Core Connections Algebra
advertisement

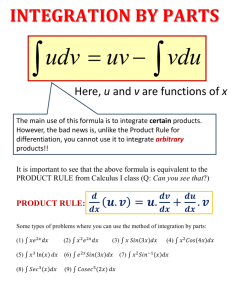
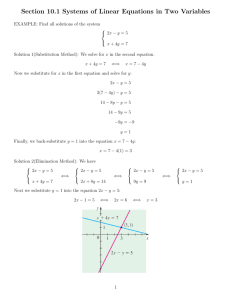
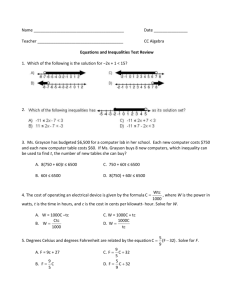
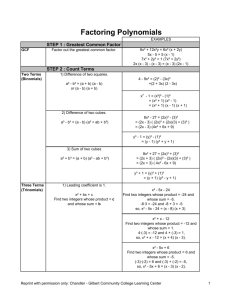
Selected Answers for Core Connections Algebra Lesson 3.1.1 3-6. a: d: 3-7. 1 h2 n8 b: x 7 c: 9k10 e: 8y 3 f: 28x 3 y 6 a: incorrect, x100 c: incorrect, 8m 6 n 45 b: correct y 3-8. x 3-9. Let x = number of weeks. 150 + 10x 1 2 3-10. a: 9 b: –4 c: –1 d: 7 3-11. a: – 10 b: –2 23 c: 3 13 d: –3 b: 1 c: 3-21. a: x = 3 b: x = 6 c: x = 2 3-22. a: m = – 13 b: y = – 13 x – 2 Lesson 3.1.2 3-19. b, c, d, f 3-20. a: 1 4 1 52 = 1 25 d: 1 x2 d: x = 4 3-23. Let x = number of weeks. 1500 ! 35x = 915; x = 17 weeks 3-24. 2 y = 3x – 1 Core Connections Algebra Lesson 3.2.1 3-33. a: 4x 2 + 6x + 13 b: 5y 2 + 8x + 19 c: 9x 2 + x + 44 d: 5y 2 + 6xy + 30 3-34. a: x = –8 b: x = 1 3-35. A pair of parallel lines. 3-36. Let x = the number of votes for candidate B, x + (x – 15,000) = 109,000. 62,000 votes 3-37. a: 1 19 3-38. y= 1 2 3 b: –13 10 c: –14 17 20 d: –7 16 x +1 3-39. a: 4x + 2y + 6 c: 4y + 2x + 6 b: 2x + 4 d: 2y + 2x + 6 3-40. Possible equation: 2 + (!2x) ! (4 ! x) = 2 + (!3) ! (x ! 2) or 2 + (!2x) ! (!x) ! 4 = 2 + !3 ! x ! (!2) 3-41. a: x = 8 b: x y –2 –5 0 –4 2 –3 4 –2 6 –1 8 0 10 1 c: It is the point where the lines intersects the x-axis on the graph. It is the x-value when y = 0 in the table. 3-42. a: 16 b: 2 c: undefined d: 0 b: 8x c: 6x 2 d: 7x y x 3-43. B 3-44. a: 15x 2 Selected Answers 3 Lesson 3.2.2 3-48. 77 + 56 + 33 + 24 = 190 square units 3-49. (2x + 4)(x + 2) = 2x 2 + 8x + 8 3-50. a: Multiply by 6. b: x = 15 c: x = 4 3-51. a: m = 3 b: (0, –2) c: y = 3x – 2 3-52. 10, 000 + 1500x = 18, 000 + 1300x , x = 40 months y 3-53. The x-intercepts are (1.5, 0) and (–1, 0); the y-intercept is (0, –3). x y –2 7 –1 0 0 –3 1 –2 2 3 3 12 x Lesson 3.2.3 3-58. a: (x + 1)(x + 3) = x 2 + 4x + 3 b: (2x + 1)(x + 2) = 2x 2 + 5x + 2 3-59. a: 238 square units b: 112 square units 3-60. a: x = 6 b: x = 16 c: x = 15 d: x = 8 b: –5 14 c: 17 d: –10 58 3-61. 30 ounces 3-62. y= 2 3 x–3 1 3-63. a: –15 12 4 Core Connections Algebra Lesson 3.2.4 3-70. a: 2x 2 + 17x + 30 b: 3m 2 – 4m – 15 c: 12x 3 + x 2 – 60x – 5 3-71. d: 6 – 7y – 5y 2 y y = –2x + 13 3-72. a: After 3 hours b: 8 x 3-73. (–2, –1) See graph at right. 3-74. They are not. An odd number added to an odd number is an even number. 3-75. a: –15x b: 64 p 6 q 3 c: 3m 8 b: –36x + 90xy c: x 4 + 3x 3 + 3x 2 ! 6x ! 10 Lesson 3.3.1 3-81. a: –20xy – 32y 2 3-82. Yes, for even numbers. On a number line, if you start at any multiple of two and add a multiple of two (an even number), you will always be stepping up the number line in multiples of two; you will always land on an even number. No for odd numbers. For example, 3 + 5 = 8; the sum of two odd numbers is not always odd. 3-83. (x – 5)(x + 3) = x 2 – 2x – 15 3-84. a: x = 8 or x = –2 b: x = ±7 c: x = 1 or x = –3 d: no solution 3-85. a: b: c: d: –4 4 –1 –4 3 3-86. a: 12 Selected Answers 16 –4 –8 b: 59 c: 7 –33 –1 –3 11 7 6 8 d: 9 –7 e: –13 f: –5 5 Lesson 3.3.2 3-93. a: x = ±7 b: x = ±16 c: x = 3, –17 d: x = ±53.1 3-94. a: x = 6 + 23 y b: y = c: r = d: r = 3-95. a: 5 59 b: –11 17 35 3-96. a: y = –11 b: y = – 3 2 x–9 3 4 d t c: 6 30 49 C 2! d: 1 163 350 x + 21 y 3-97. See graph at right. (2, –5) x 3-98. a: x 4 y3 b: xy c: –6x 6 3-99. a: x = 10 or x = !16 b: x = 92 , ! 11 2 c: x = ! 13 or x = ! 13 d: no solution d: 8x 3 3-100. a: 5x 2 – 30x b: –54y + 27y 2 3-101. a: 2x(x + 5) = 2x 2 + 10x b: (2x + 3)(x + 5) = 2x 2 + 13x + 15 3-102. a: x = 5 c: y = 0 b: x = 2 3-103. a: 4x 2 + 17x + 15 b: –6x 3 – 20x 2 – 16x c: –3xy + 3y 2 8x – 8y 3-104. a: x = 6 y+5 2 d: x = 38 d: 3xy + 5y 2 – 22y – 12x + 8 b: w = p–9 –3 c: m = (4n+10) 2 d: y = –3x Core Connections Algebra Lesson 3.3.3 3-107. a: x = 0 b: x = 8 c: x = 1 d: x = –3, 13 3-108. y = 3x – 5 3-109. y = 1 5 x+7 3-110. a: – 19 24 b: 4 d: – 83 = –2 23 5 6 c: 7 e: –3 12 3-11. a: 6(13x – 21) = 78x – 126 Selected Answers b: y = 1 25 f: 2 27 b: (x + 3)(x – 5) = x 2 – 2x – 15 c: 4(4x 2 – 6x + 1) = 16x 2 – 24x + 4 3-112. a: 15x 3 y 7 5 c: x 5 d: (3x – 2)(x + 4) = 3x 2 + 10x – 8 d: 8 x3 7