Contract Law: The Offer
Requirements for an Offer
Intent to Contract
Definiteness of Terms
Communicated to Oferee
Intent to Contract
Objective Standard
Measured by the offeror’s words, acts,
and circumstances
Intent to enter into contract upon
acceptance
Offeror not joking, haggling,
equivocating
Copyright © 2012, Thomas P. Langdon. All Rights Reserved
1
Objective Standard of Intent
“A contract has, strictly speaking, nothing to do
with the personal, or individual, intent of the
parties. A contract is an obligation attached by
the mere force of law to certain acts of the
parties, usually words, which ordinarily
accompany and represent a known intent. If
however, it were proved by 20 bishops that either
party when he used the words intended
something else than the usual meaning which the
law imposes on them, he would still be held,
unless there were mutual mistake or something
else of the sort.”
Judge Learned Hand
Hotchkiss v. National City Bank 200 F.287, 293 (1911)
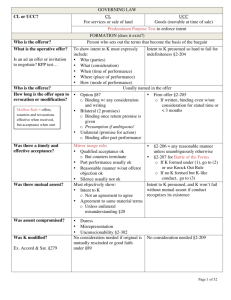
Definiteness of Terms
Definiteness and specificity tend to
indicate intent to contract
Courts need to know terms to
determine if breach occurs
Definiteness of Terms – Common Law
Traditionally, required all essential
terms to be stated in the offer
Modern Trend a bit looser
Copyright © 2012, Thomas P. Langdon. All Rights Reserved
2
Definiteness of Terms - UCC
Very broad look; more generous than Common
law
Contract is created
“in any manner sufficient to show agreement,
including conduct which recognizes the existence of
a contract.” UCC Art 2-204(1).
If terms are left out of the contract, gap-filling
provisions of the code apply.
Price 2-305
Quantity 2-306
Delivery 2-307, 2-308 and 2-309
Time for Payment 2-310
Communication to Offeree
Indicates objective intent to be
bound by the terms of the offer
Advertisements
Generally, not an offer
Treated as an invitation to offer or
negotiate
Some Ads can be offers
Very specific about the nature and
number of items offered for sale and
what is requested in return
Copyright © 2012, Thomas P. Langdon. All Rights Reserved
3
Rewards
Unilateral Contracts result for
advertisements offering rewards for
Lost property
Information
Capture of criminals
Offeree accepts by performing
Auctions
Sellers at auctions are generally treated
as making an invitation to offer
Auctioneer may withdraw the goods at
any time before acceptance
If advertised “without reserve”, goods
cannot be withdrawn unless no bids are
made in a reasonable time.
Bids
Generally treated as invitation to
offer
Previously announced terms of
bidding may alter the normal rules
Copyright © 2012, Thomas P. Langdon. All Rights Reserved
4
Which Terms are Included in Offer?
Traditional View: Let the parties
beware – protect yourself.
Modern view: courts often find
that offerees are bound only by
terms of which they had actual or
reasonable notice.
Termination of Offers
Terms of the Offer
Lapse of Time
Definite vs. General
“Reasonable” Time
Facts & Circumstances
Revocation
Rejection
Death/Insanity of either party
Destruction of subject matter
Intervening Illegality
Revocation of Offers
General Rule: may revoke offer any
time prior to acceptance, even if they
promise to hold the offer open
Exceptions to General Rule
1.
2.
3.
4.
Options – Separate K to keep offer open
Offers for unilateral contracts
Promissory Estoppel
Firm offers for the sale of goods [UCC 2-205]
Copyright © 2012, Thomas P. Langdon. All Rights Reserved
5
Firm Offers under the UCC
Unlike common law, does not
require consideration
Requirements:
made by an offeror who is a merchant
contained in a signed writing
Give assurances that the offer will be
kept open
A “Firm Offer”
Is irrevocable for the time stated
If no time stated, irrevocable for a
reasonable time
Regardless of the time in the offer,
the outer limit for irrevocability is 3
months.
When is a Revocation Effective?
General Rule: when it is actually
received by the offeree.
Exception:
Offers to the General Public –
revocation made in same manner as
offer is effective when published,
without proof of communication to the
offeree
Copyright © 2012, Thomas P. Langdon. All Rights Reserved
6
Rejection
Terminates power to accept
Can be
Express rejection
Implied rejection (counteroffer)
Effective only when actually
received by the offeror
Copyright © 2012, Thomas P. Langdon. All Rights Reserved
7