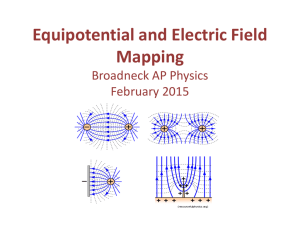
AP Physics C Mapping..
advertisement

AP Physics C Electric Fields Electrostatic Fields Mark H. Hoffman Objective: 1. Using Pasco Conductive Paper, Silver Conductive Ink (in lieu of aluminum pre-cut shapes), measure contour lines of equal voltage between two shapes, having a potential difference between 10-20 volts DC. 2. Using the equipotential lines, draw the electric field lines normal to the equipotential lines, to establish a mapping of the electric field between two metal conductors. Equipment Used: • • • • • • • Pasco Conductive Paper PK-9025 Pasco Silver Conductive Ink Pen PK-9031B or Pre-Cut Aluminum Electrodes Pasco Voltmeter & Ammeter (Galvanometer) Probes Pasco Model 750 Interface E-Mac Computer Conducting Wires & Alligator Clips 0-20 VDC Regulated Power Supply Procedure: 1. Using the enclosed “Mapping of Electric Fields” Experiment, set-up and map lines of equi-potential on the conductive paper. 2. Attach the Voltmeter and Ammeter (Galvanometer) probes to channel A & B, respectively, of the Model 750 Interface. Be sure the interface is connected to the E-Mac computer via the USB cable, and that the DataStudio software recognizes the connection of the probes. Set the voltmeter scale to 0-20VDC, to monitor the potential difference between the electrodes, and set the Galvanometer to measure ± 5 uA full scale. 3. Set the potential difference between the electrodes between 10-20V DC; set for optimum galvanometer deflection. 4. Measure the potential difference between an arbitrary starting point (middle of the conductive paper initially) on the conductive paper, and another point adjacent to it, to find points which are at the same electric potential. Follow the mapping procedure in the Experiment write-up. 5. Use the Conductive Ink Pen to draw the electrode surfaces, or the pre-cit aluminum shapes, shown in the Board Layout, of the Experiment write-up. Do up to three electrode geometries, time permitting. 6. Plot the equipotential lines and map the electric field lines, for each set of electrodes used.