Logarithmic Functions and Their Graphs (I)
advertisement

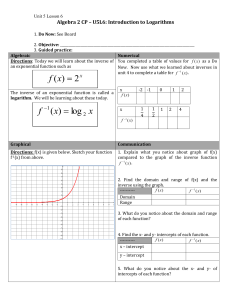
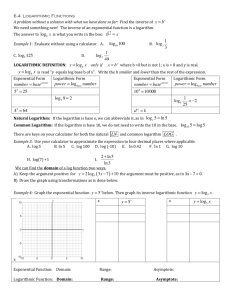
Logarithmic Functions and Their Graphs (I) • Review of what a logarithm is • Going from exponential form to logarithmic form……and ……. going from logarithmic form to exponential form One-to-One function Includes (0,1) Domain: all Real Numbers We have seen that the exponential function is one-to-one, so it has an inverse. It’s inverse is the logarithmic function. A LOGARITHM IS AN EXPONENT! Exponential _ form : f (x) = b x → example → 5 2 = 25 In logarithm terms, 2 is the LOGARITHM of 25 for a base of 5. A LOGARITHM IS AN EXPONENT! Exponential _ form : example → 33 = 27 In logarithm terms, 3 is the LOGARITHM of 27 for a base of 3. In logarithm terms, 1.5 is the LOGARITHM of 8 for a base of 4. Definition of a LOGARITHM: The logarithm y is the exponent to which a is raised to get x. Notice the difference between exponential form and logarithmic form. Notice the difference between exponential form and logarithmic form. Since, exponential functions are one-to-one with b > 0 and b not equal to one it follows that . . . . For instance . . . . Example Evaluating Logarithm problems: Example Evaluating Logarithm problems: In other words, 4 to what power equals 64? In other words, e to what power equals e to the fourth power? Since b 0 = 1 for b ≠ 0 and b1 = b...... Examples of solving logarithmic equations …….. Often it is easiest to change the equation to exponential form to solve. Examples of solving logarithmic equations …….. Often it is easiest to change the equation to exponential form to solve. One more …….. One more …….. 1. First, solve for the log term. 2. Second, put in exponential form and solve for x. Base 10 is the “common logarithm” and can be determined using the LOG button on your calculator Base e is the “natural logarithm” and can be determined using the LN button on your calculator Problems for you . . . . . From page 203 Do problems #1-37 (odds)