Vagina
advertisement

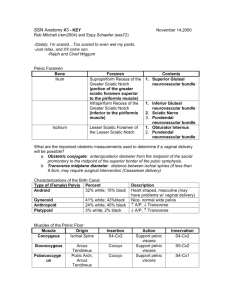
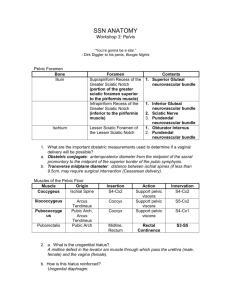
Femal genital system II Pelvic floor, urogenital diaphragm Mayer-Rokitansky-Küster-Hauser syndrome The cause of MRKH syndrome is unknown, although it probably results from a combination of genetic and environmental factors. The reproductive abnormalities of MRKH syndrome are due to incomplete development of the Müllerian duct from which develops the uterus, fallopian tubes, and the upper part of the vagina.. It is unclear why some affected individuals have abnormalities in parts of the body other than the reproductive system. Most cases of MRKH syndrome occur in people with no history of the disorder in their family. The uterus in place in the pelvis of the recipient with bilateral end-to side anastomoses on the recipient's external iliac vessels. Br€annstr€om. Uterus transplantation trial. Fertil Steril 2014. Brännström M et al.: Livebirth after uterus transplantation The Lancet, 385: 9968, pp.607 - 616 (2015) http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(14)61728-1 Vagina (kolpos) fornix, ostium, hymen, rugae, columns, urethral carina, trigonal area of vagina, mucous membrane, muscular layer, spongy layer, parakolpium, urogenital hiatus, pubovaginal m., promontorium of vagina, urethrovaginal sphincter muscle, bulbospongiosus muscle, Magnetic resonance image of female pelvis in sagittal plane Sling of the pubovaginalis muscle Magnetic resonance image of female pelvis in plane of urogenital hiatus (level 2 according to DeLancey) Anatomy of the pelvic outlet (scheme based on MRI) Symphysis Urogenital hiatus Urethra Vagina Anal canal Puborectal sling (levator ani) Tendinous arch of levator ani Tendinous arch of pelvic fascia Vagina The vagina has mucosal, muscular, and adventitial layers. There are no secretory glands, but the cells of the thick, nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium become filled with glycogen before desquamation. The lamina propria mucosae contains thin—walled veins and muscular layers exude fluid on the surface of the epithelium. The papillae and entire lamina propria are very rich in protective lymphocytes and neutrophils. The muscular layer has bundles of smooth muscle arranged in a circular manner near the mucosa and longitudinally near the adventitia. The wall of vagina (mucosal, muscular, and adventitial layers) (a): The micrograph shows the lamina propria (L) is highly cellular and extends narrow papillae into the epithelium (E). (b): Higher magnification of the epithelium and lamina propria (LP) shows invasion of leukocytes (arrows) between epithelial cells from the connective tissue External genital organs Pudendum (vulva) Mons pubis Labium majus Labium minus Pudendal cleft Vestibule Bulb of vestibule Clitoris Female external genitalia (vulva): mons pubis, pudendal cleft, labia majora, praepuce of clitoris, glans of clitoris, frenulum of clitoris, labia minora, ostium urethrae externum, ostium vaginae, carunculae hymenales, commisura labiorum posterior, perineum, ostium of greater vestibular gland n. ilioinguinalis, n. genitofemoralis, n.cutaneus femoris posterior, n. pudendus Clitoris, bulbus vestibuli glans clitoridis, corpus clitoridis, crus clitoridis, bulbus vestibuli Perineal muscles in urogenital region: bulbospongiosus, ischocavernosus, compressor of urethra, urethrovaginal sphincter, superficial transverse perineal m. Sources of illustrations used : Gray´s Anatomy, Sobotta: Atlas der Anatomie des Menschen Grim, Druga: Regional Anatomy, Galen, Prague 2012 Benninghoff, Drenckhahn: Anatomie I., II. Carlson,B.M.: Human Embryology and Developmental Anatomy Recommended Textbooks: R. S. Snell: Clinical Anatomy. 7th Edition, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2004, pp. 478 – 562 or K. L. Moore: Clinically oriented Anatomy, 3rd Edition, Williams & Wilkins 1992, pp. 501 – 635 and W. Kahle: Color Atlas/Text of Human Anatomy, Vol. 2 Internal organs. Thieme, 4th English Edition, 1993 Langman´s Medical Embryology,11th Edition, 2010 Junqueira´s Basic Histology 12th Edition, 2010 Ross MH, Pawlina W: Histology, 5th edition, Lippincott Wiliams, Wilkins, 2005 Vessels and lymphatics of organs of urogenital systems Pelvic floor, Perineum Internal iliac artery Internal iliac artery, blood vessels of the pelvis Perineal region - blood supply, innervation Internal iliac vein Parietal pelvic lymph nodes Lymph nodes in the retroperitoneal space and pelvic cavity Lymph nodes: common iliac, external iliac, inguinal Vessels of pelvic organs venous vesical plexus, venous vesicovaginal plexus Nerves of retroperitoneal and subperitoneal spaces Lumbar and sacral plexuses, Abdominal and pelvic plexuses and ganglia of autonomic system Suprapiriform foramen infrapiriform foramen Retroperitoneal space, topography of its organs and main vessels Pelvic floor Pelvic diaphragm Urogenital diaphragm Perineal muscles Pelvic diaphragm Levator ani muscle Pubic part – pubovisceral m. pubovaginal m. puboprostatic m. puboperineal m. puborectal m. - pubococcygeal m. Iliac part – iliococcygeal m. Urogenital hiatus, Anal hiatus Coccygeal muscle Fibrous structures: anococcygeal lig., perineal body, tendinous arch of levator ani, tendinous arch of pelvic fascia, Levator ani Ischioanal fossa, middle part Levator ani (1,2,3) and cocygeus (4) 1 – pubococygeus 2 – iliococcygeus 3 – puborectal 4 – coccygeus 5 – obturatorius int. Pelvic diaphragm Pelvic diaphragm Levator ani, tendinous arch of levator ani Anatomy of the pelvic outlet (scheme based on MRI) Symphysis Urogenital hiatus Urethra Vagina Anal canal Puborectal sling (levator ani) Tendinous arch of levator ani Tendinous arch of pelvic fascia The levator hiatus in axial plane with minimally distensible (left) and highly distensible puborectalis muscle (middle) compared to the dimensions of fetal head at the term (right). The ultrasound data sets of 227 nulliparous women examined at 36–38 week’s gestation were investigated. Minimal hiatal diameters were measured at rest, on Valsalva and pelvic floor muscle contraction. Results: some women will have to distend only 25%, others by 245%. Since childbirth-related trauma to the levator ani is common and clinically important, one should consider potential preventative measures. One approach would be to avoid vaginal delivery by performing elective Caesarean Section. (Švabik et al. 2009) MRI picture of levator ani muscle Normal condition Avulsion after childbirth Urogenital diapragm Deep transverse perineal muscle (in male only) + variable superficial transversal perineal muscle, perineal membrane Fibrous structure - perineal body Perineal muscles of female, blood supply, inmnervation Perineal region, regio perinealis - Urogenital triangle, regio urogenitalis - Anal triangle, regio analis, - Ischio-anal fossa, fossa ischioanalis (ischiorectalis) Perineum Ischioanal fossa Female external genitalia and perineal muscles - Bulbospongiosus, Ischocavernosus, Compressor of urethra, Urethrovaginal sphincter, Superficial transverse perineal muscle Perineal muscles Mm. of urogenital triangle: External urethral sphincter (+ Urethrovaginal sphincter + Compressor urethrae ) Ischiocavernosus, Bulbospongiosus, M. of anal triangle External anal sphincter Fibrous structures: Perineal body, Anococcygeal lig. Sources of illustrations used : Gray´s Anatomy, Sobotta: Atlas der Anatomie des Menschen Grim, Druga: Regional Anatomy, Galen, Prague 2012 Benninghoff, Drenckhahn: Anatomie I., II. Carlson,B.M.: Human Embryology and Developmental Anatomy Recommended Textbooks: R. S. Snell: Clinical Anatomy. 7th Edition, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2004, pp. 478 – 562 or K. L. Moore: Clinically oriented Anatomy, 3rd Edition, Williams & Wilkins 1992, pp. 501 – 635 and W. Kahle: Color Atlas/Text of Human Anatomy, Vol. 2 Internal organs. Thieme, 4th English Edition, 1993 Langman´s Medical Embryology,11th Edition, 2010 Junqueira´s Basic Histology 12th Edition, 2010