version of the Rational Method to estimate peak discharge runoff Return to Table of Contents Applying the Rational method Applying the Rational method 1. Decide on the design ARI e.g. a 1 in 10 yr event (see Chapter 4 Design for risk) 2. Allocate locations on the plan for design points (refer to Chapter 2, Soil Conservation Planning). 3. Estimate the ‘time of concentration’ for the design point. 4. From the IFD diagram for the district, determine the design rainfall intensity relevant to the ‘time of concentration’ and the required ARI. 5. Identify and measure component areas within the catchment and assign a runoff coefficient to each. 6. Calculate the design peak discharge by substitution into Equations 6.1 or 6.2 as appropriate. The pro forma on the next slide guides you through the process 44 Figure 6.6 Waterway design proforma Landholder Date Contact details Property description Farm Code 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 Design Point Design ARI in years Length of overland flow (m) Average slope (%) Time of travel for overland flow (min) Length of stream flow (m) Average slope of stream (%) Stream velocity (m/s) Time of travel in stream (minutes) Length of interception bank flow (m) Interception bank velocity (m/s) Time of travel in interception bank (min) Tc previous design point (minutes) 14 Length of waterway flow (m) 15 Waterway velocity (m/s) 16 17 Time of travel in waterway (minutes) Time of concentration, tc, (minutes) 18 19 Rainfall Intensity, Itc,y (mm/h) Area at previous design point 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 Area of pasture & average slope (ha) Runoff co-efficient EIA, pasture (ha) Area of cultivation & average slope (ha) Runoff co-efficient EIA, cultivation (ha) Other area & average slope (ha) Runoff co-efficient EIA, other (ha) Total area (ha) Total EIA, Aei,y (ha) Peak discharge, Qy (m3/s) Design point slope (%) Retaining bank batters (1:Z (V:H)) Minimum retardance value Design velocity, V (m/s) Bottom width, W (m) Maximum retardance value Flow depth, d (m) Settled bank height (m) Comments Plan Number From survey or farm plan Row 6 / (Row 8 *60) Row 10 / (Row 11 * 60) Previous design point Time Additional length if Row 13 is used Estimated or previous design point Row 14 / (Row 15 * 60) Total Rows 5,9,12, 13, 16 as applic From IFD data for this location Previous point Total area Equivalent Impervious Area (EIA) Additional area if Row 19 is used Row 20 x Row 21 Additional area if Row 19 is used Row 23 x Row 24 Additional area if Row 19 is used Row 26 x Row 27 Rows: 19+20+23+26 Rows: 19+22+25+28 Qy = 0.00278 x I x Aei,y d + 0.15 m freeboard Shire Form used to estimate peak discharge and waterway dimensions for design points along a waterway Selecting Design Points • the commencement and outlet of waterways • points where a waterway enters and exits a property, paddock or unfenced property lot • points where there is a significant change in the specifications for a waterway such as: – at a change in slope – where two waterways join – at a bend in a waterway • where key works are required for public utilities such as, road/rail culverts, access inverts Peak discharge estimation example Calculate the peak discharges for the waterway design points H3, H4 and H5 and waterway H6 – H7 using the design form and the data provided on the next slide Runoff potential Soil permeability ARI Waterway velocity Contour bank velocity Overland flow Location Topography 220m 2 M 10 years 1 m/s 0.5 m/s Average grassed Pittsworth Rolling Q = C* I * A * 0.00278 9 ha 350m 4 ha 180m 11 ha 1ha 180m 530m 11 ha 280m 70m 12 ha 14 ha 4 ha The Excel Spreadsheet RAMWADE allows you to estimate runoff and design the waterway for a series of design points Rational Method Waterway Design Example of the use of RAMWADE for waterway design The Empirical version of the Rational Method is recommended for catchments up to 1000 ha. Beyond that, more sophisticated methods should be considered. Survey by Mike Stephens (DPI) in 1988 Comparing the ‘Empirical’ and the Darling Downs Flood Frequency (DDFF) versions of the Rational Method For the design of soil conservation measures in Queensland, the ‘Empirical’ version of the Rational Method is usually used. It is named because the parameters it uses (apart from rainfall data) are arbitrary and are generally based on experience or observation rather than field measurements obtained over a long period of time. The publication Australian rainfall and run-off recommends that any method of peak discharge estimation for design purposes should be based on measured data from a range of catchments. This data is then used to develop what is known as a ‘statistical’ version of the Rational Method. However, while we have some streamflow data for major creeks and streams there is very little data collected from small agricultural catchments. There was a program in place to collect this data from some small agricultural catchments of Queensland in the 1970s and 1980s but this work has virtually ceased. A project carried out in 1987 used all of the runoff data available for the Darling Downs to develop a statistical version of the rational method ( the DDFF). This version is described in Chapter 7 of Soil Conservation Measures – Design Manual for Queensland. It is a simpler method than the Empirical Method because the time of concentration is based entirely on the area of the catchment contributing to the design point. However, the method has no way of allowing for the reduction in runoff caused by different land management methods and the use of contour banks. As a result, the Empirical version of the Rational Method is generally used in Queensland for the design of soil conservation measures. 52 A study guide on the Empirical version of the Rational Method to estimate peak discharge runoff Return to Table of Contents End